Transmission#
Initialization#
To ensure the host and the Z-Wave module are in sync at application startup, the host should begin an initialization sequence. The initialization sequence is different depending on whether the host has access to a module hard reset.
With Hard Reset#
Close host serial port if it is open.
Assert module reset.
Open the host serial port at 115200 baud 8N1.
Release module reset.
Wait 500 ms.
Without Hard Reset#
Close host serial port if it is open.
Open the host serial port at 115200 baud 8N1.
Send the NAK.
Send Serial API command: FUNC_ID_SERIAL_API_SOFT_RESET.
Wait 1.5 s.
This solution is not recommended because it relies on retrieval and execution of the Serial API command FUNC_ID_SERIAL_API_SOFT_RESET.
Frame Timing#
Data Frame Reception Timeout#
A receiving host or Z-Wave chip MUST abort reception of a Data frame if the reception has lasted for more than 1500 ms after the reception of the SOF byte. A host or Z-Wave chip MUST NOT issue a NAK frame after aborting the reception of a Data frame.
Data Frame Delivery Timeout#
A host or Z-Wave chip MUST wait for an ACK frame after transmitting a Data frame. The receiver may be waiting for up to 1500 ms for the remains of a corrupted frame. Therefore, the transmitter MUST wait for at least 1600 ms before deeming the Data frame lost.
The loss of a Data frame MUST be treated as the reception of a NAK frame. The transmitter MAY compensate for the 1600 ms already elapsed when calculating the retransmission waiting period.
Retransmission#
A transmitter may time out waiting for an ACK frame after transmitting a Data frame or it may receive a NAK or a CAN frame. In either case, the transmitter SHOULD retransmit the Data frame. A waiting period MUST be applied before the retransmission.
The waiting period MUST be calculated per the following formula:
Where:
n is incremented at each retransmission.
n=0 is used for the first waiting period.
A host or Z-Wave chip MUST NOT carry out more than three retransmissions. Note that a host MAY choose to do a hard reset of the Z-Wave module if it is not able to successfully deliver the frame after three retransmissions. Flush/reopen the serial port after the three retransmissions.
Exception Handling#
Unresponsive Z-Wave Module#
In the unlikely event that the Z-Wave module becomes unresponsive for more than 4 seconds, it is RECOMMENDED to issue a hard reset of the module. A module may be deemed unresponsive if it has not responded with any character after three consecutive frame retransmissions, each with a 1600 ms interval. See Initialization.
Persistent CRC Errors#
If a host application detects an invalid checksum three times in a row when receiving data frames, the host application SHOULD invoke a hard reset of the device. If a hard reset line is not available, a soft reset indication SHOULD be issued for the device.
Missing Callbacks#
In some situations, a serial API callback may be lost due to an overflow in the UART transmit buffer. This condition may occur if a lot of unsolicited traffic comes in from the Z-Wave side. For this reason, a Serial API-based host application SHOULD guard all its callbacks with a timer. The timer values are given in references [3] for each of the Z-Wave API functions which use callbacks.
Frame Flow#
The frame flow between a host and a Z-Wave module (ZW) running the Serial API embedded sample code depends on the API call. There are two classes of communication between a host and a Z-Wave chip: Unsolicited and Request/Response. Each of the classes is presented below.
Unsolicited Frame Flow#
The most basic frame flow is a Request (REQ) Data frame that is acknowledged by an ACK frame.
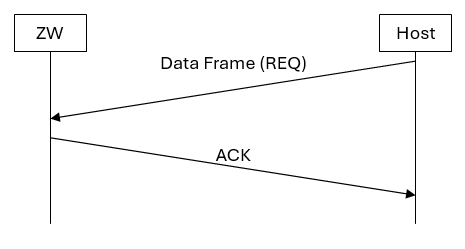

