System Architecture#
The SOC-Empty example application with Micrium RTOS or FreeRTOS support requires several tasks in order to operate
Link Layer Task
Bluetooth Host Task
Event Handler Task
Idle Task
Silicon Labs has implemented these tasks for the Micrium RTOS and FreeRTOS.
Note that there are ready-made examples for the following:
Bluetooth – SoC Empty (bare metal)
Bluetooth – SoC Empty FreeRTOS
Bluetooth – SoC Empty Micrium OS
Since Simplicity SDK 2024.12, these are also available for Bluetooth mesh:
Bluetooth Mesh – SoC Empty (bare metal)
Bluetooth Mesh – Soc Empty FreeRTOS
Bluetooth Mesh – Soc Empty Micrium OS
Inter-Task Communication#
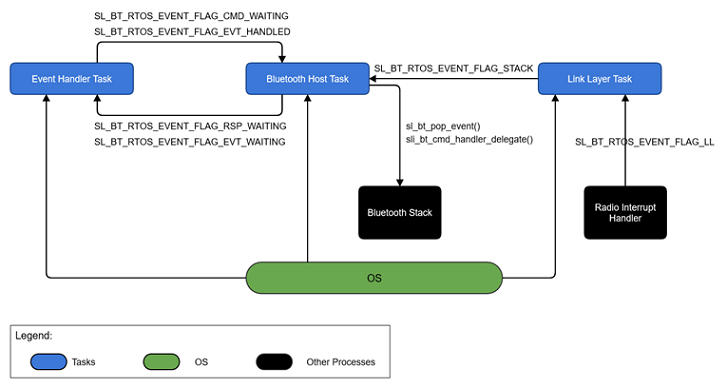
Before describing the tasks, it is important to understand how the tasks communicate with each other. The tasks in this application synchronize with each other through the use of a number of flags. The flags are internal of the sl_bt_rtos_adaptation layer. These flags are summarized in the following table:
FLAG | Sender | Receiver | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_STACK | Link Layer Task | Bluetooth Host Task | Bluetooth stack needs an update, call sl_bt_pop_event() |
SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_LL | Radio Interrupt | Link Layer Task | Link Layer needs an update, call sl_bt_priority_handle() |
SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_CMD_WAITING | Event Handler and Application Tasks | Bluetooth Host Task | Command is ready in shared memory, call sli_bt_cmd_handler_delegate() |
SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_RSP_WAITING | Bluetooth Host Task | Event Handler and Application Tasks | Response is ready in shared memory. |
SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_EVT_WAITING | Bluetooth Host Task | Event Handler Task | Event is ready in shared memory. |
SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_EVT_HANDLED | Event Handler Task | Bluetooth Host Task | Event is handled and shared memory is free to use for next event. |
The following diagram illustrates how these flags are used in synchronizing the tasks.
In addition to these flags, a mutex is used by the gecko command handler to make it thread-safe. This makes it possible to call BGAPI commands from multiple tasks.

Link Layer Task#
The purpose of this task is to update the upper link layer. The link layer task waits for the SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_LL flag to be set before running. The upper link layer is updated by calling sl_bt_priority_handle(). The SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_LL flag is set by sli_bt_rtos_ll_callback(), which is a callback function specified to scheduler_callback in the stack configuration. The callback is called from a kernel-aware interrupt handler (lower link layer). This task is given the highest priority.
Bluetooth Host Task#
The purpose of this task is to update the Bluetooth stack, issue events, and handle commands. This task waits for any of the SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_STACK, SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_CMD_WAITING and SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_EVT_HANDLED flags to be set before running. The SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_STACK flag is set by sli_bt_rtos_stack_callback(), which is a callback function specified to stack_schedule_callback in the stack configuration. This task has higher priority than the Event Handler Task and any of the Application Tasks, but lower than the Link Layer Task.
Before this task starts running, it prepares the application to run the Bluetooth stack. This task calls sl_bt_init() to initialize and configure the Bluetooth stack, and then calls sl_bt_rtos_create_tasks() to create the Link Layer Task and Event Handler Task.
Updating the Stack#
The Bluetooth stack must be updated periodically. The Bluetooth Host Task updates the stack by calling sl_bt_event_pending() and reads the next stack event from the stack by calling sl_bt_pop_event(). This allows the stack to process messages from the link layer as well as its own internal messages for timed actions that it needs to perform.
Issuing Events#
The Bluetooth Host Task sets the SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_EVT_WAITING flag to indicate to the event handler task that an event is ready to be retrieved. Only one event can be retrieved at a time. The SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_EVT_WAITING flag is cleared by the Event Handler Task when it has retrieved the event. The SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_EVT_HANDLED flag is set by the Event Handler Task to indicate that event handling is complete.
