Memory Manager Architecture#
High-Level Architecture Diagram#
The following diagram presents the high-level architecture of the Memory Manager components.
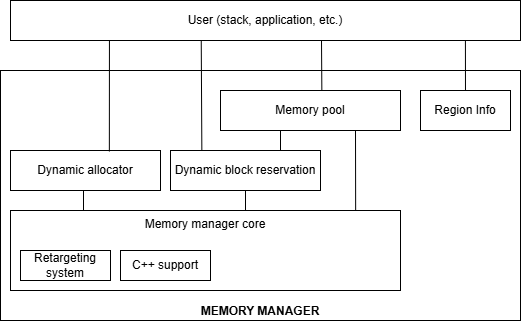

Core Components#
The Memory Manager includes six main components that work together to provide comprehensive memory management capabilities:
Dynamic Allocation System#
File:
sl_memory_manager.cPurpose: Provides malloc/free/calloc/realloc functionality with advanced features
Key Features:
First-fit allocation algorithm with block splitting
Long-term (LT) vs short-term (ST) allocation strategies
Configurable alignment (1-512 bytes, power-of-2)
Thread-safe operation with critical sections
Heap fragmentation reduction through LT/ST allocation
Memory Pool System#
File:
sl_memory_manager_pool.cPurpose: Fixed-size block allocation for deterministic memory management
Key Features:
Guaranteed allocation quotas
More robust against unexpected allocation failures
Static or dynamic pool handle management
Deterministic allocation/deallocation timing
Dynamic Reservation System#
File:
sl_memory_manager_dynamic_reservation.cPurpose: Special construct for reserving blocks from short-term heap section
Key Features:
Block reservation with specific alignment
Reservation handle management
Different usage pattern from dynamic allocation API
Memory Region Management#
File:
sl_memory_manager_region.cPurpose: Provides heap and stack region information
Key Features:
Stack region size and location queries
Heap region size and location queries
Retargeting System#
File:
sl_memory_manager_retarget.cPurpose: Redirects standard C library functions to Memory Manager
Key Features:
malloc/free/calloc/realloc retargeting
Linker wrap functionality for GCC and IAR
Implementation Details:
Linker Wrapping: Uses GCC
--wrapand IAR$Sub$$mechanisms to intercept standard library callsFunction Mapping: Maps
malloc/free/calloc/reallocto Memory Manager equivalentsToolchain Support: Supports both GCC and IAR toolchains with appropriate wrapping mechanisms
Reentrant Support: Handles reentrant versions of memory functions for multi-threaded environments
C++ Support#
File:
sl_memory_manager_cpp.cppPurpose: C++ operator overloading for new/delete
Key Features:
Standard C++ new/delete operator overloading
Exception handling integration
Multiple allocation variants
Implementation Details:
Operator Overloading: Overloads
new,new[],delete, anddelete[]operatorsException Safety: Integrates with C++ exception handling mechanisms
Multiple Variants: Supports different allocation variants (sized, aligned, etc.)
Resource Acquisition Is Initialization (RAII) Integration: Enables automatic memory management through C++ RAII patterns (i.e., resources are properly released when they are no longer needed)
Standard Compliance: Follows C++ standard requirements for operator overloading
Internal Architecture and Design Rationale#
Memory Layout Strategy#
The Memory Manager implements a sophisticated memory layout strategy to minimize fragmentation:
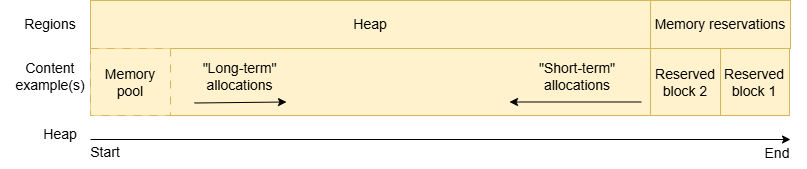

Dual-End Allocation Model:
Long-term allocations start from the heap beginning and grow upward
Short-term allocations start from the heap end and grow downward
Free space exists between the two allocation regions
Fragmentation reduction is achieved by grouping similar lifetime allocations
Allocation Algorithm Details#
First-Fit with Block Splitting:
Search Strategy: Traverse the implicit block list starting from the start of the heap (long-term allocations) or from the end of the heap (short-term allocations)
Block Selection: Choose the first block that can satisfy the request
Splitting Logic: If free block is significantly larger than requested, create a new free block with the surplus
Minimum Size: Respects
SL_MEMORY_MANAGER_BLOCK_ALLOCATION_MIN_SIZEto prevent excessive fragmentationAlignment Handling: Ensures proper alignment while minimizing waste
Free Operation with Merging:
Adjacent Block Detection: Scan for physically adjacent free blocks
Merge Strategy: Combine adjacent free blocks to reduce fragmentation
List Updates: Update long-term and/or short-term free block head pointers to reflect merged blocks
Metadata Cleanup: Reset metadata for merged blocks
Thread Safety Implementation#
Critical Section Strategy:
Global Mutex: Single critical section protects all heap operations
Interrupt Disable: Brief interrupt disable during critical operations
RTOS Integration: Compatible with RTOS task switching
ISR Considerations: Documented latency warnings for interrupt context usage
Dependencies#
The Memory Manager integrates with multiple platform components and hardware interfaces:
Hardware Dependencies#
Component | Function | Integration Details |
|---|---|---|
RAM Memory | Heap management | Direct access to device RAM for heap structure, block allocation, and memory pool operations |
Energy Management Unit (EMU) | Memory retention | Integration with power management hardware for memory retention across power mode transitions |
Software Dependencies#
Component | Dependency Level | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
Platform Common Library | Required | Core platform utilities including assertion handling, bit manipulation, and status code definitions |
Component Catalog System | Required | Conditional compilation support and component presence detection |
Build System (CMake) | Required | Automatic linker wrap configuration for standard library retargeting (GCC |
SL System/Main | Recommended | Proper initialization sequencing and component lifecycle management, early initialization before C++ static constructors |
RTOS Integration | Optional | Thread-safe operation support through CMSIS-OS2 and FreeRTOS compatibility for multi-threaded environments |
Memory Profiler | Optional | Runtime memory usage analysis and optimization for debugging and performance tuning |
Development Tool Dependencies#
Simplicity Studio: IDE integration for configuration, debugging, and memory usage analysis
Universal Configurator: Configuration interface for memory management settings and optimization parameters
Linker Configuration: Automatic linker wrap options for standard C library function retargeting
Memory Analysis Tools: Integration with platform debugging tools for heap monitoring and fragmentation analysis