API call ZW_SetExtIntLevel is an example of the frame flow outlined in the figure above.
A variant of the REQ Data frame flow is a request (REQ) Data frame in one direction followed by a request (REQ) Data frame in the opposite direction. The first Data frame is acknowledged before a Data frame is transmitted in the opposite direction.
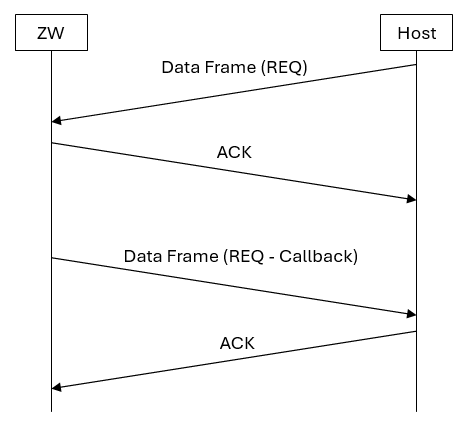

Typically, the REQ Data frame in the opposite direction follows after some time.
The API call ZW_SetDefault is an example of the frame flow outlined in the figure above, where the second Data frame is carrying a callback message indicating the completion of the operation.
Request/Response Frame Flow#
A Request (REQ) Data frame may be followed by a Result (RES) Data frame within a few second interval. This flow is used for all functions which have a non-void return value. Note that, due to the simple nature of the simple acknowledge mechanism, only one REQ->RES session is allowed.
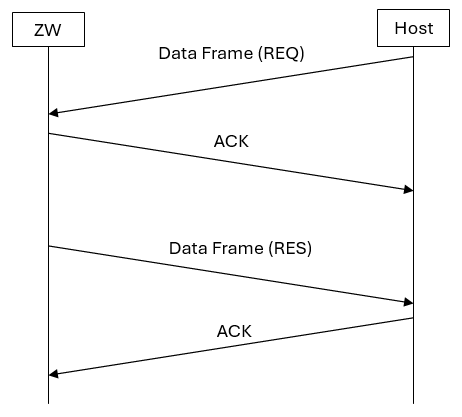

The API call ZW_GetControllerCapabilities is an example of the frame flow outlined in the figure above, where the Result Data frame is carrying the requested controller capabilities.
A variant of the Request/Response Data frame involves an unsolicited Data frame following the Request/Response Data frame pair. Typically, the REQ Data frame in the opposite direction follows after some time.
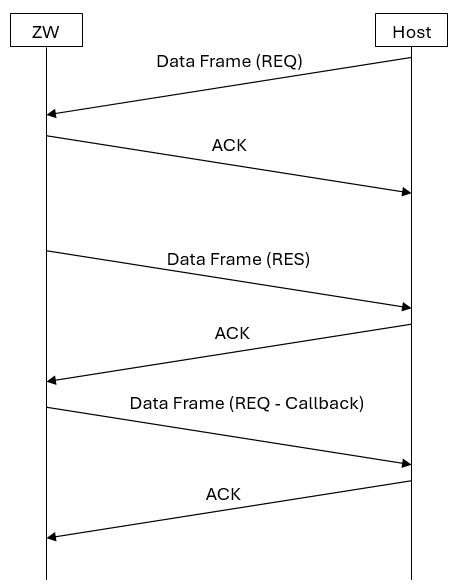

