Little File System (LittleFS) Architecture#
The Little File System (LittleFS) is a lightweight, fault-tolerant file system optimized for embedded systems with limited flash memory and processing resources. It provides data reliability, wear leveling, and power-loss recovery, making it a robust choice for persistent storage on SiWx917 and similar devices.
High-Level Diagram#
The following diagram shows the LittleFS architecture and its interaction with the underlying flash storage.
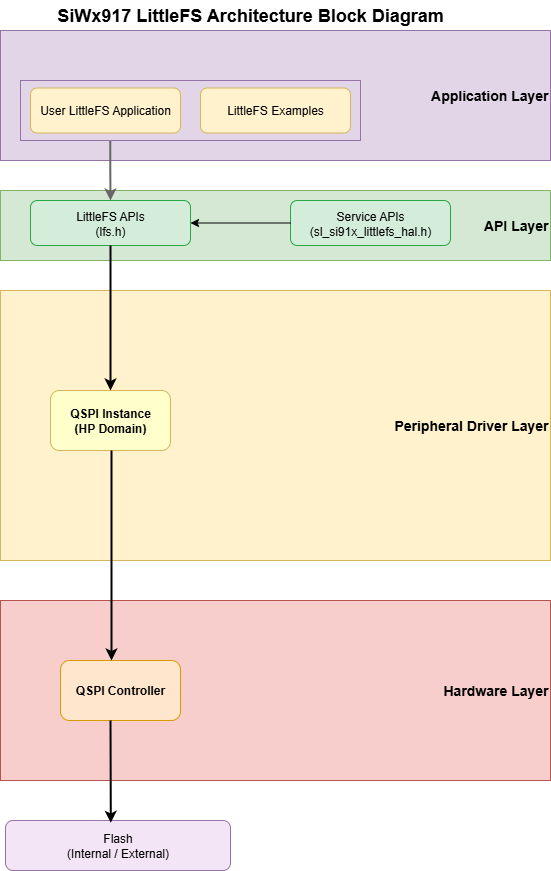

Overview#
LittleFS is designed to make the most efficient use of flash storage while maintaining high reliability.
Its architecture addresses key flash-specific challenges such as limited write endurance, power-failure safety, and bad-block management—all within a small memory footprint.
Key Capabilities#
Reliable storage with atomic updates
Fault tolerance and recovery after unexpected resets or power failures
Dynamic wear leveling to extend flash lifetime
Low RAM and ROM footprint suitable for constrained microcontrollers (MCUs)
General Concepts#
Power-loss resilience:
Uses copy-on-write (COW) and rollback mechanisms to guarantee data integrity.
After a sudden power loss, the system automatically recovers to the last stable state.
Wear leveling
Distributes write and erase cycles evenly across flash memory blocks.
Prevents premature wear-out of specific regions, ensuring long-term durability.
Small footprint
Optimized for minimal RAM and ROM use.
Ideal for microcontrollers with limited flash capacity (as low as 64 KB).
Block-based design
Divides the flash storage into fixed-size blocks, which are the primary data management units.
Simplifies memory mapping and improves access consistency.
Copy-on-write (COW)
When modifying data, LittleFS writes updates to a new block instead of overwriting the existing one.
Guarantees atomic operations and eliminates the risk of partial data corruption.
Bad-block detection
Continuously scans for defective flash blocks.
Automatically marks bad blocks as unusable and remaps data accordingly.
Note: LittleFS is an open-source, third-party file system actively maintained by the community.
For in-depth technical information, visit the LittleFS GitHub repository.
Core Components#
The LittleFS stack consists of key components that work together to manage file operations, memory access, and system consistency.
Block-Based Storage
Manages data allocation and organization within logical blocks.
Each block serves as a base unit for reading, writing, and erasing data.
Abstracts flash memory details to ensure portability across different hardware.
Configuration Structure
Defines essential parameters for operation, including:
Block read/write functions
Block and page sizes
Cache and lookahead buffer settings
Typically initialized using the
lfs_configstructure.
State Structure (lfs_t)
Represents the runtime state of the file system.
Developers must allocate and manage this structure to mount and operate multiple LittleFS instances within the same project.
You can add LittleFS to a project through software components (.slcp). For details, see the UC Configuration section.
Directory Structure#
The following directory structure shows how LittleFS integrates into the development environment:
wiseconnect/
├── examples/
│ └── si91x_soc/
│ └── service/
│ └── sl_si91x_littlefs_common_flash
├── third_party/
│ └── littlefs/
│ ├── inc/
│ │ └── lfs.h
│ └── src/
│ └── lfs.cDependencies#
LittleFS depends on several software and hardware components to function correctly in embedded projects:
WiSeConnect Software Development Kit (SDK): Must be installed and configured in Simplicity Studio.
Simplicity Studio Configuration: Provides integration and management of project components.
Universal Configurator (UC): Used to set operational parameters for LittleFS.
Clock Source and Divider Settings: Managed through the microcontroller (MCU) clock architecture for Quad Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI).
QSPI Controller: Provides high-speed communication with external flash memory.
Non-Volatile Memory (Flash): Serves as the underlying storage medium for the file system.
