Migration Guide#
System Requirements and Document#
Simplicity Studio 5
GSDK v3.1.1 (Mbed TLS v2.24.0) or later
The latest SE Firmware image and release note can be found in the Windows folder below.
For GSDK v3.1.x and v3.2.x:
C:\SiliconLabs\SimplicityStudio\v5\developer\sdks\gecko_sdk_suite\<GSDK VERSION\>\util\se_release\publicFor GSDK v4.0.0 and higher:
C:\Users\<PC USER NAME\>\SimplicityStudio\SDKs\gecko_sdk\util\se_release\public
PSA Crypto API (aka PSA Cryptography API) document: ARM
Mbed TLS Versus PSA Crypto API#
| Item | Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto API |
|---|---|---|
Key input |
APIs take key input directly. |
• APIs do not take key input directly. |
Symmetric cryptographic operation |
Individual API (one-shot and streaming) for algorithm-specific functions. |
• APIs are grouped by algorithm category for one-shot and streaming modes. |
|
Except for AEAD (encrypt and decrypt), a one-shot function is not in a pair. |
Single-part (one-shot) functions are in a pair. For example, compute and verify, or encrypt and decrypt. |
|
|
Initialization and free a context are required. |
Initialization and abort an operation are only required in multi-part (streaming) operations. |
|
Error code |
APIs always return an integer. |
APIs always return |
Migration#
In Key Handling, Symmetric Cryptographic Operation, Asymmetric Cryptographic Operation the following items will be considered when migrating from Mbed TLS to PSA Crypto.
The algorithms that can be used in a cryptographic operation.
The key attributes type and usage flags for specific algorithms in the PSA Crypto.
Security Software Components.
The functions (APIs) for the Mbed TLS and PSA Crypto. For each type of symmetric cryptographic operation, the functions include:
A pair of single-part (one-shot) functions
A series of functions that implement multi-part (streaming) operations
Quick Reference Examples. These examples do not have error checking, but the user should always check the return code (psa_status_t =
PSA_SUCCESSorPSA_ERROR_XXX) from PSA Crypto to determine whether to use the output parameters in the application.
Platform Examples#
Simplicity Studio 5 includes the PSA Crypto platform examples to evaluate the performance on key handling, symmetric and asymmetric cryptographic operations, and X.509 certificate.
Refer to the corresponding
readmefile for details about each PSA Crypto platform example. This file also includes the procedures to create the project and run the example.Unless specified in the example, the PSA Crypto platform examples will use the software fallback feature in Mbed TLS if the cryptography hardware accelerator of the selected device does not support the corresponding ECC key or algorithm.
The figures in the following sections are based on GSDK v4.1.0. These figures may be different on other versions of the GSDK.
Security Software Components#
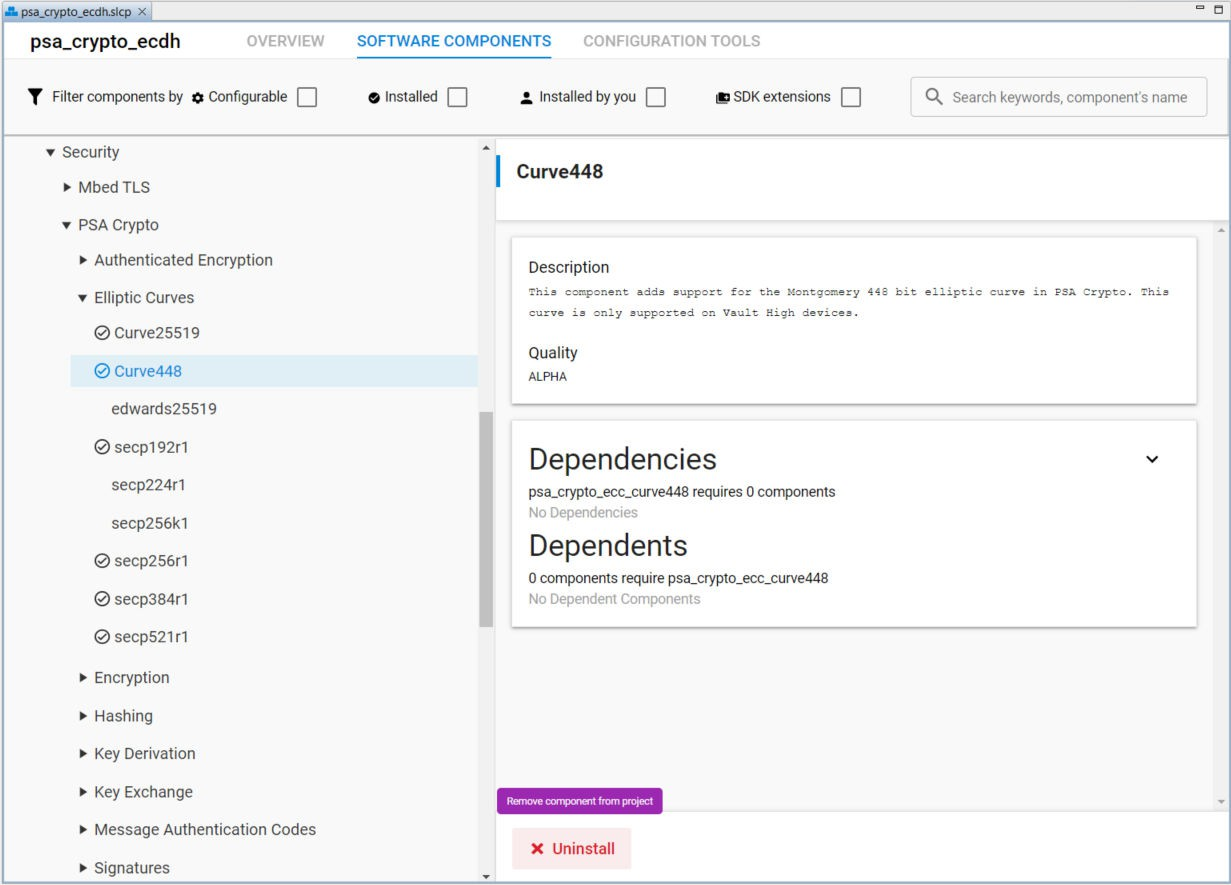
The slcp file for each PSA Crypto platform example defines the software components installed in the project. The following figure shows the installed security software components (under the Platform → Security category) in the PSA Crypto ECDH example (psa_crypto_ecdh.slcp) on an HSE-SVH device.
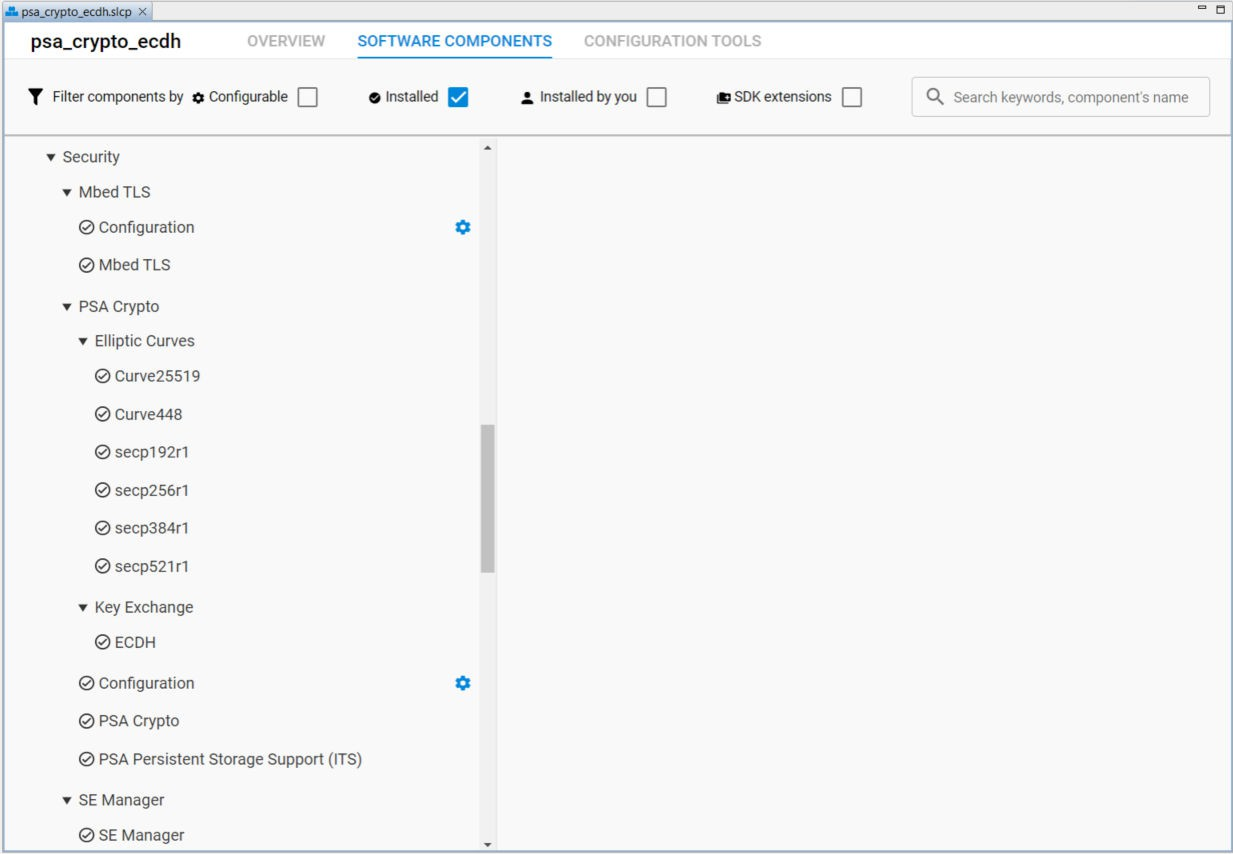

The Simplicity IDE uses the installed security software components to automatically generate the configuration files for Mbed TLS (mbedtls_config_autogen.h) and PSA Crypto (psa_crypto_config_autogen.h) in the autogen folder when creating the project.

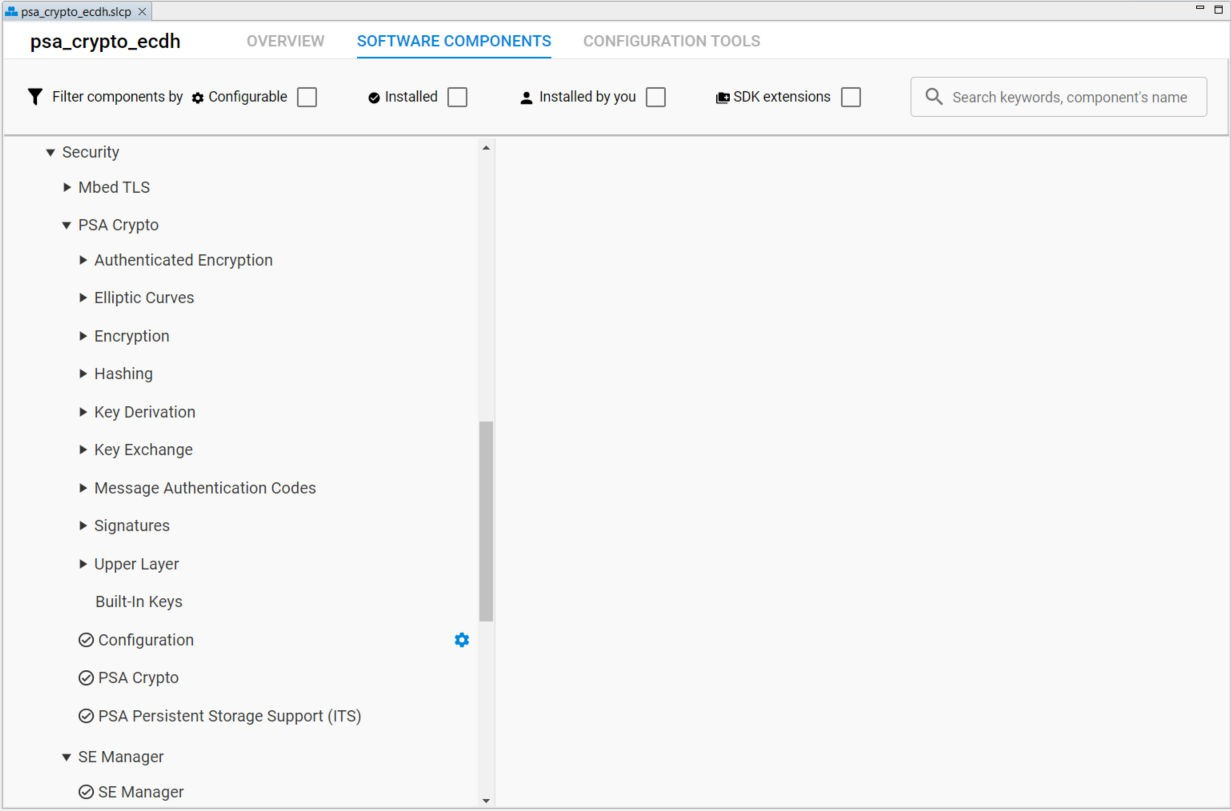
The user can browse the available security software components (under the Platform → Security category) on the target MCU or Wireless SoC if the [Installed Components] checkbox is unchecked.

The Mbed TLS and PSA Crypto configuration files automatically regenerates when the user installs or uninstalls a security software component in the project.
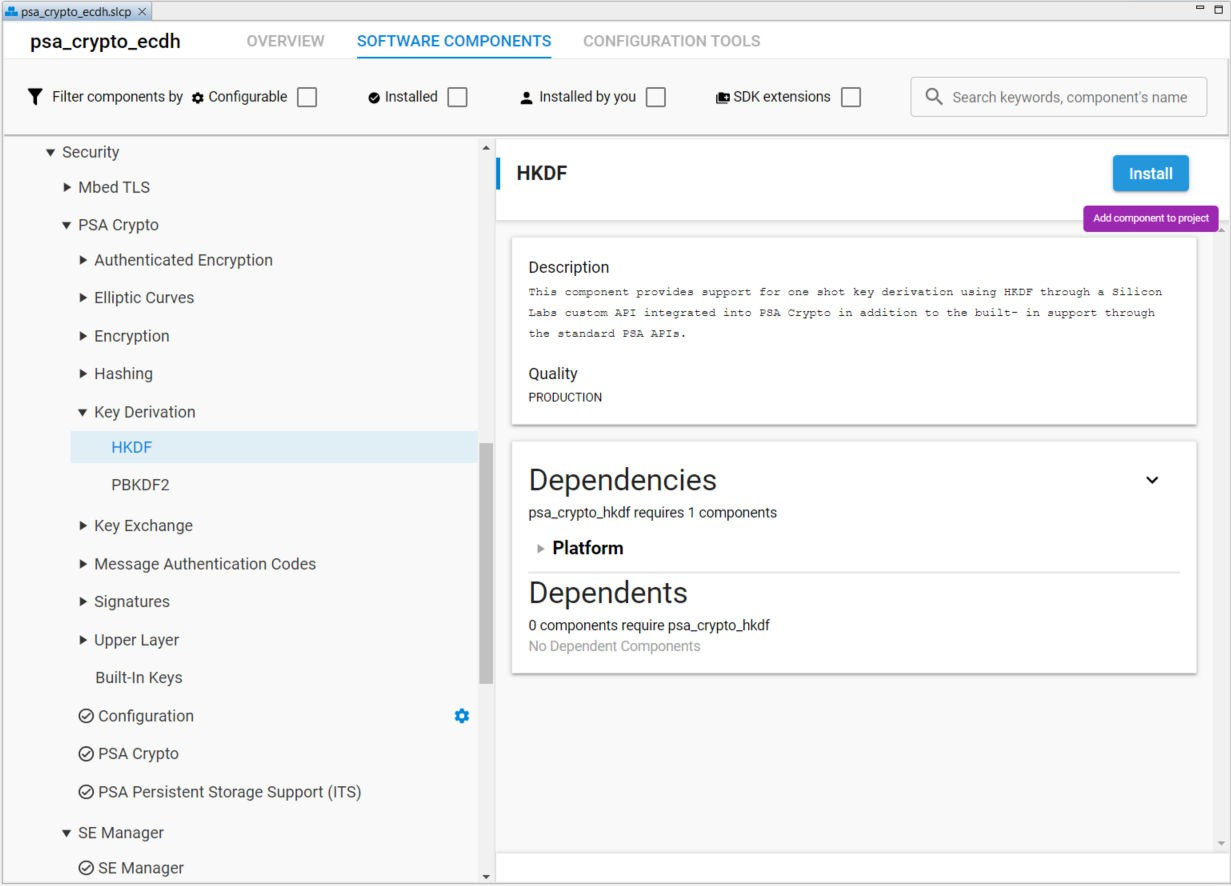


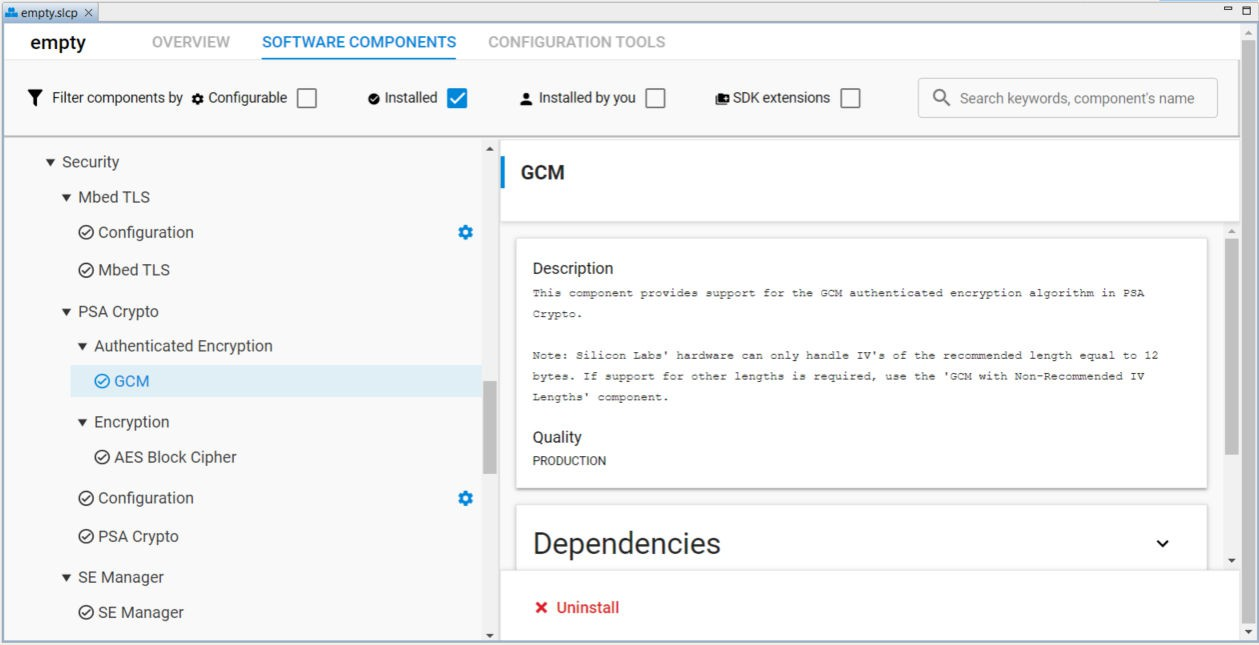
For a new project (like empty.slcp), the required security software components will be automatically added to the project after installing any cryptographic operation in PSA Crypto (like GCM) from the user. The SE Manager component is only for the HSE devices.