The API call ZW_SendSUCID is an example of the frame flow outlined in the figure above, where the Result Data frame is carrying the requested controller capabilities and the second Data frame is carrying a callback message indicating the completion of the operation.
If a host application repeatedly receives a reception timeout error indication rather than a valid response Data frame, the host application SHOULD invoke a hard reset of the device. If a hard reset line is not available, a soft reset indication SHOULD be issued for the device.
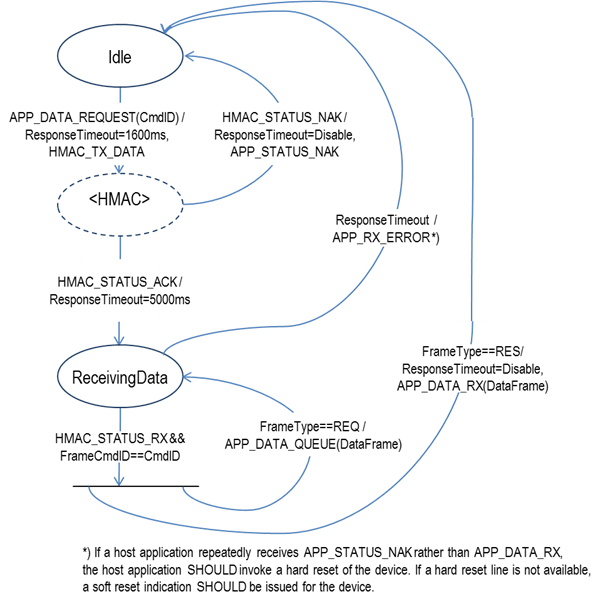
State Diagrams#
This section outlines a transmission and reception of Control and Data frames.
Host Data Frame Reception#
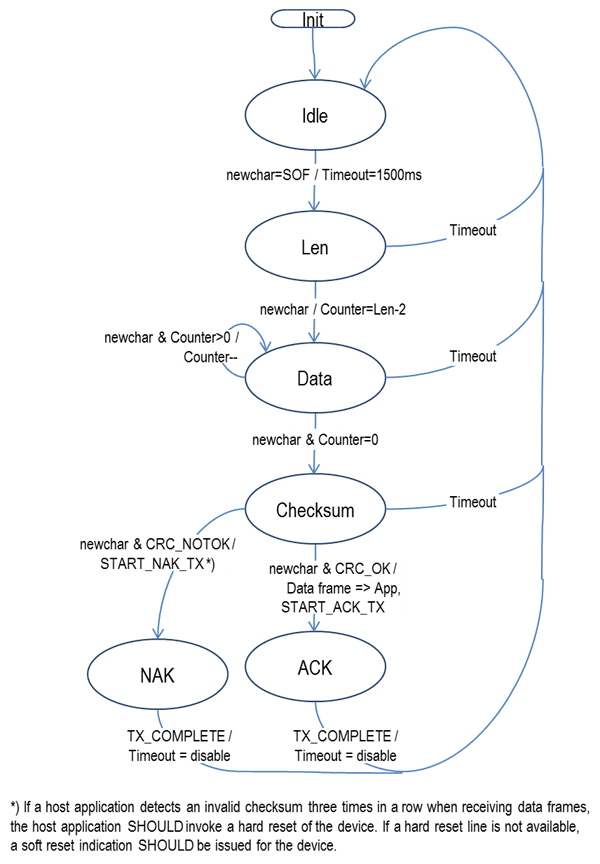

