Multi-Instance OpenThread Support#
This section describes how to enable multi-PAN support for OpenThread SoC applications through the use of multiple OpenThread instances. By default, OpenThread is configured to support a single instance per device. Enabling multiple instances allows a single device to participate in multiple independent Thread networks simultaneously, which is useful for scenarios requiring network isolation or concurrent operation of separate Thread networks.
Key Points#
Understanding multiple OpenThread instances.
Build configuration requirements.
Application code modifications.
Understanding Multiple OpenThread Instances#
OpenThread supports running multiple independent instances on a single SoC device. Each instance operates as a separate Thread network stack with its own:
Network configuration and credentials.
Thread network state.
Routing tables.
Security keys and certificates.
Network buffers and memory resources.
This multi-instance capability enables scenarios such as:
Participating in multiple Thread networks simultaneously.
Network isolation for security or testing purposes.
Gateway applications connecting different Thread networks.
Comparison With Multi-PAN RCP#
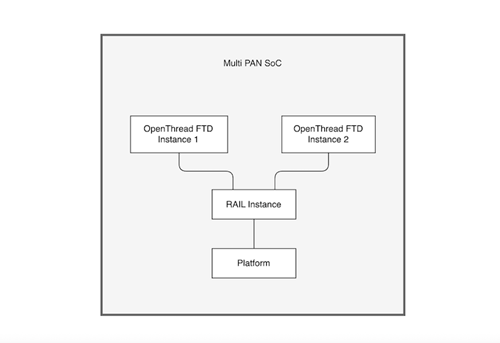

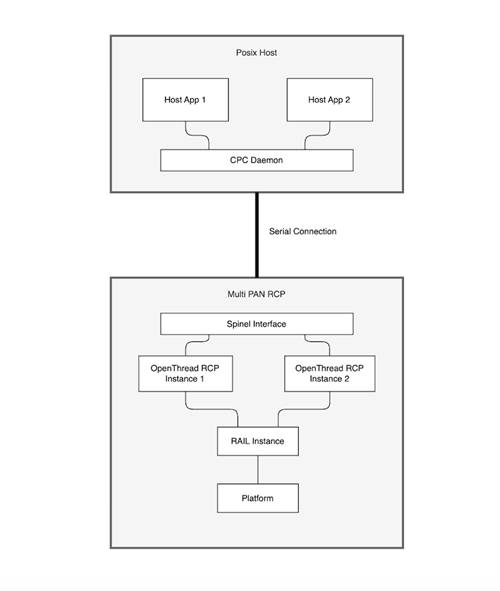

In a multi-instance SoC application, multiple OpenThread network stacks run concurrently on a single SoC device, enabling it to participate in several independent Thread networks using local resources.
In contrast, a multi-PAN RCP (Radio Co-Processor) configuration allows a host processor to control multiple IEEE 802.15.4 networks by connecting to a single RCP, where the RCP itself does not manage network state but instead provides radio services for multiple networks managed by the host. Typically, this configuration is intended to manage a Zigbee and a Thread network, but multiple Thread networks are architecturally possible.
The key distinction is that multi-instance is handled fully on the SoC, whereas multi-PAN RCP splits network management between the host and the RCP.
Prerequisites#
Before enabling multiple OpenThread instances, ensure that:
Sufficient memory and processing resources are available (see Memory Comparison for details).
You are using a compatible version of the Silicon Labs OpenThread SDK.
Simplicity Studio is installed and configured.
Enabling Multiple Instances in Build Configuration#
Using Simplicity Studio#
Open your OpenThread project in Simplicity Studio.
Navigate to the Software Components tab.
Open the configuration for the selected OpenThread Stack, and enable the following options:
Multiple OpenThread InstancesMultiple Static Instance SupportSet
Number of OpenThread Instancesto the desired number of instances
If running instances on separate channels, enable the following, under RAIL_IEEE802154_OPTIONS: (Platform > Radio):
RAIL Utility, IEEE802.15.4 Fast Channel Switching ConfigurationRAIL Utility, DMA
Generate and build your project.
