Network Analyzer#
Introduction#
Silicon Labs Network Analyzer is a packet capture and debugging tool used to analyze connectivity between wireless nodes running the Wi-SUN stack on the EFR32 platform.
It significantly accelerates network and application development by providing graphical views of network traffic, activity, and duration.
Once a capture is complete, it can be exported to formats compatible with external tools such as Wireshark.
Packet Trace Interface (PTI)#
The Packet Trace application captures the packets directly from the Packet Trace Interface (PTI) available on the Wireless Gecko SoCs and modules. It therefore provides a more accurate capture of the packets compared to air-based capture.
To capture Wi-SUN packets using the Silicon Labs Network Analyzer, in the Debug Adapters view, first make sure you are connected and then right-click the device that is running on a Wi-SUN network and select Start capture.
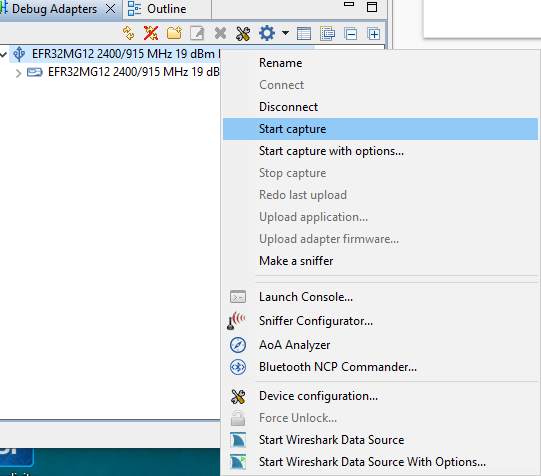

You should now be able to see the Wi-SUN traffic as shown below. Click the packets to see more details about its contents in the Event Detail view (on the right).
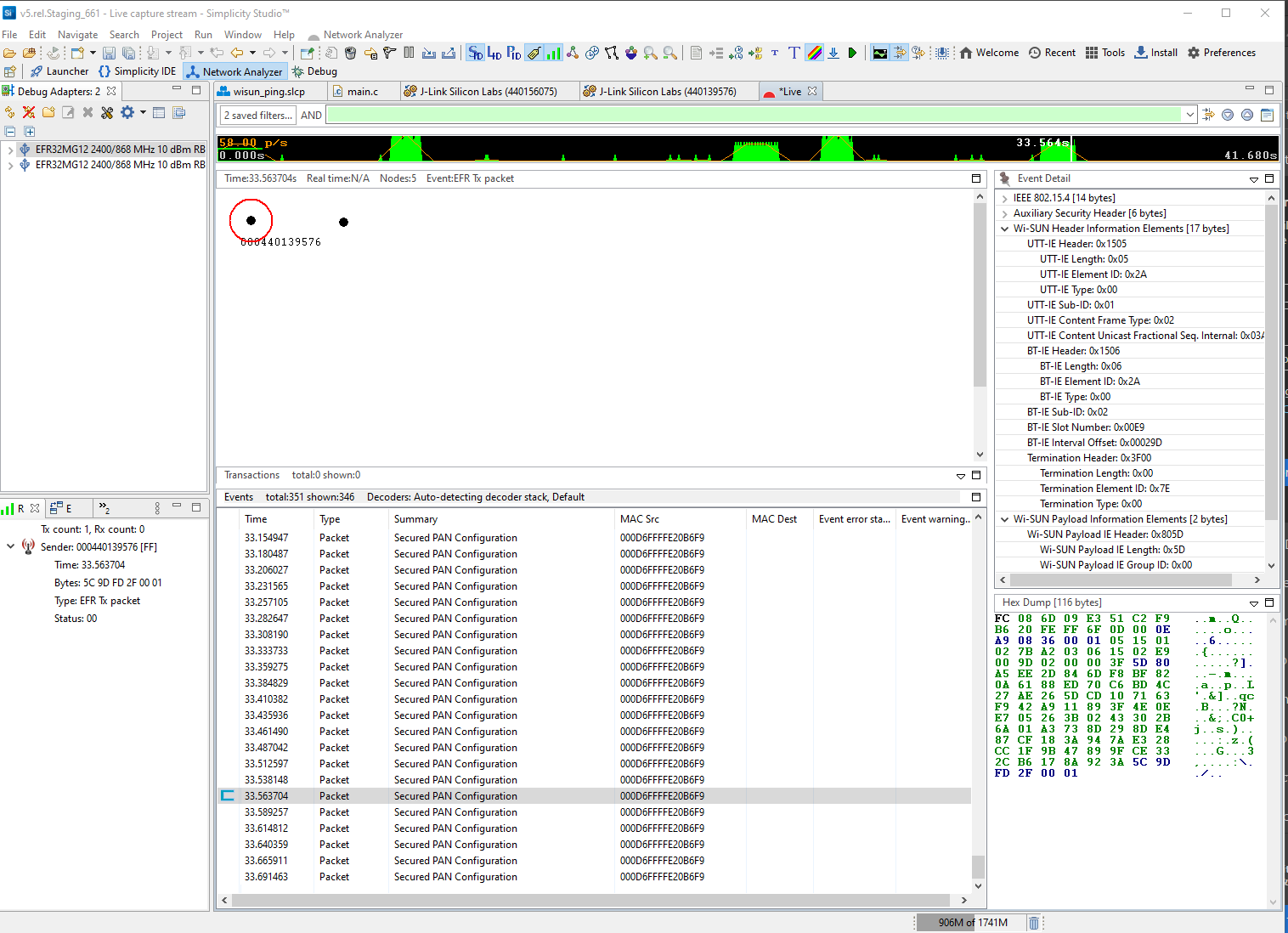

Note: If you don't see packets being captured, you may have a mismatch between your project's PTI Baud Rate (Hertz) setting in the RAIL Utility, PTI component and your Debug Adapter's PTI Bitrate settings (which you can access by right-clicking your Debug Adapter, selecting Device Configuration, then opening the Packet Trace tab).
In the current state, the Network Analyzer does not decrypt the Wi-SUN Upper Layer Application Data. To decrypt the packet and analyze the complete payload including the data, the external tool Wireshark is recommended. To export PTI captures in readable Wireshark's pcapng format, follow these steps:
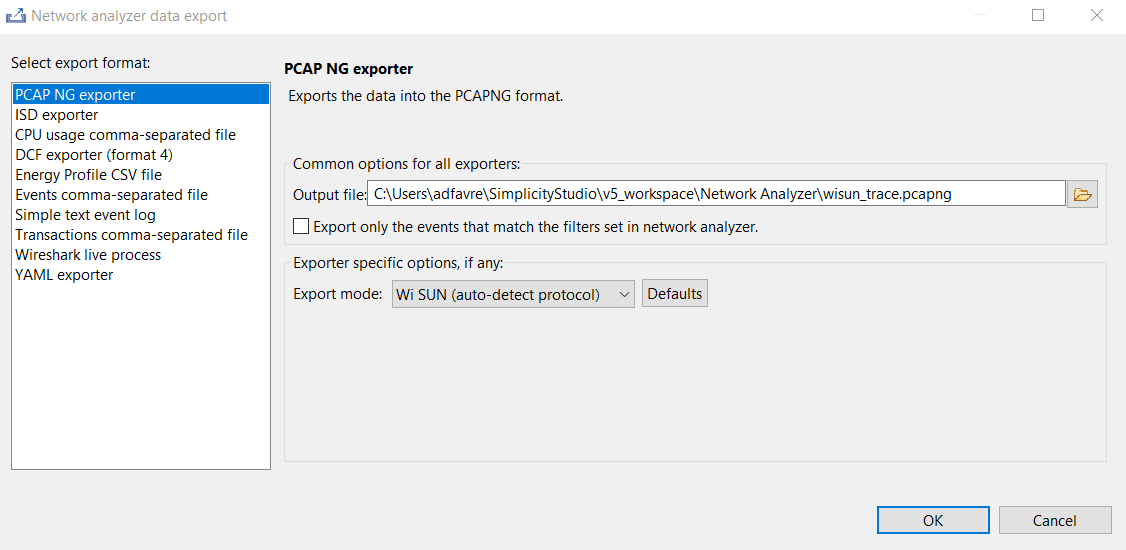
When you have traced the communication, click Export.
