EFR Connect Mobile App#
Introduction#
Silicon Labs EFR Connect is a generic BLE mobile app for testing and debugging Bluetooth® Low Energy applications. With EFR Connect, you can quickly troubleshoot your BLE embedded application code, Over-the-Air (OTA) firmware update, data throughput, and interoperability with Android and iOS mobiles, among the many other features. You can use the EFR Connect app with all Silicon Labs Bluetooth development kits, Systems on Chip (SoC), and modules.
This application has two main functional areas, the demo and the develop view. By default, the app opens in the Develop view and the selection between them is achieved through the two icons on the bottom side of the app, as shown in the Demo view and Develop view sections.
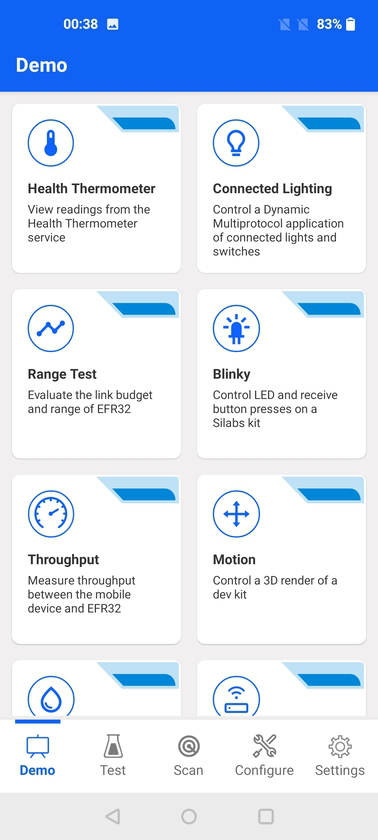
EFR Connect includes many demos to test sample apps in the Silicon Labs GSDK quickly. The following are the demo examples:
Blinky: The ”Hello World” of BLE – Toggling a LED is only one tap away.
Throughput: Measure application data throughput between the BLE hardware and your mobile device in both directions
Health Thermometer: Connect to a BLE hardware kit and receive the temperature data from the on-board sensor.
Connected Lighting DMP: Leverage the dynamic multi-protocol (DMP) sample apps to control a DMP light node from a mobile and protocol-specific switch node (Zigbee, proprietary) while keeping the light status in sync across all devices.
Range Test: Visualize the RSSI and other RF performance data on the mobile phone while running the Range Test sample application on a pair of Silicon Labs radio boards.
EFR Connect helps developers create and troubleshoot Bluetooth applications running on Silicon Labs’ BLE hardware. The following is a rundown of some example functionalities.
Bluetooth Browser - A powerful tool to explore the BLE devices around you. Key features include the following:
Scan and sort results with a rich data set
Label favorite devices to surface on the top of scanning results
Advanced filtering to identify the types of devices you want to find
Save filters for later use
Multiple connections
Bluetooth 5 advertising extensions
Rename services and characteristics with 128-bit UUIDs (mappings dictionary)
Over-the-air (OTA) device firmware upgrade (DFU) in reliable and fast modes
Configurable MTU and connection interval
All GATT operations
Bluetooth Advertiser – Create and enable multiple parallel advertisement sets:
Legacy and extended advertising
Configurable advertisement interval, TX Power, primary/secondary PHYs
Manual advertisement start/stop and stop based on a time/event limit
Support for multiple AD types
Bluetooth GATT Configurator – Create and manipulate multiple GATT databases
Add services, characteristics and descriptors
Operate the local GATT from the browser when connected to a device
Import/export GATT database between the mobile device and Simplicity Studio GATT Configurator
Bluetooth Interoperability Test – Verify interoperability between the BLE hardware and your mobile device
Runs a sequence of BLE operations to verify interoperability
Export results log
The EFR Connect mobile application source code for both iOS and Android is available on GitHub under the Apache 2.0 license.
EFR Connect mobile app is under constant development with new demos and developer-focused features introduced over time, which will be added to this document.
This version of the document refers to the version 2.3.2 for both iOS and Android app. Because the apps have the same UI for most features, this document uses screen shots from the Android app. For a UI feature that affects how the user interacts with the app, screen shots from both apps will be shown and an explanation will be provided for each separately.
Demo View#
Demo view shows a selection of demos used to quickly test and demo sample apps in the Silicon Labs Bluetooth SDK.

Health Thermometer#
This demo scans for devices that advertise the Health Thermometer service (UUID 0x1809). Once connected, it subscribes to indications from the Temperature Measurement characteristic (UUID 0x2A1C). Because the indications are received by the app, the temperature value is displayed.
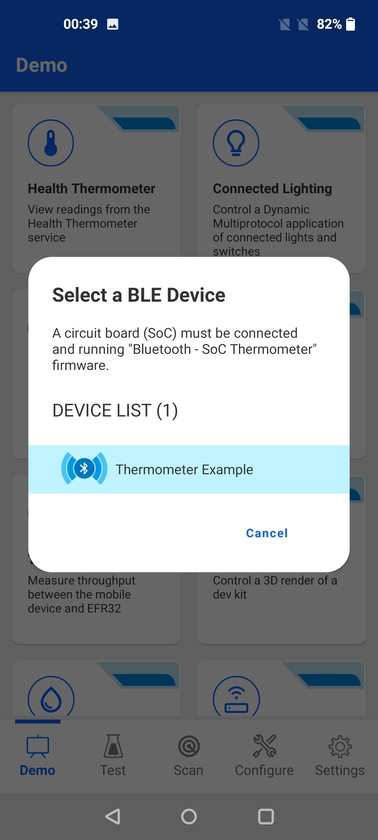

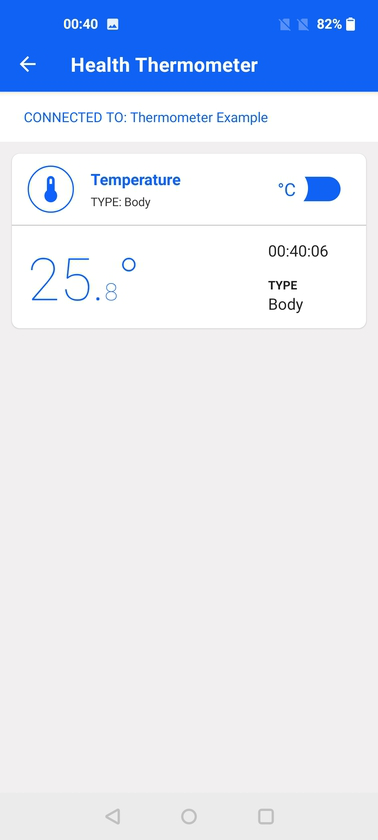

Use this demo with the Bluetooth - SoC Thermometer sample application from the Silicon Labs Bluetooth SDK. For more information, see the Getting Started section of the Bluetooth documentation.
Connected Lighting#
The Connected Lighting demo demonstrates the Dynamic Multiprotocol (DMP) capabilities of Silicon Labs' devices and software. It requires two kits running dedicated sample apps which are documented in QSG155: Using the Silicon Labs Dynamic Multiprotocol Demonstration Applications in GSDK v2.x.
When launched, the demo will scan for devices which are advertising themselves as a DMP node, running BLE and a second wireless protocol, for example Zigbee or Proprietary.
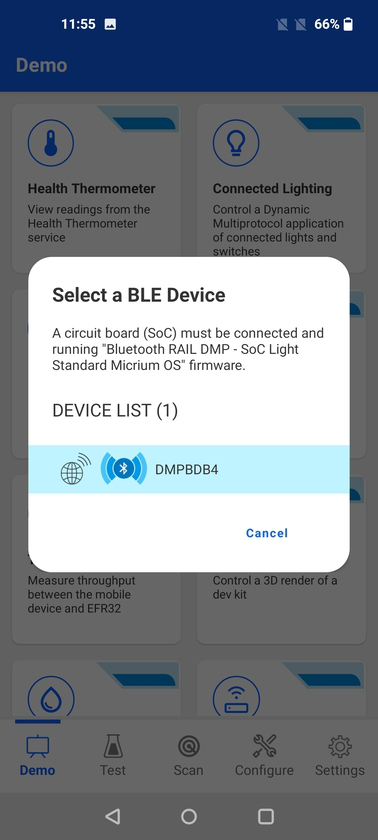

After establishing the connection with the DMP node, the demo allows controlling the light on the DMP board by tapping the lightbulb icon. If the user changes the light status using the physical push button on the kits, the light status on the app will be updated accordingly.
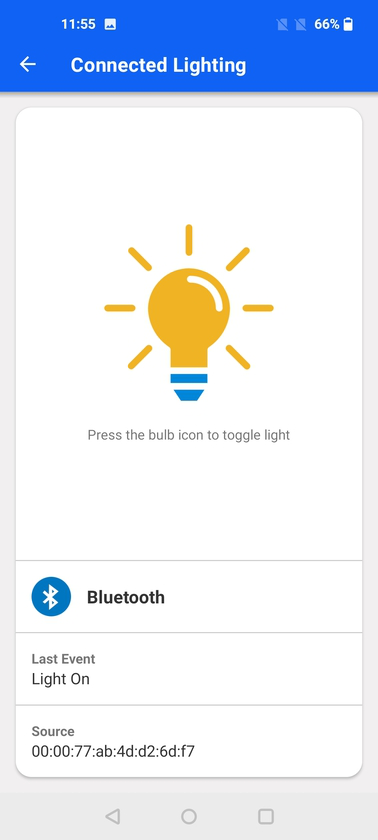