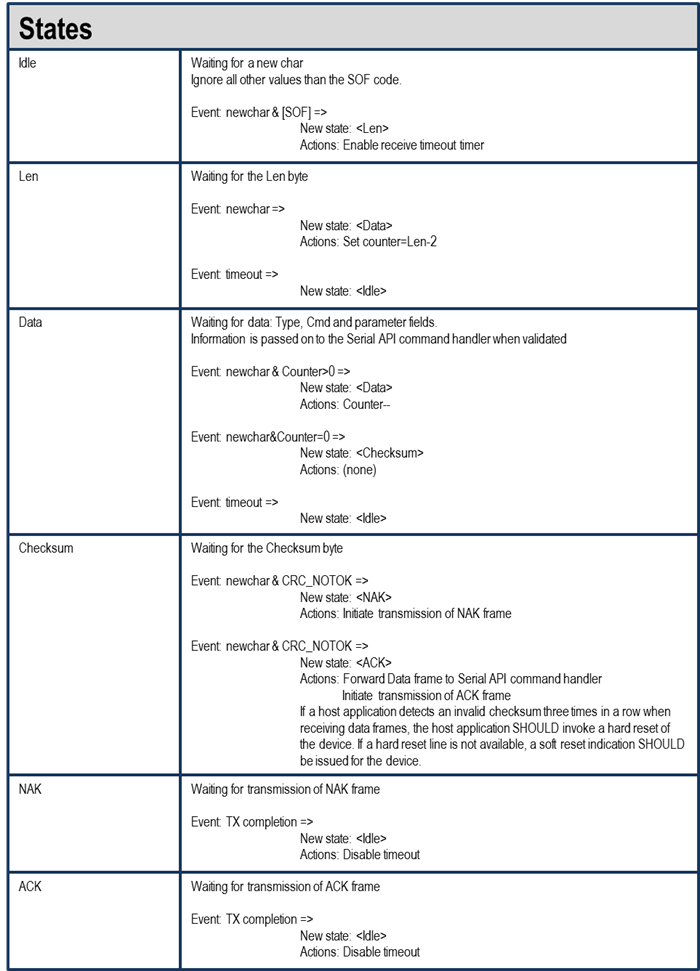

Counter Maintenance#
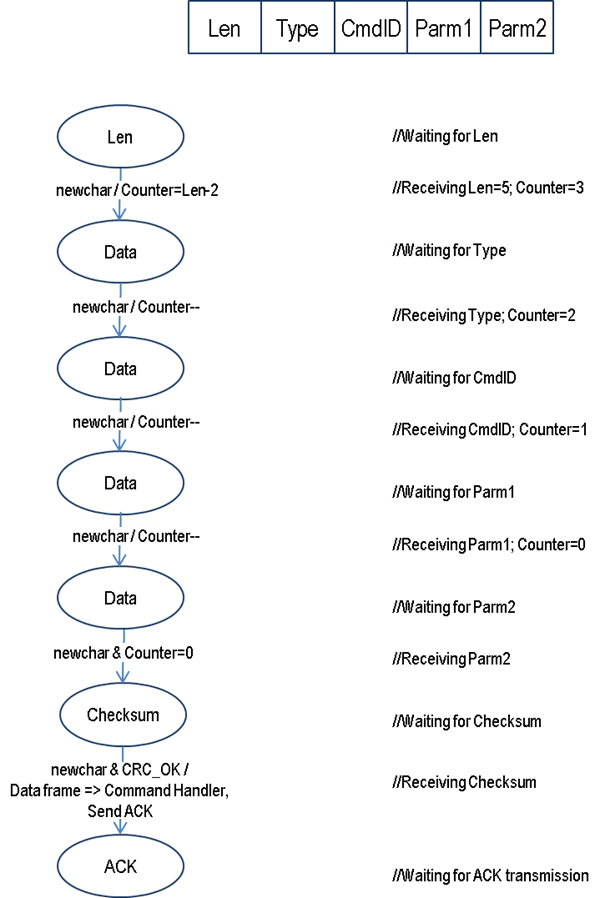

Host Media Access Control#