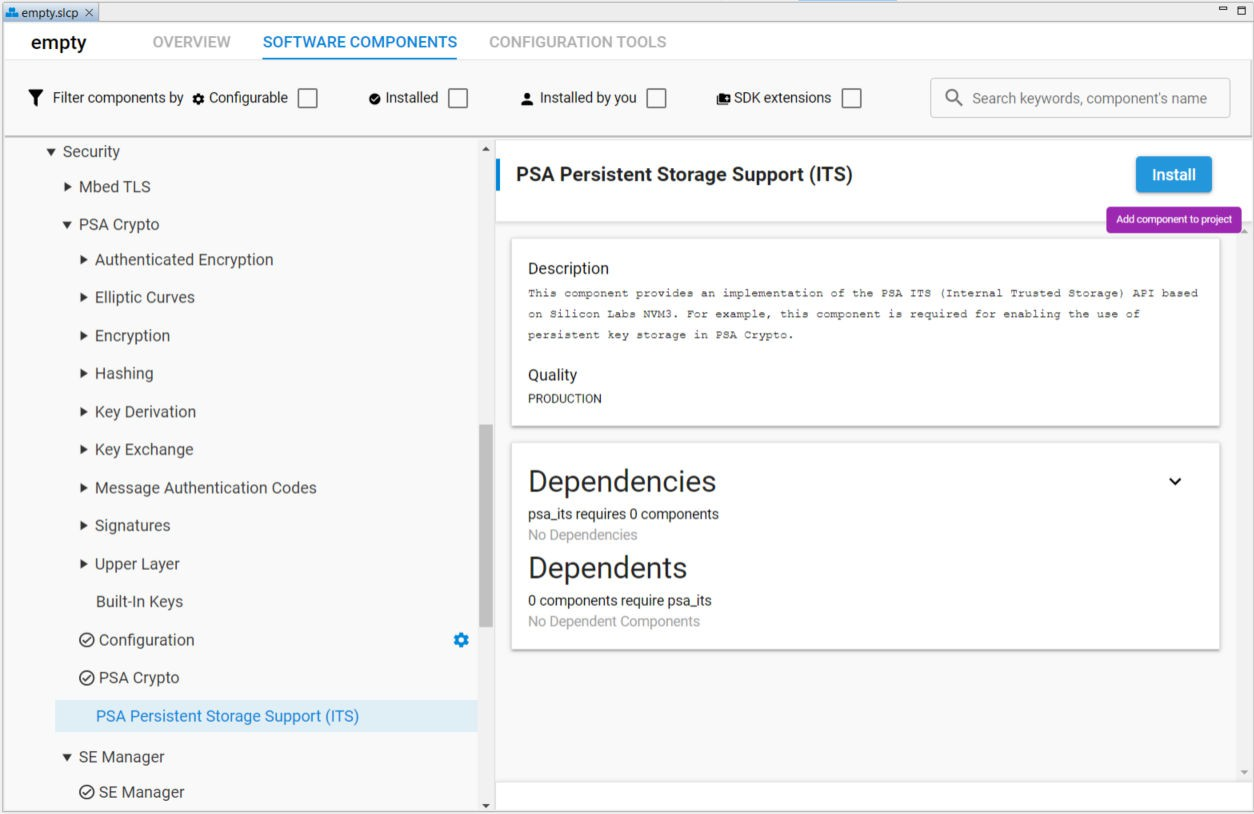
If users are about to use the PSA Crypto for persistent key storage (either plain or wrapped) in their application, make sure to add the PSA Persistent Storage Support (ITS) component to the project.

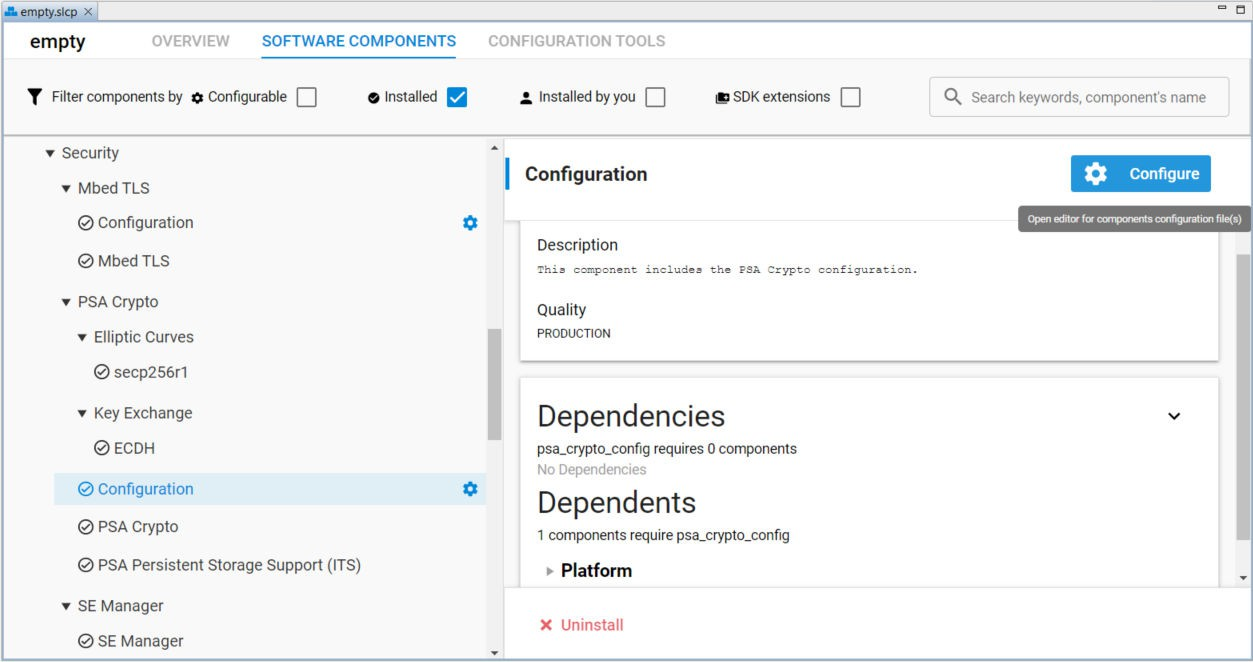
PSA Crypto Configuration#
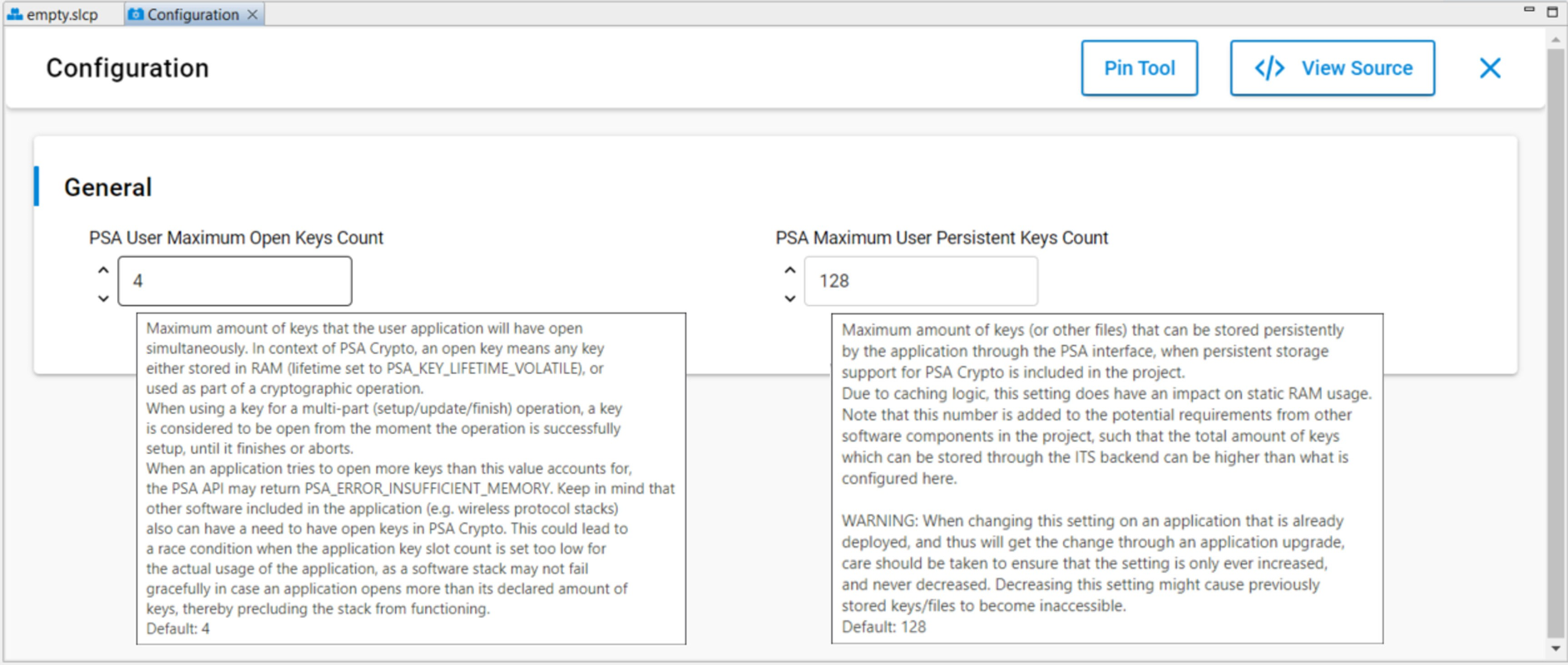
Click Configuration in Installed Components. Click [Configure] to open the Configuration Wizard in Context Menu.

Enter the desired values in PSA User Maximum Open Keys Count (SL_PSA_KEY_USER_SLOT_COUNT) and PSA Maximum User Persistent Keys Count (SL_PSA_ITS_USER_MAX_FILES) to replace the default values. Click [X] to exit.
The default value of PSA User Maximum Open Keys Count is equal to 0 if the project installed any Wireless Stack before.

The PSA Crypto configuration file (psa_crypto_config_autogen.h) in the autogen folder Figure Mbed TLS and PSA Crypto Configuration Files includes the definitions for PSA key slot count and maximum PSA ITS files.
#define MBEDTLS_PSA_KEY_SLOT_COUNT (2 + 1 + SL_PSA_KEY_USER_SLOT_COUNT)
#define SL_PSA_ITS_MAX_FILES (1 + SL_PSA_ITS_USER_MAX_FILES)The first digit in MBEDTLS_PSA_KEY_SLOT_COUNT is Wireless Stack (if installed) dependent. The second digit should be 1 for the PSA Crypto.
The first digit in SL_PSA_ITS_MAX_FILES is equal to 1 if the project installed the PSA persistent storage support (ITS) component Figure Security Software Component for Persistent Key Storage before.
Initialization and Random Number Generation (RNG)#
In PSA Crypto, applications must call psa_crypto_init() to initialize the library before using any other function. The PSA Crypto initialization includes seeding the pseudo-random generator (CTR-DRBG) with a hardware entropy source during the execution of psa_crypto_init().
| Item | Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|---|
Initialization |
Initialize CTR-DRBG |
Initialize PSA Crypto |
Generate random bytes |
|
|
Free resources |
• |
|
If a device includes a True Random Number Generator (TRNG) hardware module, the example will use the TRNG as an entropy source to seed the CTR-DRBG. If the device does not incorporate a TRNG, the example will use RAIL, Non-volatile (NV) seed (requires NVM3 driver), or ADC as the entropy source.
Device | Entropy Source |
|---|---|
MCU Series 1 - EFM32JG1, EFM32PG1 | NV seed (default) or ADC |
MCU Series 1 - EFM32JG12, EFM32PG12, EFM32GG11, EFM32GG12, EFM32TG11 | TRNG |
Wireless SoC Series 1 - EFR32xG1, EFR32xG14 | RAIL |
Wireless SoC Series 1 - EFR32xG12, EFR32xG13 (Revision D or later) | TRNG |
All MCU Series 2 and Wireless SoC Series 2 devices | TRNG |
Quick Reference Examples
PSA Crypto Initialization and Random Number Generation
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t rand_buf[32];
psa_status_t ret;
// Initialize the PSA Crypto and generate random numbers
ret = psa_crypto_init();
ret = psa_generate_random(rand_buf, sizeof(rand_buf));
}Key Handling#
The following table describes the main differences in key handling between Mbed TLS and PSA Crypto.
Item | Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|---|
Random Number Generation (RNG) | It requires application code to keep track of RNG. | The core keeps track of RNG. |
Buffer | It requires dedicated key buffers. | The core manages the key. |
Key export | The key is exportable. | The usage flag manages this option. |
Lifetime | It is volatile. | It can be volatile or persistent. |
Location | Local | Local or Secure |
Symmetric Key#
A symmetric key can be used with a block cipher or a stream cipher.
Algorithms
Refer to the Symmetric Cryptographic Operation section.
Key Attributes in PSA Crypto
Refer to the Symmetric Cryptographic Operation section.
Security Software Components
Refer to the Symmetric Cryptographic Operation section.
Functions
| Item | Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|---|
Create a random key |
Generate random numbers to a buffer |
Create a key from randomly generated data |
Import a key from a buffer |
API is algorithm dependent |
|
Copy a key |
— |
|
Export a key to a buffer |
The key is always in a buffer. |
|
Destroy a key |
Zero the key buffer. |
|
Note: The
psa_export_key()can export a symmetric key in plaintext if the PSA_KEY_USAGE_EXPORT usage flag is set.
Quick Reference Examples
Symmetric Plain Key Creation and Import
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t aes_ecb_key[16] = {0};
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t generate_key_id;
psa_key_id_t import_key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a AES ECB key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES);
psa_set_key_bits(&key_attr, 128);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_ECB_NO_PADDING);
// Generate a random volatile plain key for AES ECB
ret = psa_generate_key(&key_attr, &generate_key_id);
// Import a volatile plain key for AES ECB
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, aes_ecb_key, sizeof(aes_ecb_key), &import_key_id);
// Destroy the volatile plain keys for AES ECB
ret = psa_destroy_key(generate_key_id);
ret = psa_destroy_key(import_key_id);
// Generate a random persistent plain key for AES ECB (ID = 0x02)
psa_set_key_id(&key_attr, 0x02);
ret = psa_generate_key(&key_attr, &generate_key_id);
// Import a persistent plain key for AES ECB (ID = 0x03)
psa_set_key_id(&key_attr, 0x03);
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, aes_ecb_key, sizeof(aes_ecb_key), &import_key_id);
// Destroy the persistent plain keys for AES ECB
ret = psa_destroy_key(generate_key_id);
ret = psa_destroy_key(import_key_id);
}Symmetric Wrapped Key Creation and Import (HSE-SVH only)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t aes_ecb_key[16] = {0};
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t generate_key_id;
psa_key_id_t import_key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a AES ECB key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES);
psa_set_key_bits(&key_attr, 128);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_ECB_NO_PADDING);
psa_set_key_lifetime(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_LIFETIME_FROM_PERSISTENCE_AND_LOCATION(PSA_KEY_PERSISTENCE_VOLATILE, 0x01));
// Generate a random volatile wrapped key for AES ECB
ret = psa_generate_key(&key_attr, &generate_key_id);
// Import a volatile wrapped key for AES ECB
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, aes_ecb_key, sizeof(aes_ecb_key), &import_key_id);
// Destroy the volatile wrapped keys for AES ECB
ret = psa_destroy_key(generate_key_id);
ret = psa_destroy_key(import_key_id);
// Generate a random persistent wrapped key for AES ECB (ID = 0x02)
psa_set_key_id(&key_attr, 0x02);
psa_set_key_lifetime(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_LIFETIME_FROM_PERSISTENCE_AND_LOCATION(PSA_KEY_PERSISTENCE_DEFAULT, 0x01));
ret = psa_generate_key(&key_attr, &generate_key_id);
// Import a persistent wrapped key for AES ECB (ID = 0x03)
psa_set_key_id(&key_attr, 0x03);
psa_set_key_lifetime(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_LIFETIME_FROM_PERSISTENCE_AND_LOCATION(PSA_KEY_PERSISTENCE_DEFAULT, 0x01));
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, aes_ecb_key, sizeof(aes_ecb_key), &import_key_id);
// Destroy the persistent wrapped keys for AES ECB
ret = psa_destroy_key(generate_key_id);
ret = psa_destroy_key(import_key_id);
}PSA Crypto Platform Example
Click the View Project Documentation link to open the readme file.

