Add WiSeConnect™ SDK v3.x to Your Application#
Prerequisites#
Your host application must contain the CMSIS-RTOS2 API and an RTOS library.
As an example, for STM32F411RE™ (hereafter referred to as STM32), let us consider a sample Keil µVision project host application project (Sample_STM32_project) created using STM32CubeMX tool. By default, the STM32CubeMX provides the CMSIS-RTOS2 API ported onto FreeRTOS library. This implementation is present at path: <STM32 project>\Middlewares\Third_Party\FreeRTOS\Source

Follow the below sequence of steps to port WiSeConnect™ SDK v3.x (hereafter referred to as SDK v3.x) to your host MCU application.
Prepare Project for Porting#
The initial step in porting is to integrate the SDK v3.x into your host application. The SDK v3.x depends on few header and c source files present in the Silicon Labs Simplicity SDK (formerly Gecko SDK) (hereafter referred to as SiSDK (formerly GSDK)). Therefore, it is necessary to integrate the required files from SiSDK (formerly GSDK) as well as SDK v3.x for developing an SiWx917 application using a host platform.
Create a new folder or a directory in the host platform project’s root directory or any convenient location in the project.
For example, let us consider a sample STM32 Keil µVision project (Sample_STM32_project) created using the STM32CubeMX tool. In this case, create a directory, say
SiliconLabs_SDKin the sample project’s root directory.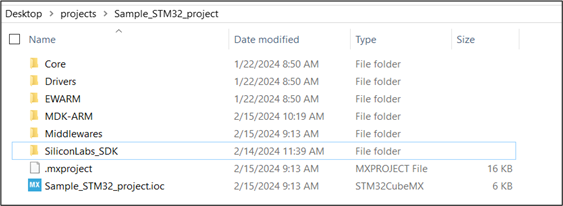

Within
SiliconLabs_SDK, create two sub-directories for SiSDK (formerly GSDK) and SDK v3.x.For STM32 project, two sub-directories with names
SiSDK (formerly GSDK)andWSDKare created.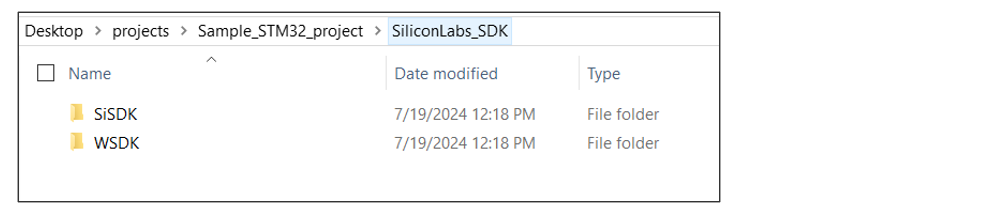

Add Code from Simplicity SDK (formerly Gecko SDK) (SiSDK (formerly GSDK))#
Add the following c source files from SiSDK (formerly GSDK)present at path: <simplicity_sdk>/platform to your project.
In case of STM32F411RE, the required c source files are added at
SiSDK (formerly GSDK)/srcfolder.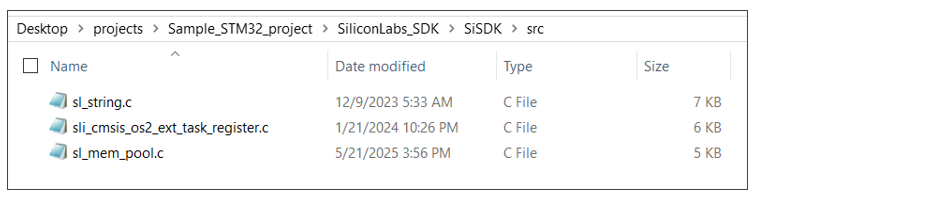