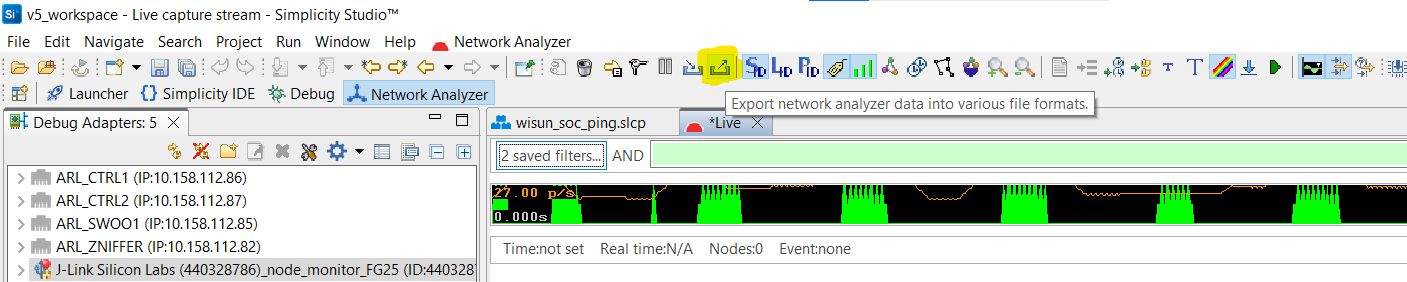

Under Select export format, select PCAP NG exporter.
Enter a path and a file name in which the trace will be stored.
In Export mode, select Wi-SUN (auto-detect protocol).
Click OK.

Once .pcapng is created, it can easily be opened in Wireshark.
Note: PTI captures may occasionally contain corrupted packets that cannot be analyzed or decrypted. This is due to bit-shifting issues between the Wi-SUN preamble and PTI. However, this problem only affects the capture process. Frames are still correctly transmitted and received by the devices. Therefore, this issue should not prevent the use of PTI or Wireshark for analysis.
Wireshark#
Wireshark is the recommended network protocol analyzer for use with Wi-SUN networks. Download instructions are provided for Windows/Mac users or Linux users. Simplicity Studio 5 supports live interaction between the application running on a Silicon Labs device and Wireshark.
To decrypt the communications, the GAK key and key index set information are required. They can be retrieved on the border router CLI by issuing the following command:
> wisun get wisun
wisun.state = started (2)
wisun.network_name = "Wi-SUN Network"
(...)
wisun.allowed_channels = "0-255"
wisun.gak1 = 76:ab:9f:ce:8a:08:b8:88:6d:fc:56:fa:0e:6f:1e:ce
wisun.gak2 = 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00
wisun.gak3 = 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00
wisun.gak4 = 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00
wisun.lfn_gak1 = 7b:92:f2:9e:68:a5:41:37:b3:5e:e7:14:04:be:37:04
wisun.lfn_gak2 = 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00
wisun.lfn_gak3 = 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00
(...)On Wi-SUN Border Router Linux, the GAK Key can be retrieved using wsbrd_cli command or directly from /var/lib/wstk/network-keys:
> wsbrd_cli status
network_name: Wi-SUN Network
(...)
size: SMALL
GAK[0]: eb:7b:11:dd:f0:23:c3:7e:36:64:c5:9b:5b:ed:c6:c7
GAK[1]: fc:d3:1f:a7:4c:c8:c4:0f:96:7e:d0:5d:0e:a1:01:fc
GAK[2]: fc:d3:1f:a7:4c:c8:c4:0f:96:7e:d0:5d:0e:a1:01:fc
GAK[3]: fc:d3:1f:a7:4c:c8:c4:0f:96:7e:d0:5d:0e:a1:01:fc
GTK[0]: a8:d6:dc:7c:66:14:2f:b8:db:dd:af:fb:c2:27:0c:18
GTK[1]: 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00
GTK[2]: 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00
GTK[3]: 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00
84:fd:27:ff:fe:fe:55:bdSilicon Labs Wi-SUN devices in the network use wisun.gak1 as the GAK key. In the first capture the GAK key is
76:ab:9f:ce:8a:08:b8:88:6d:fc:56:fa:0e:6f:1e:ce and in the second capture the GAK key is
eb:7b:11:dd:f0:23:c3:7e:36:64:c5:9b:5b:ed:c6:c7. The key index to use in Wireshark is 1 in both cases, for the first GAK
in the list.
In Wireshark:
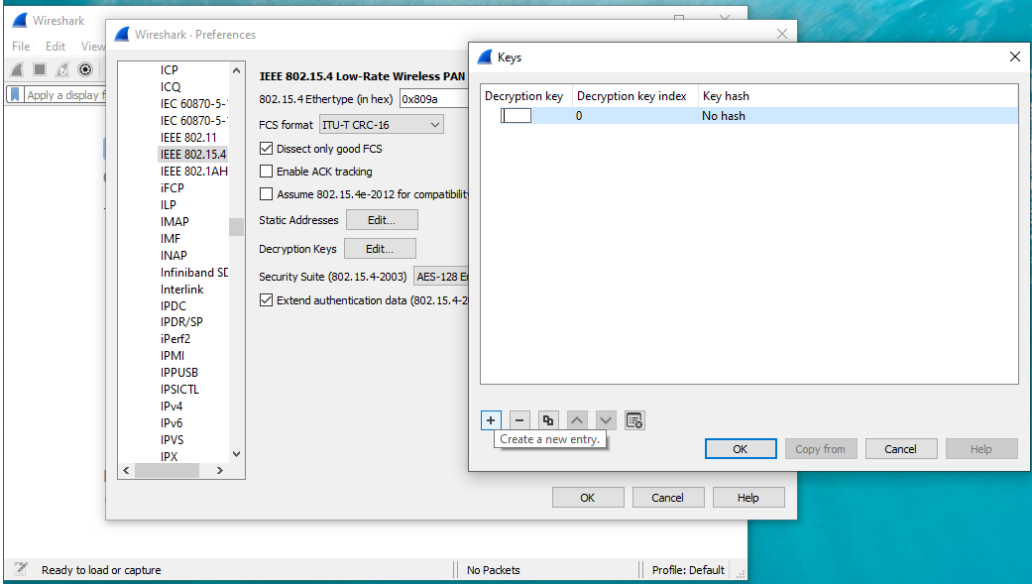
Click Edit.
Click Preferences....
Expand the Protocols list and select IEEE 802.15.4.
Next to Decryption Keys, click Edit.
In the Keys window, click [+].
Under Decryption key enter the GAK key, and under Decryption key index, enter the key index (starting at 1 for GAKs, starting at 5 for LFN-GAKs).
Click OK.

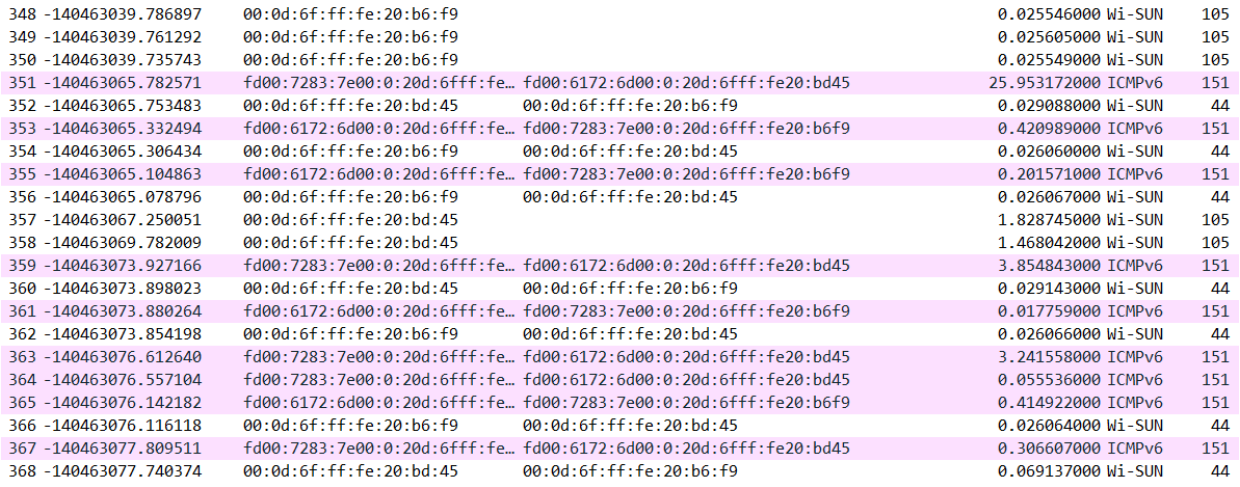
Wireshark is now able to decrypt the traces and the higher-level protocols (ICMP, TCP, UDP...). The following example of traces shows a router pinging its border router.