Using Command Line Build#
If building from the command line, add the following configuration options:
OPENTHREAD_CONFIG_MULTIPLE_INSTANCE_ENABLE:1OPENTHREAD_CONFIG_MULTIPLE_STATIC_INSTANCE_ENABLE:1OPENTHREAD_CONFIG_MULTIPLE_INSTANCE_NUM:\<number of instances\>
If running instances on separate channels, add the following to enable channel switching support:
Add the following configuration option:
SL_RAIL_UTIL_IEEE802154_FAST_CHANNEL_SWITCHING_DEFAULT_ENABLED:1
Generate your project with the following components:
sl_rail_util_ieee802154_fast_channel_switchingsl_rail_util_dma
Application Code Modifications#
After enabling multiple instances in the build configuration, update your application code to create and manage multiple OpenThread instances.
API Changes#
Use
otInstanceInitMultipleto initialize multiple instances rather thanotInstanceInitSingle.Use
otInstanceGetIndexto retrieve the index of a provided instance pointer.Use
otInstanceGetInstanceto retrieve the instance pointer associated with a provided index.
Example: Multi-Instance CLI Sample Application#
To help you get started, we provide a ready-to-use sample application and a utility component designed specifically for multi-instance OpenThread development:
Sample App: OpenThread - SoC CLI (FTD multi-instance)
This sample demonstrates how to build and use a CLI-based app that manages and interacts with multiple Thread instances.
Multi-Instance CLI Utility Component: OpenThread | Multi-Instance CLI Support
This component provides support for CLI control of multiple OpenThread instances by adding an
instanceCLI user command set to the OpenThread CLI interpreter, which can perform the following operations:List initialized instances, their static index, and their id value.
Print the index of the instance that the CLI is controlling.
Reset the CLI context to operate on a different instance of a specified index.
Using the CLI with Multiple Instances:
The sample application initializes 2 instances and sets the CLI to operate on instance 0. The following shows a representative interaction with forming a network on each instance using the CLI:
Initialized CLI for instance 0
Use 'instance list' to list all instances
Use 'instance set <index>' to change between instances (0-1)
> instance list
* Index: 0, Id: 657576498
Index: 1, Id: 468683675
Done
> instance get
Current instance index: 0
Done
> instanceid
657576498
Done
> state
disabled
Done
> dataset init new
Done
> dataset commit active
Done
> dataset active
Active Timestamp: 1
Channel: 12
Wake-up Channel: 19
Channel Mask: 0x07fff800