Include the following c header files from SiSDK (formerly GSDK) present at path: <simplicity_sdk>/platform in your project.
All header files from path: https://github.com/SiliconLabs/simplicity_sdk/tree/sisdk-2024.12/platform/common/inc
In case of STM32F411RE, the header files are added at
SiSDK (formerly GSDK)/incas shown below.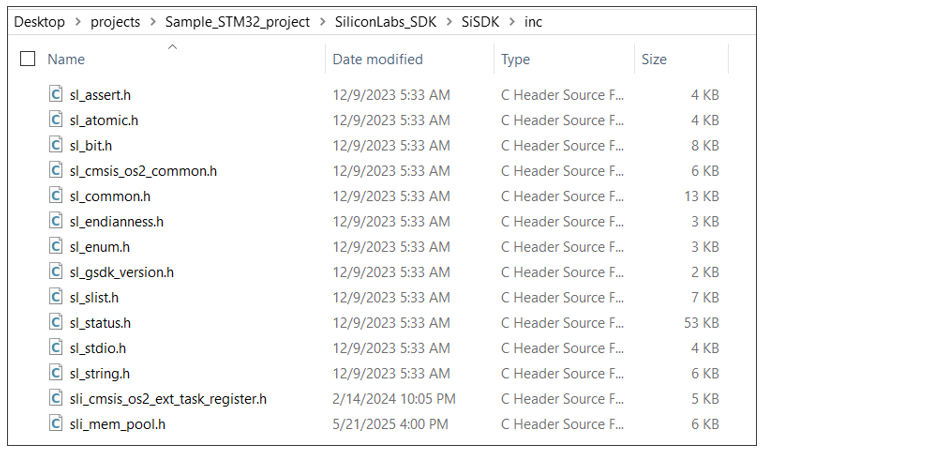

Port Compiler and Architecture-Specific Functions#
The following compiler-specific function prototypes present in sl_core.h should be defined based on the compiler used for your project.
CORE_EnterAtomic | CORE_ExitAtomic | CORE_EnterCritical | CORE_ExitCritical
Create a C source file to define the compiler-specific functions to define the above functions. In case of STM32F411RE, a file named sl_host_core.c is created and added at
SiSDK (formerly GSDK)/srcfolder.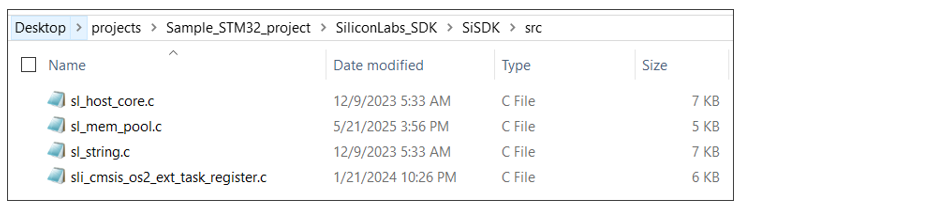