The following table describes the implementation status of the PSA Crypto symmetric key platform example.
Key | Series 1 | Series 2 - VSE | Series 2 - HSE | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Extractable | Y | Y | Y | — |
Copyable | Y | Y | Y | The PSA_KEY_USAGE_COPY usage flag does not apply to the wrapped key. |
Wrapped | — | — | Y | Only on HSE-SVH devices. |
128-bit | Y | Y | Y | — |
192-bit | Y | Y | Y | — |
256-bit | Y | Y | Y | — |
Asymmetric Key#
An asymmetric key pair consists of a (secret) private key and a public key (not secret). A public key cryptographic algorithm can be used for key distribution and digital signatures.
Algorithms
Refer to the Asymmetric Cryptographic Operation section.
Key Attributes in PSA Crypto
Refer to the Asymmetric Cryptographic Operation section.
Security Software Components
Refer to the Asymmetric Cryptographic Operation section.
Functions
| Item | Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|---|
Create a random key |
ECDH |
Create a key from randomly generated data |
Import a private or public key from a buffer |
• |
|
Copy a key |
— |
|
Export a private key to a buffer |
• |
|
Export a public key to a buffer |
• |
|
Destroy a key |
ECDH |
|
Note:
The
psa_import_key()cannot store a public key in wrapped form.The
psa_export_key()can export a private key in plaintext if the PSA_KEY_USAGE_EXPORT usage flag is set.
ECC Key | Private Key Size (Import and Export) | Public Key Size (Import and Export) |
|---|---|---|
secp192r1 | 24-byte | 49-byte |
secp224r1 | 28-byte | 57-byte |
secp256r1 | 32-byte | 65-byte |
secp384r1 | 48-byte | 97-byte |
secp521r1 | 66-byte | 133-byte |
secp256k1 | 32-byte | 65-byte |
Curve25519 | 32-byte | 32-byte |
Curve448 | 56-byte | 56-byte |
Edwards25519 | 32-byte | 32-byte |
Note:
The public key of the
secpxxxcurve is stored in an uncompressed format (prefix0x04with the X and Y coordinates).EFR32xG21A/B devices do not support hardware acceleration on the secp224r1 curve.
Only the VSE-SVM devices support hardware acceleration on the secp256k1 curve.
The secp224r1 and secp256k1 with wrapped keys are not supported yet.
Quick Reference
Examples Asymmetric Key Creation and Import
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t public_key[65]; // Uncompressed point format
size_t pubkey_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Check if there is already a persistent key with the given identifier (ID = 0x02)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
ret = psa_get_key_attributes(0x02, &key_attr);
if (ret == PSA_ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE) {
// Key identifier does not exist, set up attributes for a persistent private wrapped key (secp256r1)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_ECC_KEY_PAIR(PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1));
psa_set_key_bits(&key_attr, 256);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_SIGN_HASH | PSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_HASH);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_ECDSA_ANY);
psa_set_key_id(&key_attr, 0x02);
psa_set_key_lifetime(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_LIFETIME_FROM_PERSISTENCE_AND_LOCATION(PSA_KEY_PERSISTENCE_DEFAULT, 0x01));
// Generate a random persistent private wrapped key (ID = 0x02)
ret = psa_generate_key(&key_attr, &key_id);
// Export a public key from a persistent private wrapped key (ID = 0x02)
ret = psa_export_public_key(0x02, public_key, sizeof(public_key), &pubkey_len);
// Set up attributes for a public key (secp256r1)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_ECC_PUBLIC_KEY(PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1));
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_HASH);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_ECDSA_ANY);
// Import a public key
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, public_key, sizeof(public_key), &key_id);
// Destroy a persistent private wrapped key (ID = 0x02) and public key
ret = psa_destroy_key(0x02);
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
} else if (ret == PSA_SUCCESS) {
// Key identifier already exists
return;
} else {
// Unexpected error
return;
}
}Note: Remove the code for the
psa_set_key_lifetime()function to generate a random persistent private plain key on non-HSE-SVH devices.
PSA Crypto Platform Example
Click the View Project Documentation link to open the readme file.

The following table describes the implementation status of the PSA Crypto asymmetric key platform example.
ECC Key | Series 1 | Series 2 - VSE | Series 2 - HSE | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Extractable | Y | Y | Y | — |
Copyable | Y | Y | Y | The PSA_KEY_USAGE_COPY usage flag does not apply to the wrapped key. |
Wrapped | — | — | Y | Only on HSE-SVH devices. |
secp192r1 | Y | Y | Y | — |
secp256r1 | Y | Y | Y | — |
secp384r1 | Y | Y | Y | Hardware acceleration only on HSE-SVH devices. |
secp521r1 | Y | Y | Y | Hardware acceleration only on HSE-SVH devices. |
Curve25519 | Y | Y | Y | Hardware acceleration only on HSE devices. |
Curve448 | — | — | Y | Only on HSE-SVH devices with hardware acceleration. |
Edwards25519 | — | — | Y | Only on HSE devices with hardware acceleration. |
Note:
This example does not include secp224r1 and secp256k1.
The PSA Crypto does not yet support software fallback on the Curve448 and Edwards25519.
The HSE-SVM devices require SE firmware v1.2.11 or higher (EFR32xG21) and v2.1.7 or higher (other HSE devices) to support hardware acceleration on Curve25519 and Edwards25519. This feature also requires GSDK v4.0.1 or higher.
Symmetric Cryptographic Operation#
Message Digests#
Message digests are designed to protect the integrity of a piece of data or media to detect changes to any part of a message. They are a type of cryptography utilizing hash values that can warn the receiver of any modifications applied to a message transmitted over an insecure channel.
Algorithms
| Algorithm | Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|---|
SHA-1 |
|
|
SHA-2 |
• |
• |
Security Software Components
Algorithm | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
PSA_ALG_SHA_1 | SHA-1 |
PSA_ALG_SHA_224 | SHA-224 |
PSA_ALG_SHA_256 | SHA-256 |
PSA_ALG_SHA_384 | SHA-384 |
PSA_ALG_SHA_512 | SHA-512 |
Single-Part Functions
| Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|
|
Generic |
|
— |
|
Multi-Part Operations
| Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|
|
Generic |
|
|
Generic |
|
|
Generic |
|
|
Generic |
|
— |
|
|
Generic |
|
|
Generic |
|
Note: The multi-part operation allows the data to be processed for message digest in fragments instead of all at once.
Quick Reference Examples
SHA-256 (One-shot)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
char test_msg[] = {"abcdbcdecdefdefgefghfghighijhijkijkljklmklmnlmnomnopnopq"};
uint8_t expect_sha256_hash[] = {
0x24, 0x8d, 0x6a, 0x61, 0xd2, 0x06, 0x38, 0xb8, 0xe5, 0xc0, 0x26, 0x93, 0x0c, 0x3e, 0x60, 0x39,
0xa3, 0x3c, 0xe4, 0x59, 0x64, 0xff, 0x21, 0x67, 0xf6, 0xec, 0xed, 0xd4, 0x19, 0xdb, 0x06, 0xc1
};
uint8_t hash_buf[32];
size_t hash_len;
psa_status_t ret;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Calculate the hash of a message
ret = psa_hash_compute(PSA_ALG_SHA_256,
(uint8_t *)test_msg,
sizeof(test_msg) - 1,
hash_buf,
sizeof(hash_buf),
&hash_len);
// Calculate the hash of a message and compare it with a reference value
ret = psa_hash_compare(PSA_ALG_SHA_256,
(uint8_t *)test_msg,
sizeof(test_msg) - 1,
expect_sha256_hash,
sizeof(expect_sha256_hash));
}SHA-256 (Streaming)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
char test_msg[] = {"abcdbcdecdefdefgefghfghighijhijkijkljklmklmnlmnomnopnopq"};
uint8_t hash_buf[32];
size_t hash_len;
uint32_t hash_total;
uint32_t stream_block_size = 16; // Block size for streaming
psa_status_t ret;
psa_hash_operation_t hash_op;
psa_hash_operation_t verify_op;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
hash_op = psa_hash_operation_init();
ret = psa_hash_setup(&hash_op, PSA_ALG_SHA_256);
// Streaming block
hash_total = 0;
while ((sizeof(test_msg) - 1 - hash_total) > stream_block_size) {
ret = psa_hash_update(&hash_op, (uint8_t *)(test_msg + hash_total), stream_block_size);
hash_total += stream_block_size;
}
ret = psa_hash_update(&hash_op, (uint8_t *)(test_msg + hash_total), sizeof(test_msg) -1 - hash_total);
// Generate hash and verify
// Expected hash:
// 24 8d 6a 61 d2 06 38 b8 e5 c0 26 93 0c 3e 60 39 a3 3c e4 59 64 ff 21 67 f6 ec ed d4 19 db 06 c1
verify_op = psa_hash_operation_init();
ret = psa_hash_clone(&hash_op, &verify_op);
ret = psa_hash_finish(&hash_op, hash_buf, sizeof(hash_buf), &hash_len);
ret = psa_hash_verify(&verify_op, hash_buf, hash_len);
}PSA Crypto Platform Example
Click the View Project Documentation link to open the readme file.

The following table describes the implementation status of the PSA Crypto hash platform example.
Algorithm | Series 1 | Series 2 - VSE | Series 2 - HSE | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
SHA-1 | Y | Y | Y | — |
SHA-224 | Y | Y | Y | — |
SHA-256 | Y | Y | Y | — |
SHA-384 | Y | Y | Y | Hardware acceleration only on HSE-SVH devices. |
SHA-512 | Y | Y | Y | Hardware acceleration only on HSE-SVH devices. |
Message Authentication Codes (MAC)#
A Message Authentication Code (MAC), sometimes known as a tag, is a short piece of information used to confirm that the message came from the stated sender (its authenticity) and has not been changed.
Algorithms
| Algorithm | Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|---|
HMAC |
|
• |
CMAC |
• |
• |
Key Attributes in PSA Crypto
| Algorithm | Key Type | Key Size in Bits | Key Usage Flag |
|---|---|---|---|
| •PSA_ALG_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_1) •PSA_ALG_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_224) •PSA_ALG_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_256) •PSA_ALG_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_384) •PSA_ALG_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_512) •PSA_ALG_TRUNCATED_MAC(PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg), mac_length) •PSA_ALG_FULL_LENGTH_MAC(PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg)) •PSA_ALG_AT_LEAST_THIS_LENGTH_MAC(PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg), min_mac_length) |
PSA_KEY_TYPE_HMAC | Multiple of 8 | •PSA_KEY_USAGE_SIGN_MESSAGE •PSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_MESSAGE |
| •PSA_ALG_CMAC •PSA_ALG_TRUNCATED_MAC(PSA_ALG_CMAC, mac_length) •PSA_ALG_FULL_LENGTH_MAC(PSA_ALG_CMAC) •PSA_ALG_AT_LEAST_THIS_LENGTH_MAC(PSA_ALG_CMAC, min_mac_length) |
PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES | •128 (16-byte) •192 (24-byte) •256 (32-byte) |
Note: For GSDK lower than v4.1.0, use usage flag
PSA_KEY_USAGE_SIGN_HASHandPSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_HASHinstead ofPSA_KEY_USAGE_SIGN_MESSAGEandPSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_MESSAGE.
Security Software Components
Algorithm | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
PSA_ALG_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_1) | HMAC and SHA-1 |
PSA_ALG_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_224) | HMAC and SHA-224 |
PSA_ALG_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_256) | HMAC and SHA-256 |
PSA_ALG_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_384) | HMAC and SHA-384 |
PSA_ALG_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_512) | HMAC and SHA-512 |
PSA_ALG_TRUNCATED_MAC(PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg), mac_length) | HMAC and SHA-X |
PSA_ALG_FULL_LENGTH_MAC(PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg)) | HMAC and SHA-X |
PSA_ALG_AT_LEAST_THIS_LENGTH_MAC(PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg), min_mac_length) | HMAC and SHA-X |
PSA_ALG_CMAC | CMAC |
PSA_ALG_TRUNCATED_MAC(PSA_ALG_CMAC, mac_length) | CMAC |
PSA_ALG_FULL_LENGTH_MAC(PSA_ALG_CMAC) | CMAC |
PSA_ALG_AT_LEAST_THIS_LENGTH_MAC(PSA_ALG_CMAC, min_mac_length) | CMAC |
Single-Part Functions
| Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|
|
HMAC |
|
— |
|
Multi-Part Operations
| Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|
|
HMAC |
|
|
HMAC |
|
— |
|
|
HMAC |
|
|
HMAC |
|
— |
|
|
HMAC |
|
Note: The multi-part operation allows the data to be processed for MAC in fragments instead of all at once.
Quick Reference Examples
CMAC (One-shot)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t cmac_key[] = {
0x60, 0x3d, 0xeb, 0x10, 0x15, 0xca, 0x71, 0xbe, 0x2b, 0x73, 0xae, 0xf0, 0x85, 0x7d, 0x77, 0x81,
0x1f, 0x35, 0x2c, 0x07, 0x3b, 0x61, 0x08, 0xd7, 0x2d, 0x98, 0x10, 0xa3, 0x09, 0x14, 0xdf, 0xf4
};
uint8_t cmac_msg[] = {
0x6b, 0xc1, 0xbe, 0xe2, 0x2e, 0x40, 0x9f, 0x96, 0xe9, 0x3d, 0x7e, 0x11, 0x73, 0x93, 0x17, 0x2a,
0xae, 0x2d, 0x8a, 0x57, 0x1e, 0x03, 0xac, 0x9c, 0x9e, 0xb7, 0x6f, 0xac, 0x45, 0xaf, 0x8e, 0x51,
0x30, 0xc8, 0x1c, 0x46, 0xa3, 0x5c, 0xe4, 0x11
};
uint8_t mac_buf[16];
size_t mac_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a CMAC key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_SIGN_MESSAGE | PSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_MESSAGE);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_CMAC);
// Import a volatile plain key for CMAC
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, cmac_key, sizeof(cmac_key), &key_id);
// Calculate the CMAC MAC of a message
// Expected CMAC MAC: aa f3 d8 f1 de 56 40 c2 32 f5 b1 69 b9 c9 11 e6
ret = psa_mac_compute(key_id, PSA_ALG_CMAC,
cmac_msg, sizeof(cmac_msg),
mac_buf, sizeof(mac_buf), &mac_len);
// Verify the CMAC MAC of a message
ret = psa_mac_verify(key_id, PSA_ALG_CMAC,
cmac_msg, sizeof(cmac_msg),
mac_buf, mac_len);
// Destroy a volatile plain key for CMACss
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
}Note: There are two ways to change the CMAC MAC length (default 16 bytes).
Replace all MAC algorithm
PSA_ALG_CMACwithPSA_ALG_TRUNCATED_MAC``(PSA_ALG_CMAC, mac_length)for the desired size (≥ 4) of the MAC in bytes.Replace the MAC algorithm
PSA_ALG_CMACin thepsa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_CMAC)function withPSA_ALG_AT_LEAST_THIS_LENGTH_MAC(PSA_ALG_CMAC, min_mac_length)to set the minimum MAC length (≥ 4) in bytes. Replace the MAC algorithmPSA_ALG_CMACinpsa_mac_compute()andpsa_mac_verify()withPSA_ALG_TRUNCATED_MAC``(PSA_ALG_CMAC, mac_length)to set the desired MAC length (≥min_mac_lengthand ≤PSA_MAC_LENGTH``(PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES, 256, PSA_ALG_CMAC))in bytes.
HMAC SHA-256 (One-shot)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t hmac_key[] = {
0x30, 0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 0x34, 0x35, 0x36, 0x37, 0x38, 0x39, 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x65, 0x66
};
uint8_t hmac_msg[] = {
0x30, 0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 0x34, 0x35, 0x36, 0x37, 0x38, 0x39, 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x65, 0x66
};
uint8_t mac_buf[32];
size_t mac_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a HMAC key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_HMAC);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_SIGN_MESSAGE | PSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_MESSAGE);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_256));
// Import a volatile plain key for HMAC
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, hmac_key, sizeof(hmac_key), &key_id);
// Calculate the HMAC MAC of a message
// Expected HMAC MAC:
// fb 5b 26 22 9c 20 b7 ed 86 67 06 a2 fb fa e6 7e 3f 40 4b b6 ab e7 7f f4 50 63 a4 59 a4 29 24 a4
ret = psa_mac_compute(key_id, PSA_ALG_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_256),
hmac_msg, sizeof(hmac_msg),
mac_buf, sizeof(mac_buf), &mac_len);
// Verify the HMAC MAC of a message
ret = psa_mac_verify(key_id, PSA_ALG_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_256),
hmac_msg, sizeof(hmac_msg),
mac_buf, mac_len);
// Destroy a volatile plain key for HMAC
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
}Notes: There are two ways to change the HMAC MAC length (default is
hash_algdependent).
Replace all MAC algorithm
PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg)withPSA_ALG_TRUNCATED_MAC(PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg),mac_length) for the desired size (≥ 4) of the MAC in bytes.Replace the MAC algorithm
PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg)in thepsa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg))function withPSA_ALG_AT_LEAST_THIS_LENGTH_MAC(PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg), min_mac_length)to set the minimum MAC length (≥ 4) in bytes.Replace the MAC algorithm
PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg)inpsa_mac_compute()andpsa_mac_verify()withPSA_ALG_TRUNCATED_MAC(PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg), mac_length)to set the desired MAC length(≥ min_mac_lengthand≤ PSA_MAC_LENGTH(PSA_KEY_TYPE_HMAC, 256, PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg)))in bytes.
CMAC (Streaming)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t cmac_key[] = {
0x60, 0x3d, 0xeb, 0x10, 0x15, 0xca, 0x71, 0xbe, 0x2b, 0x73, 0xae, 0xf0, 0x85, 0x7d, 0x77, 0x81,
0x1f, 0x35, 0x2c, 0x07, 0x3b, 0x61, 0x08, 0xd7, 0x2d, 0x98, 0x10, 0xa3, 0x09, 0x14, 0xdf, 0xf4
};
uint8_t cmac_msg[] = {
0x6b, 0xc1, 0xbe, 0xe2, 0x2e, 0x40, 0x9f, 0x96, 0xe9, 0x3d, 0x7e, 0x11, 0x73, 0x93, 0x17, 0x2a,
0xae, 0x2d, 0x8a, 0x57, 0x1e, 0x03, 0xac, 0x9c, 0x9e, 0xb7, 0x6f, 0xac, 0x45, 0xaf, 0x8e, 0x51,
0x30, 0xc8, 0x1c, 0x46, 0xa3, 0x5c, 0xe4, 0x11
};
uint8_t mac_buf[16];
size_t mac_len;
uint32_t mac_total;
uint32_t stream_block_size = 8;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
psa_mac_operation_t mac_op;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a CMAC key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_SIGN_MESSAGE | PSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_MESSAGE);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_CMAC);
// Import a volatile plain key for CMAC
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, cmac_key, sizeof(cmac_key), &key_id);
// Stream message and calculate the CMAC MAC
// Expected CMAC MAC: aa f3 d8 f1 de 56 40 c2 32 f5 b1 69 b9 c9 11 e6
mac_op = psa_mac_operation_init();
ret = psa_mac_sign_setup(&mac_op, key_id, PSA_ALG_CMAC);
mac_total = 0; // Streaming block
while ((sizeof(cmac_msg) - mac_total) > stream_block_size) {
ret = psa_mac_update(&mac_op, cmac_msg + mac_total, stream_block_size);
mac_total += stream_block_size;
}
ret = psa_mac_update(&mac_op, cmac_msg + mac_total, sizeof(cmac_msg) - mac_total);
ret = psa_mac_sign_finish(&mac_op, mac_buf, sizeof(mac_buf), &mac_len);
// Stream message and verify the CMAC MAC
mac_op = psa_mac_operation_init();
ret = psa_mac_verify_setup(&mac_op, key_id, PSA_ALG_CMAC);
mac_total = 0; // Streaming block
while ((sizeof(cmac_msg) - mac_total) > stream_block_size) {
ret = psa_mac_update(&mac_op, cmac_msg + mac_total, stream_block_size);
mac_total += stream_block_size;
}
ret = psa_mac_update(&mac_op, cmac_msg + mac_total, sizeof(cmac_msg) - mac_total);
ret = psa_mac_verify_finish(&mac_op, mac_buf, mac_len);
// Destroy a volatile plain key for CMAC
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
}Notes: There are two ways to change the CMAC MAC length (default 16 bytes).
Replace all MAC algorithm
PSA_ALG_CMACwithPSA_ALG_TRUNCATED_MAC(PSA_ALG_CMAC, mac_length)for the desired size (≥ 4) of the MAC in bytes.Replace the MAC algorithm
PSA_ALG_CMACin thepsa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_CMAC)function withPSA_ALG_AT_LEAST_THIS_LENGTH_MAC(PSA_ALG_CMAC, min_mac_length)to set the minimum MAC length (≥ 4) in bytes.Replace the MAC algorithm
PSA_ALG_CMACinpsa_mac_sign_setup()andpsa_mac_verify_setup()withPSA_ALG_TRUNCATED_MAC(PSA_ALG_CMAC, mac_length)to set the desired MAC length(≥ min_mac_length and ≤ PSA_MAC_LENGTH(PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES, 256, PSA_ALG_CMAC))in bytes.
HMAC SHA-256 (Streaming)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t hmac_key[] = {
0x30, 0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 0x34, 0x35, 0x36, 0x37, 0x38, 0x39, 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x65, 0x66
};
uint8_t hmac_msg[] = {
0x30, 0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 0x34, 0x35, 0x36, 0x37, 0x38, 0x39, 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x65, 0x66
};
uint8_t mac_buf[32];
size_t mac_len;
uint32_t mac_total;
uint32_t stream_block_size = 8;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
psa_mac_operation_t mac_op;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a HMAC key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_HMAC);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_SIGN_MESSAGE | PSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_MESSAGE);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_256));
// Import a volatile plain key for HMAC
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, hmac_key, sizeof(hmac_key), &key_id);
// Stream message and calculate the HMAC MAC
// Expected HMAC MAC:
// fb 5b 26 22 9c 20 b7 ed 86 67 06 a2 fb fa e6 7e 3f 40 4b b6 ab e7 7f f4 50 63 a4 59 a4 29 24 a4
mac_op = psa_mac_operation_init();
ret = psa_mac_sign_setup(&mac_op, key_id, PSA_ALG_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_256));
mac_total = 0; // Streaming block
while ((sizeof(hmac_msg) - mac_total) > stream_block_size) {
ret = psa_mac_update(&mac_op, hmac_msg + mac_total, stream_block_size);
mac_total += stream_block_size;
}
ret = psa_mac_update(&mac_op, hmac_msg + mac_total, sizeof(hmac_msg) - mac_total);
ret = psa_mac_sign_finish(&mac_op, mac_buf, sizeof(mac_buf), &mac_len);
// Stream message and verify the HMAC MAC
mac_op = psa_mac_operation_init();
ret = psa_mac_verify_setup(&mac_op, key_id, PSA_ALG_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_256));
mac_total = 0; // Streaming block
while ((sizeof(hmac_msg) - mac_total) > stream_block_size) {
ret = psa_mac_update(&mac_op, hmac_msg + mac_total, stream_block_size);
mac_total += stream_block_size;
}
ret = psa_mac_update(&mac_op, hmac_msg + mac_total, sizeof(hmac_msg) - mac_total);
ret = psa_mac_verify_finish(&mac_op, mac_buf, mac_len);
// Destroy a volatile plain key for HMAC
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
}Notes: There are two ways to change the HMAC MAC length (default is
hash_algdependent).
Replace all MAC algorithm
PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg)withPSA_ALG_TRUNCATED_MAC(PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg), mac_length)for the desired size (≥ 4) of the MAC in bytes.Replace the MAC algorithm
PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg)in thepsa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg))function withPSA_ALG_AT_LEAST_THIS_LENGTH_MAC(PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg), min_mac_length)to set the minimum MAC length (≥ 4) in bytes.Replace the MAC algorithm
PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg)inpsa_mac_sign_setup()andpsa_mac_verify_setup()withPSA_ALG_TRUNCATED_MAC(PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg), mac_length)to set the desired MAC length(≥ min_mac_length and ≤ PSA_MAC_LENGTH(PSA_KEY_TYPE_HMAC, 256, PSA_ALG_HMAC(hash_alg)))in bytes.
PSA Crypto Platform Example
Click the View Project Documentation link to open the readme file.

