Secure Identification on HSE-SVH Devices#
The goal of secure identification is to prove the ownership of a device's unique public key to an external service. It enables the external service to identify the device as legitimate and to authenticate device-generated data or messages.
Chain of Trust#
The chain of trust on HSE-SVH devices is illustrated in the following figure.
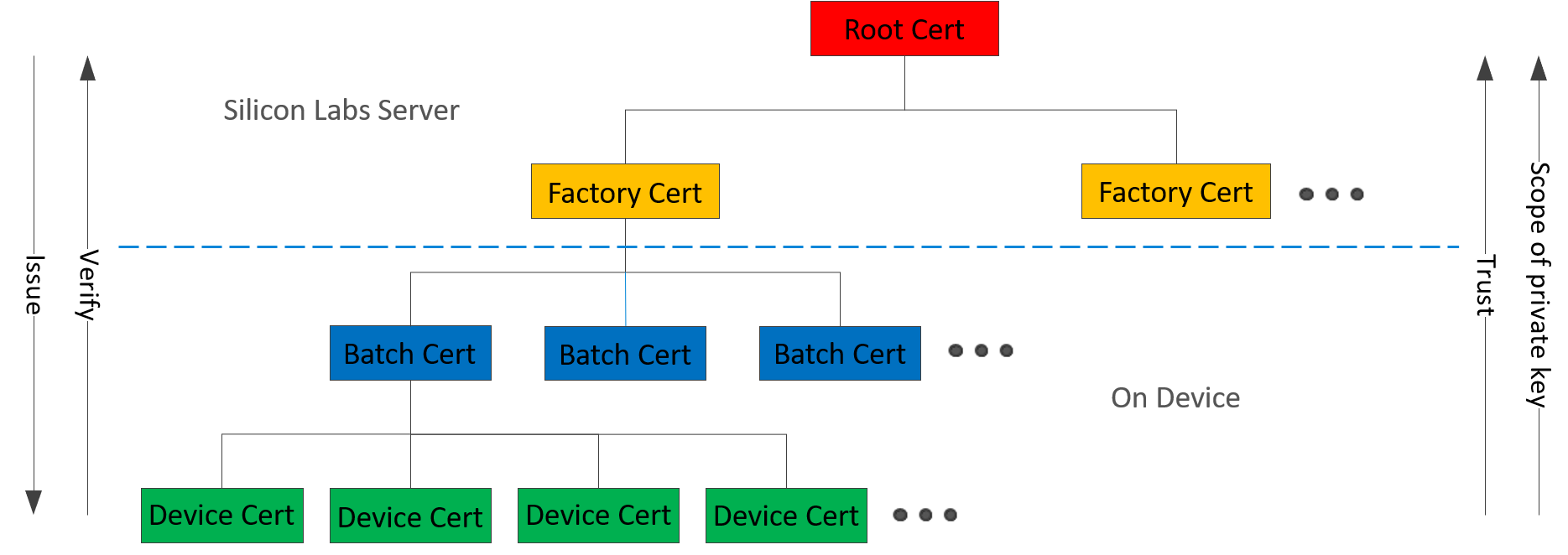

Silicon Labs is a Certificate Authority (CA).
The root certificate and factory certificate are stored in the Silicon Labs Server.
The factory certificate is static per factory.
The batch certificate and device certificate are stored on the device.
The batch certificate is rolled per production batch.
The device certificate is a unique cryptographic identity.
All certificates are X.509 standard format.
TLS-compliant: Standard endpoint authentication methods are used in internet communications
Signature algorithm: ECDSA-prime256v1 with SHA256
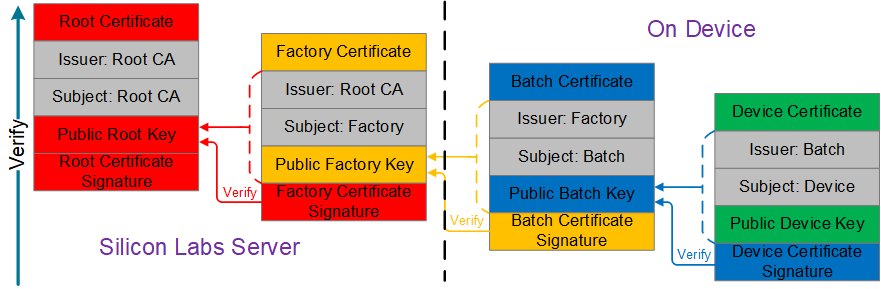
Each certificate in the chain is signed by the certificate above it (Signing and Verification figure).
Note: A certificate can be revoked if needed, for instance if security issues arise. The certificate revocation lists are stored in the Silicon Labs Server.
Device Certificate#
The device certificate example is described in the following figure.


The device certificate is in X.509 DER format (~0.5 kB).
The device certificate is stored in HSE one-time programmable memory (OTP). It cannot be modified once programmed.
The batch number (
Issuer: CN = Batchfield) identifies the factory and batch in which the device was produced.The validity period is 100 years from device manufacture date.
The device 64-bit hard-coded unique ID (EUI) is encoded in the
Subject: CNfield, which blinds this certificate to the device.The device-specific public key is embedded in the device certificate and the corresponding private key is securely stored in the Secure Key Storage on the chip.
The Issuer's private key is used to sign the hash of the certificate data to create a device certificate signature.
Signing and Verification#
Signing and verification for certificates on HSE-SVH devices are described in the following figures.