Ensure to include compiler-specific CMSIS header file in the C source file created in above step 2. For example, for ARMCC compiler, include "cmsis_armcc.h", for GCC compiler, include "cmsis_gcc.h" etc.
CORE_EnterAtomic#
Prototype#
CORE_irqState_t CORE_EnterAtomic(void);
Description#
This function disables global interrupts to ensure the specific code executes atomically, without interruption from ISRs. It returns the previous interrupt state, allowing safe restoration later.
Parameters#
None.
Return values#
CORE_irqState_t - The saved interrupt state, indicating whether interrupts were enabled before entering the atomic section.
Note: The CORE_irqState_t is defined in sl_core.h file of SiSDK (formerly GSDK).
Examples#
EFR32: Refer here for the definition of function.
STM32:
CORE_irqState_t CORE_EnterAtomic(void)
{
CORE_irqState_t irqState = __get_PRIMASK();
__disable_irq();
return irqState;
}CORE_ExitAtomic#
Prototype#
void CORE_ExitAtomic(CORE_irqState_t irqState);
Description#
This function restores the interrupt state saved by CORE_EnterAtomic(). If interrupts were enabled before entering the atomic section, they are re-enabled.
Parameters#
CORE_irqState_t - The interrupt state returned by CORE_EnterAtomic(), used to determine whether interrupts should be re-enabled.
Return values#
None
Examples#
EFR32: Refer here for the definition of function.
STM32:
void CORE_ExitAtomic(CORE_irqState_t irqState)
{
if (irqState == 0) {
__enable_irq();
}
}CORE_EnterCritical#
Prototype#
CORE_irqState_t CORE_EnterCritical(void);
Description#
This function disables global interrupts to prevent preemption while executing time-sensitive or shared-resource code. It returns the previous interrupt state to be restored later using CORE_ExitCritical().
Parameters#
None.
Return values#
CORE_irqState_t - The saved interrupt state before disabling interrupts.
Note: The CORE_irqState_t is defined in sl_core.h file of SiSDK (formerly GSDK).
Examples#
EFR32: Refer here for the definition of function.
STM32:
CORE_irqState_t CORE_EnterCritical(void)
{
CORE_irqState_t irqState = __get_PRIMASK();
__disable_irq();
return irqState;
}CORE_ExitCritical#
Prototype#
void CORE_ExitCritical(CORE_irqState_t irqState)
Description#
This function re-enables global interrupts only if they were enabled prior to entering the critical section, using the saved interrupt state from CORE_EnterCritical().
Parameters#
CORE_irqState_t - The interrupt state returned by CORE_EnterCritical(), the saved interupt state.
Return values#
None
Examples#
EFR32: Refer here for the definition of function.
STM32:
void CORE_ExitCritical(CORE_irqState_t irqState)
{
if (irqState == 0) {
__enable_irq();
}
}
Add Code from WiSeConnect SDK v3.x#
It is not required to add all the files and folders present in the SDK v3.x to your project. The SDK v3.x contains the SiWx917 features such as Wi-Fi, BLE, application layer protocols etc., and their implementations organized into components. This benefits the user to add only the required files and folders associated with the respective feature from the components folder to their host MCU application project.
The following figure shows the hierarchy of files and folders present in the components and resources folders of SDK v3.x.
The entities (component/c source file/header file/folder) that are marked Mandatory must be added to your application project.
The entities that are marked Optional can be added based on the features your application requires. For example, if your application requires HTTP Client functionality, add the
http_clientfolder from/components/serviceto your application project.The entities that are marked Options imply that any of the available options (marked in red) can be chosen while adding Mandatory or Optional entities. For example, the memory configuration used by SDK v3.x can be static, malloc (dynamic memory allocation), lwip buffers, memory pool buffers, and memory pool buffer quota. lwip buffers can be used only when using LWIP network stack.
The entities that are marked Not required need not be added. The
board,console,console_autogen,segger_sysview, andsi91x_supportfolders are related to SiWx917 SoC and Simplicity Studio IDE. These need not be added if you are using a non-silicon Labs host MCU and IDE.The
socketcomponent present atcomponents/device/silabs/si91x/wirelessis mandatory when your application needs socket-based data transfers.The resources folder contains the default values required by the network_management component.
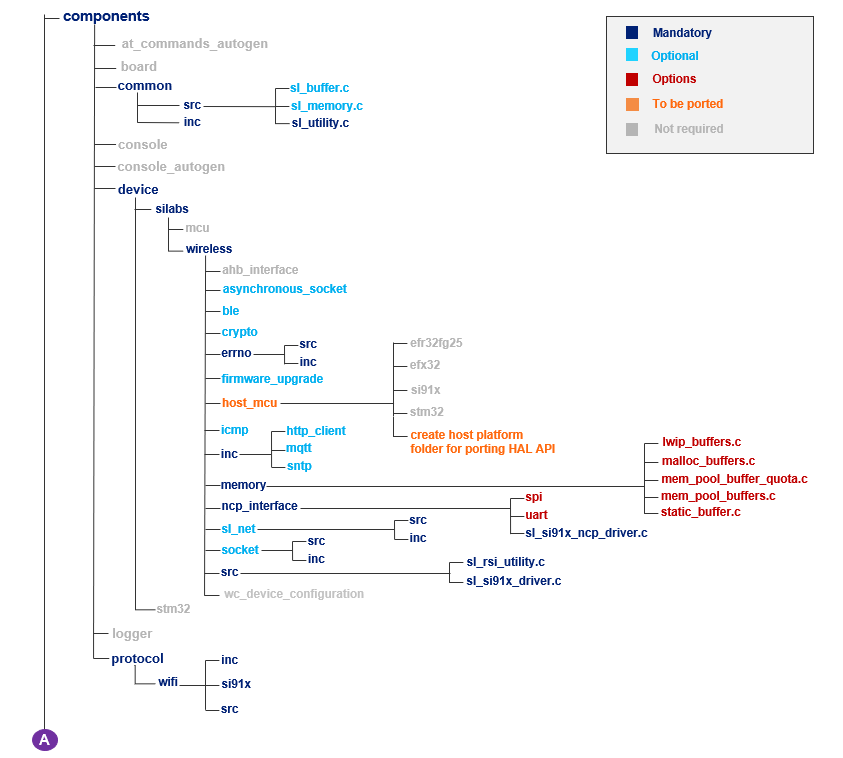