The following table describes the implementation status of the PSA Crypto MAC platform example.
| Algorithm | Series 1 | Series 2 - VSE | Series 2 - HSE | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
HMAC |
Y |
Y |
Y |
- Hardware acceleration only on Series 2 devices. |
CMAC |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Series 1 devices do not support a 192-bit key. |
Note:
The MAC platform example uses the default MAC length.
The single-part MAC functions are only available on GSDK v4.0.0 and higher.
Unauthenticated Ciphers#
The unauthenticated cipher API is for use cases where the data integrity and authenticity are guaranteed by non-cryptographic means.
Algorithms
| Algorithm | Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|---|
AES ECB |
• |
|
AES CBC |
• |
|
AES CFB |
• |
|
AES CTR |
• |
|
CHACHA20 |
|
|
Key Attributes in PSA Crypto
| Algorithm | Key Type | Key Size in Bits | Key Usage Flag |
|---|---|---|---|
PSA_ALG_ECB_NO_PADDING |
PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES |
128 (16-byte) 192 (24-byte) 256 (32-byte) |
PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPTPSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT |
PSA_ALG_CBC_NO_PADDING |
|||
PSA_ALG_CFB |
|||
PSA_ALG_CTR |
|||
PSA_ALG_STREAM_CIPHER |
PSA_KEY_TYPE_CHACHA20 |
256 (32-byte) |
Security Software Components
Algorithm and Built-in Key | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
PSA_ALG_ECB_NO_PADDING | ECB Mode |
PSA_ALG_CBC_NO_PADDING | CBC Mode |
PSA_ALG_CFB | CFB Mode |
PSA_ALG_CTR | CTR Mode |
PSA_ALG_STREAM_CIPHER | Chacha20 Stream Cipher |
Built-in Key | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
secp256r1 keys in SE OTP | Built-In Keys |
Single-Part Functions
| Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|
|
Generic |
|
|
Generic |
|
Note:
The
psa_cipher_encrypt()encrypts a message with a random initialization vector (IV). The output of this function is the IV followed by the ciphertext. Use the multi-part operations to manage the IV and ciphertext separately.The input to
psa_cipher_decrypt()must contain the IV followed by the ciphertext, as output bypsa_cipher_encrypt(). Use the multi-part operations to decrypt data that is not in the expected input format.
Multi-Part Operations
| Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|
|
Generic |
|
|
Generic |
|
|
Generic |
|
|
Generic |
|
|
Generic |
|
|
Generic |
|
|
|
|
Generic |
|
Note: The following situations require the use of a multi-part operation:
Processing messages that cannot be assembled in memory.
Using a deterministic initialization vector (IV) for unauthenticated encryption.
Providing the IV separately for unauthenticated encryption or decryption.
Quick Reference Examples
AES ECB (One-shot)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t aes_ecb_key[] = {
0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08, 0x09, 0x0a, 0x0b, 0x0c, 0x0d, 0x0e, 0x0f
};
uint8_t plain_msg_buf[] = {
0x00, 0x11, 0x22, 0x33, 0x44, 0x55, 0x66, 0x77, 0x88, 0x99, 0xaa, 0xbb, 0xcc, 0xdd, 0xee, 0xff
};
uint8_t cipher_buf[16];
size_t out_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
psa_cipher_operation_t cipher_op;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a AES ECB key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_ECB_NO_PADDING);
// Import a volatile plain key for AES ECB
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, aes_ecb_key, sizeof(aes_ecb_key), &key_id);
// AES ECB encryption and decryption
// Expected ciphertext: 69 c4 e0 d8 6a 7b 04 30 d8 cd b7 80 70 b4 c5 5a
// Single-part
ret = psa_cipher_encrypt(key_id, PSA_ALG_ECB_NO_PADDING,
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
cipher_buf, sizeof(cipher_buf), &out_len);
ret = psa_cipher_decrypt(key_id, PSA_ALG_ECB_NO_PADDING,
cipher_buf, out_len,
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf), &out_len);
// Multi-part
cipher_op = psa_cipher_operation_init();
ret = psa_cipher_encrypt_setup(&cipher_op, key_id, PSA_ALG_ECB_NO_PADDING);
ret = psa_cipher_update(&cipher_op, plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
cipher_buf, sizeof(cipher_buf), &out_len);
ret = psa_cipher_finish(&cipher_op,
cipher_buf + out_len,
sizeof(cipher_buf) - out_len,
&out_len);
cipher_op = psa_cipher_operation_init();
ret = psa_cipher_decrypt_setup(&cipher_op, key_id, PSA_ALG_ECB_NO_PADDING);
ret = psa_cipher_update(&cipher_op, cipher_buf, sizeof(cipher_buf),
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf), &out_len);
ret = psa_cipher_finish(&cipher_op,
plain_msg_buf + out_len,
sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - out_len,
&out_len);
// Destroy a volatile plain key for AES ECB
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
}AES CFB (One-shot)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t aes_cbc_key[] = {
0x2b, 0x7e, 0x15, 0x16, 0x28, 0xae, 0xd2, 0xa6, 0xab, 0xf7, 0x15, 0x88, 0x09, 0xcf, 0x4f, 0x3c
};
uint8_t iv_buf[] = {
0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08, 0x09, 0x0a, 0x0b, 0x0c, 0x0d, 0x0e, 0x0f
};
uint8_t plain_msg_buf[] = {
0x6b, 0xc1, 0xbe, 0xe2, 0x2e, 0x40, 0x9f, 0x96, 0xe9, 0x3d, 0x7e, 0x11, 0x73, 0x93, 0x17, 0x2a
};
uint8_t cipher_buf[32]; // Random IV + Ciphertext for single-part
size_t out_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
psa_cipher_operation_t cipher_op;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a AES CBC key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_CBC_NO_PADDING);
// Import a volatile plain key for AES CBC
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, aes_cbc_key, sizeof(aes_cbc_key), &key_id);
// AES CBC encryption and decryption
// Single-part - Random IV generated during encryption is embedded in the ciphertext buffer
ret = psa_cipher_encrypt(key_id, PSA_ALG_CBC_NO_PADDING,
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
cipher_buf, sizeof(cipher_buf), &out_len);
ret = psa_cipher_decrypt(key_id, PSA_ALG_CBC_NO_PADDING,
cipher_buf, out_len,
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf), &out_len);
// Multi-part
// Expected ciphertext: 76 49 ab ac 81 19 b2 46 ce e9 8e 9b 12 e9 19 7d
cipher_op = psa_cipher_operation_init();
ret = psa_cipher_encrypt_setup(&cipher_op, key_id, PSA_ALG_CBC_NO_PADDING);
ret = psa_cipher_set_iv(&cipher_op, iv_buf, sizeof(iv_buf));
ret = psa_cipher_update(&cipher_op,
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
cipher_buf, sizeof(cipher_buf),
&out_len);
ret = psa_cipher_finish(&cipher_op,
cipher_buf + out_len,
sizeof(cipher_buf) - out_len,
&out_len);
cipher_op = psa_cipher_operation_init();
ret = psa_cipher_decrypt_setup(&cipher_op, key_id, PSA_ALG_CBC_NO_PADDING);
ret = psa_cipher_set_iv(&cipher_op, iv_buf, sizeof(iv_buf));
ret = psa_cipher_update(&cipher_op,
cipher_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
&out_len);
ret = psa_cipher_finish(&cipher_op,
plain_msg_buf + out_len,
sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - out_len,
&out_len);
// Destroy a volatile plain key for AES CBC
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
}Note: The multi-part operations provide the IV separately for AES CFB encryption or decryption.
AES CTR (One-shot)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t aes_ctr_key[] = {
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff,
};
uint8_t iv_buf[] = {
0x22, 0x22, 0x1a, 0x70, 0x22, 0x22, 0x1a, 0x70, 0x22, 0x22, 0x1a, 0x70, 0x22, 0x22, 0x1a, 0x70
};
uint8_t plain_msg_buf[] = {
0xd8, 0x65, 0xc9, 0xcd, 0xea, 0x33, 0x56, 0xc5, 0x48, 0x8e, 0x7b, 0xa1, 0x5e, 0x84, 0xf4, 0xeb,
0xa3, 0xb8, 0x25, 0x9c, 0x05, 0x3f, 0x24, 0xce, 0x29, 0x67, 0x22, 0x1c, 0x00, 0x38, 0x84, 0xd7,
0x9d, 0x4c, 0xa4, 0x87, 0x7f, 0xfa, 0x4b, 0xc6, 0x87, 0xc6, 0x67, 0xe5, 0x49, 0x5b, 0xcf, 0xec,
0x12, 0xf4, 0x87, 0x17, 0x32, 0xaa, 0xe4, 0x5a, 0x11, 0x06, 0x76, 0x11, 0x3d, 0xf9, 0xe7, 0xda
};
uint8_t cipher_buf[80]; // Random IV + Ciphertext for single-part
size_t out_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
psa_cipher_operation_t cipher_op;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a AES CTR key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_CTR);
// Import a volatile plain key for AES CTR
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, aes_ctr_key, sizeof(aes_ctr_key), &key_id);
// AES CTR encryption and decryption
// Single-part - Random IV generated during encryption is embedded in the ciphertext buffer
ret = psa_cipher_encrypt(key_id, PSA_ALG_CTR,
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
cipher_buf, sizeof(cipher_buf), &out_len);
ret = psa_cipher_decrypt(key_id, PSA_ALG_CTR,
cipher_buf, out_len,
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf), &out_len);
// Multi-part
// Expected ciphertext:
// b6 72 f2 af 6a cc 20 ae ee 1a d8 14 12 8c 31 8b 95 5b be 80 5b 38 92 49 89 76 00 f5 20 74 54 32
// 7d 6d 0f b4 ac 0a 94 f3 7c a0 9e 45 05 33 98 fe a8 9c 20 0a d3 58 12 6d 9e 89 a4 05 26 5c 96 e7
cipher_op = psa_cipher_operation_init();
ret = psa_cipher_encrypt_setup(&cipher_op, key_id, PSA_ALG_CTR);
ret = psa_cipher_set_iv(&cipher_op, iv_buf, sizeof(iv_buf));
ret = psa_cipher_update(&cipher_op,
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
cipher_buf, sizeof(cipher_buf),
&out_len);
ret = psa_cipher_finish(&cipher_op,
cipher_buf + out_len,
sizeof(cipher_buf) - out_len,
&out_len);
cipher_op = psa_cipher_operation_init();
ret = psa_cipher_decrypt_setup(&cipher_op, key_id, PSA_ALG_CTR);
ret = psa_cipher_set_iv(&cipher_op, iv_buf, sizeof(iv_buf));
ret = psa_cipher_update(&cipher_op,
cipher_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
&out_len);
ret = psa_cipher_finish(&cipher_op,
plain_msg_buf + out_len,
sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - out_len,
&out_len);
// Destroy a volatile plain key for AES CTR
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
}Note: The multi-part operations provide the IV separately for AES CTR encryption or decryption.
CHACHA20 (One-shot)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t chacha20_key[32] = {0};
uint8_t iv_buf[12] = {0};
uint8_t plain_msg_buf[64] = {0};
uint8_t cipher_buf[76]; // Random IV + Ciphertext for single-part
size_t out_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
psa_cipher_operation_t cipher_op;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a CHACHA20 key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_CHACHA20);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_STREAM_CIPHER);
// Import a volatile plain key for CHACHA20
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, chacha20_key, sizeof(chacha20_key), &key_id);
// CHACHA20 encryption and decryption
// Single-part - Random IV generated during encryption is embedded in the ciphertext buffer
ret = psa_cipher_encrypt(key_id, PSA_ALG_STREAM_CIPHER,
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
cipher_buf, sizeof(cipher_buf), &out_len);
ret = psa_cipher_decrypt(key_id, PSA_ALG_STREAM_CIPHER,
cipher_buf, out_len,
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf), &out_len);
// Multi-part
// Expected ciphertext:
// 76 b8 e0 ad a0 f1 3d 90 40 5d 6a e5 53 86 bd 28 bd d2 19 b8 a0 8d ed 1a a8 36 ef cc 8b 77 0d c7
// da 41 59 7c 51 57 48 8d 77 24 e0 3f b8 d8 4a 37 6a 43 b8 f4 15 18 a1 1c c3 87 b6 69 b2 ee 65 86
cipher_op = psa_cipher_operation_init();
ret = psa_cipher_encrypt_setup(&cipher_op, key_id, PSA_ALG_STREAM_CIPHER);
ret = psa_cipher_set_iv(&cipher_op, iv_buf, sizeof(iv_buf));
ret = psa_cipher_update(&cipher_op,
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
cipher_buf, sizeof(cipher_buf),
&out_len);
ret = psa_cipher_finish(&cipher_op,
cipher_buf + out_len,
sizeof(cipher_buf) - out_len,
&out_len);
cipher_op = psa_cipher_operation_init();
ret = psa_cipher_decrypt_setup(&cipher_op, key_id, PSA_ALG_STREAM_CIPHER);
ret = psa_cipher_set_iv(&cipher_op, iv_buf, sizeof(iv_buf));
ret = psa_cipher_update(&cipher_op,
cipher_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
&out_len);
ret = psa_cipher_finish(&cipher_op,
plain_msg_buf + out_len,
sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - out_len,
&out_len);
// Destroy a volatile plain key for CHACHA20
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
}Note: The multi-part operations provide the IV separately for CHACHA20 encryption or decryption.
AES CTR (Streaming)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t aes_ctr_key[] = {
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff,
};
uint8_t iv_buf[] = {
0x22, 0x22, 0x1a, 0x70, 0x22, 0x22, 0x1a, 0x70, 0x22, 0x22, 0x1a, 0x70, 0x22, 0x22, 0x1a, 0x70
};
uint8_t plain_msg_buf[] = {
0xd8, 0x65, 0xc9, 0xcd, 0xea, 0x33, 0x56, 0xc5, 0x48, 0x8e, 0x7b, 0xa1, 0x5e, 0x84, 0xf4, 0xeb,
0xa3, 0xb8, 0x25, 0x9c, 0x05, 0x3f, 0x24, 0xce, 0x29, 0x67, 0x22, 0x1c, 0x00, 0x38, 0x84, 0xd7,
0x9d, 0x4c, 0xa4, 0x87, 0x7f, 0xfa, 0x4b, 0xc6, 0x87, 0xc6, 0x67, 0xe5, 0x49, 0x5b, 0xcf, 0xec,
0x12, 0xf4, 0x87, 0x17, 0x32, 0xaa, 0xe4, 0x5a, 0x11, 0x06, 0x76, 0x11, 0x3d, 0xf9, 0xe7, 0xda
};
uint8_t cipher_buf[64];
size_t out_len;
uint32_t out_total;
uint32_t stream_block_size = 14; // Block size for streaming
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
psa_cipher_operation_t cipher_op;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a AES CTR key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_CTR);
// Import a volatile plain key for AES CTR
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, aes_ctr_key, sizeof(aes_ctr_key), &key_id);
// AES CTR stream encryption and decryption
// Expected ciphertext:
// b6 72 f2 af 6a cc 20 ae ee 1a d8 14 12 8c 31 8b 95 5b be 80 5b 38 92 49 89 76 00 f5 20 74 54 32
// 7d 6d 0f b4 ac 0a 94 f3 7c a0 9e 45 05 33 98 fe a8 9c 20 0a d3 58 12 6d 9e 89 a4 05 26 5c 96 e7
cipher_op = psa_cipher_operation_init();
ret = psa_cipher_encrypt_setup(&cipher_op, key_id, PSA_ALG_CTR);
ret = psa_cipher_set_iv(&cipher_op, iv_buf, sizeof(iv_buf));
out_total = 0; // Streaming block
while ((sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - out_total) > stream_block_size) {
ret = psa_cipher_update(&cipher_op,
plain_msg_buf + out_total, stream_block_size,
cipher_buf + out_total, sizeof(cipher_buf) - out_total,
&out_len);
out_total += out_len;
}
ret = psa_cipher_update(&cipher_op, // Last block
plain_msg_buf + out_total, sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - out_total,
cipher_buf + out_total, sizeof(cipher_buf) - out_total,
&out_len);
out_total += out_len;
ret = psa_cipher_finish(&cipher_op,
cipher_buf + out_total,
sizeof(cipher_buf) - out_total,
&out_len);
cipher_op = psa_cipher_operation_init();
ret = psa_cipher_decrypt_setup(&cipher_op, key_id, PSA_ALG_CTR);
ret = psa_cipher_set_iv(&cipher_op, iv_buf, sizeof(iv_buf));
out_total = 0; // Streaming block
while ((sizeof(cipher_buf) - out_total) > stream_block_size) {
ret = psa_cipher_update(&cipher_op,
cipher_buf + out_total, stream_block_size,
plain_msg_buf + out_total, sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - out_total,
&out_len);
out_total += out_len;
}
ret = psa_cipher_update(&cipher_op, // Last block
cipher_buf + out_total, sizeof(cipher_buf) - out_total,
plain_msg_buf + out_total, sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - out_total,
&out_len);
out_total += out_len;
ret = psa_cipher_finish(&cipher_op,
plain_msg_buf + out_total,
sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - out_total,
&out_len);
// Destroy a volatile plain key for AES CTR
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
}AES CTR with Built-in AES-128 Key (HSE only)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t iv_buf[16] = {0};
uint8_t plain_msg_buf[16] = {0};
uint8_t cipher_buf[32]; // Random IV + Ciphertext for single-part
size_t out_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_cipher_operation_t cipher_op;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// AES CTR encryption and decryption with built-in AES-128 key
// ret = -140 (PSA_ERROR_DOES_NOT_EXIST) if the AES-128 key has not been provisioned
// Single-part - Random IV generated during encryption is embedded in the ciphertext buffer
ret = psa_cipher_encrypt(SL_SE_BUILTIN_KEY_AES128_ID, PSA_ALG_CTR,
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
cipher_buf, sizeof(cipher_buf), &out_len);
ret = psa_cipher_decrypt(SL_SE_BUILTIN_KEY_AES128_ID, PSA_ALG_CTR,
cipher_buf, out_len,
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf), &out_len);
// Multi-part
// Built-in AES-128 key: 81 a5 e2 1f a1 52 86 f1 df 44 5c 2c c1 20 fa 3f
// Expected ciphertext: 66 d2 0f 99 65 3e a8 d0 83 05 a6 39 d4 4e 98 a6
cipher_op = psa_cipher_operation_init();
ret = psa_cipher_encrypt_setup(&cipher_op, SL_SE_BUILTIN_KEY_AES128_ID, PSA_ALG_CTR);
ret = psa_cipher_set_iv(&cipher_op, iv_buf, sizeof(iv_buf));
ret = psa_cipher_update(&cipher_op,
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
cipher_buf, sizeof(cipher_buf),
&out_len);
ret = psa_cipher_finish(&cipher_op,
cipher_buf + out_len,
sizeof(cipher_buf) - out_len,
&out_len);
cipher_op = psa_cipher_operation_init();
ret = psa_cipher_decrypt_setup(&cipher_op, SL_SE_BUILTIN_KEY_AES128_ID, PSA_ALG_CTR);
ret = psa_cipher_set_iv(&cipher_op, iv_buf, sizeof(iv_buf));
ret = psa_cipher_update(&cipher_op,
cipher_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
&out_len);
ret = psa_cipher_finish(&cipher_op,
plain_msg_buf + out_len,
sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - out_len,
&out_len);
}PSA Crypto Platform Example
Click the View Project Documentation link to open the readme file.

