Memory
Gecko OS requires memory (RAM) as working space to hold intermediate calculations and to buffer serial and network data. The amount of memory available in a device impacts the number of features that can be run concurrently, as well as the maximum achievable throughput.
Devices with more RAM support more features and achieve higher throughput.
Gecko OS runs on devices with differing amounts of RAM as shown in the follow table.
| Part Number | Name | RAM (kB) | Max. CPU Speed (MHz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| WGM160P | 512 |
Memory Management
Gecko OS features require varying amounts of RAM. Features like the HTTP Server, TLS server and mDNS are memory intensive. In some cases it may not be possible to run memory intensive features simultaneously.
For example, it may not be possible to run multiple TLS or HTTPS sessions simultaneously.
Some websites use large TLS certificate chains that may exceed the RAM capacity of the device resulting in a failed connection.
When memory usage is greater than 90%, the system displays a warning every 30 seconds:
WARN: Low memory, system may become unstable
Determining Memory Usage
Applications use heap memory. To see the percentage of available heap currently allocated, use the
system.memory.usage
variable:
get system.memory.usage
The diagram below shows a high level map of system memory allocation.
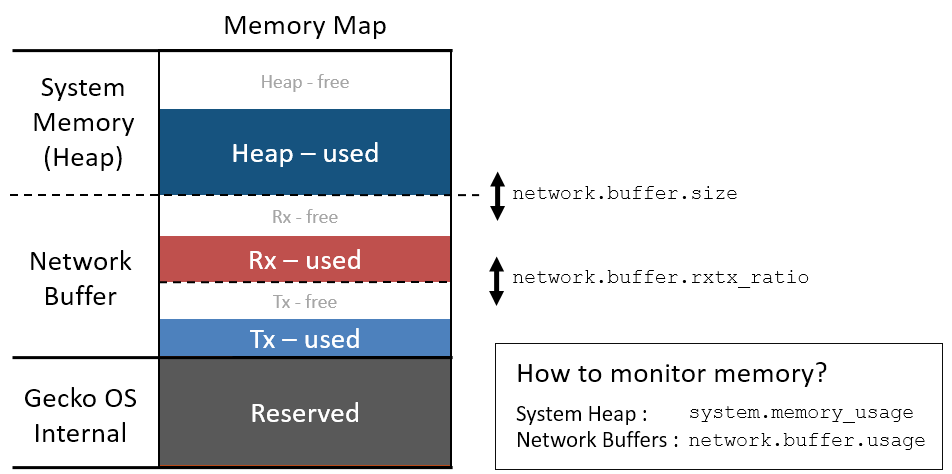
The percentage memory usage returned by system.memory.usage is calculated as follows:
system.memory.usage = 100*heap_used/heap_size
where
heap_size = total_memory_size - reserved_size - network.buffer.size
Notes :
- Adjusting network.buffer.size alters the total heap size available.
- Adjusting network.buffer.rxtx_ratio changes the proportion of the network buffer available for Rx and Tx. It does not change network buffer size.
Minimizing Memory Usage
To minimize memory usage, disable services that are not in use and set default memory allocations to the minimum.
Default features that consume memory include:
- NTP client - see NTP variables
- Broadcast of properties - see Broadcast variables
- RSSI averaging - see wlan.rssi_average
- Network buffer size set above minimum value - see network.buffer.size
Of these features, network buffer size has the most impact on memory usage. Setting network buffer size to the maximum can consume 30% or more of available heap. NTP client, RSSI averaging and broadcast each consume less than 1% of available heap.
However, Gecko OS needs around 20K of network buffer for normal operation.
To minimize memory usage, disable defaults using the following Gecko OS commands:
| Gecko OS Commands | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Streams
Applications that use streams consume memory according to the number of streams in use. Streams are used by the file system, and the various servers and clients. For usage and limits on streams, see Network Connections and Streams .
Memory Management Variables
Some variables allow control of the size and proportion of memory allocated to various tasks.
HTTP clients
It may be necessary to restrict the maximum number of clients the HTTP server allows. Since each HTTP client uses a stream, restricting clients prevents excessive memory usage, and it also avoids web browsers opening multiple streams for a single connection (some browsers do this in an effort to minimize page load time).
Network Buffer
Reducing the network buffer size may prevent excessive memory usage. In some applications that are either receive or transmit intensive, efficiency can be improved by adjusting the ratio of Rx and Tx buffer usage. Monitor network buffer usage with the network.buffer.usage variable.