NWP Debugging Wi-Fi#
This section provides information about the prerequisites for debugging NWP issues.
NWP issues can be analyzed/debugged using the following methods:
Checking NWP responsiveness through debug logs.
Collecting and sharing RAM dumps with Silabs for detailed analysis.
Collecting and sharing sniffer logs with silabs for detailed analysis.
Checking NWP Responsiveness Through Debug Logs#
Trigger any query command from the application. For example:
Firmware Version: Use the
sl_si91x_get_firmware_versioncommand to get the firmware version.Network Parameters: If the device is connected to a network, use the
network_paramscommand.


Trigger a Ping test between the device and AP.


Collecting and Sharing RAM Dumps with Silabs for Detailed Analysis#
RAM dumps are used to debug NWP-related issues. We can collect a RAM dump as explained in the link below:
Collecting and Sharing Sniffer Logs with Silabs for Detailed Analysis#
In the following scenarios, debugging may require wireless sniffer logs (e.g., Wireshark):
If the NWP is in a responsive state and the issue is protocol-related (DHCP, DNS, MQTT, HTTP, etc.).
Wi-Fi connection failure.
TLS handshake failure.
Certificate-based authentication issues (e.g., EAP TLS, TTLS, PEAP, etc.,).
Collect certificates used for authentication.
If possible, obtain radius server logs.
Network application connection failure.
Data stall.
Interoperability issues (e.g., the SiWx91x module fails to connect to a specific Access Point (AP) while successfully
connecting to other APs).For TWT and power save related issues.
Example
EAPOL 4-Way Handshake Sniffer Capture
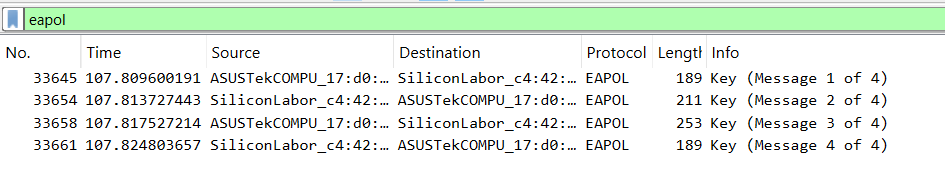

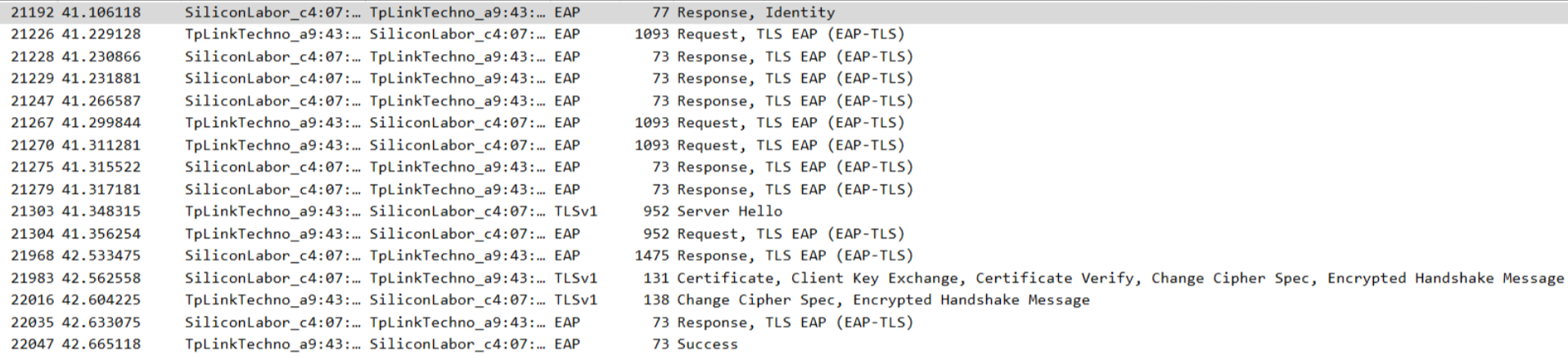
EAP Authentication Sniffer Capture

Note
For network application protocol issues, it is essential to capture all EAPOL (Extensible Authentication Protocol over LAN) Wi-Fi frames exchanged during the Wi-Fi authentication process in the sniffer log. Additionally, any decryption keys must be provided to facilitate the analysis.
For any EAP-related issues, capturing EAP packets is mandatory in the sniffer log.