The following table describes the implementation status of the PSA Crypto cipher platform example.
Algorithm/Key | Series 1 | Series 2 - VSE | Series 2 - HSE | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
AES ECB | Y | Y | Y | Series 1 devices do not support a 192-bit key. |
AES CBC | Y | Y | Y | Series 1 devices do not support a 192-bit key. |
AES CFB | Y | Y | Y | Series 1 devices do not support a 192-bit key. |
AES CTR | Y | Y | Y | Series 1 devices do not support a 192-bit key. |
CHACHA20 | Y | Y | Y | Hardware acceleration only on HSE-SVH devices. |
AES-128 Key | — | — | Y | — |
Note: The single-part unauthenticated cipher functions are only available on GSDK v4.0.0 and higher.
Authenticated Encryption with Associated Data (AEAD)#
The authenticated encryption with associated data (AEAD) is a form of encryption that simultaneously assures the confidentiality and authenticity of data.
Algorithms
| Algorithm | Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|---|
AES GCM |
• MBEDTLS_CIPHER_AES_128_GCM |
• PSA_ALG_GCM |
AES CCM |
• MBEDTLS_CIPHER_AES_128_CCM |
• PSA_ALG_CCM |
CHACHA20_POLY1305 |
MBEDTLS_CIPHER_CHACHA20_POLY1305 |
PSA_ALG_CHACHA20_POLY1305 |
Algorithm | Nonce Length (Bytes) | Authentication Tag Length (Bytes) |
|---|---|---|
AES GCM | 1 - 16 (Default 12) | 4, 8, 12, 13, 14, 15, and 16 (Default) |
AES CCM | 7 - 13 | 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, and 16 (Default) |
CHACHA20_POLY1305 | 12 | 16 |
Key Attributes in PSA Crypto
| Algorithm | Key Type | Key Size in Bits | Key Usage Flag |
|---|---|---|---|
PSA_ALG_GCM orPSA_ALG_AEAD_WITH_*(PSA_ALG_GCM…)
|
PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES |
128 (16-byte) 192 (24-byte) 256 (32-byte) |
PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPTPSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT
|
PSA_ALG_CCM orPSA_ALG_AEAD_WITH_*(PSA_ALG_CCM…)
|
|||
PSA_ALG_CHACHA20_POLY1305 |
PSA_KEY_TYPE_CHACHA20 |
256 (32-byte) |
Security Software Components
Algorithm | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
PSA_ALG_GCM or PSA_ALG_AEAD_WITH_*(PSA_ALG_GCM…) | GCM (12-byte IV) or GCM with Non-Recommended IV Lengths |
PSA_ALG_CCM or PSA_ALG_AEAD_WITH_*(PSA_ALG_CCM…) | CCM Mode |
PSA_ALG_CHACHA20_POLY1305 | ChachaPoly |
Single-Part Functions
| Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|
|
Generic |
|
|
Generic |
|
Note: The single-part functions use one buffer for the ciphertext and AEAD authentication tag.
Multi-Part Operations
| Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|
|
Generic |
|
|
Generic |
|
|
Generic |
|
— |
|
|
Generic |
|
|
Generic |
|
|
Generic |
|
|
Generic |
|
| Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|
|
Generic |
|
— |
|
|
Generic |
|
Note:
For
PSA_ALG_CCM, callingpsa_aead_set_lengths()is required.For the other AEAD algorithms, calling
psa_aead_set_lengths()is not required.The following situations require the use of a multi-part operation:
Processing messages that cannot be assembled in memory.
Separating the AEAD authentication tag from the ciphertext.
Quick Reference Examples
AES CCM (One-shot)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t key_buf[] = {
0xea, 0x4f, 0x6f, 0x3c, 0x2f, 0xed, 0x2b, 0x9d, 0xd9, 0x70, 0x8c, 0x2e, 0x72, 0x1a, 0xe0, 0x0f
};
uint8_t nonce_buf[] = {0xf9, 0x75, 0x80, 0x9d, 0xdb, 0x51, 0x72, 0x38, 0x27, 0x45, 0x63, 0x4f};
uint8_t ad_buf[] = {0x5c, 0x65, 0xd4, 0xf2, 0x61, 0xd2, 0xc5, 0x4f, 0xfe, 0x6a};
uint8_t plain_msg_buf[] = {0x8d, 0x6c, 0x08, 0x44, 0x6c, 0xb1, 0x0d, 0x9a, 0x20, 0x75};
uint8_t cipher_tag_buf[32]; // Ciphertext + Tag
size_t out_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a AES CCM key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_CCM);
// Import a volatile plain key for AES CCM
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, key_buf, sizeof(key_buf), &key_id);
// AES CCM encryption and descryption
// Expected ciphertext: e2 2f 37 3b eb f6 4a 3e 9b 87
// Expected tag: 75 2b f9 db 34 dc 4d 43 3f 00 f5 5c 3f 53 0c 89
ret = psa_aead_encrypt(key_id, PSA_ALG_CCM,
nonce_buf, sizeof(nonce_buf),
ad_buf, sizeof(ad_buf),
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
cipher_tag_buf, sizeof(cipher_tag_buf),
&out_len);
ret = psa_aead_decrypt(key_id, PSA_ALG_CCM,
nonce_buf, sizeof(nonce_buf),
ad_buf, sizeof(ad_buf),
cipher_tag_buf, out_len,
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
&out_len);
// Destroy a volatile plain key for AES CCM
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
}Notes:
There are two ways to change the CCM authentication tag length (default 16 bytes).
Replace all AEAD algorithm
PSA_ALG_CCMwithPSA_ALG_AEAD_WITH_SHORTENED_TAG(PSA_ALG_CCM, tag_length)for the desired size of the authentication tag in bytes.Replace the AEAD algorithm
PSA_ALG_CCMin thepsa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_CCM)function withPSA_ALG_AEAD_WITH_AT_LEAST_THIS_LENGTH_TAG(PSA_ALG_CCM, min_tag_length)to set the minimum authentication tag length in bytes. Replace the AEAD algorithmPSA_ALG_CCM in psa_aead_encrypt()andpsa_aead_decrypt()withPSA_ALG_AEAD_WITH_SHORTENED_TAG(PSA_ALG_CCM, tag_length)to set the desired tag length(≥ min_tag_length and ≤ PSA_AEAD_TAG_LENGTH(PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES, 256, PSA_ALG_CCM))in bytes.
AES GCM (One-shot)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t key_buf[] = {
0xea, 0x4f, 0x6f, 0x3c, 0x2f, 0xed, 0x2b, 0x9d, 0xd9, 0x70, 0x8c, 0x2e, 0x72, 0x1a, 0xe0, 0x0f
};
uint8_t nonce_buf[] = {0xf9, 0x75, 0x80, 0x9d, 0xdb, 0x51, 0x72, 0x38, 0x27, 0x45, 0x63, 0x4f};
uint8_t ad_buf[] = {0x5c, 0x65, 0xd4, 0xf2, 0x61, 0xd2, 0xc5, 0x4f, 0xfe, 0x6a};
uint8_t plain_msg_buf[] = {0x8d, 0x6c, 0x08, 0x44, 0x6c, 0xb1, 0x0d, 0x9a, 0x20, 0x75};
uint8_t cipher_tag_buf[32]; // Ciphertext + Tag
size_t out_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a AES GCM key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_GCM);
// Import a volatile plain key for AES GCM
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, key_buf, sizeof(key_buf), &key_id);
// AES GCM encryption and decryption
// Expected ciphertext: 0f 51 f7 a8 3c 5b 5a a7 96 b9
// Expected tag: 70 25 9c dd fe 8f 9a 15 a5 c5 eb 48 5a f5 78 fb
ret = psa_aead_encrypt(key_id, PSA_ALG_GCM,
nonce_buf, sizeof(nonce_buf),
ad_buf, sizeof(ad_buf),
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
cipher_tag_buf, sizeof(cipher_tag_buf),
&out_len);
ret = psa_aead_decrypt(key_id, PSA_ALG_GCM,
nonce_buf, sizeof(nonce_buf),
ad_buf, sizeof(ad_buf),
cipher_tag_buf, out_len,
plain_msg_buf, sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
&out_len);
// Destroy a volatile plain key for AES GCM
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
}Notes:
There are two ways to change the GCM authentication tag length (default 16 bytes).
Replace all AEAD algorithm
PSA_ALG_GCMwithPSA_ALG_AEAD_WITH_SHORTENED_TAG(PSA_ALG_GCM, tag_length)for the desired size of the authentication tag in bytes.Replace the AEAD algorithm
PSA_ALG_GCM in the psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_GCM)function withPSA_ALG_AEAD_WITH_AT_LEAST_THIS_LENGTH_TAG(PSA_ALG_GCM, min_tag_length)to set the minimum authentication tag length in bytes. Replace the AEAD algorithmPSA_ALG_GCM in psa_aead_encrypt()andpsa_aead_decrypt()withPSA_ALG_AEAD_WITH_SHORTENED_TAG(PSA_ALG_GCM, tag_length)to set the desired tag length(≥ min_tag_length and ≤ PSA_AEAD_TAG_LENGTH(PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES, 256, PSA_ALG_GCM))in bytes.
CHACHA20_POLY1305 (One-shot)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t key_buf[] = {
0x80, 0x81, 0x82, 0x83, 0x84, 0x85, 0x86, 0x87, 0x88, 0x89, 0x8a, 0x8b, 0x8c, 0x8d, 0x8e, 0x8f,
0x90, 0x91, 0x92, 0x93, 0x94, 0x95, 0x96, 0x97, 0x98, 0x99, 0x9a, 0x9b, 0x9c, 0x9d, 0x9e, 0x9f
};
uint8_t nonce_buf[] = {0x07, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x40, 0x41, 0x42, 0x43, 0x44, 0x45, 0x46, 0x47};
uint8_t ad_buf[] = {0x50, 0x51, 0x52, 0x53, 0xc0, 0xc1, 0xc2, 0xc3, 0xc4, 0xc5, 0xc6, 0xc7};
uint8_t plain_msg_buf[] = {
0x4c, 0x61, 0x64, 0x69, 0x65, 0x73, 0x20, 0x61, 0x6e, 0x64, 0x20, 0x47, 0x65, 0x6e, 0x74, 0x6c,
0x65, 0x6d, 0x65, 0x6e, 0x20, 0x6f, 0x66, 0x20, 0x74, 0x68, 0x65, 0x20, 0x63, 0x6c, 0x61, 0x73,
0x73, 0x20, 0x6f, 0x66, 0x20, 0x27, 0x39, 0x39, 0x3a, 0x20, 0x49, 0x66, 0x20, 0x49, 0x20, 0x63,
0x6f, 0x75, 0x6c, 0x64, 0x20, 0x6f, 0x66, 0x66, 0x65, 0x72, 0x20, 0x79, 0x6f, 0x75, 0x20, 0x6f,
0x6e, 0x6c, 0x79, 0x20, 0x6f, 0x6e, 0x65, 0x20, 0x74, 0x69, 0x70, 0x20, 0x66, 0x6f, 0x72, 0x20,
0x74, 0x68, 0x65, 0x20, 0x66, 0x75, 0x74, 0x75, 0x72, 0x65, 0x2c, 0x20, 0x73, 0x75, 0x6e, 0x73,
0x63, 0x72, 0x65, 0x65, 0x6e, 0x20, 0x77, 0x6f, 0x75, 0x6c, 0x64, 0x20, 0x62, 0x65, 0x20, 0x69,
0x74, 0x2e
};
uint8_t cipher_tag_buf[130]; // Ciphertext + Tag
size_t out_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a CHACHA20_POLY1305 key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_CHACHA20);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_CHACHA20_POLY1305);
// Import a volatile plain key for CHACHA20_POLY1305
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, key_buf, sizeof(key_buf), &key_id);
// CHACHA20_POLY1305 encryption
// Expected ciphertext:
// d3 1a 8d 34 64 8e 60 db 7b 86 af bc 53 ef 7e c2 a4 ad ed 51 29 6e 08 fe a9 e2 b5 a7 36 ee 62 d6
// 3d be a4 5e 8c a9 67 12 82 fa fb 69 da 92 72 8b 1a 71 de 0a 9e 06 0b 29 05 d6 a5 b6 7e cd 3b 36
// 92 dd bd 7f 2d 77 8b 8c 98 03 ae e3 28 09 1b 58 fa b3 24 e4 fa d6 75 94 55 85 80 8b 48 31 d7 bc
// 3f f4 de f0 8e 4b 7a 9d e5 76 d2 65 86 ce c6 4b 61 16
// Expected tag: 1a e1 0b 59 4f 09 e2 6a 7e 90 2e cb d0 60 06 91
ret = psa_aead_encrypt(key_id,
PSA_ALG_CHACHA20_POLY1305,
nonce_buf,
sizeof(nonce_buf),
ad_buf,
sizeof(ad_buf),
plain_msg_buf,
sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
cipher_tag_buf,
sizeof(cipher_tag_buf),
&out_len);
// CHACHA20_POLY1305 decryption
ret = psa_aead_decrypt(key_id,
PSA_ALG_CHACHA20_POLY1305,
nonce_buf,
sizeof(nonce_buf),
ad_buf,
sizeof(ad_buf),
cipher_tag_buf,
out_len,
plain_msg_buf,
sizeof(plain_msg_buf),
&out_len);
// Destroy a volatile plain key for CHACHA20_POLY1305
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
}AES CCM (Streaming)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t key_buf[] = {
0x9c, 0xde, 0xba, 0xee, 0xe8, 0x69, 0x0b, 0x68, 0x75, 0x10, 0x70, 0x69, 0x1f, 0x49, 0x59, 0x36,
0x68, 0xa6, 0xde, 0x12, 0xd3, 0xa9, 0x48, 0xb3, 0x8d, 0xdb, 0xd3, 0xf7, 0x52, 0x18, 0xb2, 0xd4
};
uint8_t nonce_buf[] = {0xaf, 0x1a, 0x97, 0xd4, 0x31, 0x51, 0xf5, 0xea, 0x9c, 0x48, 0xad, 0x36, 0xa3};
uint8_t ad_buf[] = {
0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08, 0x09, 0x0a, 0x0b, 0x0c, 0x0d, 0x0e, 0x0f,
0x10, 0x11, 0x12, 0x13
};
uint8_t plain_msg_buf[] = {
0x3c, 0xbb, 0x08, 0xf1, 0x33, 0x27, 0x0e, 0x44, 0x54, 0xbc, 0xaa, 0xa0, 0xf2, 0x0f, 0x6d, 0x63,
0xc3, 0x8b, 0x65, 0x72, 0xe7, 0x66
};
uint8_t cipher_buf[22];
uint8_t tag_buf[16];
size_t tag_len;
size_t out_len;
uint32_t out_total;
uint32_t stream_cnt;
uint32_t stream_block_size = 14; // Block size for streaming
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
psa_aead_operation_t aead_op;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a AES CCM key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_CCM);
// Import a volatile plain key for AES CCM
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, key_buf, sizeof(key_buf), &key_id);
// AES CCM stream encryption and decryption
// Expected ciphertext:
// 39 66 93 0a 2a e8 fd d8 f4 0e 70 07 f3 fd e0 bd 6e b4 8a 46 e6 d2
// Expected tag: 7c 0c 1b a4 bf d2 bd 21 5b 0c d9 21 f0 6a 8f 3b
aead_op = psa_aead_operation_init();
ret = psa_aead_encrypt_setup(&aead_op, key_id, PSA_ALG_CCM);
ret = psa_aead_set_lengths(&aead_op, sizeof(ad_buf), sizeof(plain_msg_buf));
ret = psa_aead_set_nonce(&aead_op, nonce_buf, sizeof(nonce_buf));
ret = psa_aead_update_ad(&aead_op, ad_buf, sizeof(ad_buf));
stream_cnt = 0; // Streaming block
out_total = 0;
while ((sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - (stream_cnt * stream_block_size)) > stream_block_size) {
ret = psa_aead_update(&aead_op,
plain_msg_buf + (stream_cnt * stream_block_size), stream_block_size,
cipher_buf + out_total, sizeof(cipher_buf) - out_total,
&out_len);
stream_cnt++;
out_total += out_len;
}
ret = psa_aead_update(&aead_op, // Last block
plain_msg_buf + (stream_cnt * stream_block_size),
sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - (stream_cnt * stream_block_size),
cipher_buf + out_total, sizeof(cipher_buf) - out_total,
&out_len);
out_total += out_len;
ret = psa_aead_finish(&aead_op, // Generate tag
cipher_buf + out_total, sizeof(cipher_buf) - out_total,
&out_len,
tag_buf, sizeof(tag_buf),
&tag_len);
out_total += out_len;
aead_op = psa_aead_operation_init();
ret = psa_aead_decrypt_setup(&aead_op, key_id, PSA_ALG_CCM);
ret = psa_aead_set_lengths(&aead_op, sizeof(ad_buf), sizeof(plain_msg_buf));
ret = psa_aead_set_nonce(&aead_op, nonce_buf, sizeof(nonce_buf));
ret = psa_aead_update_ad(&aead_op, ad_buf, sizeof(ad_buf));
stream_cnt = 0; // Streaming block
out_total = 0;
while ((sizeof(cipher_buf) - (stream_cnt * stream_block_size)) > stream_block_size) {
ret = psa_aead_update(&aead_op,
cipher_buf + (stream_cnt * stream_block_size), stream_block_size,
plain_msg_buf + out_total, sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - out_total,
&out_len);
stream_cnt++;
out_total += out_len;
}
ret = psa_aead_update(&aead_op, // Last block
cipher_buf + (stream_cnt * stream_block_size),
sizeof(cipher_buf) - (stream_cnt * stream_block_size),
plain_msg_buf + out_total, sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - out_total,
&out_len);
out_total += out_len;
ret = psa_aead_verify(&aead_op, // Verify tag
plain_msg_buf + out_total, sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - out_total,
&out_len,
tag_buf, sizeof(tag_buf));
out_total += out_len;
// Destroy a volatile plain key for AES CCM
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
}AES GCM (Streaming)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t key_buf[] = {
0x5f, 0xe0, 0x1c, 0x4b, 0xaf, 0x01, 0xcb, 0xe0, 0x77, 0x96, 0xd5, 0xaa, 0xef, 0x6e, 0xc1, 0xf4,
0x51, 0x93, 0xa9, 0x8a, 0x22, 0x35, 0x94, 0xae, 0x4f, 0x0e, 0xf4, 0x95, 0x2e, 0x82, 0xe3, 0x30
};
uint8_t nonce_buf[] = {0xbd, 0x58, 0x73, 0x21, 0x56, 0x6c, 0x7f, 0x1a, 0x5d, 0xd8, 0x65, 0x2d};
uint8_t ad_buf[] = {
0x90, 0x13, 0x61, 0x78, 0x17, 0xdd, 0xa9, 0x47, 0xe1, 0x35, 0xee, 0x6d, 0xd3, 0x65, 0x33, 0x82
};
uint8_t plain_msg_buf[] = {
0x88, 0x1d, 0xc6, 0xc7, 0xa5, 0xd4, 0x50, 0x9f, 0x3c, 0x4b, 0xd2, 0xda, 0xab, 0x08, 0xf1, 0x65,
0xdd, 0xc2, 0x04, 0x48, 0x9a, 0xa8, 0x13, 0x45, 0x62, 0xa4, 0xea, 0xc3, 0xd0, 0xbc, 0xad, 0x79,
0x65, 0x84, 0x7b, 0x10, 0x27, 0x33, 0xbb, 0x63, 0xd1, 0xe5, 0xc5, 0x98, 0xec, 0xe0, 0xc3, 0xe5,
0xda, 0xdd, 0xdd
};
uint8_t cipher_buf[51];
uint8_t tag_buf[16];
size_t tag_len;
size_t out_len;
uint32_t out_total;
uint32_t stream_cnt;
uint32_t stream_block_size = 14; // Block size for streaming
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
psa_aead_operation_t aead_op;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a AES GCM key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_GCM);
// Import a volatile plain key for AES GCM
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, key_buf, sizeof(key_buf), &key_id);
// AES GCM stream encryption and decryption
// Expected ciphertext:
// 16 e3 75 b4 97 3b 33 9d 3f 74 6c 1c 5a 56 8b c7 52 6e 90 9d df f1 e1 9c 95 c9 4a 6c cf f2 10 c9
// a4 a4 06 79 de 57 60 c3 96 ac 0e 2c eb 12 34 f9 f5 fe 26
// Expected tag: ab d3 d2 6d 65 a6 27 5f 7a 4f 56 b4 22 ac ab 49
aead_op = psa_aead_operation_init();
ret = psa_aead_encrypt_setup(&aead_op, key_id, PSA_ALG_GCM);
ret = psa_aead_set_nonce(&aead_op, nonce_buf, sizeof(nonce_buf));
ret = psa_aead_update_ad(&aead_op, ad_buf, sizeof(ad_buf));
stream_cnt = 0; // Streaming block
out_total = 0;
while ((sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - (stream_cnt * stream_block_size)) > stream_block_size) {
ret = psa_aead_update(&aead_op,
plain_msg_buf + (stream_cnt * stream_block_size), stream_block_size,
cipher_buf + out_total, sizeof(cipher_buf) - out_total,
&out_len);
stream_cnt++;
out_total += out_len;
}
ret = psa_aead_update(&aead_op, // Last block
plain_msg_buf + (stream_cnt * stream_block_size),
sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - (stream_cnt * stream_block_size),
cipher_buf + out_total, sizeof(cipher_buf) - out_total,
&out_len);
out_total += out_len;
ret = psa_aead_finish(&aead_op, // Generate tag
cipher_buf + out_total, sizeof(cipher_buf) - out_total,
&out_len,
tag_buf, sizeof(tag_buf),
&tag_len);
out_total += out_len;
aead_op = psa_aead_operation_init();
ret = psa_aead_decrypt_setup(&aead_op, key_id, PSA_ALG_GCM);
ret = psa_aead_set_nonce(&aead_op, nonce_buf, sizeof(nonce_buf));
ret = psa_aead_update_ad(&aead_op, ad_buf, sizeof(ad_buf));
stream_cnt = 0; // Streaming block
out_total = 0;
while ((sizeof(cipher_buf) - (stream_cnt * stream_block_size)) > stream_block_size) {
ret = psa_aead_update(&aead_op,
cipher_buf + (stream_cnt * stream_block_size), stream_block_size,
plain_msg_buf + out_total, sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - out_total,
&out_len);
stream_cnt++;
out_total += out_len;
}
ret = psa_aead_update(&aead_op, // Last block
cipher_buf + (stream_cnt * stream_block_size),
sizeof(cipher_buf) - (stream_cnt * stream_block_size),
plain_msg_buf + out_total, sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - out_total,
&out_len);
out_total += out_len;
ret = psa_aead_verify(&aead_op, // Verify tag
plain_msg_buf + out_total, sizeof(plain_msg_buf) - out_total,
&out_len,
tag_buf, sizeof(tag_buf));
out_total += out_len;
// Destroy a volatile plain key for AES GCM
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
}PSA Crypto Platform Example
Click the View Project Documentation link to open the readme file.