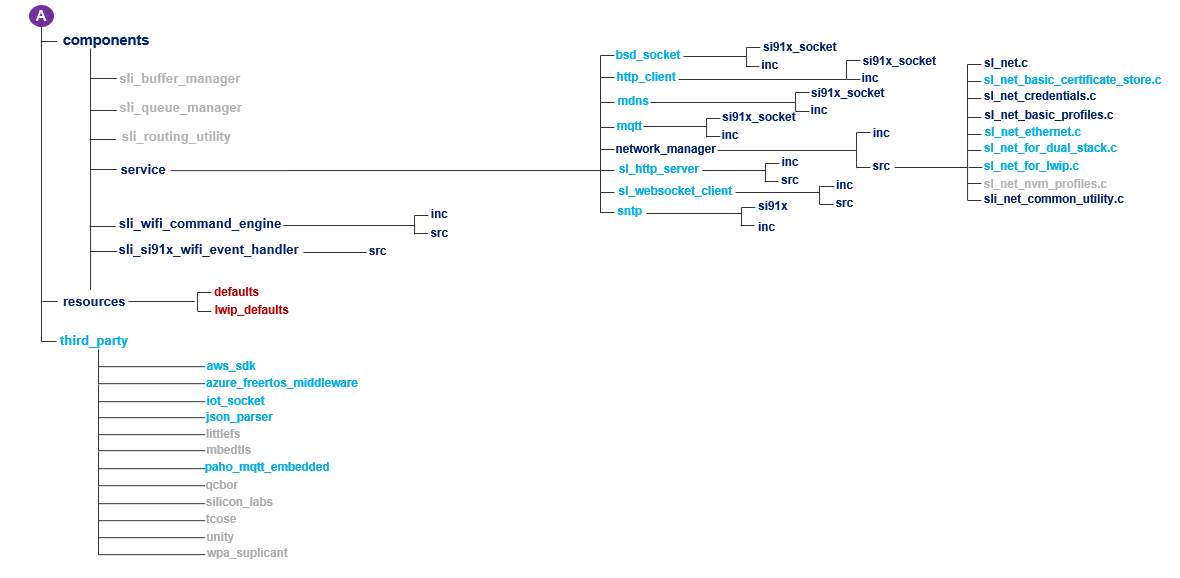

The files and folders that are to be added entirely depends on the application requirements. For instance, consider a typical example application where the SiWx917 as a Wi-Fi client must connect to a Wi-Fi network, send application data to a TCP Server and then should be set in connected sleep mode. This SiWx917 application requires the wifi and asynchronous_socketor socketor bsd_socket components. In this case, let us choose the bsd_socket component. At this point, add the complete folders or only those required as per your choice.
NOTE: Ensure the "malloc" is made thread safe in your project. For more details, refer to malloc_thread_safety.c file at path:
<SDK>\components\device\silabs\si91x\mcu\core\common\src.
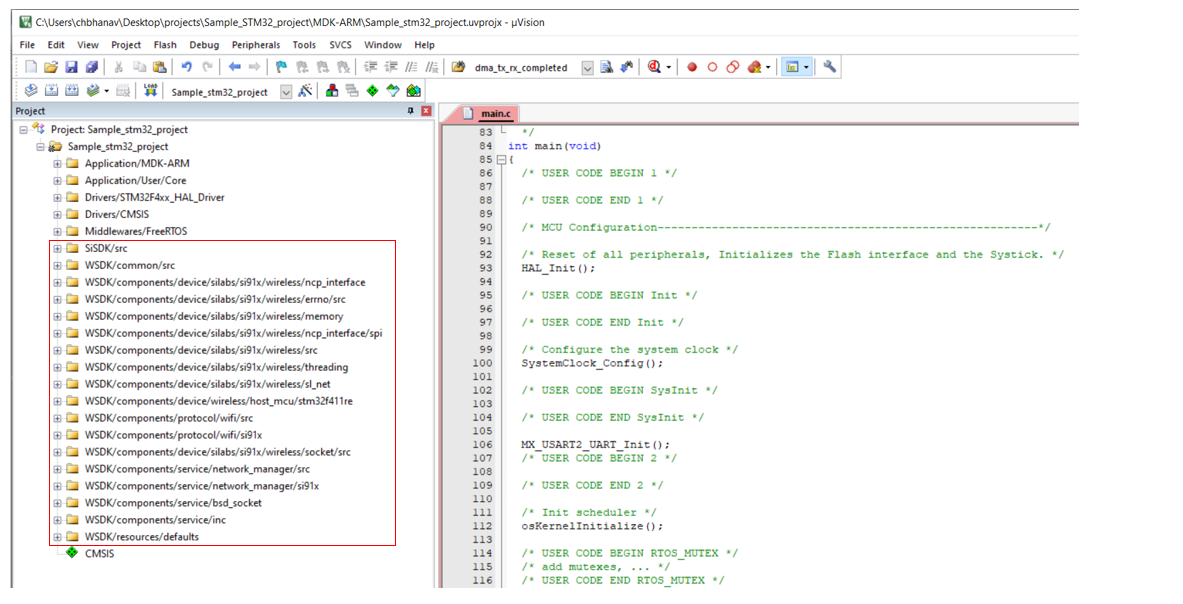
For STM32 project, copy the required entities from the components and resources folders to the WSDK directory. From the components folder, add the required files/folders from the common, device, protocol, and service entities.