Command Handling#
Commands can be sent to the stack from multiple tasks. Responses to these commands are forwarded to the calling task. Commands and responses are synchronized with the SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_CMD_WAITING and SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_RSP_WAITING flags and the BluetoothMutex mutex.
Commands are prepared and sent to the stack by a helper function called sli_bt_cmd_handler_rtos_delegate(). This function is called by any of the BGAPI functions and is made re-entrant through the use of a mutex. The function starts by pending on the mutex. When it gains control of the mutex the command is prepared and placed into shared memory, then the SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_CMD_WAITING flag is set to indicate to the stack that a command is waiting to be handled. This flag is cleared by the Bluetooth Host Task to indicate that the command has been sent to the stack and that it is now safe to send another command.
Then execution pends on the SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_RSP_WAITING flag, which is set by the Bluetooth Host Task when the command has been executed. This indicates that a response to the command is waiting. Finally, the mutex is released.
The following diagram illustrates how the Bluetooth Host Task operates.
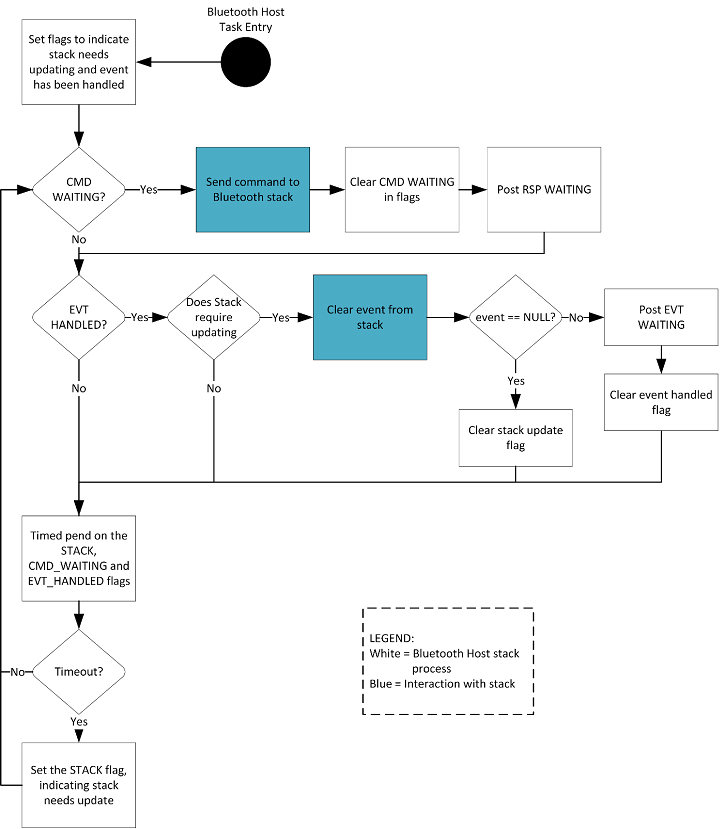

On task startup, the
SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_STACKis set to indicate that the stack needs updating and theSL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_EVT_HANDLEDflag is set to indicate that no event is currently being handled.If the
SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_CMD_WAITINGflag is set,sli_bt_cmd_handler_rtos_delegate()is called to handle the command.If the
SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_STACKand theSL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_EVT_HANDLEDflags are set,sl_bt_pop_event()is called to get an event from the stack. If an event is found waiting, theSL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_EVT_WAITINGflag is set and theSL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_EVT_HANDLEDflag is cleared to indicate to the Event Handler Task that an event is ready to be handled and to the Bluetooth Host Task that an event is currently in the process of being handled. Otherwise, theSL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_STACKflag is cleared to indicate that the stack does not require updating.At this point, the task checks to see if the stack requires updating and whether any events are waiting to be handled. If no events are waiting to be handled and the stack does not need updating then it is safe to sleep and the Bluetooth Host Task does a pend on the
SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_STACK,SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_EVT_HANDLEDandSL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_CMD_WAITINGflags.Steps 2 – 4 are repeated indefinitely.
Event Handler Task#
The purpose of this task is to handle events sent by the Bluetooth stack. This task waits for the SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_EVT_WAITING flag to be set. This flag is set by the Bluetooth Host Task to indicate that there is an event waiting to be handled. Once this flag has been set, sl_bt_process_event() is called to handle the event. Finally, the SL_BT_RTOS_EVENT_FLAG_EVT_HANDLED flag is set to indicate to the Bluetooth Host Task that the event has been handled and the Event Handler Task is ready to handle another event. This task has a lower priority than the Bluetooth Host Task and Link Layer Task.
This task handles the gatt_server_user_write_request event for the user-type OTA control characteristic and boot the device to OTA DFU mode. This task then dispatches events to sl_bt_on_event(), which needs to be integrated in the application.
Idle Task#
When no tasks are ready to run, the OS calls the Idle Task. The Idle Task puts the MCU into lowest available sleep mode, EM2, by default.