The following table describes the implementation status of the PSA Crypto AEAD platform example.
Algorithm | Series 1 | Series 2 - VSE | Series 2 - HSE | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
AES CCM | Y | Y | Y | Series 1 devices do not support a 192-bit key. |
AES GCM | Y | Y | Y | Series 1 devices do not support a 192-bit key. |
CHACHA20_POLY1305 | Y | Y | Y | Hardware acceleration only on HSE-SVH devices. |
Notes:
The AEAD platform example uses default nonce (12-byte for GCM) and tag length (16-byte for CCM and GCM).
The multi-part AEAD operations are only available on GSDK v4.2.0 and higher.
The multi-part AEAD operations for CHACHA20_POLY1305 are not yet implemented.
The multi-part AEAD operations for a shortened tag length (AES CCM and GCM) are not yet implemented.
The multi-part GCM operations do not support non-12-byte nonce (GCM with Non-Recommended IV Lengths).
The AEAD platform example for multi-part AEAD operations is pending for fully-featured multi-part AEAD drivers.
Key Derivation#
A Key Derivation Function (KDF) derives one or many secret keys from a secret value such as a master key, a password, or a pass-phrase using a pseudo-random function. The typical usage of a key derivation function is to use a secret, such as a password or an ECDH shared secret, and a salt to produce a symmetric key and initialization vector (IV) for use with AES.
Algorithms
| Algorithm | Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|---|
HKDF (SHA-1) |
|
|
HKDF (SHA-2) |
• |
• |
PBKDF2 (SHA-1) |
|
|
PBKDF2 (SHA-2) |
• |
• |
PBKDF2 CMAC |
— |
|
ECDH + HKDF |
— |
|
Key Attributes in PSA Crypto
Algorithm | Key Type | Key Size in Bits | Key Usage Flag |
|---|---|---|---|
- PSA_ALG_HKDF(PSA_ALG_SHA_1) | PSA_KEY_TYPE_DERIVE | Multiple of 8 | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DERIVE |
- PSA_ALG_HKDF(PSA_ALG_SHA_224) | |||
- PSA_ALG_HKDF(PSA_ALG_SHA_256) | |||
- PSA_ALG_HKDF(PSA_ALG_SHA_384) | |||
- PSA_ALG_HKDF(PSA_ALG_SHA_512) | |||
- PSA_ALG_PBKDF2_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_1) | |||
- PSA_ALG_PBKDF2_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_224) | |||
- PSA_ALG_PBKDF2_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_256) | |||
- PSA_ALG_PBKDF2_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_384) | |||
- PSA_ALG_PBKDF2_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_512) | |||
PSA_ALG_PBKDF2_AES_CMAC_PRF_128 |
Security Software Components
Algorithm | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
PSA_ALG_HKDF(PSA_ALG_SHA_1) | HKDF and SHA-1 |
PSA_ALG_HKDF(PSA_ALG_SHA_224) | HKDF and SHA-224 |
PSA_ALG_HKDF(PSA_ALG_SHA_256) | HKDF and SHA-256 |
PSA_ALG_HKDF(PSA_ALG_SHA_384) | HKDF and SHA-384 |
PSA_ALG_HKDF(PSA_ALG_SHA_512) | HKDF and SHA-512 |
PSA_ALG_PBKDF2_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_1) | PBKDF2 and SHA-1 |
PSA_ALG_PBKDF2_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_224) | PBKDF2 and SHA-224 |
PSA_ALG_PBKDF2_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_256) | PBKDF2 and SHA-256 |
PSA_ALG_PBKDF2_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_384) | PBKDF2 and SHA-384 |
PSA_ALG_PBKDF2_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_512) | PBKDF2 and SHA-512 |
PSA_ALG_PBKDF2_AES_CMAC_PRF_128 | PBKDF2 |
PSA_ALG_KEY_AGREEMENT(PSA_ALG_ECDH, PSA_ALG_HKDF(hash_alg)) | ECDH and HKDF and SHA-X |
Note:
It should add the components for the derived key algorithm to implement the HKDF. For example, it requires the
CTR Modecomponent if the derived key algorithm isPSA_ALG_CTR.Refer to Key Agreement (ECDH) to add the ECDH components to derive the shared secret for the ECDH + HKDF algorithm (
PSA_ALG_KEY_AGREEMENT(PSA_ALG_ECDH, PSA_ALG_HKDF(hash_alg))).
Single-Part Functions
Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|
int mbedtls_hkdf(…) | psa_status_t sl_psa_key_derivation_single_shot(…) |
int mbedtls_pkcs5_pbkdf2_hmac(…) | psa_status_t sl_psa_key_derivation_single_shot(…) |
Note: The
sl_psa_key_derivation_single_shot(…)is a Silicon Labs custom API. It can only use on HSE-SVH devices.
Multi-Part Operations
Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|
— | psa_key_derivation_operation_t psa_key_derivation_operation_init(void) |
— | psa_status_t psa_key_derivation_setup(…) |
— | psa_status_t psa_key_derivation_get_capacity(…) |
— | psa_status_t psa_key_derivation_set_capacity(…) |
— | psa_status_t psa_key_derivation_input_bytes(…) |
— | psa_status_t psa_key_derivation_input_key(…) |
— | psa_status_t psa_key_derivation_output_bytes(…) |
— | psa_status_t psa_key_derivation_output_key(…) |
— | psa_status_t psa_key_derivation_abort(…) |
Note: The multi-part operation allows the data to be processed for KDF in fragments instead of all at once.
Quick Reference Examples HKDF (SHA-256)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t hkdf_ikm[] = {
0x0b, 0x0b, 0x0b, 0x0b, 0x0b, 0x0b, 0x0b, 0x0b, 0x0b, 0x0b, 0x0b, 0x0b, 0x0b, 0x0b, 0x0b, 0x0b,
0x0b, 0x0b, 0x0b, 0x0b, 0x0b, 0x0b
};
uint8_t hkdf_salt[] = {0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08, 0x09, 0x0a, 0x0b, 0x0c};
uint8_t hkdf_info[] = {0xf0, 0xf1, 0xf2, 0xf3, 0xf4, 0xf5, 0xf6, 0xf7, 0xf8, 0xf9};
uint8_t key_buf[32];
size_t key_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t master_key_id;
psa_key_id_t hkdf_key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
psa_key_derivation_operation_t kdf_op;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a volatile master plain key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_DERIVE);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_DERIVE);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_HKDF(PSA_ALG_SHA_256));
// Import a volatile master plain key
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, hkdf_ikm, sizeof(hkdf_ikm), &master_key_id);
// Set up attributes for a volatile derived plain key (exportable for verification)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES);
psa_set_key_bits(&key_attr, sizeof(key_buf) * 8);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_EXPORT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_CTR);
// Derive (HKDF SHA256) a volatile plain key for AES CTR
#if defined(SEMAILBOX_PRESENT) && (_SILICON_LABS_SECURITY_FEATURE == _SILICON_LABS_SECURITY_FEATURE_VAULT)
// Silicon Labs custom API for Secure Vault High devices
ret = sl_psa_key_derivation_single_shot(PSA_ALG_HKDF(PSA_ALG_SHA_256), master_key_id,
hkdf_info, sizeof(hkdf_info),
hkdf_salt, sizeof(hkdf_salt),
0, &key_attr, &hkdf_key_id);
#else
kdf_op = psa_key_derivation_operation_init();
ret = psa_key_derivation_setup(&kdf_op, PSA_ALG_HKDF(PSA_ALG_SHA_256));
ret = psa_key_derivation_set_capacity(&kdf_op, sizeof(key_buf));
ret = psa_key_derivation_input_bytes(&kdf_op, PSA_KEY_DERIVATION_INPUT_SALT, hkdf_salt, sizeof(hkdf_salt));
ret = psa_key_derivation_input_bytes(&kdf_op, PSA_KEY_DERIVATION_INPUT_INFO, hkdf_info, sizeof(hkdf_info));
ret = psa_key_derivation_input_key(&kdf_op, PSA_KEY_DERIVATION_INPUT_SECRET, master_key_id);
ret = psa_key_derivation_output_key(&key_attr, &kdf_op, &hkdf_key_id);
ret = psa_key_derivation_abort(&kdf_op);
#endif
// Export derived volatile plain key (expected value of HKDF SHA256):
// 3c b2 5f 25 fa ac d5 7a 90 43 4f 64 d0 36 2f 2a 2d 2d 0a 90 cf 1a 5a 4c 5d b0 2d 56 ec c4 c5 bf
ret = psa_export_key(hkdf_key_id, key_buf, sizeof(key_buf), &key_len);
// Destroy the master and derived keys
ret = psa_destroy_key(master_key_id);
ret = psa_destroy_key(hkdf_key_id);
}PBKDF2-HMAC-SHA256 (HSE-SVH only)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t pbkdf2_ikm[] = {0x70, 0x61, 0x73, 0x73, 0x77, 0x6f, 0x72, 0x64};
uint8_t pbkdf2_salt[] = {0x73, 0x61, 0x6c, 0x74};
uint8_t key_buf[32];
size_t key_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t master_key_id;
psa_key_id_t pbkdf2_key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a volatile master plain key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_DERIVE);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_DERIVE);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_PBKDF2_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_256));
// Import a volatile master plain key
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, pbkdf2_ikm, sizeof(pbkdf2_ikm), &master_key_id);
// Set up attributes for a volatile derived plain key (exportable for verification)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES);
psa_set_key_bits(&key_attr, sizeof(key_buf) * 8);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_EXPORT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_CTR);
// Derive (PBKDF2 SHA256 with 4096 iterations) a volatile plain key for AES CTR
// Silicon Labs custom API for Secure Vault High devices
ret = sl_psa_key_derivation_single_shot(PSA_ALG_PBKDF2_HMAC(PSA_ALG_SHA_256), master_key_id,
NULL, 0,
pbkdf2_salt, sizeof(pbkdf2_salt),
4096, &key_attr, &pbkdf2_key_id);
// Export derived volatile plain key (expected value of PBKDF2 SHA256 with 4096 iterations):
// c5 e4 78 d5 92 88 c8 41 aa 53 0d b6 84 5c 4c 8d 96 28 93 a0 01 ce 4e 11 a4 96 38 73 aa 98 13 4a
ret = psa_export_key(pbkdf2_key_id, key_buf, sizeof(key_buf), &key_len);
// Destroy the master and derived keys
ret = psa_destroy_key(master_key_id);
ret = psa_destroy_key(pbkdf2_key_id);
}Note: The PBKDF2-HMAC implementation of PSA Crypto is not yet available.
PBKDF2-AES-CMAC-PRF-128 (HSE-SVH only)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t pbkdf2_ikm[] = {0x4a, 0x30, 0x31, 0x4e, 0x4d, 0x45};
uint8_t pbkdf2_salt[] = {
0x54, 0x68, 0x72, 0x65, 0x61, 0x64, 0x37, 0x33, 0x35, 0x63, 0x38, 0x37, 0x62, 0x34, 0x4f, 0x70,
0x65, 0x6e, 0x54, 0x68, 0x72, 0x65, 0x61, 0x64, 0x44, 0x65, 0x6d, 0x6f
};
uint8_t key_buf[16];
size_t key_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t master_key_id;
psa_key_id_t pbkdf2_key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a volatile master plain key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_DERIVE);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_DERIVE);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_PBKDF2_AES_CMAC_PRF_128);
// Import a volatile master plain key
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, pbkdf2_ikm, sizeof(pbkdf2_ikm), &master_key_id);
// Set up attributes for a volatile derived plain key (exportable for verification)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES);
psa_set_key_bits(&key_attr, sizeof(key_buf) * 8);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_EXPORT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_CTR);
// Derive (PBKDF2 AES_CMAC_PRF_128 with 16384 iterations) a volatile plain key for AES CTR
// Silicon Labs custom API for Secure Vault High devices
ret = sl_psa_key_derivation_single_shot(PSA_ALG_PBKDF2_AES_CMAC_PRF_128, master_key_id,
NULL, 0,
pbkdf2_salt, sizeof(pbkdf2_salt),
16384, &key_attr, &pbkdf2_key_id);
// Export derived volatile plain key (expected value of PBKDF2 AES_CMAC_PRF_128 with 16384 iterations):
// 8b 27 be ed 7e 7a 4d d6 c5 31 38 c8 79 a8 e3 3c
ret = psa_export_key(pbkdf2_key_id, key_buf, sizeof(key_buf), &key_len);
// Destroy the master and derived keys
ret = psa_destroy_key(master_key_id);
ret = psa_destroy_key(pbkdf2_key_id);
}Note:
The PBKDF2-AES-CMAC-PRF-128 implementation of PSA Crypto is not yet available.
EFR32xG21B (HSE-SVH) devices do not support PBKDF2-AES-CMAC-PRF-128.
ECDH and HKDF
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t client_private_key[] = {
0xc8, 0x8f, 0x01, 0xf5, 0x10, 0xd9, 0xac, 0x3f, 0x70, 0xa2, 0x92, 0xda, 0xa2, 0x31, 0x6d, 0xe5,
0x44, 0xe9, 0xaa, 0xb8, 0xaf, 0xe8, 0x40, 0x49, 0xc6, 0x2a, 0x9c, 0x57, 0x86, 0x2d, 0x14, 0x33
};
uint8_t client_public_key[] = { // Uncompressed point format
0x04, 0xda, 0xd0, 0xb6, 0x53, 0x94, 0x22, 0x1c, 0xf9, 0xb0, 0x51, 0xe1, 0xfe, 0xca, 0x57, 0x87, 0xd0,
0x98, 0xdf, 0xe6, 0x37, 0xfc, 0x90, 0xb9, 0xef, 0x94, 0x5d, 0x0c, 0x37, 0x72, 0x58, 0x11, 0x80,
0x52, 0x71, 0xa0, 0x46, 0x1c, 0xdb, 0x82, 0x52, 0xd6, 0x1f, 0x1c, 0x45, 0x6f, 0xa3, 0xe5, 0x9a,
0xb1, 0xf4, 0x5b, 0x33, 0xac, 0xcf, 0x5f, 0x58, 0x38, 0x9e, 0x05, 0x77, 0xb8, 0x99, 0x0b, 0xb3
};
uint8_t server_private_key[] = {
0xc6, 0xef, 0x9c, 0x5d, 0x78, 0xae, 0x01, 0x2a, 0x01, 0x11, 0x64, 0xac, 0xb3, 0x97, 0xce, 0x20,
0x88, 0x68, 0x5d, 0x8f, 0x06, 0xbf, 0x9b, 0xe0, 0xb2, 0x83, 0xab, 0x46, 0x47, 0x6b, 0xee, 0x53
};
uint8_t server_public_key[] = { // Uncompressed point format
0x04, 0xd1, 0x2d, 0xfb, 0x52, 0x89, 0xc8, 0xd4, 0xf8, 0x12, 0x08, 0xb7, 0x02, 0x70, 0x39, 0x8c, 0x34,
0x22, 0x96, 0x97, 0x0a, 0x0b, 0xcc, 0xb7, 0x4c, 0x73, 0x6f, 0xc7, 0x55, 0x44, 0x94, 0xbf, 0x63,
0x56, 0xfb, 0xf3, 0xca, 0x36, 0x6c, 0xc2, 0x3e, 0x81, 0x57, 0x85, 0x4c, 0x13, 0xc5, 0x8d, 0x6a,
0xac, 0x23, 0xf0, 0x46, 0xad, 0xa3, 0x0f, 0x83, 0x53, 0xe7, 0x4f, 0x33, 0x03, 0x98, 0x72, 0xab
};
uint8_t hkdf_salt[] = {0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08, 0x09, 0x0a, 0x0b, 0x0c};
uint8_t hkdf_info[] = {0xf0, 0xf1, 0xf2, 0xf3, 0xf4, 0xf5, 0xf6, 0xf7, 0xf8, 0xf9};
uint8_t key_buf[32];
size_t key_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t master_key_id;
psa_key_id_t hkdf_key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
psa_key_derivation_operation_t kdf_op;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a volatile master plain key (algorithm for ECDH and HKDF)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_ECC_KEY_PAIR(PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1));
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_DERIVE);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_KEY_AGREEMENT(PSA_ALG_ECDH, PSA_ALG_HKDF(PSA_ALG_SHA_256)));
// Import a volatile master plain key (client private key)
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, client_private_key, sizeof(client_private_key),
&master_key_id);
// Set up attributes for a volatile derived plain key (exportable for verification)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES);
psa_set_key_bits(&key_attr, sizeof(key_buf) * 8);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_EXPORT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_CTR);
// Derive (HKDF SHA256) a volatile plain key from ECDH shared secret (server public key) for AES CTR
kdf_op = psa_key_derivation_operation_init();
ret = psa_key_derivation_setup(&kdf_op, PSA_ALG_KEY_AGREEMENT(PSA_ALG_ECDH, PSA_ALG_HKDF(PSA_ALG_SHA_256)));
ret = psa_key_derivation_set_capacity(&kdf_op, sizeof(key_buf));
ret = psa_key_derivation_input_bytes(&kdf_op, PSA_KEY_DERIVATION_INPUT_SALT, hkdf_salt, sizeof(hkdf_salt));
ret = psa_key_derivation_input_bytes(&kdf_op, PSA_KEY_DERIVATION_INPUT_INFO, hkdf_info, sizeof(hkdf_info));
ret = psa_key_derivation_key_agreement(&kdf_op, PSA_KEY_DERIVATION_INPUT_SECRET, master_key_id, server_public_key,
sizeof(server_public_key));
ret = psa_key_derivation_output_key(&key_attr, &kdf_op, &hkdf_key_id);
ret = psa_key_derivation_abort(&kdf_op);
// Export derived volatile plain key (client shared secret):
// B7 CA BD A7 42 60 DE D5 4C 4C 11 FA BC A3 56 4B 77 35 CC 9F 89 E9 BF E8 08 24 8A F3 54 99 B0 55
ret = psa_export_key(hkdf_key_id, key_buf, sizeof(key_buf), &key_len);
// Destroy the master and derived keys
ret = psa_destroy_key(master_key_id);
ret = psa_destroy_key(hkdf_key_id);
// Set up attributes for a volatile master plain key (algorithm for ECDH and HKDF)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_ECC_KEY_PAIR(PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1));
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_DERIVE);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_KEY_AGREEMENT(PSA_ALG_ECDH, PSA_ALG_HKDF(PSA_ALG_SHA_256)));
// Import a volatile master plain key (server private key)
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, server_private_key, sizeof(server_private_key),
&master_key_id);
// Set up attributes for a volatile derived plain key (exportable for verification)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_AES);
psa_set_key_bits(&key_attr, sizeof(key_buf) * 8);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_EXPORT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_ENCRYPT | PSA_KEY_USAGE_DECRYPT);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_CTR);
// Derive (HKDF SHA256) a volatile plain key from ECDH shared secret (client public key) for AES CTR
kdf_op = psa_key_derivation_operation_init();
ret = psa_key_derivation_setup(&kdf_op, PSA_ALG_KEY_AGREEMENT(PSA_ALG_ECDH, PSA_ALG_HKDF(PSA_ALG_SHA_256)));
ret = psa_key_derivation_set_capacity(&kdf_op, sizeof(key_buf));
ret = psa_key_derivation_input_bytes(&kdf_op, PSA_KEY_DERIVATION_INPUT_SALT, hkdf_salt, sizeof(hkdf_salt));
ret = psa_key_derivation_input_bytes(&kdf_op, PSA_KEY_DERIVATION_INPUT_INFO, hkdf_info, sizeof(hkdf_info));
ret = psa_key_derivation_key_agreement(&kdf_op, PSA_KEY_DERIVATION_INPUT_SECRET, master_key_id, client_public_key,
sizeof(client_public_key));
ret = psa_key_derivation_output_key(&key_attr, &kdf_op, &hkdf_key_id);
ret = psa_key_derivation_abort(&kdf_op);
// Export derived volatile plain key (server shared secret):
// B7 CA BD A7 42 60 DE D5 4C 4C 11 FA BC A3 56 4B 77 35 CC 9F 89 E9 BF E8 08 24 8A F3 54 99 B0 55
ret = psa_export_key(hkdf_key_id, key_buf, sizeof(key_buf), &key_len);
// Destroy the master and derived keys
ret = psa_destroy_key(master_key_id);
ret = psa_destroy_key(hkdf_key_id);
}PSA Crypto Platform Example
Click the View Project Documentation link to open the readme file.