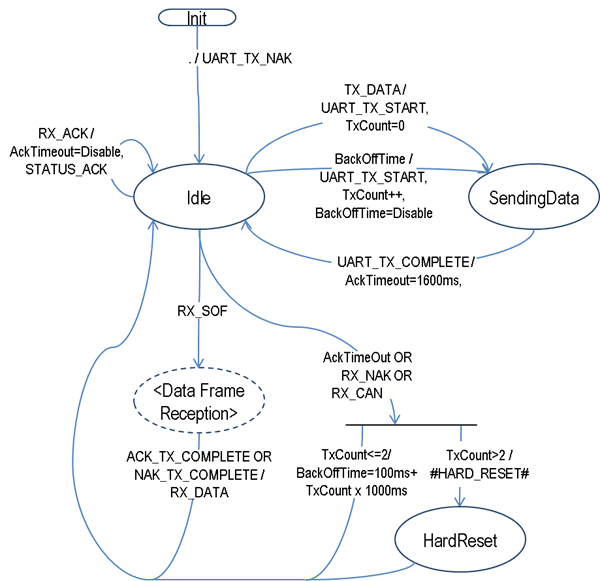

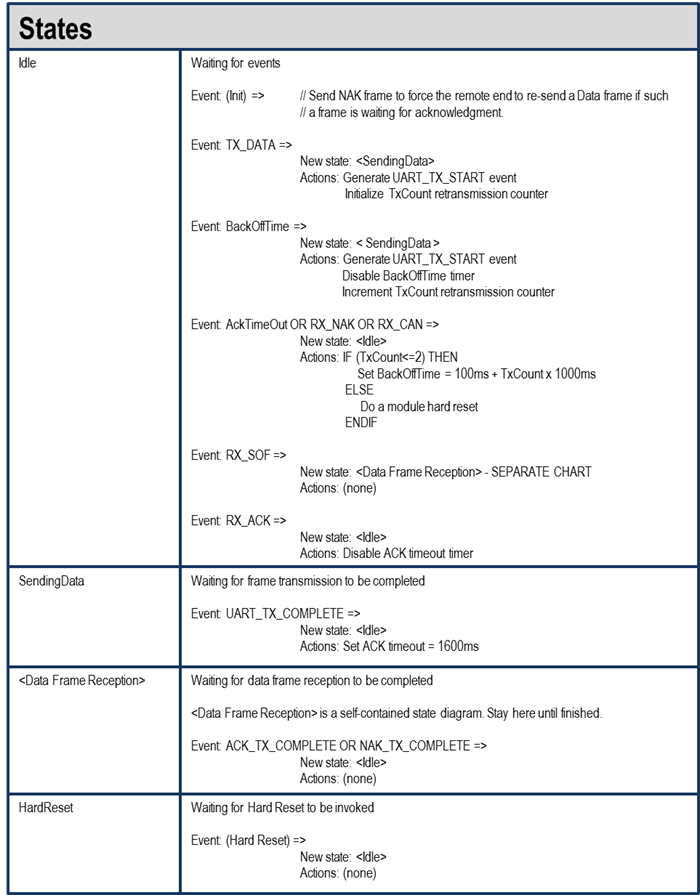

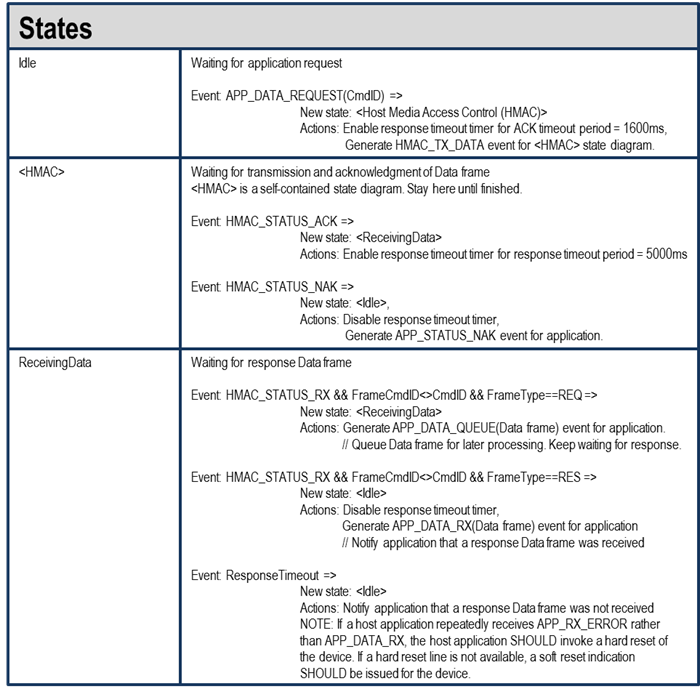
Host Request/Response Session#