Bluetooth Connection Flowcharts#
Introduction#
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) defines a framework for a wide variety of communication types. It allows devices to discover each other, broadcast data, establish connections, and many other fundamental operations.
These procedures are described comprehensively in a series of sequence diagrams, which focus on the following items:
BGAPI function calls.
Messages exchanged over the air.
Events raised by the BLE stack.
This page does not expose the Bluetooth stack packet management nor does it describe the host controller interface (HCI).
The document assumes that the necessary Bluetooth hardware is used, such as an EFR32 SoC or a BGM module.
Generic Access Profile (GAP)#
To establish a BLE connection between the two devices A and B, a device A has to advertise while the device B has to scan for connectable devices. As a result, only the scanning device B can initiate the connection. The scanning device B is then the central and the advertising device A is the peripheral.
Advertising and Scanning#
BLE implements a time division duplex scheme, which means that on a given frequency channel, duplex communication (i.e., sending and receiving data) is taking place on one physical link. This differs, for example, from a wired serial link, where TX and RX wires are used respectively for transmission and reception.
As a result, a defined set of tunable timing parameters are available, such as the advertising interval, scanning interval, and scanning window. For more information, see the BLE core specification.
The advertiser periodically sends advertising packets to any listening device. The scanner starts listening and a "scan report" event is raised each time an advertising packets is received. The advertising packets convey some useful information, such as the advertiser Bluetooth address for example. This information can eventually be used to establish a connection.
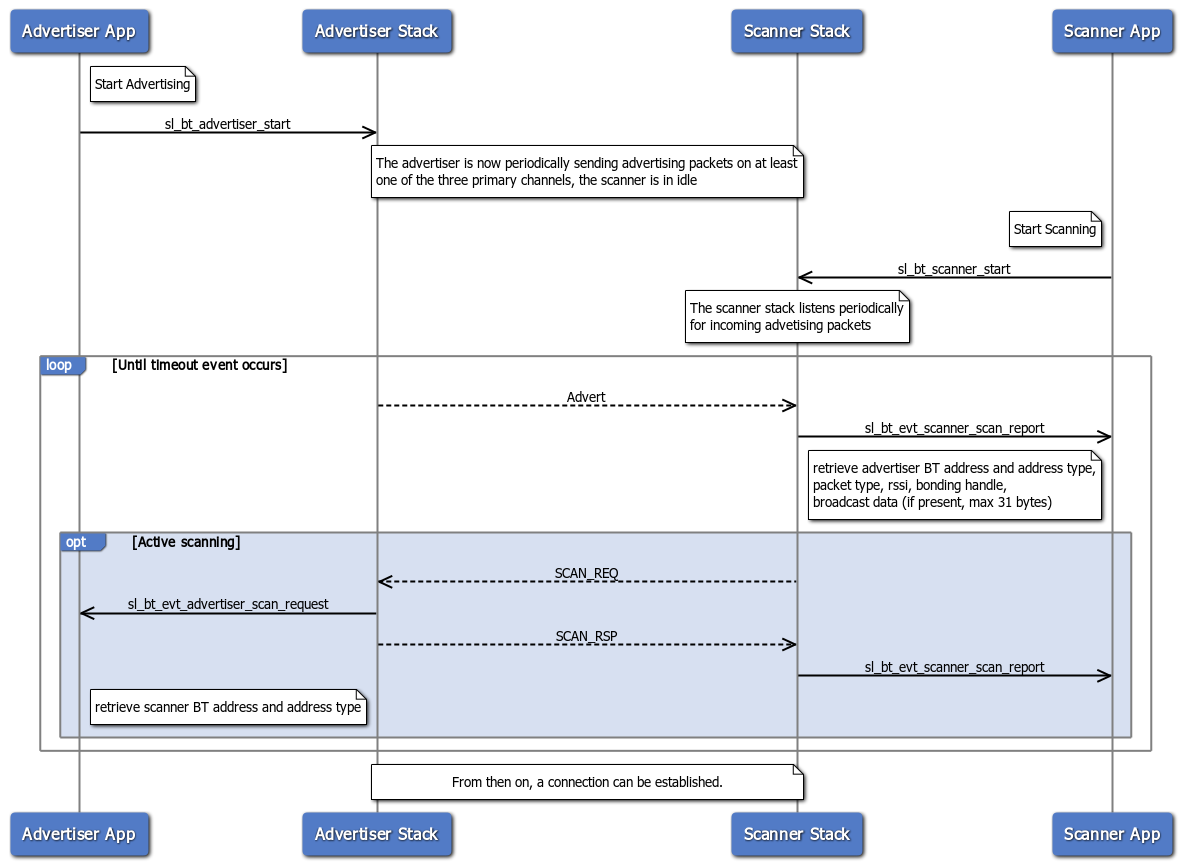

Passive and active are the two available scanning methods. In passive scanning, the scanner only receives advertising packets. In active scanning, the scanner sends "scan request" messages to the advertiser, containing the scanner Bluetooth address and its address type.
Note: This article does not cover extended advertising (https://github.com/SiliconLabs/bluetooth_stack_features/tree/master/advertising/extended_advertising).
Connection Success#
After the scanner collects all necessary information from an advertiser, it can connect to it. The following sequence diagram illustrates the steps to successfully establish a connection:
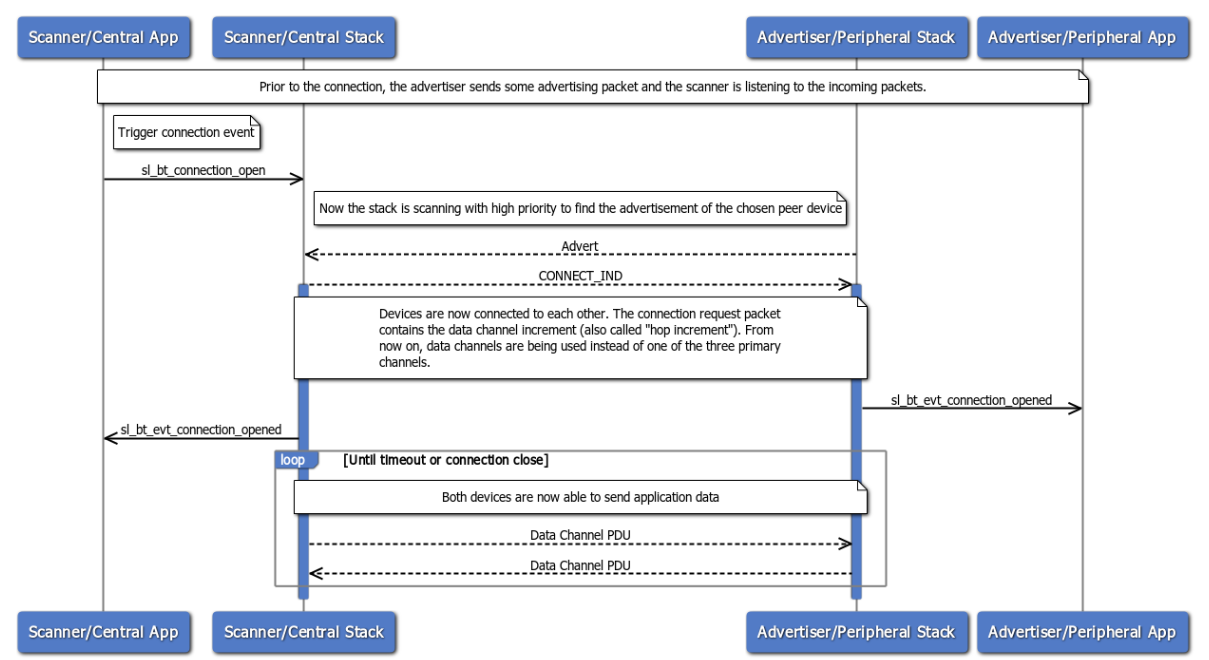

Note that the scanner is initiating the connection, which makes it the central device upon connection.