The following table describes the implementation status of the PSA Crypto KDF platform example.
Algorithm | Series 1 | Series 2 - VSE | Series 2 - HSE | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
HKDF | Y | Y | Y | Hardware acceleration only on HSE-SVH devices with Silicon Labs custom API. |
ECDH + HKDF | Y | Y | Y | Hardware acceleration (HKDF) only on HSE-SVH devices with Silicon Labs custom API. |
Note:
The PBKDF2 implementation of PSA Crypto is not yet available.
The ECDH + HKDF algorithm does not apply to the wrapped key.
Asymmetric Cryptographic Operation#
Asymmetric Signature (ECDSA and EdDSA)#
In modern cryptography, the Elliptic-Curve-based signatures (like ECDSA and EdDSA) are widely used because of shorter key lengths, shorter signature lengths, higher security levels (for the same key length), and better performance.
The Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) is a cryptographically secure digital signature scheme based on the Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC). The Edwards-curve Digital Signature Algorithm (EdDSA) is a fast digital signature algorithm, using elliptic curves in Edwards form (like Ed25519 and Ed448).
Algorithms
| Algorithm | Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|---|
ECDSA (SHA-1) |
— |
|
ECDSA (SHA-2) |
— |
• |
ECDSA (Any hash algorithm) |
— |
|
ECDSA (No hashing) |
— |
|
EdDSA |
— |
|
Note: The hash-and-sign algorithms
(PSA_ALG_ECDSA(hash_alg)andPSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_ANY_HASH))include the hashing step for ECDSA.
Key Attributes in PSA Crypto
| Algorithm | Key Type | Key Size in Bits | Key Usage Flag |
|---|---|---|---|
PSA_ALG_ECDSA_ANY |
PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1 |
secp192r1 : 192 secp224r1 : 224 secp256r1 : 256 secp384r1 : 384 secp521r1 : 521 |
PSA_KEY_USAGE_SIGN_HASHPSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_HASH
|
PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_K1 |
secp256k1 : 256 | ||
PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_1)PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_224)PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_256)PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_384)PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_512)PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_ANY_HASH)
|
PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1 |
secp192r1 : 192 secp224r1 : 224 secp256r1 : 256 secp384r1 : 384 secp521r1 : 521 |
PSA_KEY_USAGE_SIGN_MESSAGEPSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_MESSAGE
|
PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_K1 |
secp256k1 : 256 | ||
PSA_ALG_PURE_EDDSA |
PSA_ECC_FAMILY_TWISTED_EDWARDS |
Edwards25519 : 255 |
PSA_KEY_USAGE_SIGN_MESSAGEPSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_MESSAGE
|
Security Software Components
Algorithm | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
PSA_ALG_ECDSA_ANY | ECDSA |
PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_1) | ECDSA and SHA-1 |
PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_224) | ECDSA and SHA-224 |
PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_256) | ECDSA and SHA-256 |
PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_384) | ECDSA and SHA-384 |
PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_512) | ECDSA and SHA-512 |
PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_ANY_HASH) | ECDSA and SHA-X |
Algorithm | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
PSA_ALG_PURE_EDDSA | EdDSA |
PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1 | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
secp192r1 | secp192r1 |
secp224r1 | secp224r1 |
secp256r1 | secp256r1 |
secp384r1 | secp384r1 |
secp521r1 | secp521r1 |
PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_K1 | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
secp256k1 | secp256k1 |
PSA_ECC_FAMILY_TWISTED_EDWARDS | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
Edwards25519 | edwards25519 |
Built-in Key | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
secp256r1 keys in SE OTP | Built-In Keys |
Functions
| Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|
|
Hash-and-sign |
Hash-and-sign |
|
Precomputed hash |
Precomputed hash |
Quick Reference Examples
ECDSA on secp256r1 (Precomputed Hash)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t hash_data[] = {
0x24, 0x8d, 0x6a, 0x61, 0xd2, 0x06, 0x38, 0xb8, 0xe5, 0xc0, 0x26, 0x93, 0x0c, 0x3e, 0x60, 0x39,
0xa3, 0x3c, 0xe4, 0x59, 0x64, 0xff, 0x21, 0x67, 0xf6, 0xec, 0xed, 0xd4, 0x19, 0xdb, 0x06, 0xc1
};
uint8_t public_key[65]; // Uncompressed point format
size_t pubkey_len;
uint8_t signature_buf[64];
size_t signature_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a volatile private plain key (secp256r1)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_ECC_KEY_PAIR(PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1));
psa_set_key_bits(&key_attr, 256);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_SIGN_HASH | PSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_HASH);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_ECDSA_ANY);
// Generate a random volatile private plain key
ret = psa_generate_key(&key_attr, &key_id);
// Sign a hash with a volatile private plain key
ret = psa_sign_hash(key_id,
PSA_ALG_ECDSA_ANY,
hash_data,
sizeof(hash_data),
signature_buf,
sizeof(signature_buf),
&signature_len);
// Verify a signature with a volatile private plain key
ret = psa_verify_hash(key_id,
PSA_ALG_ECDSA_ANY,
hash_data,
sizeof(hash_data),
signature_buf,
signature_len);
// Export a public key from a volatile private plain key and then destroy the private key
ret = psa_export_public_key(key_id,
public_key,
sizeof(public_key),
&pubkey_len);
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
// Set up attributes for a public key (secp256r1)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_ECC_PUBLIC_KEY(PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1));
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_HASH);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_ECDSA_ANY);
// Import a public key
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, public_key, sizeof(public_key), &key_id);
// Verify a signature with a public key and then destroy the public key
ret = psa_verify_hash(key_id,
PSA_ALG_ECDSA_ANY,
hash_data,
sizeof(hash_data),
signature_buf,
signature_len);
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
}ECDSA on secp256r1 (Hash-and-Sign)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t ecdsa_msg[] = {
0xdd, 0xaf, 0x35, 0xa1, 0x93, 0x61, 0x7a, 0xba, 0xcc, 0x41, 0x73, 0x49, 0xae, 0x20, 0x41, 0x31,
0x12, 0xe6, 0xfa, 0x4e, 0x89, 0xa9, 0x7e, 0xa2, 0x0a, 0x9e, 0xee, 0xe6, 0x4b, 0x55, 0xd3, 0x9a,
0x21, 0x92, 0x99, 0x2a, 0x27, 0x4f, 0xc1, 0xa8, 0x36, 0xba, 0x3c, 0x23, 0xa3, 0xfe, 0xeb, 0xbd,
0x45, 0x4d, 0x44, 0x23, 0x64, 0x3c, 0xe8, 0x0e, 0x2a, 0x9a, 0xc9, 0x4f, 0xa5, 0x4c, 0xa4, 0x9f
};
uint8_t public_key[65]; // Uncompressed point format
size_t pubkey_len;
uint8_t signature_buf[64];
size_t signature_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a volatile private plain key (secp256r1)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_ECC_KEY_PAIR(PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1));
psa_set_key_bits(&key_attr, 256);
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_SIGN_MESSAGE | PSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_MESSAGE);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_ANY_HASH));
// Generate a random volatile private plain key
ret = psa_generate_key(&key_attr, &key_id);
// Hash-and-Sign (SHA-256) a message with a volatile private plain key
ret = psa_sign_message(key_id,
PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_256),
ecdsa_msg,
sizeof(ecdsa_msg),
signature_buf,
sizeof(signature_buf),
&signature_len);
// Hash (SHA-256) a message and verify a signature with a volatile private plain key
ret = psa_verify_message(key_id,
PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_256),
ecdsa_msg,
sizeof(ecdsa_msg),
signature_buf,
signature_len);
// Export a public key from a volatile private plain key and then destroy the private key
ret = psa_export_public_key(key_id,
public_key,
sizeof(public_key),
&pubkey_len);
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
// Set up attributes for a public key (secp256r1)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_ECC_PUBLIC_KEY(PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1));
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_MESSAGE);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_ANY_HASH));
// Import a public key
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, public_key, sizeof(public_key), &key_id);
// Hash (SHA-256) and verify a signature with a public key and then destroy the public key
ret = psa_verify_message(key_id,
PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_256),
ecdsa_msg,
sizeof(ecdsa_msg),
signature_buf,
signature_len);
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
}ECDSA with Built-in Private Device Key (HSE-SVH only)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
#if (_SILICON_LABS_SECURITY_FEATURE == _SILICON_LABS_SECURITY_FEATURE_VAULT)
uint8_t hash_data[] = {
0x24, 0x8d, 0x6a, 0x61, 0xd2, 0x06, 0x38, 0xb8, 0xe5, 0xc0, 0x26, 0x93, 0x0c, 0x3e, 0x60, 0x39,
0xa3, 0x3c, 0xe4, 0x59, 0x64, 0xff, 0x21, 0x67, 0xf6, 0xec, 0xed, 0xd4, 0x19, 0xdb, 0x06, 0xc1
};
uint8_t public_key[65]; // Uncompressed point format
size_t pubkey_len;
uint8_t signature_buf[64];
size_t signature_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Sign a hash with a built-in private device key
ret = psa_sign_hash(SL_SE_BUILTIN_KEY_APPLICATION_ATTESTATION_ID,
PSA_ALG_ECDSA_ANY,
hash_data,
sizeof(hash_data),
signature_buf,
sizeof(signature_buf),
&signature_len);
// Verify a signature with a built-in private device key
ret = psa_verify_hash(SL_SE_BUILTIN_KEY_APPLICATION_ATTESTATION_ID,
PSA_ALG_ECDSA_ANY,
hash_data,
sizeof(hash_data),
signature_buf,
signature_len);
// Export a built-in public device key
ret = psa_export_public_key(SL_SE_BUILTIN_KEY_APPLICATION_ATTESTATION_ID,
public_key,
sizeof(public_key),
&pubkey_len);
// Set up attributes for a public device key
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_ECC_PUBLIC_KEY(PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1));
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_HASH);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_ECDSA_ANY);
// Import a public device key
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, public_key, sizeof(public_key), &key_id);
// Verify a signature with a public device key
ret = psa_verify_hash(key_id,
PSA_ALG_ECDSA_ANY,
hash_data,
sizeof(hash_data),
signature_buf,
signature_len);
// Destroy a public device key
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
#endif
}EdDSA on Ed25519 (HSE only)
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
#if defined(SEMAILBOX_PRESENT)
uint8_t eddsa_msg[] = {
0xdd, 0xaf, 0x35, 0xa1, 0x93, 0x61, 0x7a, 0xba, 0xcc, 0x41, 0x73, 0x49, 0xae, 0x20, 0x41, 0x31,
0x12, 0xe6, 0xfa, 0x4e, 0x89, 0xa9, 0x7e, 0xa2, 0x0a, 0x9e, 0xee, 0xe6, 0x4b, 0x55, 0xd3, 0x9a,
0x21, 0x92, 0x99, 0x2a, 0x27, 0x4f, 0xc1, 0xa8, 0x36, 0xba, 0x3c, 0x23, 0xa3, 0xfe, 0xeb, 0xbd,
0x45, 0x4d, 0x44, 0x23, 0x64, 0x3c, 0xe8, 0x0e, 0x2a, 0x9a, 0xc9, 0x4f, 0xa5, 0x4c, 0xa4, 0x9f
};
uint8_t ed25519_private[] = {
0x83, 0x3f, 0xe6, 0x24, 0x09, 0x23, 0x7b, 0x9d, 0x62, 0xec, 0x77, 0x58, 0x75, 0x20, 0x91, 0x1e,
0x9a, 0x75, 0x9c, 0xec, 0x1d, 0x19, 0x75, 0x5b, 0x7d, 0xa9, 0x01, 0xb9, 0x6d, 0xca, 0x3d, 0x42
};
uint8_t ed25519_public[] = {
0xec, 0x17, 0x2b, 0x93, 0xad, 0x5e, 0x56, 0x3b, 0xf4, 0x93, 0x2c, 0x70, 0xe1, 0x24, 0x50, 0x34,
0xc3, 0x54, 0x67, 0xef, 0x2e, 0xfd, 0x4d, 0x64, 0xeb, 0xf8, 0x19, 0x68, 0x34, 0x67, 0xe2, 0xbf
};
uint8_t signature_buf[64];
size_t signature_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a volatile private plain key (Ed25519)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_ECC_KEY_PAIR(PSA_ECC_FAMILY_TWISTED_EDWARDS));
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_SIGN_MESSAGE | PSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_MESSAGE);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_PURE_EDDSA);
// Import a volatile private plain key
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, ed25519_private, sizeof(ed25519_private), &key_id);
// Hash-and-Sign a message with a volatile private plain key (expected EdDSA signature):
// dc 2a 44 59 e7 36 96 33 a5 2b 1b f2 77 83 9a 00 20 10 09 a3 ef bf 3e cb 69 be a2 18 6c 26 b5 89
// 09 35 1f c9 ac 90 b3 ec fd fb c7 c6 64 31 e0 30 3d ca 17 9c 13 8a c1 7a d9 be f1 17 73 31 a7 04
ret = psa_sign_message(key_id,
PSA_ALG_PURE_EDDSA,
eddsa_msg,
sizeof(eddsa_msg),
signature_buf,
sizeof(signature_buf),
&signature_len);
// Destroy a volatile private plain key
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
// Set up attributes for a public key (Ed25519)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_ECC_PUBLIC_KEY(PSA_ECC_FAMILY_TWISTED_EDWARDS));
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_MESSAGE);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_PURE_EDDSA);
// Import a public key
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, ed25519_public, sizeof(ed25519_public), &key_id);
// Hash a message and verify the signature with a public key
ret = psa_verify_message(key_id,
PSA_ALG_PURE_EDDSA,
eddsa_msg,
sizeof(eddsa_msg),
signature_buf,
signature_len);
// Destroy a public key
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
#endif
}PSA Crypto Platform Example
Click the View Project Documentation link to open the readme file.

