Polymorphic GATT#
Introduction#
Silicon Labs' Bluetooth stack implements a static GATT database structure, which means that services and characteristics are created at compile time, not at run time. As a result, software cannot change the database structure dynamically. To overcome this issue, Bluetooth SDK v2.4 introduces a new feature called Polymorphic GATT, which can be used to dynamically show or hide GATT services and characteristics. This new feature allows users to create a ‘superset’ GATT database with pre-defined hidden/visible services and characteristics and alter their visibility on the fly.
Note: Changing the visibility of services/characteristics should not be done during a connection because that can cause incorrect behavior if Service Change Indication is not enabled. The safest method is to change the visibilities when no devices are connected, or to change the visibilities after making sure that Service Change Indication was enabled on the connection.
How it Works#
The visibility of services and characteristics is controlled through the use of GATT capabilities. The usage of capabilities and their syntax in the GATT XML file is fully described in UG118: Blue Gecko Bluetooth Profile Toolkit Developer's Guide, specifically in sections 2.3, 2.4.1 and 2.5.1 with a usage example in section 2.6. Read through these sections to get a good grasp of the visibility and inheritance rules.
To summarize, each service/characteristic can declare a number of capabilities and the state of the capabilities (enable/disable) determines the visibility of those services/characteristics as a bit-wise OR operation e.g., the service/characteristic is visible when at least one of its capabilities is enabled and it is not visible when all of its capabilities are disabled.
Note: If certain services/characteristics are meant to be always visible, one good approach is to have one capability that is declared by those services/characteristics which is enabled by default and untouched by the application code.
Setting up Capabilities with GATT Configurator#
Bluetooth SDK's GATT Configurator supports the polymorphic GATT database and it allows declaring capabilities for the whole GATT database as well as subsets for each of the services and characteristics.
Always start by declaring the GATT-level capabilities and define their default value by selecting "Custom BLE GATT" and adding the capabilities in "Capability declaration". To add a capability, press the '+' on the right-hand side and then change the capability name and default value.
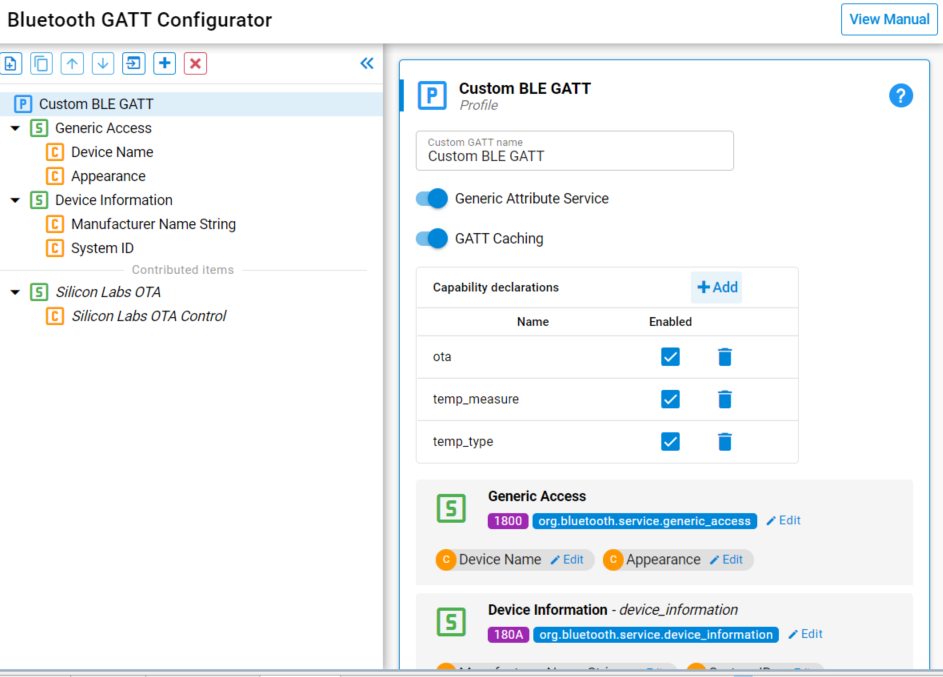

After those capabilities are added, they become available on each of the services and characteristics. They can be added through the drop-down list but this time you'll be shown the list of capabilities declared at the GATT-level where to pick from.
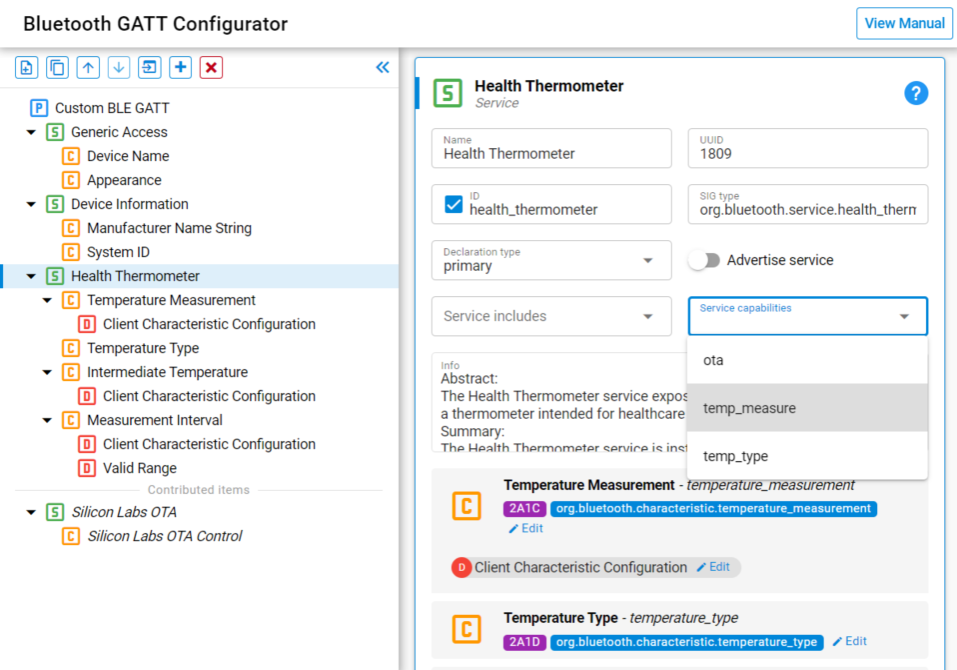

Enabling/Disabling Capabilities#
Capabilities can be enabled/disabled with the API command sl_bt_gatt_server_set_capabilities (caps, reserved) where caps is the bit flags of each capability which should be set to 1 if the capability is to be enabled or 0 if it's to be disabled.
The auto-generated gatt_db.h contains the bit flag value for each of the capabilities you defined in the GATT Configurator, e.g.,:
typedef enum
{
ota = 0x0001,
temp_measure = 0x0002,
temp_type = 0x0004,
interm_temp = 0x0008,
meas_interv = 0x0010,
bg_gattdb_data_all_caps = 0x001f
} bg_gattdb_data_cap_t;To enable ota and temp_type and disable all other capabilities, use the command call that looks like this:
sl_bt_gatt_server_set_capabilities (ota | temp_type, 0);Service Change Indications#
The stack monitors the local database change status and manages the service change indications for a GATT client that has enabled the indication configuration of the Service Changed characteristic. The Service Changed characteristic is part of the Generic Attribute service, which can be added to the GATT by ticking the Generic Attribute Service check box in the GATT Configurator (it can be found after selecting Custom BLE GATT in the GATT database). For more information, see Service Change Indication.
