Length Configuration#
The radio support 3 different modes to configure the length of the packet:
Fixed length: The length of the packet can be changed with a dedicated RAIL API.
Variable length: The length of the packet is in a field in the packet, usually at the beginning.
Frame type: We define a few different packet lengths, that we encode into maximum 3 bits.
This mode can be selected from a dropdown menu in the Frame General card.
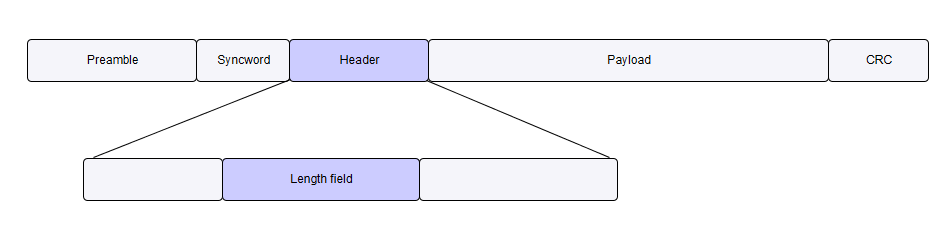
The packet itself can be built up from a header and a payload. In some cases, when talking about packet length we could mean the sum of both lengths or just the length of the payload. This chapter will highlight which meaning is used for the given mode.
Note**: The amount of data you load into the transmit buffer does not change the configured length. If it is less than the configured length, you will receive a SL_RAIL_EVENT_TX_UNDERFLOW event during transmission. Length configuration applies to both receiver and transmitter.
Fixed Length#
All packets have the same payload length, which is configured by the Fixed Payload Size field on the Frame Fixed Length card. This card is automatically hidden when a different length algorithm is selected. This input only configures the length of the payload, without the header.
In fixed length mode, the length can be changed during runtime with sl_rail_set_fixed_length(). However, RAIL does not handle the header and payload separately, so this API sets the sum of these two.
Variable Length#
In variable length mode, the length is defined by the Length field. It stores the length of the payload (without the header). The length field is at maximum 12 bits long, normally stored near the end of the header. Therefore, the header must be enabled when variable length mode is used (this happens automatically, if header was disabled when switching to variable length mode).
The length field can start at any bit in the header but the last bit of the field must be at most 7 bits from the end of the header. The length field can use different endianness from the frame and a static offset can be added or subtracted from the field. All of these can be configured on the Frame Variable Length card, which is automatically enabled upon selecting this algorithm.

If the sl_rail_set_fixed_length() is used with variable length mode, the radio will switch to fixed length mode. Returning to variable length mode is possible by calling sl_rail_set_fixed_length() with the parameter SL_RAIL_SET_FIXED_LENGTH_INVALID.
Length Decoding Process#
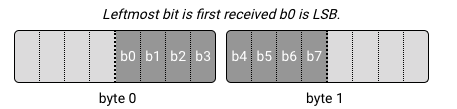
To correctly configure variable length mode, it is useful to understand the length decoding process. The radio first receives the Header, and extracts the last 2 bytes of it for length decoding. If the header is only 1 byte, the decoder prefixes it with 0x00.
If Variable Length Byte Endian is set to LSB first, it swaps the bytes (it does not do anything on a single byte length field).
It reverses the bit endianness of both bytes, if Variable Length Bit Endian is not the same as Frame Bit Endian.
Shifts right by Variable Length Bit Location number of bits.
Masks with an all-one mask with the length of Variable Length Bit Size.
Adds the value of the Variable Frame Length Adjust (which might be negative) to the result.
If the resulting length is less than Minimum Length or more than Maximum Length, it aborts the reception, and generates a SL_RAIL_EVENT_RX_FRAME_ERROR, otherwise it continuous reception with the length.
Because Variable Length Bit Location is maximum 7 bits, the last bit of the length field must be in the last byte of the header.
An element on the Frame Variable Length card will show the 2 bytes used by the length decoder and how the length field is located in it.

If the header must be used for other purposes (e.g., first few bytes are not whitened, but the length field is), the length field location can be configured independently from the header size with the Byte Position of Dynamic Length Byte field.
Frame Type#
The details of this method are configured on the Frame Type Length card, automatically enabled on selecting this algorithm.
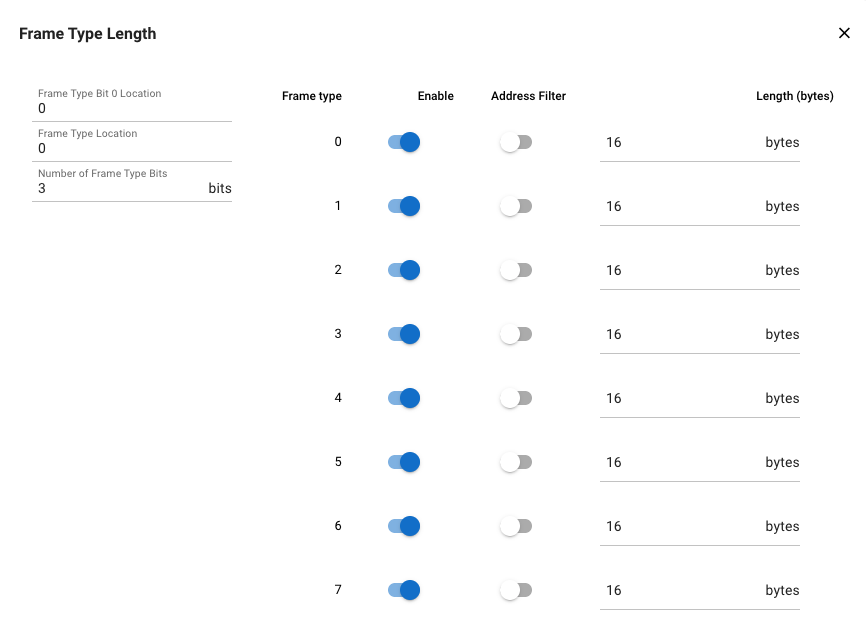
This is an option whereby the frame length information is available in the frame itself in a coded fashion. The code is then resolved by the radio hardware into preconfigured length settings. We call this code Frame Type. The Frame Type can be up to 3 bits long, which means up to 8 frame lengths can be configured. Additionally, address filtering can be configured on each frame.
This mode is handled slightly differently from RAIL, compared to Fixed and Variable length modes. While in fixed and variable length mode, the length decoder works the same in both receive and transmit, FRAME_TYPE mode is only active in receive. When transmitting, the radio will ignore the length bits and instead transmit the full FIFO.
The following options can be configured on the Frame Type field:
Number of Frame Type Bits: Sets the length of the Frame Type.
Frame Type Location: Sets the location (in Bytes) of the Frame Type.
Frame Type Bit0 Location: Sets the location (in bits) of the Frame Type.
For each Frame Type, the following can be configured:
Enable: Enables or disables the given frame type .
Address Filter: Uncheck it to disable the address filter on these types (that is, the address filter is enabled from RAIL, but these frame types would not be filtered).
Length: Sets the length of the frame coded by the given frame type.