Furthermore, the source of the last event is shown on the demo. For example, "Bluetooth" means it came from the mobile app, "Proprietary" means that the light was toggled by the push button on the Switch board which communicates with the Light board (DMP node) via proprietary protocol.
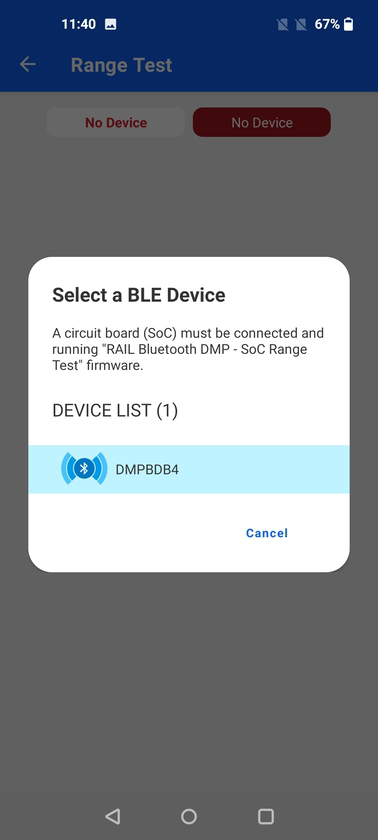
Range Test#
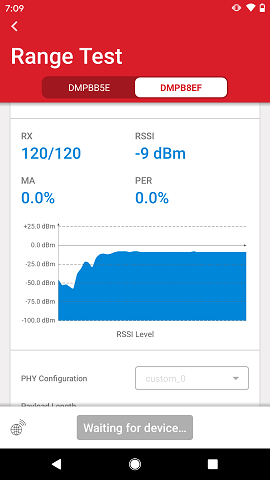
The Range Test demo is fully documented in UG471: Flex SDK v3.x Range Test Demo User's Guide. The mobile app is first used to set up the TX and RX node parameters. Then, it is used to visualize all the meaningful RF data as the test is on-going, which is relayed to the mobile app by the RX node.
When launched, the demo will scan for devices which are advertising themselves as a Range Test nodes.

After the nodes start performing the range test, the mobile app displays the performance data from the RX node.

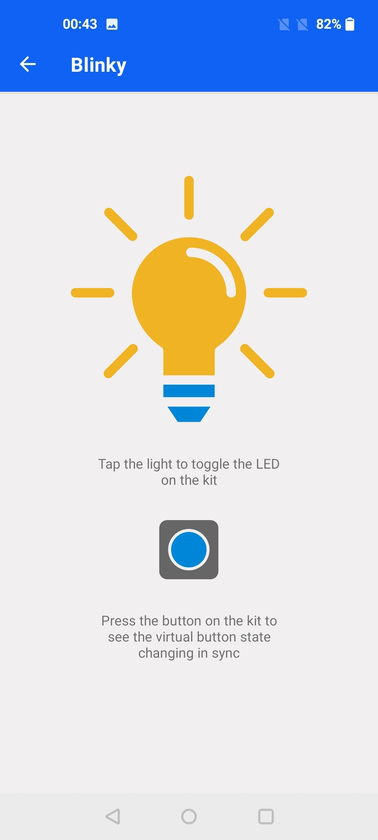
Blinky#
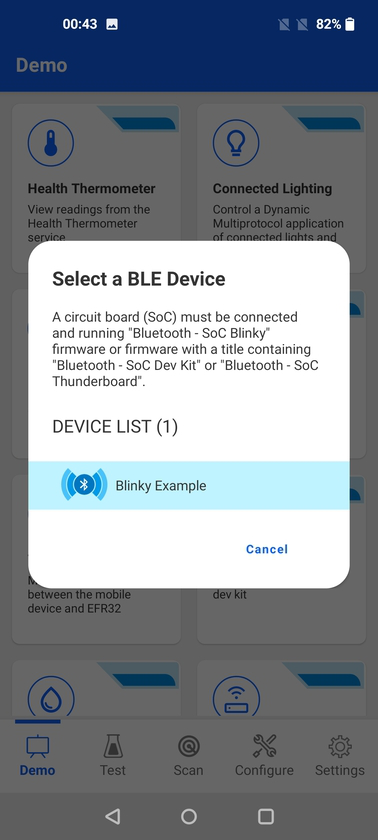
The Blinky demo is the "Hello World" of BLE, allowing to toggle an LED and receive button press indications from the BLE device. For more information, see the readme of the Bluetooth - SoC Blinky sample application from the Silicon Labs Bluetooth SDK.
When launched, the demo will scan for devices which are advertising themselves as a Blinky Example.

Once connected, the user can control the LED on the Silicon Labs kit and receive button state change indications when pressing or releasing the push button.

Throughput#
The Throughput demo allows measuring throughput between EFR32 and the mobile, on both directions. For more information, see the readme of the Bluetooth - SoC Throughput sample application from the Silicon Labs Bluetooth SDK.
When launched, the demo will scan for devices which are advertising themselves as a Throughput Example.

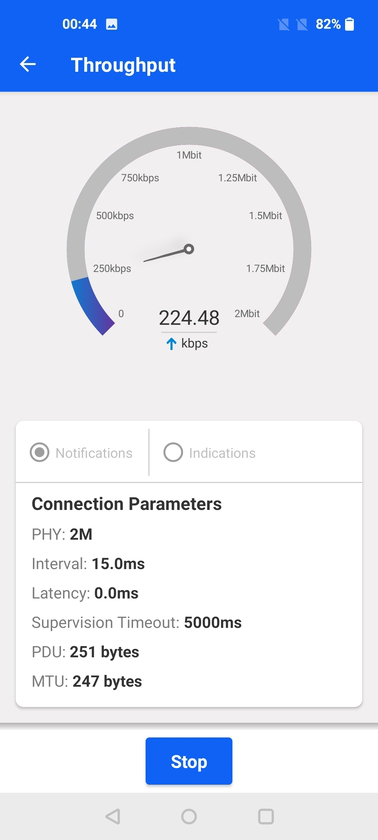
Once connected, the user can visualize the data throughput between the devices, which includes receiving data from EFR32 (triggered by button press on the kit) or sending data to the kit (triggered from within the demo view).

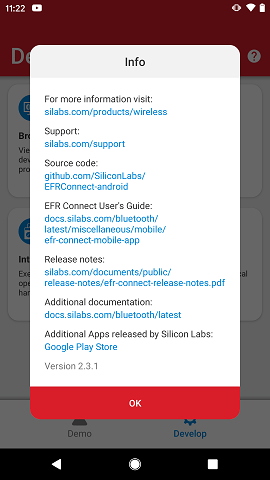
Information#
From either Demo or Develop view, you can access the Info screen through the icon on the upper right corner. The Info screen brings up a dialog with useful information about Silicon Labs products, links to the GitHub repositories, app stores as well as Bluetooth documentation, including this User's Guide and Release Notes for the mobile app.

Develop View#
The develop view contains a collection of tools focused on Bluetooth firmware application developers. They contain a number of advanced features that will be covered in the subsequent sections.

Browser#
The browser allows you to scan, connect, and exchange data over GATT with Bluetooth LE devices around you. When you access the browser from the Develop view, it automatically starts scanning and populating the screen with cards that represent each of the scanned devices. The devices appear on the list in the order in which they are discovered. As a result, to see new devices, scroll down the list.
Device Cards#
Each device discovered by the app is represented by a card containing information about that device.
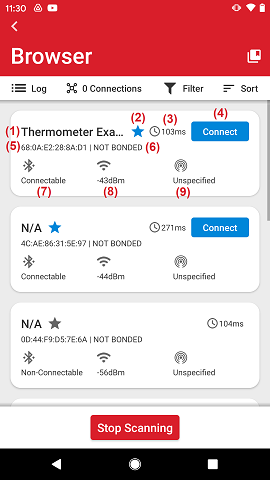

The image above shows the main elements of the device card which are as follows:
Device name, if it's part of the advertisement, either through AD type Complete Local Name (0x09) or Shortened Local Name (0x08). If the device name is not part of the advertisement packet nor the scan response packet, the app will display "N/A".
The star indicates whether the device has been marked as favorite (star with blue color). This can be easily toggled by tapping the star, which makes it gray. If a favorite device is found, it automatically surfaces to the top of the list, regardless of the order in which it is found relative to the other devices.
Advertisement interval in milliseconds.
Connect button if the advertisement is of connectable type.
Bluetooth address. Note: On iOS the Bluetooth address is not accessible to the application.
Bonding status.
Indication of whether the advertisement is connectable or non-connectable.
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator).
Indication whether the advertisement complies with a known beacon format (iBeacon, eddystone or Altbeacon). If no beacon format is identified, it will be "Unspecified".
Advertisement Details#
The device card can be expanded by tapping anywhere on the card other than the Star or the Connect button. When tapping on the device card, it expands showing the advertisement data details. Another tap will collapse it. When expanded, each row shows one of the advertisement data types which are part of the advertisement data.
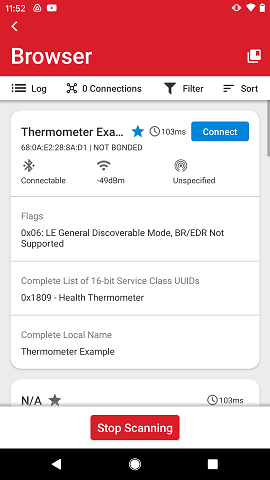