Ext PAN ID: 7d6b2f27a1b7e5b2
Mesh Local Prefix: fd9f:a842:932:a11f::/64
Network Key: 4e67428cf67b82bb2040eb8ed667096a
Network Name: OpenThread-394a
PAN ID: 0x394a
PSKc: f4716182bdeb97dfd628c38f483fa96b
Security Policy: 672 onrc 0
Done
> ifconfig up
Done
> thread start
Done
> state
leader
Done
> instance set 1
Done
Switched to instance 1
> instance get
Current instance index: 1
Done
> instanceid
468683675
Done
> state
disabled
> dataset init new
Done
> dataset commit active
Done
> dataset active
Active Timestamp: 1
Channel: 13
Wake-up Channel: 18
Channel Mask: 0x07fff800
Ext PAN ID: eb15c96173f3fff9
Mesh Local Prefix: fd47:1d63:616f:e841::/64
Network Key: 6bfe51d1392e4177af4efd0de6faf66c
Network Name: OpenThread-9d8a
PAN ID: 0x9d8a
PSKc: 7b3986c065c21435eccd7f37098cd94a
Security Policy: 672 onrc 0
Done
> ifconfig up
Done
> thread start
Done
> state
leaderTopology Examples#
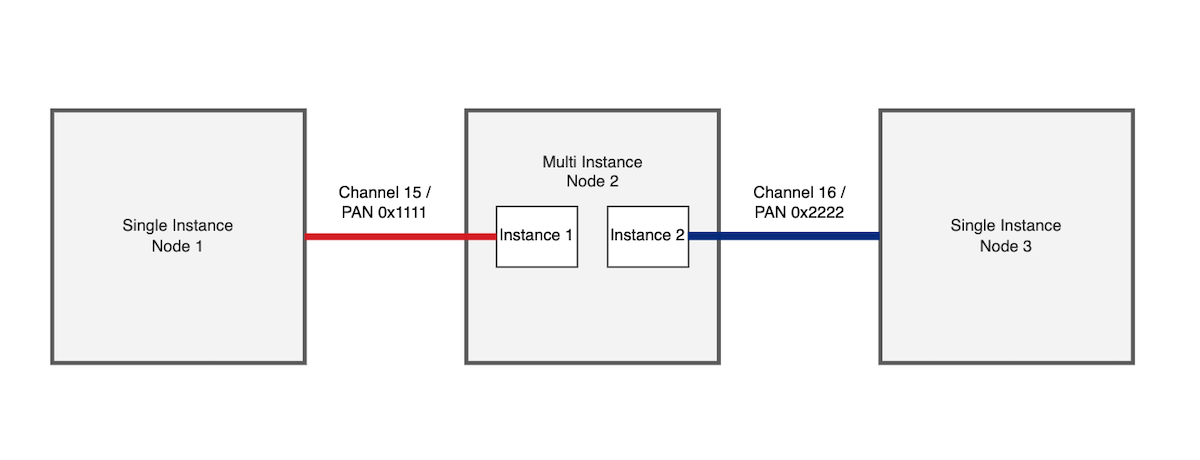
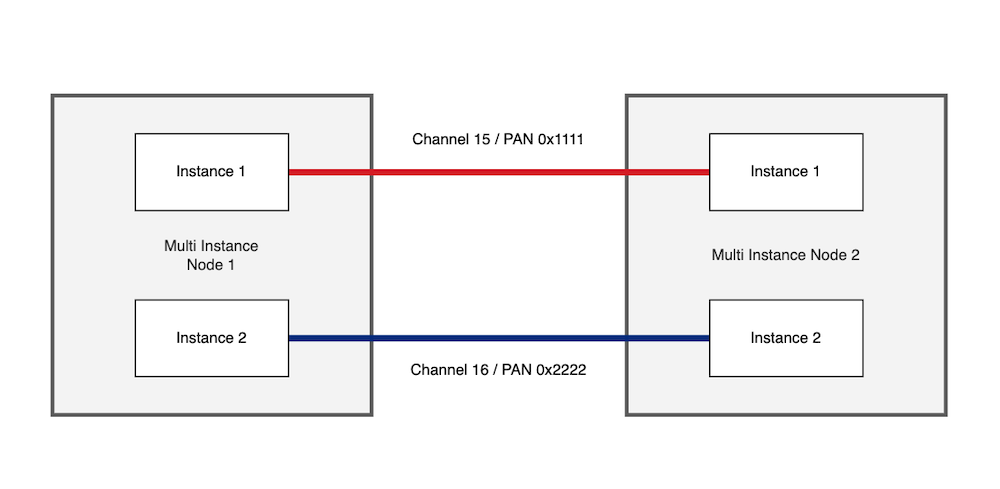
The diagrams below represent how multi-PAN SoC devices can interact with single instance SoC devices as well as other multi-PAN SoC devices.
A single multi-instance device communicating with single instance devices over separate PANs and channels:

Two multi-instance devices communicating with each other across two independent connections:

Configuration Considerations#
Network Configuration#
Each OpenThread instance must be configured with unique network parameters:
Extended PAN ID: Each instance should use a different Extended PAN ID.
Network Key: Each instance requires its own network key.
Channel: Instances can operate on the same or different channels.
PAN ID: Each instance should have a unique PAN ID if operating on the same channel.
Platform Limitations#
Some platforms may have limitations when running multiple instances:
Platform constraints may limit the number of concurrent instances to no more than 3.
Multi-instance support limited to statically initialized instances with key references enabled.
Memory Comparison#
Enabling multi-instance support will require more RAM and use more code size than a single instance application. While the exact difference will vary based on the specific OpenThread configuration values used, here is a relative comparison between applications with a comparable FTD configuration:
Application | RAM Usage (.bss+.data) | Code Size |
|---|---|---|
ot-cli-ftd | ~24 kB | ~324 kB |
ot-cli-ftd-multi-instance | ~41 kB | ~334 kB |
ot-ble-dmp | ~33 kB | ~465 kB |
Measurement Details:
SDK release: sisdk-2025.12
Target part: EFR32MG24
Link Time Optimization (LTO): Enabled