Configure the Project#
Import the project into the IDE.
For STM32, the Sample_STM32_project is imported into Keil µVision IDE. For MDK-ARM tool chain, it is mandatory to enable the preprocessor symbol: “__Keil”.
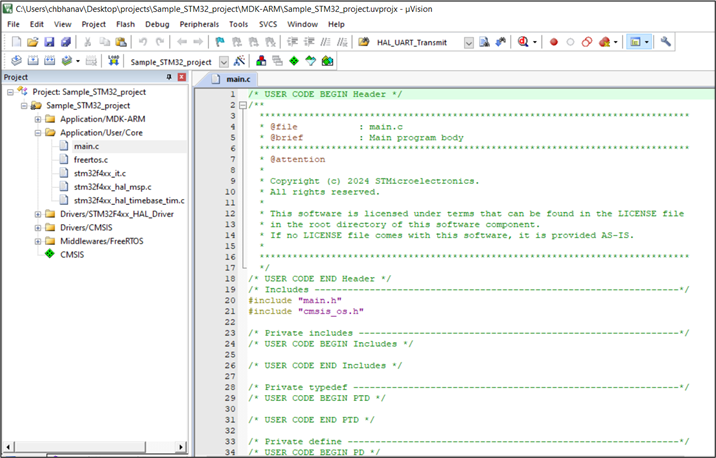

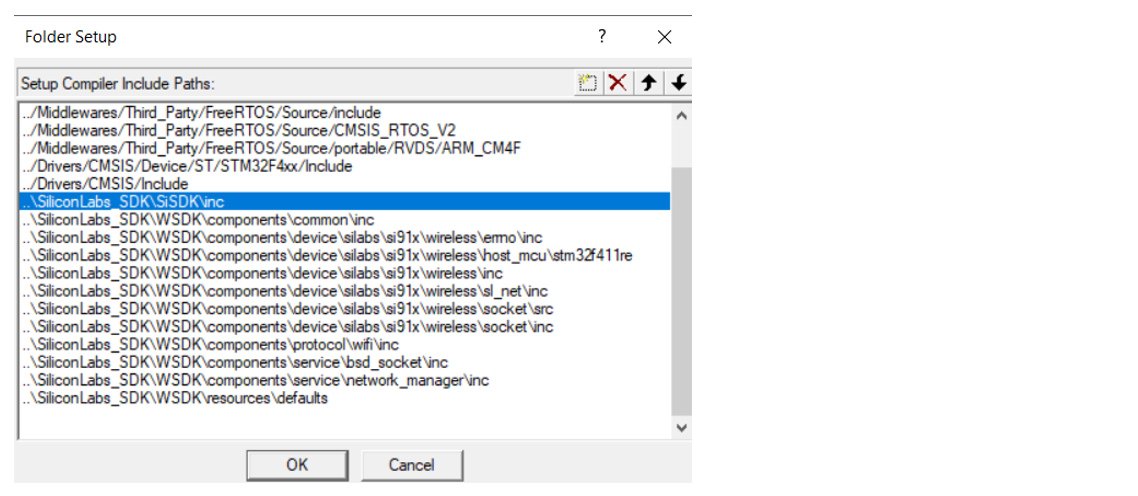
Add the required files and folders from SiSDK (formerly GSDK) and SDK v3.x to your application project. Organize the files and folders as per SDK v3.x structure. Ensure to include the respective header files present in the mandatory folders.
For STM32 project, the required files and folders are added to the project as shown below: