Key Management in PSA Crypto#
Key attributes are managed in a psa_key_attributes_t object. These are used when a key is created, after which the key attributes are impossible to change.
The actual key material is not considered an attribute of a key. Key attributes do not contain information that is generally considered highly confidential. The individual attributes (Key Types, Key Lifetimes, Key Identifiers, and Key Policies) are described in the following sections.
The crypto_values.h in the Windows folder below includes the defines for macros of key attributes.
For GSDK v3.1.x and v3.2.x: C:\SiliconLabs\SimplicityStudio\v5\developer\sdks\gecko_sdk_suite\<GSDK VERSION\>\util\third_party\crypto\mbedtls\include\psa
For GSDK v4.0.0 and higher: C:\Users\\<PC USER NAME\>\SimplicityStudio\SDKs\gecko_sdk\util\third_party\crypto\mbedtls\include\psa
Key Types#
This attribute consists of information about the key: the type, and the size used by this type. The key type and size are encoded in
psa_key_type_t and psa_key_bits_t objects. The following table describes the type and size in symmetric and asymmetric keys.
| Category | Key Type | Size in Bits |
|---|---|---|
| Symmetric Keys | HMAC key • PSA_KEY_TYPE_HMAC |
Non-zero multiple of 8 |
| Key derivation • PSA_KEY_TYPE_DERIVE |
Non-zero multiple of 8 | |
| Cipher/AEAD/MAC key • PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES |
|
|
| ChaCha20/ChaCha20-Poly1305 AEAD key • PSA_KEY_TYPE_CHACHA20 |
256 (32-byte) | |
| Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) Keys | SEC random curves over prime fields • PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1 |
|
| SEC Koblitz curve over prime fields • PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_K1 |
secp256k1 : 256 | |
| Montgomery curves • PSA_ECC_FAMILY_MONTGOMERY |
|
|
| Twisted Edwards curve • PSA_ECC_FAMILY_TWISTED_EDWARDS |
Edwards25519 : 255 |
Key Lifetimes#
The lifetime is encoded in the psa_key_lifetime_t object ([31:0]). This object consists of a persistence level (psa_key_persistence_t) and a location indicator (psa_key_location_t). The persistent level indicates whether the key is volatile, persistent, or read-only. The location indicator indicates where the key is stored and where operations on the key are performed.
Type | Persistence Level [7:0] | Location Indicator [31:8] | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|
Volatile Plain Key | PSA_KEY_PERSISTENCE_VOLATILE | Local (0x0) | RAM |
Persistent Plain Key | PSA_KEY_PERSISTENCE_DEFAULT | Local (0x0) | Flash (2) |
Volatile Wrapped Key | PSA_KEY_PERSISTENCE_VOLATILE | Secure (0x1) (1) | RAM |
Persistent Wrapped Key | PSA_KEY_PERSISTENCE_DEFAULT | Secure (0x1) (1) | Flash (2) |
Public Sign Key | PSA_KEY_PERSISTENCE_READ_ONLY | Secure (0x1) | SE OTP |
Public Command Key | PSA_KEY_PERSISTENCE_READ_ONLY | Secure (0x1) | SE OTP |
AES-128 Key | PSA_KEY_PERSISTENCE_READ_ONLY | Secure (0x1) | SE OTP |
Private Device Key | PSA_KEY_PERSISTENCE_READ_ONLY | Secure (0x1) | SE OTP |
PUF-derived Hardware Unique Key | PSA_KEY_PERSISTENCE_READ_ONLY | Secure (0x1) | PUF Module |
Notes:
If the key cannot be stored persistently inside the SE, it must be stored in a wrapped form in RAM or flash such that only the SE can access the key material in plaintext.
Persistent storage in flash memory is implemented by the NVM3 driver.
Type | Series 1 | Series 2 - VSE | Series 2 - HSE |
|---|---|---|---|
Volatile Plain Key | Y | Y | Y |
Persistent Plain Key | Y | Y | Y |
Volatile Wrapped Key | — | — | HSE-SVH |
Persistent Wrapped Key | — | — | HSE-SVH |
Public Sign Key | — | — (1) | Y (2) |
Public Command Key | — | — (1) | Y (2) |
AES-128 Key | — | — | Y (3) |
Private Device Key | — | — | HSE-SVH (2) |
PUF-derived Hardware Unique Key | — | Y (4) | — |
Notes:
The PSA Crypto cannot access the Public Sign Key and Public Command Key in the VSE-SVM OTP.
These keys can only be used for ECDSA (SECP256R1) precomputed hash operations.
This key can only be used for AES cipher operations. The
SL_SE_BUILTIN_KEY_AES128_ALGinsli_se_opaque_types.horsl_psa_values.hin the Windows folder below defines the default AES cipher algorithm (AES CTR) for this key.For GSDK v3.1.x and v3.2.x (
sli_se_opaque_types.h):C:\SiliconLabs\SimplicityStudio\v5\developer\sdks\gecko_sdk_suite\<GSDK VERSION>\util\third_party\crypto\sl_component\sl_psa_driver\incFor GSDK v4.0.x (
sli_se_opaque_types.h):C:\Users\\<PC USER NAME\>\SimplicityStudio\SDKs\gecko_sdk\util\third_party\crypto\sl_component\sl_psa_driver\incFor GSDK v4.1.x (
sl_psa_values.h):C:\Users\\<PC USER NAME\>\SimplicityStudio\SDKs\gecko_sdk\util\third_party\crypto\sl_component\sl_psa_driver\inc\publicFor GSDK v4.2.x (
sl_psa_values.h):C:\Users\\<PC USER NAME\>\SimplicityStudio\SDKs\gecko_sdk\platform\security\sl_component\sl_psa_driver\inc\publicFor GSDK v4.3.x (
sl_psa_values.h):C:\Users\\<PC USER NAME\>\SimplicityStudio\SDKs\gecko_sdk\platform\security\sl_component\sl_mbedtls_support\inc
The PUF-derived Hardware Unique Key is only available on VSE-SVM devices with a built-in PUF module (e.g., EFR32xG27C). This key can only be used by the CRYPTOACC peripheral for Message Authentication Codes (MAC) and Key Derivation.
The
SL_CRYPTOACC_BUILTIN_KEY_PUF_ALGinsl_psa_values.hin the Windows folder below defines the default algorithm (PBKDF2 CMAC) for this key.For GSDK v4.3.x and higher:
C:\Users\\<PC USER NAME\>\SimplicityStudio\SDKs\gecko_sdk\platform\security\sl_compon ent\sl_mbedtls_support\inc
Key Identifiers#
A key identifier can be a permanent name for a persistent key, or a transient reference to a volatile key. Key identifiers are encoded in a
psa_key_id_t object. The identifier and lifetime of a key indicate the location of the key in storage.
The sli_se_opaque_types.h or sl_psa_values.h in the Windows folder below includes the defines for SE key identifier macros.
For GSDK v3.1.x and v3.2.x (sli_se_opaque_types.h): C:\SiliconLabs\SimplicityStudio\v5\developer\sdks\gecko_sdk_suite\\<GSDK VERSION\>\util\third_party\crypto\sl_component\sl_psa_driver\inc
For GSDK v4.0.x (sli_se_opaque_types.h): C:\Users\\<PC USER NAME\>\SimplicityStudio\SDKs\gecko_sdk\util\third_party\ crypto\sl_component\sl_psa_driver\inc
For GSDK v4.1.x (sl_psa_values.h): C:\Users\\<PC USER NAME\>\SimplicityStudio\SDKs\gecko_sdk\util\third_party\crypto\sl_component\sl_psa_driver\inc\public
For GSDK v4.2.x (sl_psa_values.h): C:\Users\\<PC USER NAME\>\SimplicityStudio\SDKs\gecko_sdk\platform\security\sl_component\sl_psa_driver\inc\public
For GSDK v4.3.x (sl_psa_values.h): C:\Users\\<PC USER NAME\>\SimplicityStudio\SDKs\gecko_sdk\platform\security\sl_component\sl_mbedtls_support\inc
Type | Key Identifier (Key ID) | SE Key Identifier |
|---|---|---|
Volatile Plain Key | 0 (Assigned by the PSA Crypto) | — |
Persistent Plain Key | PSA_KEY_ID_USER_MIN to PSA_KEY_ID_USER_MAX | — |
Volatile Wrapped Key | 0 (Assigned by the PSA Crypto) | — |
Persistent Wrapped Key | PSA_KEY_ID_USER_MIN to PSA_KEY_ID_USER_MAX | — |
Public Sign Key | PSA_KEY_ID_VENDOR_MIN to PSA_KEY_ID_VENDOR_MAX | SL_SE_BUILTIN_KEY_SECUREBOOT_ID |
Public Command Key | PSA_KEY_ID_VENDOR_MIN to PSA_KEY_ID_VENDOR_MAX | SL_SE_BUILTIN_KEY_SECUREDEBUG_ID |
AES-128 Key | PSA_KEY_ID_VENDOR_MIN to PSA_KEY_ID_VENDOR_MAX | SL_SE_BUILTIN_KEY_AES128_ID |
Private Device Key | PSA_KEY_ID_VENDOR_MIN to PSA_KEY_ID_VENDOR_MAX | SL_SE_BUILTIN_KEY_APPLICATION_ATTESTATION_ID |
PUF-derived Hardware Unique Key | PSA_KEY_ID_VENDOR_MIN to PSA_KEY_ID_VENDOR_MAX | SL_CRYPTOACC_BUILTIN_KEY_PUF_ID (GSDK ≥ v4.3.0) |
If users are about to use the PSA Crypto for persistent key storage in their application, adhere to the identifier (Key ID) allocation below. The value 0 is reserved as an invalid key identifier.
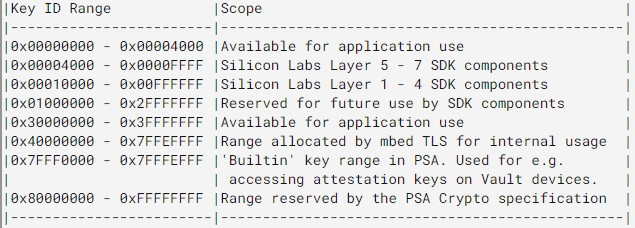

Key Policies#
This attribute consists of usage flags and a specification of the permitted algorithm. The psa_key_usage_t encodes the usage flags in a bit-mask. The following table describes three kinds of usage flag in the PSA Crypto.
| Flag | Bit-mask | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Extractable | PSA_KEY_USAGE_EXPORT | Permission to export the key. |
| Copyable | PSA_KEY_USAGE_COPY | Permission to copy the key. |
| Other usage | PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPT | Permission for a symmetric encryption operation, for an AEAD encryption-and-authentication operation, or for an asymmetric encryption operation. |
| # | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT | Permission for a symmetric decryption operation, for an AEAD decryption-and-verification operation, or for an asymmetric decryption operation. |
| # | PSA_KEY_USAGE_SIGN_MESSAGE | Permission for a MAC calculation operation or for an asymmetric message signature operation. |
| # | PSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_MESSAGE | Permission for a MAC verification operation or for an asymmetric message signature verification operation. |
| # | PSA_KEY_USAGE_SIGN_HASH | Permission to sign a message hash as part of an asymmetric signature operation. |
| # | PSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_HASH | Permission to verify a message hash as part of an asymmetric signature verification operation. |
| # | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DERIVE | Permission to derive other keys from this key. |
Note: Users can always export a public key or the public part of a key pair regardless of the value of the
PSA_KEY_USAGE_EXPORTflag.
The psa_algorithm_t encodes the permitted algorithm with the key. The Symmetric Cryptographic Operation and Asymmetric Cryptographic Operation describe which algorithms can apply to the corresponding cryptographic operations.
The application must supply the algorithm to use for the operation. This algorithm is checked against the permitted algorithm policy of the key.
Summary#
The psa_key_attributes_t object specifies the attributes for the new key during the creation process. The attributes are immutable once the key has been created.
The key identifier and lifetime in the attributes determine the location of the key in storage. The application must set the key type and size, key algorithm policy, and the appropriate key usage flags in the attributes for the key to be used in any cryptographic operations.
The key material can be copied into a new key, which can have a different lifetime or a more restrictive usage policy.
If the key creation succeeds, the PSA Crypto will return an identifier for the newly created key. The PSA Crypto can destroy a key from volatile memory and non-volatile storage NVM3 object. The destroying process makes the key identifier invalid, and the key identifier must not be used again by the application until it is allocated to a newly created key.
If not necessary, the extractable usage flag (PSA_KEY_USAGE_EXPORT) should not be set to allow the key to export in binary format.
