Secure Firmware Update#
In case of Bootloader and OTA based firmware update mechanisms, a secure firmware update can be done by enabling the security in the firmware image using the Manufacturing Utility (Refer to the UG574: SiWx917 SoC Manufacturing Utility User Guide). The process of firmware update remains the same for Non-Secure and Secure Firmware updates, except that in the case of secure firmware image, the integrity checks are done.
The following flowchart shows the secure firmware update process.
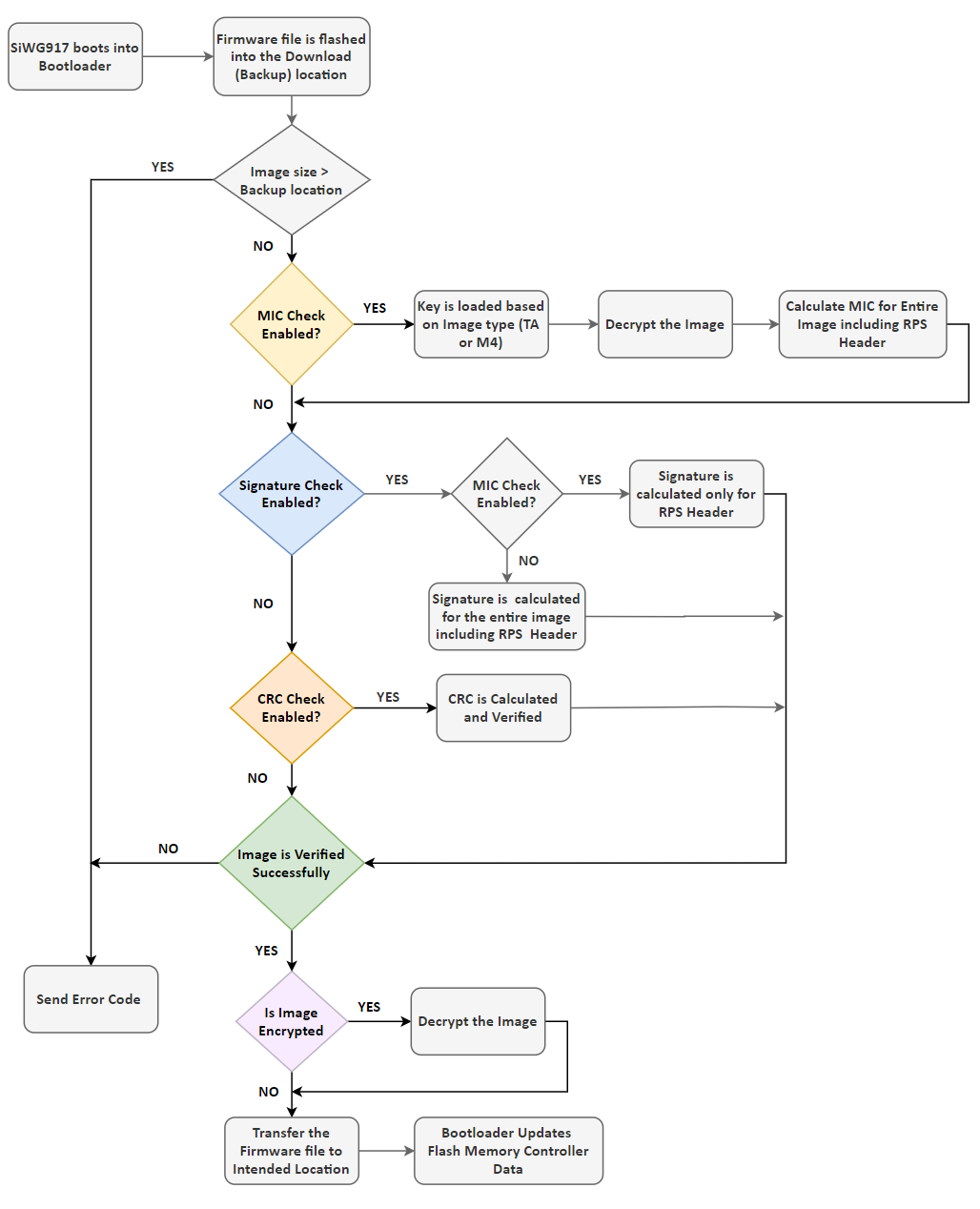

The firmware image for both NWP and M4 supports the following:
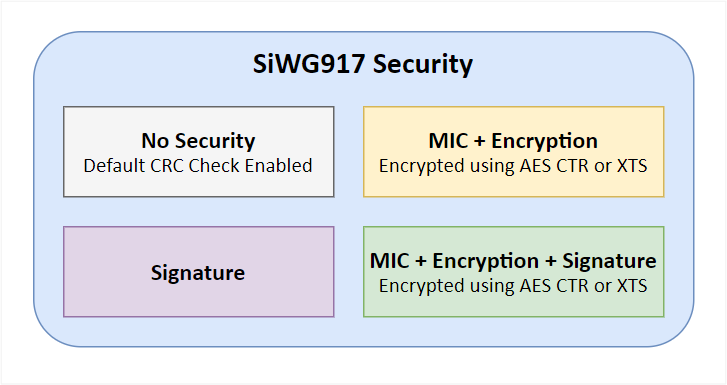

No Security: Default CRC of the image within the RPS header.
MIC + Encryption: The MIC is calculated for the whole plain image and saved within the RPS header. The image is encrypted and appended to the RPS header. The image can be encrypted using AES CTR or XTS mode.
Signature: The size of the image in the RPS header is incremented by the size of the signature. Finally, the whole RPS file's (RPS Header+ image) signature is calculated and appended to the end of the file.
MIC + Encryption + Signature: The MIC is calculated for the whole plain image and saved within the RPS header. The image is encrypted and appended to the RPS header. The image can be encrypted using AES CTR or XTS mode. The size of the image in the RPS header is incremented by the size of the signature. Finally, the whole RPS file's (RPS Header + image) signature is calculated and appended to the end of the file.
In each mode, the Control Flag of the RPS Header is updated with the correct configuration.
Flash Memory Controller#
The Bootloader has a reserved space in flash where it saves the details of the current firmware. These details are saved when a new valid firmware saved in the flash. This data includes the start address in the flash where the valid firmware is available, as well as the firmware's size, CRC and MIC value of the firmware, security flags, and the image's version number.
We have 2 FMCs for NWP and M4 separately. The FMCs are located in the flash and have flash protection, so they don't get corrupted. The FMC data itself is protected with CRC and MIC validation. Each time the FMC is modified after a new image is updated, the FMC is saved in a backup location and then the original location is updated to avoid any issues arising from the FMC getting corrupted while modifying it or a power down happening during the FMC modification process.
If there is a power outage during the copying of firmware from the backup (downloaded) location to the primary (target) location, the SiWG917 will restart the backup process from the beginning when you power up the device next time. It will not resume from where it left off. This behavior is the same for both NWP and M4. In the event of a power outage, the NWP FMC will retain the existing firmware start address. The NWP FMC is updated with the new firmware details only after the firmware update is fully completed.