If the advertisement is a known beacon format, the details are also parsed according to that specific beacon format. The image below shows the details from an iBeacon advertisement (Bluetooth - SoC iBeacon sample application running on an EFR32BG22 kit)
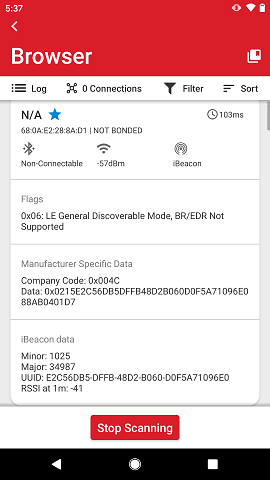

EFR Connect also supports extended advertising, however, that must also be supported by the specific mobile device where the app is running. If the phone supports it and devices are sending extended advertising, that will be visible at the top of the advertisement details.
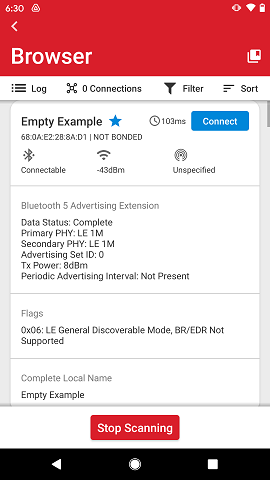

Start and Stop Scanning#
The user can control when scanning starts and stops. There are only four situations where the app does this automatically:
When entering the browser from the Develop main view, scanning automatically starts
When connecting to a device scanning automatically stops
Refreshing the list automatically starts scanning if it was stopped
Locking the screen will automatically stop scanning
Scanning will continue indefinitely until the user taps the Stop Scanning button at the bottom side, which will toggle the button color to blue and the text to Start Scanning.
Start/Stop action does not clear the list of devices, which means that if scanning resumes with an existing device list, new devices will be added to the end of the list.
Pulling down and releasing the device list causes the list to refresh. As mentioned above, this will also automatically start scanning if it was stopped.
Log#
The log keeps a record of all the Bluetooth activity. It can be shared via email or other methods for later analysis, filtered via text based search, and cleared.


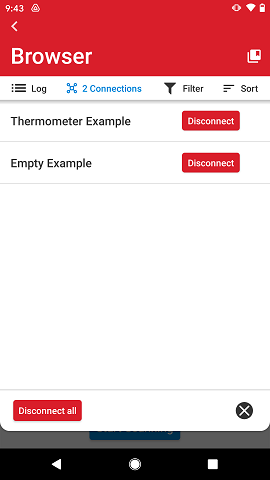
Connections#
The connection drop-down lists all active connections, which allows the user to go into each of those connection views or disconnect from those devices. Devices can be disconnected individually through each device's Disconnect button or altogether with the Disconnect all button at the bottom.

You can also disconnect devices from the main browser view, if they are listed in the scan list. Connected devices have a Disconnect button in red color instead of the blue Connect button.
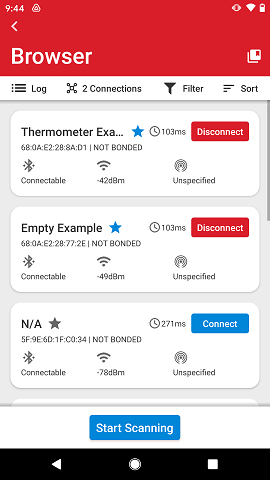

If the scan list is refreshed, those devices will disappear from the list unless they continue advertising after a connection has been established.
Filter#
The filter allows narrowing down your search to a list of devices that fulfills a specific set of parameters. To reach the filter tap the Filter icon on the top which will reveal the filter options on a pull-down.
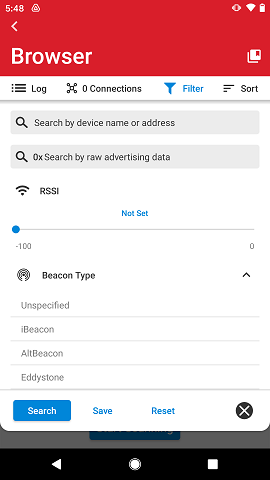

To collapse the filter, either tap the filter icon or the X icon on the lower right hand side.
The filter allows searching for devices with the following parameters:
Device name or Bluetooth address. The Bluetooth address can be entered with or without colon. Note: EFR Connect for iOS only displays device name because the iOS Bluetooth stack does not provide the Bluetooth address to the application.
Raw advertising data. Note: This feature is only supported on EFR Connect for Android. iOS provides pre-parsed advertisement data and does not provide access to raw advertising data.
RSSI above a given value so that a user can limit results by signal strength threshold.
Beacon type: iBeacon, Altbeacon, Eddystone or Unspecified (none of the other 3).
Only favorites
Only connectable
Only bonded
Touching the Search option causes the new filter parameters to take effect, which also automatically collapses the filter. An active filter can be visible in the filter icon where a small check mark is added. The filter will be applied to the list of devices regardless of whether scanning is on-going or not.
Tapping Reset clears all the filter parameters, disables the filter and collapses it.
You can also save an existing set of filter parameters for later use. To save filter selections, touch the Save button. Saved filter parameters are listed in the Saved Searches at the bottom of the filter pull-down.
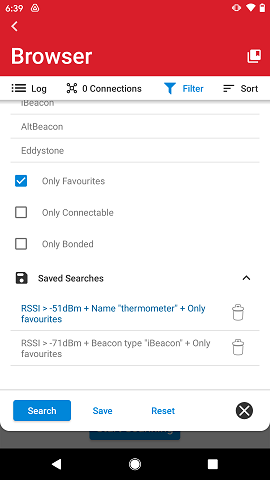

Loading filtering parameters can be done by touching a saved search. The selected saved search is marked with blue font. To delete a saved search, tap the garbage bin on the right hand side. To take the newly loaded filter parameters into effect, tap the Search button.
When a filter is active in the browser a bar shows up at the top listing the filtering criteria.

Sort#
The sort feature allows sorting scan results by ascending/descending RRSI as well as A->Z or Z->A device name. To disable sorting simply tap on the enabled sorting option. To collapse the sorting options tap on the sort icon or anywhere outside the drop-down.

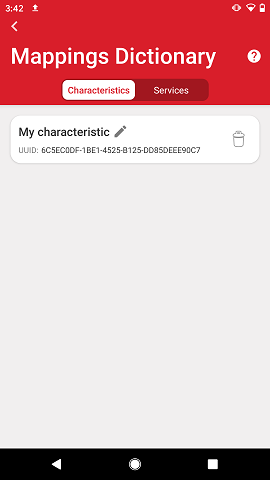
Mappings Dictionary#
The mappings dictionary can be accessed via the dictionary icon on the top right of the browser main view, which contains a list of all the 128-bit UUIDs that have been renamed by the user. Within the mappings dictionary, the user can further edit their names as well as delete them.

Device#
When either a connection with a device is established or the user goes to an existing connection via the connections pull-down, the app will go to the device view where it displays the GATT database for both the remote device as well as the local one.
Remote (Cliente) vs Local (Server)#
At the bottom of the device view, the user can switch between the GATT of the remote device (where the app is in the client role) or the GATT of the local mobile device (where the app acts as server role). The representation of both GATT databases is the same, as well as the associated controls.
The local GATT database can be modified through the GATT Configurator feature.
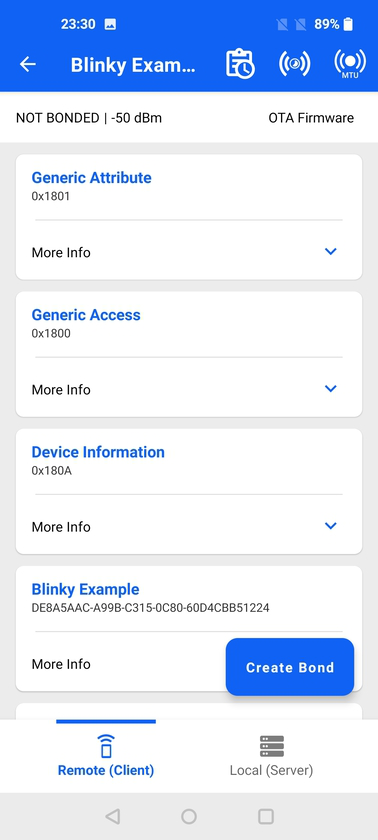
GATT Services#
Each card represents a GATT service and contains the service name and UUID. A custom service (128-bit UUID), which has not been renamed by the user is displayed as Unknown service. Similarly, a custom characteristic, which has not been renamed, displays as Unknown characteristic. One exception to this is the Silicon Labs OTA service (UUID 1D14D6EE-FD63-4FA1-BFA4-8F47B42119F0) and all its characteristics, which cannot be modified.

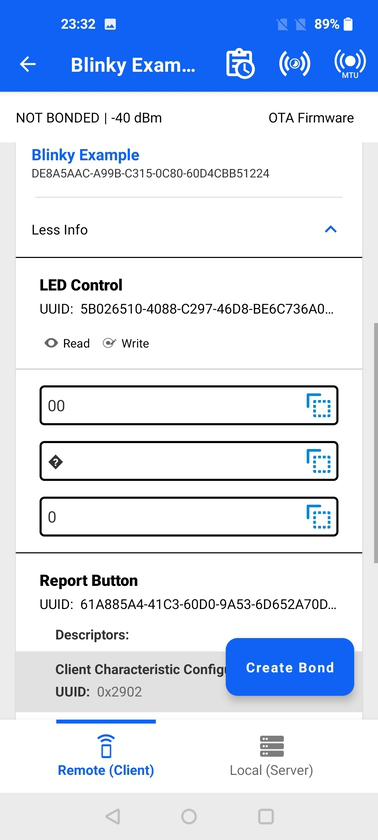
GATT Characteristics#
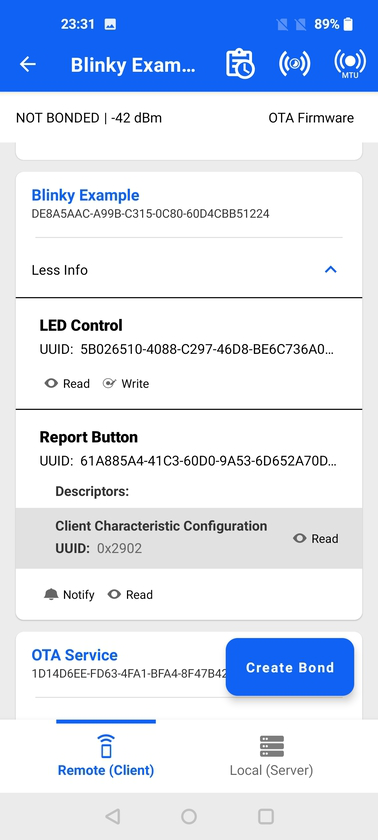
Tapping anywhere on the card causes it to expand, which reveals the characteristics within that service as well as the supported properties for each characteristic (e.g., read, indicate).

Tapping into a characteristic causes it to expand further and expose data within the characteristic. This will not automatically read the characteristic, which means that the data fields may be empty. Reading needs to be done explicitly by the user (if the property is available) by tapping the Read icon.
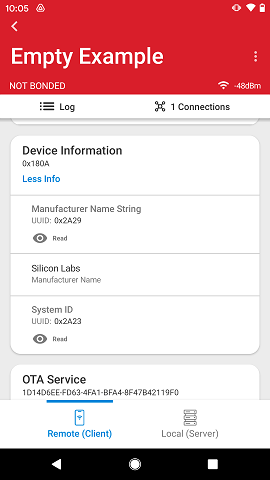

If other properties are available, they will have additional associated icons. For characteristics without any specific data format, you can copy data to the clipboard with the copy icon on the right side of the characteristic data. Data will be copied using the respective format (hex, ascii, or decimal).

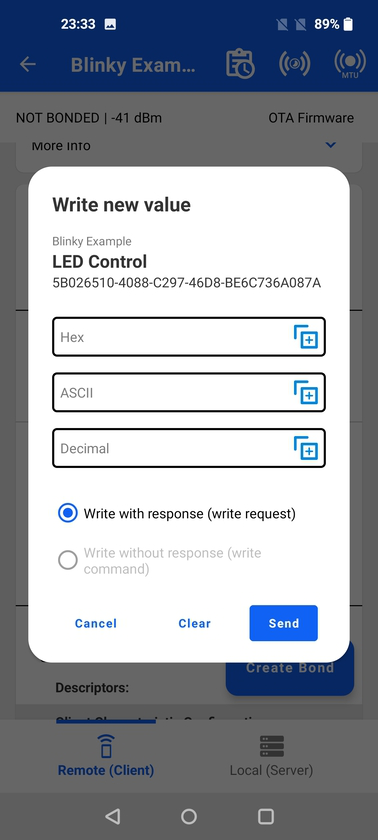
If the write property is available for instances, when tapping the write icon it brings a dialog that allows writing data into the characteristic.
Within that dialog, you can select which write operation to use (write request or write command) depending on what is supported by the characteristic. If one is not supported, it will be grayed-out.
You can also paste data from the clipboard by using the paste button on the right side of the characteristic data. Data you paste in must have the same format as the field where it is pasted or the app will throw an incorrect format error.

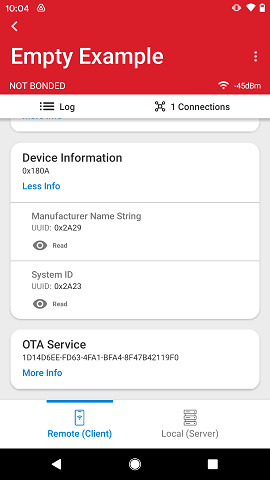
GATT Descriptors#
If a characteristic has descriptors, they are listed underneath the characteristic UUID.

Additional Options#
In the Device view, the user retains access to the Log and the list of connections so that it is easy to swap between connected devices. An RSSI value, which is refreshed each second, is located in the top right hand corner. Furthermore, there is a menu with additional options.
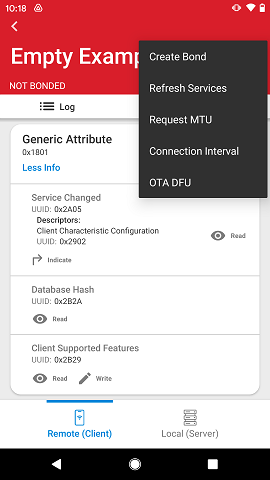

Create Bond: Bond with this device
Refresh services: rediscovers the GATT database as some devices have dynamic databases which can change in run-time. On iOS, this is accomplished with a pull-down action.
Request MTU: allows changing from 23 to 250 bytes.
Note: this is not available on iOS.
Connection Interval: allows changing the interval between 3 different ranges.
Low priority (100-125 ms)
Balanced priority (30-100 ms)
High priority (7-15 ms)
Note: this is not available on iOS. The ranges are defined by the Android stack and are not a limitation imposed by EFR Connect mobile app.
OTA: Updates a Silicon Labs device running the Silicon Labs Bluetooth stack.
OTA#
Over-the-air device firmware updates (OTA DFU) allow updating a device with a new firmware sent over a Bluetooth connection. OTA option is shown in the menu if the Silicon Labs OTA service is included in the GATT, in which case it is assumed that the device supports OTA.
Tapping into that option opens a dialog with the following options:
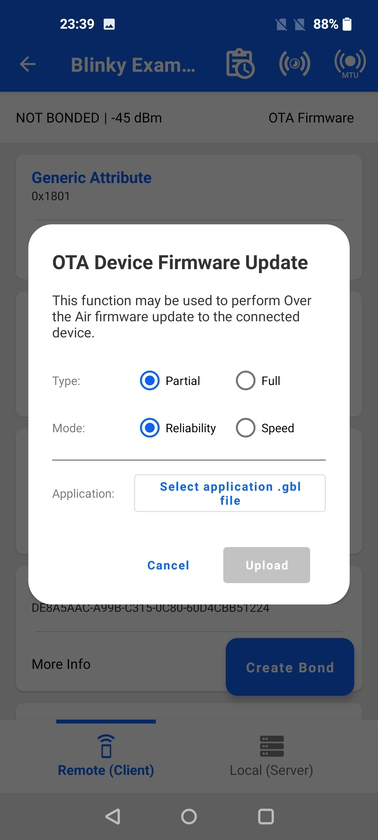

OTA type
Partial: only application is updated
Full: both application and apploader are updated. This is require uploading 2 separate gbl files, one for the application and one for the apploader.
OTA mode
Reliability: uses write operation to send the GBL file data
Speed: uses write without response operation to send the GBL data
Application/Apploader: retrieve the GBL files from your device (local folders or cloud storage)
MTU: from 23 to 250 bytes (not available on iOS)
Priority: Maps to the same connection intervals explained in the previous section.
During the OTA process, information about progress is displayed until OTA is finalized.
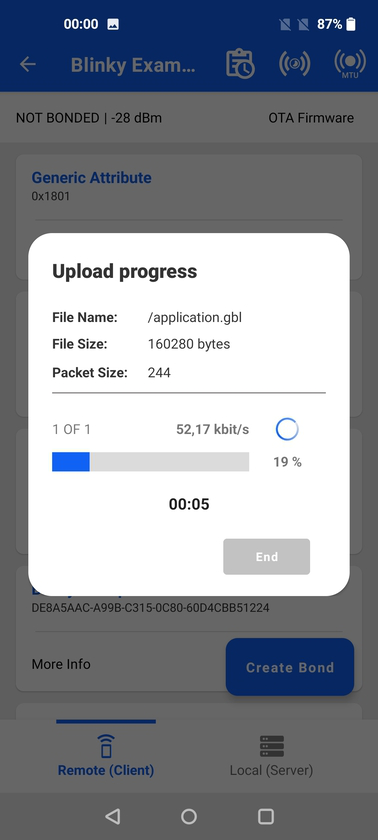

For additional guidance on OTA process using EFR Connect, see Using EFR Connect Mobile App for OTA DFU.
Advertiser#
The advertiser allows you to use the mobile phone as a BLE peripheral by creating and customizing advertisement sets, both in terms of their configurations as well as payload.
This functionality comes in handy when you have a single Silicon Labs kit for a Bluetooth product, but you still want to test/evaluate/develop applications that leverage the Silicon Labs Bluetooth stack functionalities as a central device.
Creating New Advertisement Sets#
When entering the Advertiser for the first time, the user sees an empty list of advertisement sets because none have been created yet.
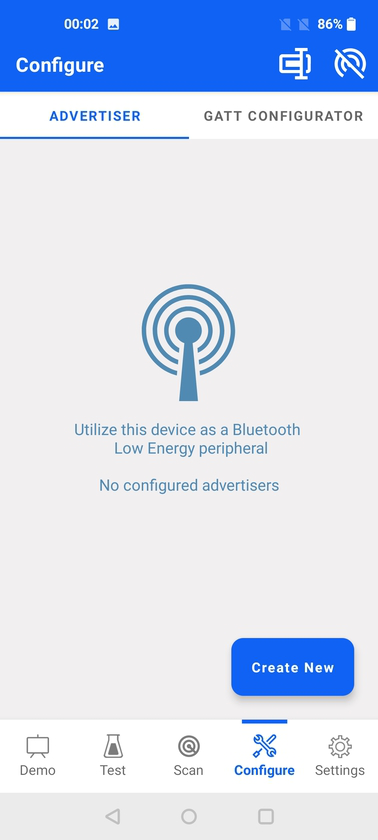

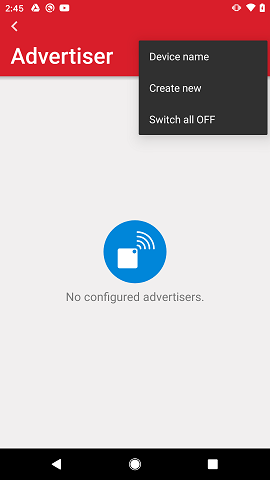
By tapping the menu icon on the top-right corner of the main advertiser view, the user is presented with the following options:
Device name
Create new
Switch all OFF

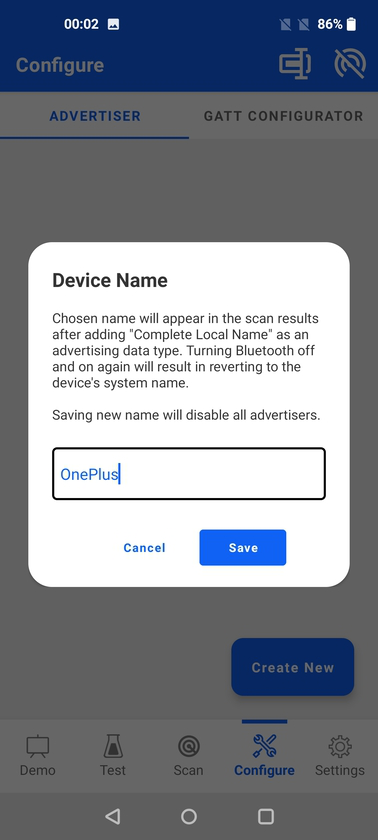
Selecting Device name brings up a dialog to change the device name, which is a global setting and cannot be set individually for each advertisement set.

Create new adds a new advertisement set that only includes the flags AD Type in its payload. The advertisement set is represented by a card, similar to the device representation in the Browser.
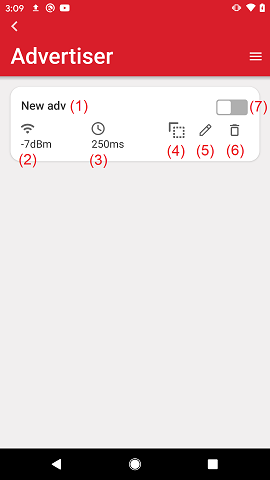

The image above shows the main elements of the device card which are as follows:
Name of the advertisement set. This is not the device name but simply a way for the user to identify each advertisement set.
TX Power in dBm
Advertisement interval in milliseconds
Copy control. This creates an exact copy of the advertisement set which is added at the end of the list of advertisement sets.
Edit control. Takes the user to the edit view of a specific advertisement set.
Delete control. Deletes the specific advertisement set.
Enable/disable advertisement set.
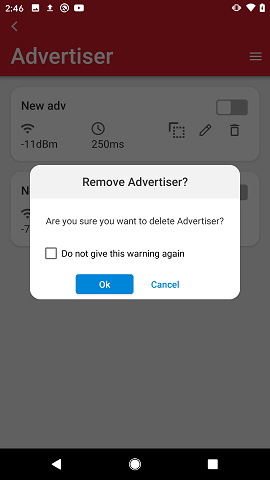
If the user taps the delete control, there is a confirmation prompt which can be dismissed on further delete actions.

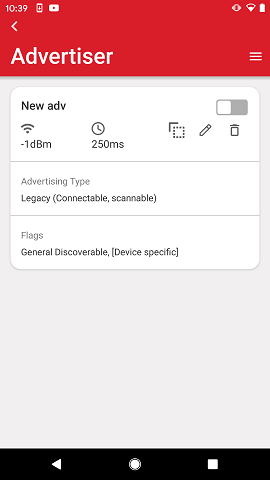
When tapping the device card, it expands with further advertisement details in the same way as device cards expand on the Browser when tapped.

Editing Advertisement Sets#
When entering the edit view for a specific advertisement set, the user is shown a list of customization options. Those options are divided into three areas:
Advertising Type
Advertising Data and Scan Response Data
Advertising Parameters
The view header displays the name of the advertisement set name, which can be changed via the very first text box at the top.
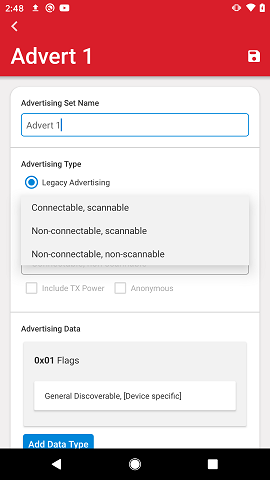
This is followed by the advertisement type, which can be selected between Legacy Advertising and Extended Advertising (introduced in Bluetooth 5.0 specification). Support for Extended Advertising depends on the underlying mobile phone and OS stack. If not supported, a note is displayed and the Extended Advertising option will be grayed out.
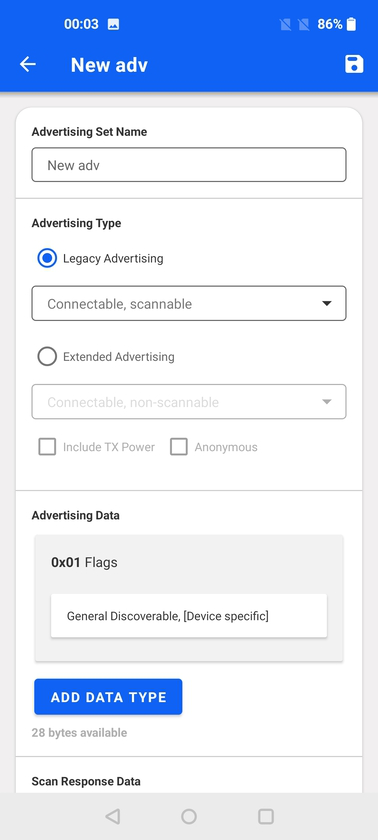

The following Legacy Advertising types are supported:
Connectable, scannable
Non-connectable, scannable
Non-connectable, non-scannable

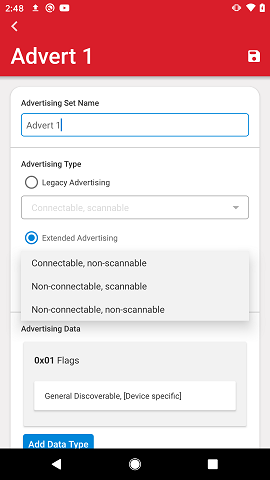
Extended Advertising supports the following types:
Connectable, non-scannable
Non-connectable, scannable
Non-connectable, non-scannable

TX power can be optionally included as part of extended advertising, and, if the type is non-connectable, non-scannable, it can optionally be set as anonymous advertising.
Depending on the selected advertisement type, the Advertising Data and Scan Response data will be available for editing. For example, a connectable, non-scannable type does not have scan response so the Add Data Type button for Scan Response Data will be grayed out.
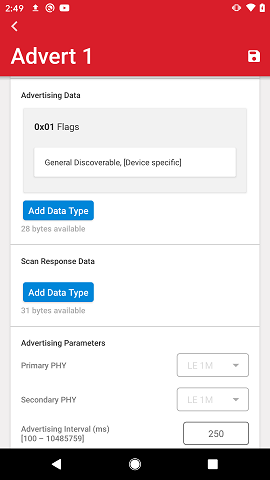

Data is added by tapping Add Data Type and selecting which data type to add.
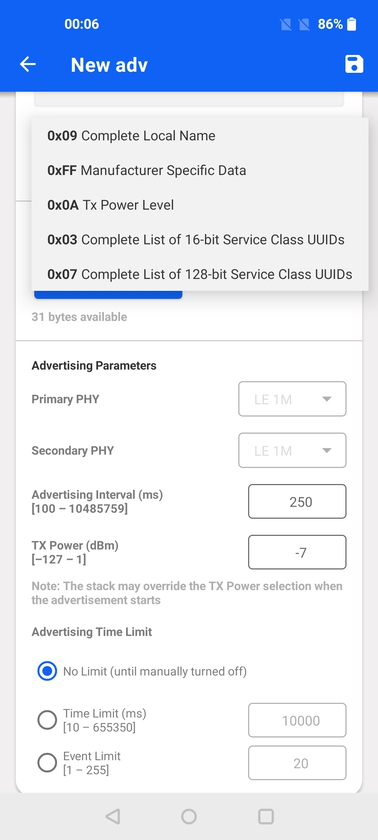

The following advertising data types are currently supported:
0x09: Complete Local Name
0x03: Complete List of 16-bit Service Class UUIDs
0x07: Complete List of 128-bit Service Class UUIDs
0x0A: TX Power Level
0xFF: Manufacturer Specific Data
The selected data type will be added to the advertisement data and below Add Data Type button the amount of bytes still available is shown.
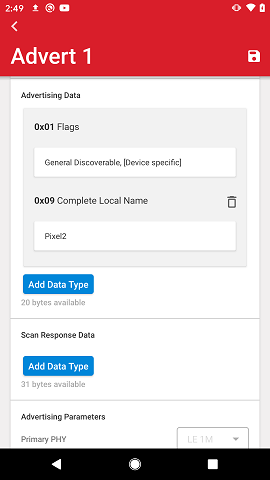

When adding AD types 0x03 or 0x07, each service needs to be added individually by tapping Add 16-bit service or Add 128-bit service buttons.
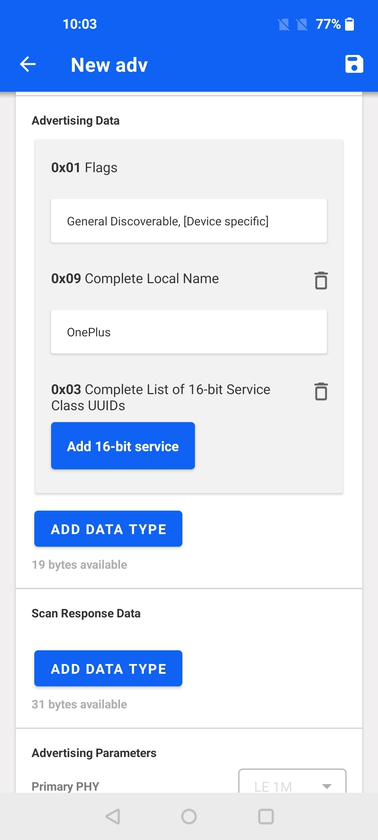

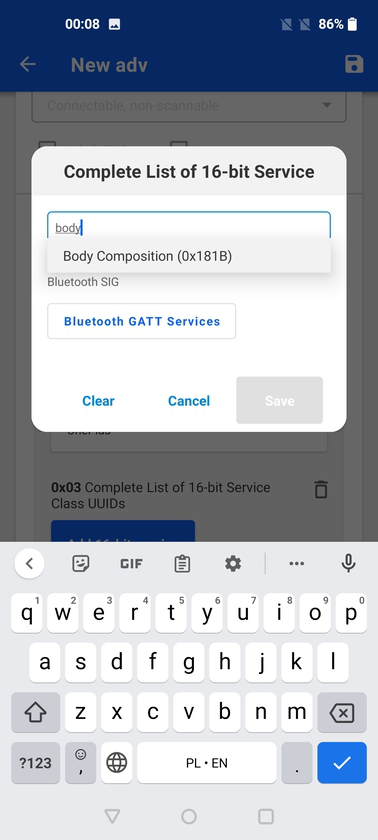
Services are added via a dialog box where the user can input the service UUID or name. For 16-bit services (so called adopted services), an auto-complete functionality suggests services as they are being typed into the text box. Below the box, a link Bluetooth GATT Services takes the user to the Bluetooth SIG Web page that lists all adopted services.

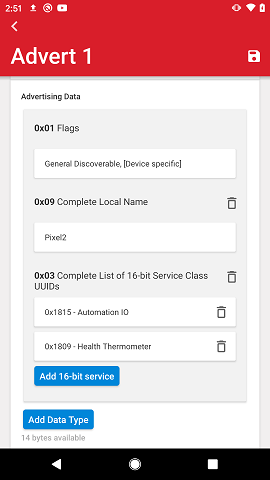
Multiple services can be added under the 0x03 and 0x07 AD Types and can be individually deleted by tapping the trash bin icon. If the trash bin icon for the AD type is tapped, all services are removed together with the AD Type.

Advertising Parameters are below the advertising data and scan response data options. These allow the user to select the advertising PHYs, advertising interval, and TX Power. Lastly, an advertising limit can also be selected for the advertising set, which automatically disables the advertisements after a set time period of a number of advertisement events.
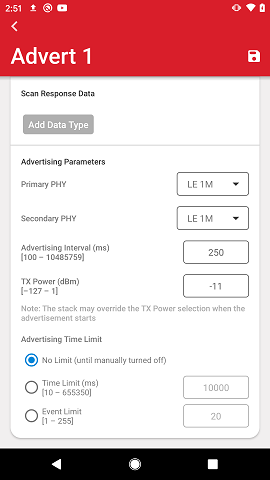

The advertising PHYs for the primary and secondary channel depend on support from the underlying smartphone and OS. They are only available if extended advertising is supported. The alternative PHYs for each of the primary and secondary channels will be available in the respective drop-down menus.
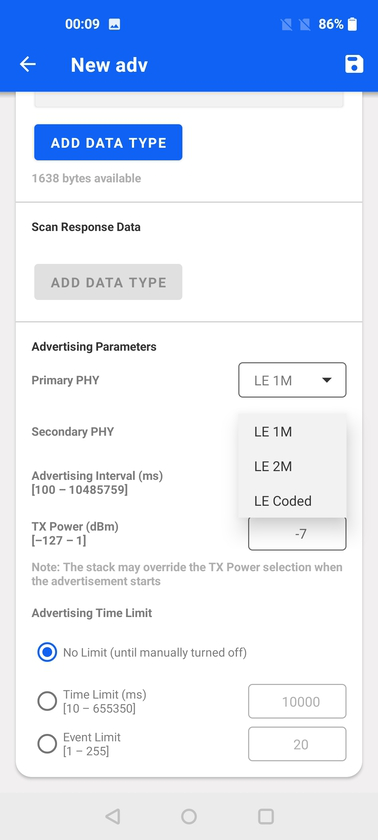

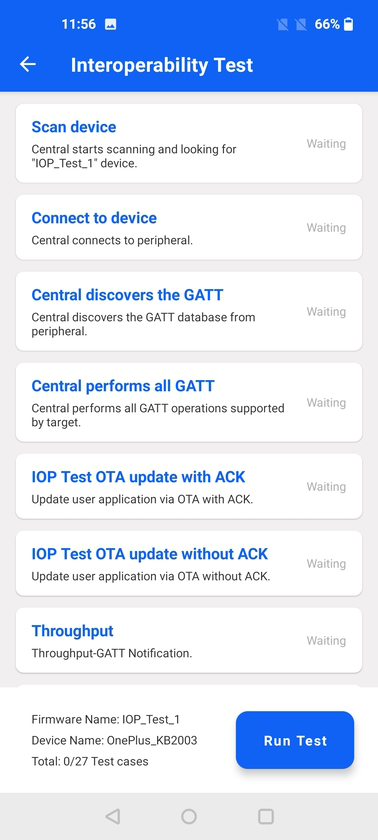
Interoperability Test (IOP)#
The Interoperability Test executes a number of BLE test cases against the Bluetooth - SoC Interoperability Test sample app running on selected EFR32 radio boards.

Once the test sequence is finalized, you have the option to share the results via a cloud drive, email or other standard mediums.
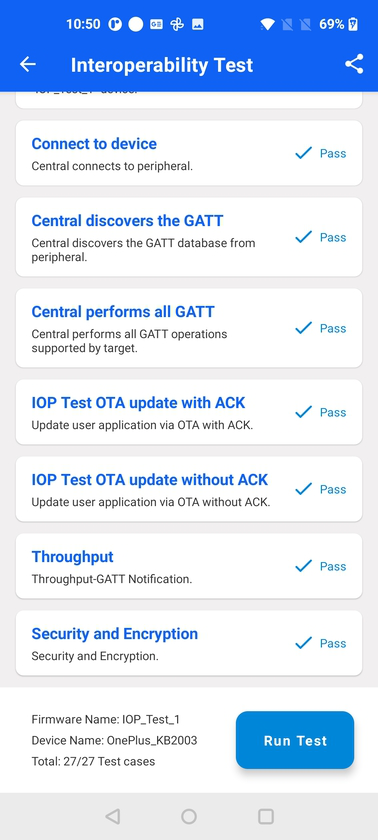

More detailed information about IOP can be found in AN1346: Running the BLE Interoperability (IOP) Test Application Note and AN1309: Bluetooth Low Energy Interoperability Testing Report.
GATT Configurator#
The GATT Configurator is a powerful feature which allows you to create and modify the local GATT database on the mobile device where EFR Connect has been installed. Furthermore, it allows you to import and export the GATT database definition between GATT Configurator on EFR Connect mobile app and GATT Configurator in Simplicity Studio 5.
This feature comes in handy when you are developing a Bluetooth device which has GATT client feature, as you can quickly emulate the GATT server side with EFR Connect without having to write a single line of code.
Creating a New GATT Server#
When entering the GATT Configurator for the first time, the user sees an empty list of servers sets because none have been created yet.

By tapping the menu icon on the top-right corner of the main GATT Configurator view, the user is presented with the following options:
Create new
Import
Export

Selecting Create new will create a new empty GATT database.
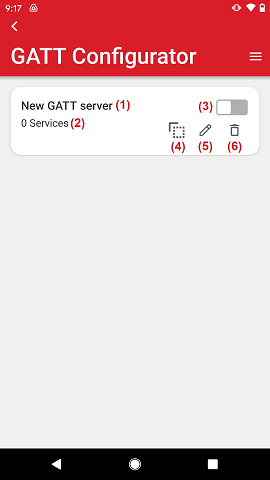

Each GATT database is represented through a card which has the following elements:
GATT database name.
Number of services within the database.
Enable/disable database (Note: only one GATT database can be enabled at any given time. Enabling a new database will automatically disable the existing one)
Copy control. This creates an exact copy of the database which is added at the end of the list.
Edit control. Takes the user to the edit view of a specific database.
Delete control. Deletes the specific database.
Import allows bringing in a GATT database file from Simplicity Studio GATT Configurator, starting from GSDK 3.0 and newer. The file can be stored on standard OS mediums, such as local drive or cloud storage, for example Dropbox or Google Drive. Before moving the file from Simplicity Studio, the extension must be changed from btconf to xml.
Export allows converting one (or more) of the existing GATT databases into the an xml file, which can be directly imported into GATT Configurator in Simplicity Studio.
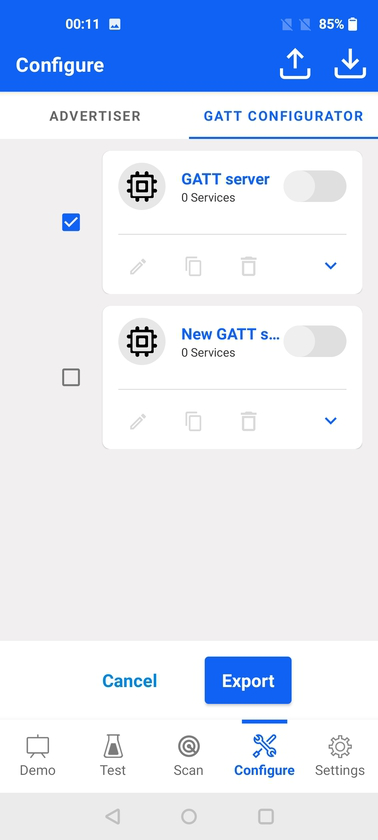

The xml filename is taken from the GATT database name. When selecting more than one database, they will be exported as individual xml files, and if there are duplicate GATT database names then the filename will be appended with a number. In the above example, the exported xml files would be new_gatt_server.xml and new_gatt_server_2.xml.
Tapping on the database card expands it with a list of each included services and how many characteristics are within each of them.
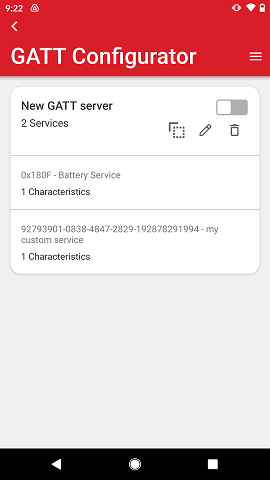

Adding Services#
Tapping the edit control on the GATT database takes the user to the edit view where one can add services, characteristics and descriptors.
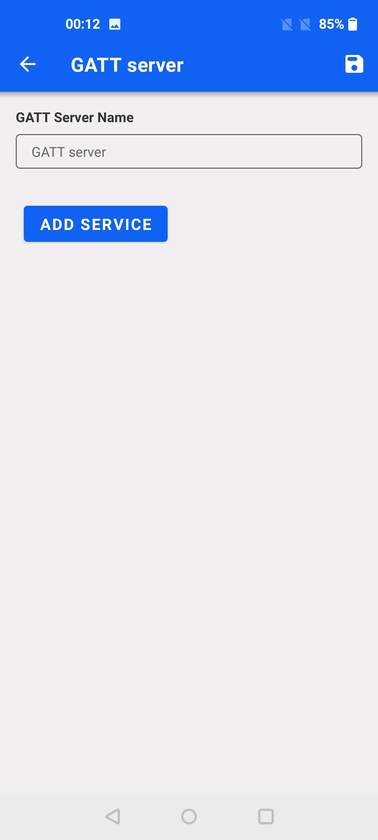

A newly created database will show an empty list of services and option to start adding a service. This will bring a pop-up where both standard as well as custom services can be added.

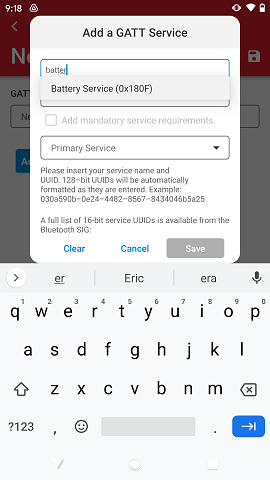
When typing a name, there is an auto-complete feature that matches the name against Bluetooth SIG standard services.

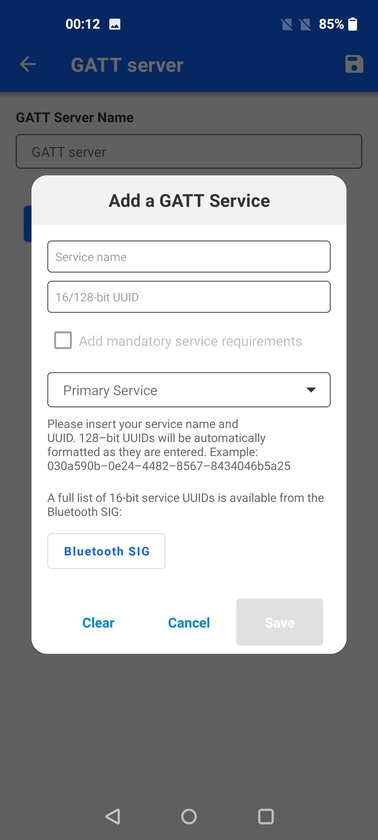
When a standard service is selected, there is the option to also add all mandatory service requirements (mandatory characteristics and descriptors within that service).
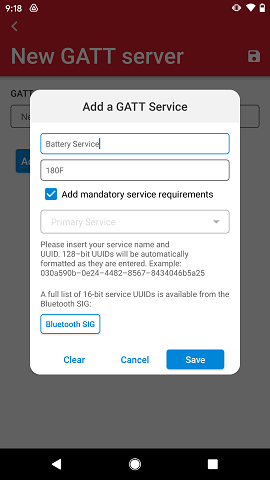

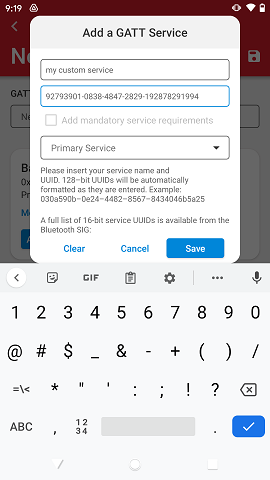
When adding a custom service, it is necessary to write both the service name and 128-bit UUID. The uuid will be automatically formatted and capped to the right size as it gets typed-in.

When the service gets added, it will be listed on the GATT server view.
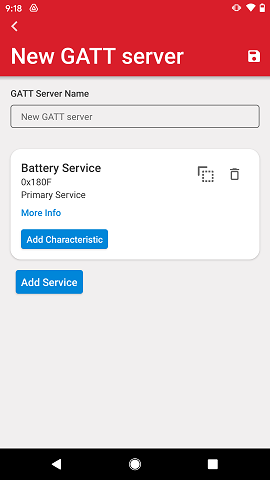

Tapping on More Info will expand the service to reveal its characteristics and descriptors.

At the service level, it is possible to make a copy of the service and delete using the respective controls which have the same icons as elsewhere on the mobile app. Editing a service is not possible.
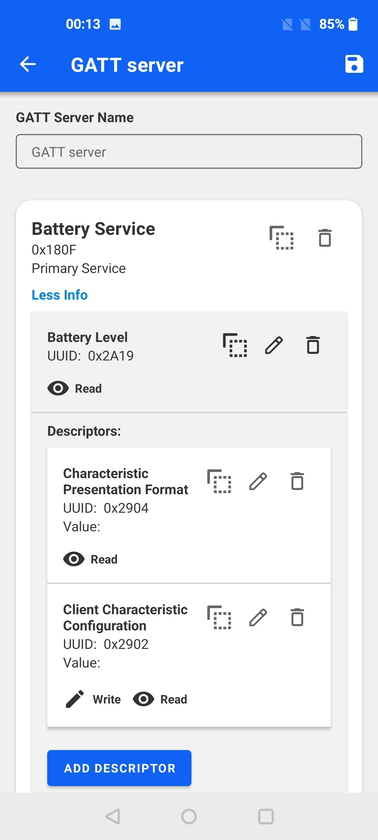
For characteristics and descriptors the copy, edit and delete controls are available. The allowed operations on each characteristic and descriptor (read, write, write without response, notify, indicate) are represented through the same icons used on the Device View.
Adding Characteristics and Descriptors#
At the bottom of each service, there is the option to add characteristics, and at the bottom of each characteristic the option to add descriptors.
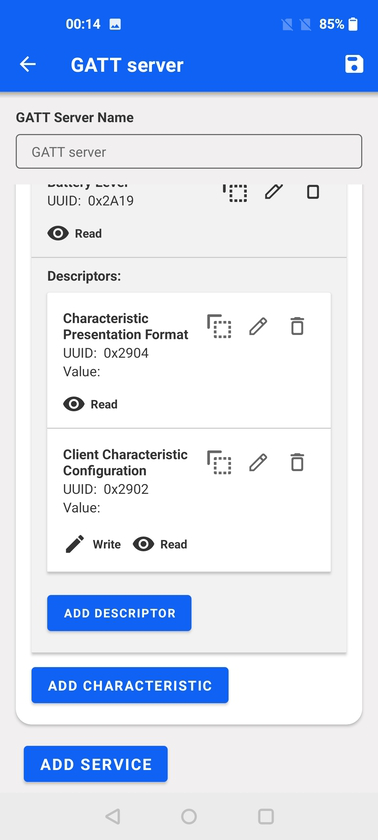

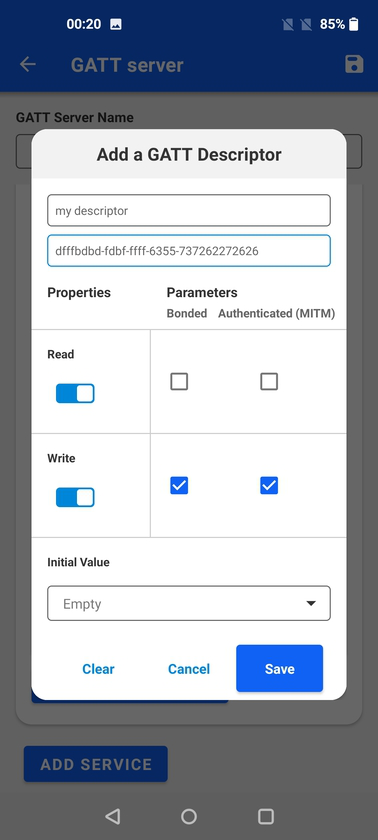
Adding characteristics, brings a pop-up where the characteristics parameters can be configured. Similarly to how services are added, there is an auto-complete feature for Bluetooth SIG standard characteristics, but also custom characteristics can be added with their respective 128-bit UUIDs.
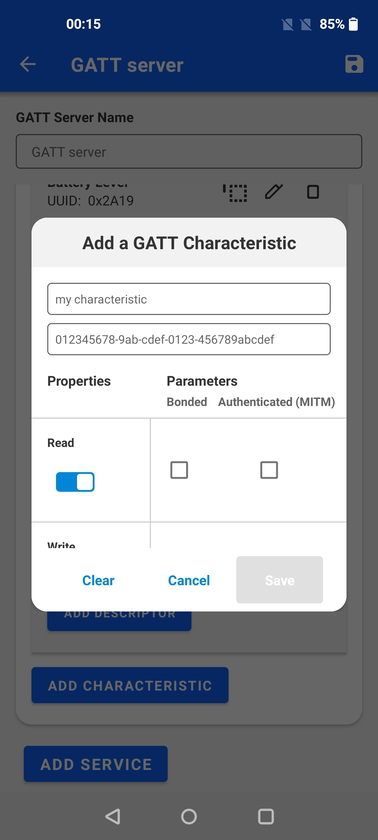

Below the characteristic, name and UUID the properties can be set as well as the access parameters. The access parameters may vary between Android and iOS platforms.
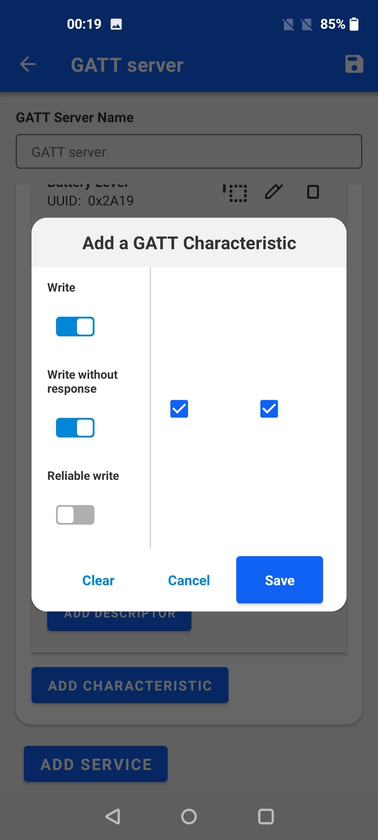

The last option is to set the initial value, which can be done in hex or ascii representation. It's also possible to simply leave it empty.
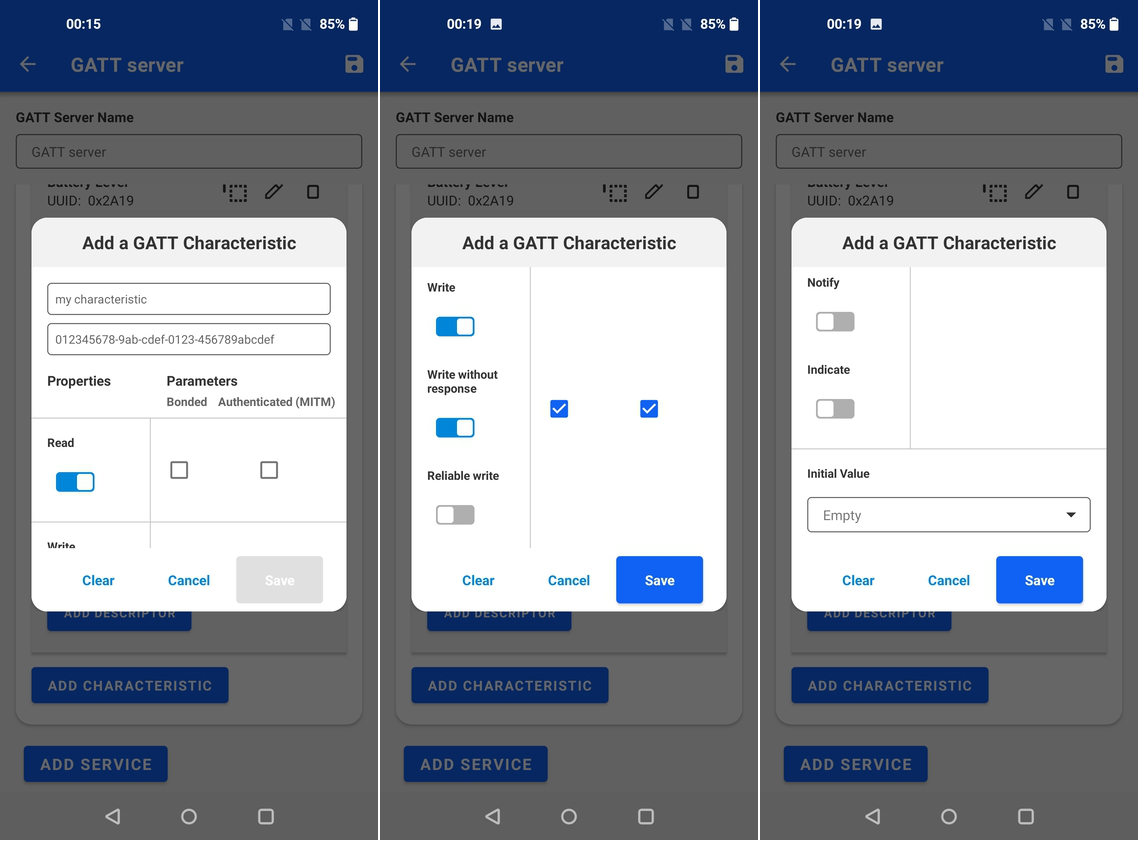

Adding descriptors is similar to adding characteristics but with less properties available.

RSSI Graph#
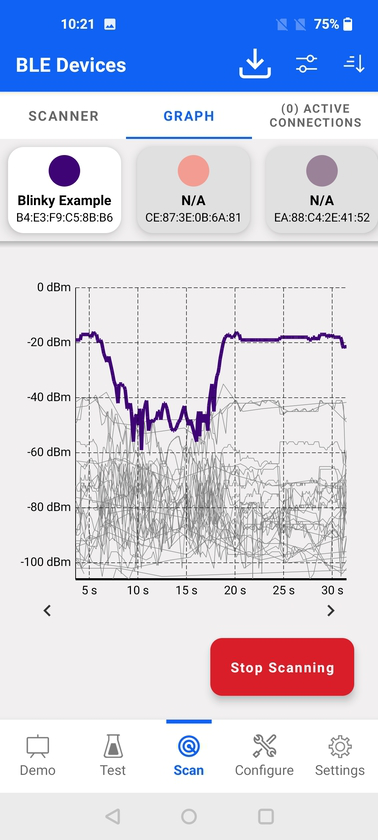
The RSSI Graph shows a graphical representation of RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) over time for all scanned devices. Functions to limit the number of devices using filters and to sort them by signal strength or name are provided.
RSSI Graph View#
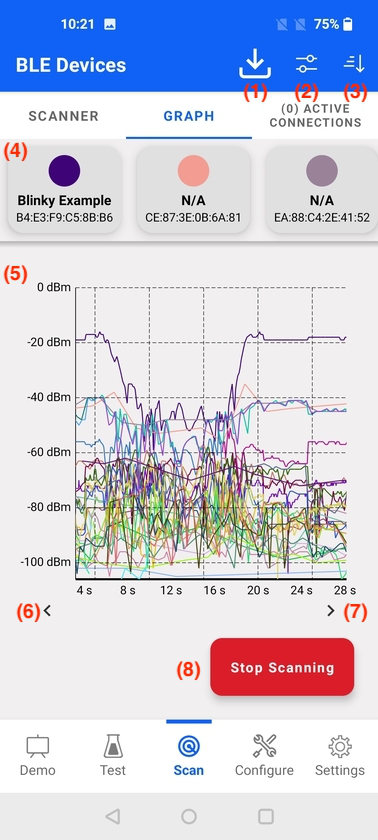

The main elements of the RSSI Graph view are:
Filter view
Sort view
Device list – horizontally scrollable
Graph data – scrollable and scalable
Scroll graph to the start time (visible if not already at start time)
Scroll graph to the actual time (visible if not already at actual time)
Start/Stop scanning
Export – save scan data to csv file
A data line belonging to a specific device can be highlighted by selecting a device name in device list section, as shown.

Filter View#
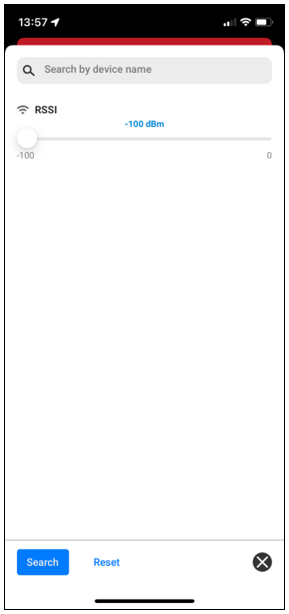
Filter view allows the user to limit the number of devices displayed in the device list as well as on the graph. Filtering can be done by device name and/or RSSI value.

Sort View#
Use sort view to order devices in device list by their name or RSSI value.


Export#
During scanning, the Export button is grayed out. It becomes active when scanning stops.