Connection Initiation Failure#
A connection initiation failure can happen either because the connection initiation is canceled or it times out. A device can cancel a pending connection immediately after creation. The peripheral must respond to the central within a given time interval. The BLE standard defines the fixed number of six connection intervals as the limit within whichever host can remain silent (not sending any packet). If one of the hosts (central or peripheral) remains silent for longer, the connection is dropped.
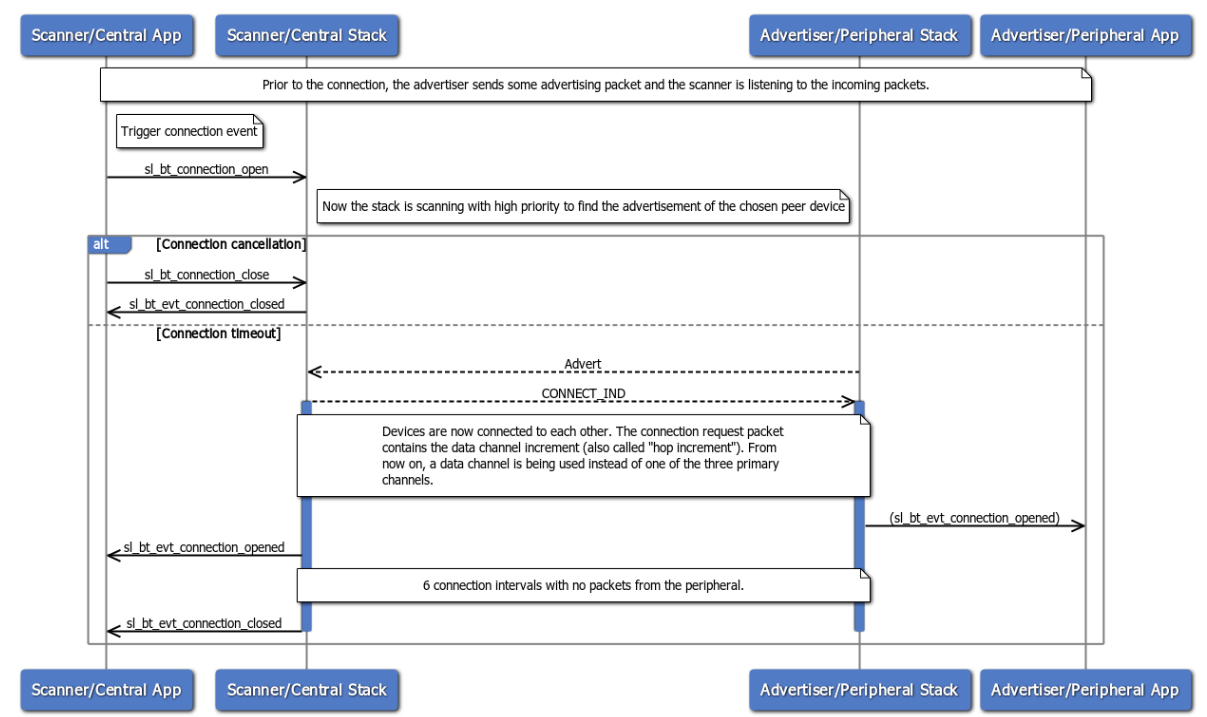

In this example, six connection intervals passed without receiving any data channel PDU from the peripheral. As a result, the connection is dropped. Similarly, If the central had failed to send data channel PDU to the peripheral for that same time interval, the connection would have dropped.
Note: This is different from the supervision timeout. It applies only for the connection initiation. In other words, there is at least one successful connection event where packets are exchanged between the central and peripheral.
Updating Connection Parameters#
After a BLE connection has been established, some parameter adjustments might be requested. To do so, the "Connection parameter request" procedure can be triggered by either host, central or peripheral. The procedure can be triggered at link layer level (i.e., without the application requesting it) during connection initiation. The BGAPI implements the routine sl_bt_connection_set_default_parameters to preset the parameter values. When the connection is initiated, it is still possible at any point in time to update the connection parameters by calling sl_bt_connection_set_parameters in the application layer:
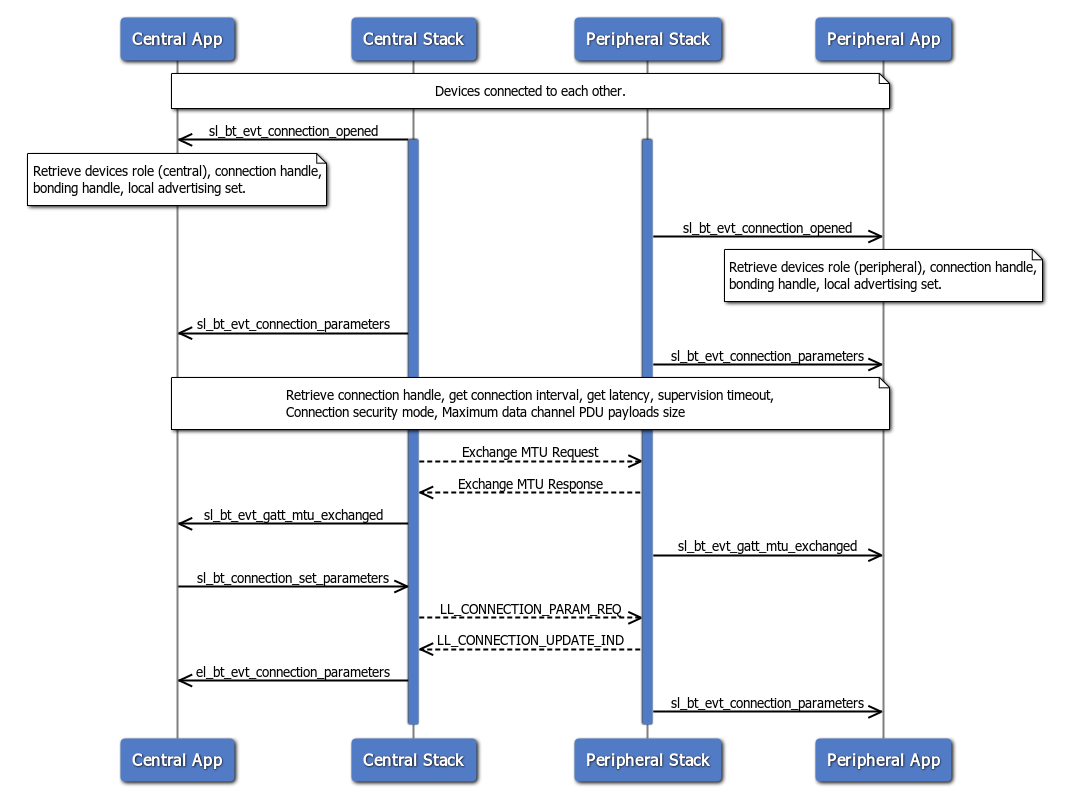

Additionally, the sequence diagram above shows the "GATT MTU exchange" sub-procedure.
The ATT protocol defines a Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) of 23 bytes by default. If the two connected devices can support a bigger ATT_MTU value, the "GATT MTU exchange" procedure is triggered to set the ATT protocol MTU. This procedure is initiated only once during a connection initiation.
Note that the security mode and the data channel PDU payload length may vary during the connection session. For more information about general BLE security features, see Bluetooth Low Energy Application Security Design Considerations in SDK v3.x (PDF).
Note: During the "Connection parameter request" procedure, the central always had the priority over parameter decision. In other words, the central always has the "last word" for parameter negotiation.