The following table describes the implementation status of the PSA Crypto DSA platform example.
ECC Key | Series 1 | Series 2 - VSE | Series 2 - HSE | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
secp192r1 | Y | Y | Y | — |
secp256r1 | Y | Y | Y | — |
secp384r1 | Y | Y | Y | Hardware acceleration only on HSE-SVH devices. |
secp521r1 | Y | Y | Y | Hardware acceleration only on HSE-SVH devices. |
Edwards25519 | — | — | Y | Only on HSE devices with hardware acceleration. |
Public Sign Key | — | — | Y | — |
Public Command Key | — | — | Y | — |
Private Device Key | — | — | Y | Only on HSE-SVH devices. |
Note:
This example does not include secp224r1 and secp256k1. The secp256k1 ECDSA on HSE devices is not yet implemented.
The PSA Crypto does not yet support software fallback on the Edwards25519.
The HSE-SVM devices require SE firmware v1.2.11 or higher (EFR32xG21) and v2.1.7 or higher (other HSE devices) to support hardware acceleration on Edwards25519. This feature also requires GSDK v4.0.1 or higher.
Key Agreement (ECDH)#
The Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman (ECDH) is an anonymous key agreement protocol that allows two parties, each having an elliptic-curve private-public key pair, to establish a shared secret over an insecure channel.
Algorithms
Algorithm | Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|---|
ECDH | — | PSA_ALG_ECDH |
ECDH and HKDF | — | PSA_ALG_KEY_AGREEMENT(PSA_ALG_ECDH, PSA_ALG_HKDF(hash_alg)) |
Key Attributes in PSA Crypto
| Algorithm | Key Type | Key Size in Bits | Key Usage Flag |
|---|---|---|---|
PSA_ALG_ECDH |
PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1 |
• secp192r1 : 192 |
PSA_KEY_USAGE_DERIVE |
PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_K1 |
secp256k1 : 256 |
||
PSA_ECC_FAMILY_MONTGOMERY |
• Curve25519 : 255 |
Security Software Components
Algorithm | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
PSA_ALG_ECDH | ECDH |
PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1 | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
secp192r1 | secp192r1 |
secp224r1 | secp224r1 |
secp256r1 | secp256r1 |
secp384r1 | secp384r1 |
secp521r1 | secp521r1 |
PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_K1 | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
secp256k1 | secp256k1 |
PSA_ECC_FAMILY_MONTGOMERY | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
Curve25519 | Curve25519 |
Curve448 | Curve448 |
Functions
Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|
int mbedtls_ecdh_compute_shared(…) | psa_status_t psa_raw_key_agreement(…) |
— | psa_status_t psa_key_derivation_key_agreement(…) |
Note: For the
psa_key_derivation_key_agreement(…)function, refer to the PSA Crypto KDF quick reference (ECDH and HKDF) and platform examples for details.
Quick Reference Examples ECDH on secp256r1
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t client_private_key[] = {
0xc8, 0x8f, 0x01, 0xf5, 0x10, 0xd9, 0xac, 0x3f, 0x70, 0xa2, 0x92, 0xda, 0xa2, 0x31, 0x6d, 0xe5,
0x44, 0xe9, 0xaa, 0xb8, 0xaf, 0xe8, 0x40, 0x49, 0xc6, 0x2a, 0x9c, 0x57, 0x86, 0x2d, 0x14, 0x33
};
uint8_t client_public_key[] = { // Uncompressed point format
0x04, 0xda, 0xd0, 0xb6, 0x53, 0x94, 0x22, 0x1c, 0xf9, 0xb0, 0x51, 0xe1, 0xfe, 0xca, 0x57, 0x87, 0xd0,
0x98, 0xdf, 0xe6, 0x37, 0xfc, 0x90, 0xb9, 0xef, 0x94, 0x5d, 0x0c, 0x37, 0x72, 0x58, 0x11, 0x80,
0x52, 0x71, 0xa0, 0x46, 0x1c, 0xdb, 0x82, 0x52, 0xd6, 0x1f, 0x1c, 0x45, 0x6f, 0xa3, 0xe5, 0x9a,
0xb1, 0xf4, 0x5b, 0x33, 0xac, 0xcf, 0x5f, 0x58, 0x38, 0x9e, 0x05, 0x77, 0xb8, 0x99, 0x0b, 0xb3
};
uint8_t server_private_key[] = {
0xc6, 0xef, 0x9c, 0x5d, 0x78, 0xae, 0x01, 0x2a, 0x01, 0x11, 0x64, 0xac, 0xb3, 0x97, 0xce, 0x20,
0x88, 0x68, 0x5d, 0x8f, 0x06, 0xbf, 0x9b, 0xe0, 0xb2, 0x83, 0xab, 0x46, 0x47, 0x6b, 0xee, 0x53
};
uint8_t server_public_key[] = { // Uncompressed point format
0x04, 0xd1, 0x2d, 0xfb, 0x52, 0x89, 0xc8, 0xd4, 0xf8, 0x12, 0x08, 0xb7, 0x02, 0x70, 0x39, 0x8c, 0x34,
0x22, 0x96, 0x97, 0x0a, 0x0b, 0xcc, 0xb7, 0x4c, 0x73, 0x6f, 0xc7, 0x55, 0x44, 0x94, 0xbf, 0x63,
0x56, 0xfb, 0xf3, 0xca, 0x36, 0x6c, 0xc2, 0x3e, 0x81, 0x57, 0x85, 0x4c, 0x13, 0xc5, 0x8d, 0x6a,
0xac, 0x23, 0xf0, 0x46, 0xad, 0xa3, 0x0f, 0x83, 0x53, 0xe7, 0x4f, 0x33, 0x03, 0x98, 0x72, 0xab
};
// Expected shared secret:
// d6 84 0f 6b 42 f6 ed af d1 31 16 e0 e1 25 65 20 2f ef 8e 9e ce 7d ce 03 81 24 64 d0 4b 94 42 de
uint8_t shared_secret_buf[32];
size_t shared_secret_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a volatile client private plain key (secp256r1)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_ECC_KEY_PAIR(PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1));
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_DERIVE);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_ECDH);
// Import a volatile client private plain key
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, client_private_key, sizeof(client_private_key), &key_id);
// Perform a key agreement with the server public key and then destroy the client private key
ret = psa_raw_key_agreement(PSA_ALG_ECDH,
key_id,
server_public_key,
sizeof(server_public_key),
shared_secret_buf,
sizeof(shared_secret_buf),
&shared_secret_len);
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
// Set up attributes for a volatile server private plain key (secp256r1)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_ECC_KEY_PAIR(PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1));
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_DERIVE);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_ECDH);
// Import a volatile server private plain key
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, server_private_key, sizeof(server_private_key), &key_id);
// Perform a key agreement with the client public key and then destroy the server private key
ret = psa_raw_key_agreement(PSA_ALG_ECDH,
key_id,
client_public_key,
sizeof(client_public_key),
shared_secret_buf,
sizeof(shared_secret_buf),
&shared_secret_len);
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
}ECDH on Curve25519
#include "psa/crypto.h"
void app_process_action(void)
{
uint8_t client_private_key[] = {
0xB0, 0x76, 0x51, 0xEA, 0x20, 0xF0, 0x28, 0xA8,0x16, 0xEE, 0x01, 0xB0, 0xD1, 0x06, 0x2A, 0x7C,
0x81, 0x58, 0xE8, 0x84, 0xE9, 0xBC, 0xC6, 0x1C, 0x5D, 0xAB, 0xDB, 0x4E, 0x38, 0x2F, 0x96, 0x69,
};
uint8_t client_public_key[] = {
0x87, 0xD8, 0x6B, 0xDA, 0xAC, 0x38, 0x3C, 0x85, 0xA6, 0xBC, 0xF8, 0xFC, 0xC6, 0x26, 0xD6, 0x14,
0x36, 0xE4, 0x8F, 0xDB, 0xFA, 0x5A, 0x45, 0xFE, 0x0C, 0x9E, 0xA8, 0x4B, 0x35, 0x3E, 0xF1, 0x37,
};
uint8_t server_private_key[] = {
0x98, 0x2E, 0xB6, 0x7D, 0x0A, 0x01, 0x57, 0x90, 0xE1, 0x45, 0xF3, 0x67, 0xF6, 0xDA, 0xA6, 0x44,
0x2C, 0x87, 0xC0, 0xED, 0x3C, 0x36, 0x71, 0xA6, 0x89, 0xC7, 0x49, 0xAC, 0x0D, 0xFE, 0x43, 0x6E,
};
uint8_t server_public_key[] = {
0x0C, 0x04, 0x10, 0x5B, 0xE8, 0x7C, 0xAB, 0x37, 0x21, 0x15, 0x7A, 0x8D, 0x49, 0x85, 0x8C, 0x7A,
0x9F, 0xC1, 0x46, 0xDA, 0xCC, 0x96, 0xEF, 0x6E, 0xD4, 0xDA, 0x71, 0xBF, 0xED, 0x32, 0x0D, 0x76,
};
// Expected shared secret:
// F2 E6 0E 1C B7 64 BC 48 F2 9D BB 12 FB 12 17 31 32 1D 79 AF 0A 9F AB AD 34 05 A2 07 39 9C 5F 15
uint8_t shared_secret_buf[32];
size_t shared_secret_len;
psa_status_t ret;
psa_key_id_t key_id;
psa_key_attributes_t key_attr;
ret = psa_crypto_init();
// Set up attributes for a volatile client private plain key (Curve25519)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_ECC_KEY_PAIR(PSA_ECC_FAMILY_MONTGOMERY));
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_DERIVE);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_ECDH);
// Import a volatile client private plain key
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, client_private_key, sizeof(client_private_key), &key_id);
// Perform a key agreement with server public key
ret = psa_raw_key_agreement(PSA_ALG_ECDH,
key_id,
server_public_key,
sizeof(server_public_key),
shared_secret_buf,
sizeof(shared_secret_buf),
&shared_secret_len);
// Destroy the client private key
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
// Set up attributes for a volatile server private plain key (Curve25519)
key_attr = psa_key_attributes_init();
psa_set_key_type(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_TYPE_ECC_KEY_PAIR(PSA_ECC_FAMILY_MONTGOMERY));
psa_set_key_usage_flags(&key_attr, PSA_KEY_USAGE_DERIVE);
psa_set_key_algorithm(&key_attr, PSA_ALG_ECDH);
// Import a volatile server private plain key
ret = psa_import_key(&key_attr, server_private_key, sizeof(server_private_key), &key_id);
// Perform a key agreement with client public key
ret = psa_raw_key_agreement(PSA_ALG_ECDH,
key_id,
client_public_key,
sizeof(client_public_key),
shared_secret_buf,
sizeof(shared_secret_buf),
&shared_secret_len);
// Destroy the server private key
ret = psa_destroy_key(key_id);
}PSA Crypto Platform Example
Click the View Project Documentation link to open the readme file.

The following table describes the implementation status of the PSA Crypto ECDH platform example.
ECC Key | Series 1 | Series 2 - VSE | Series 2 - HSE | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
secp192r1 | Y | Y | Y | — |
secp256r1 | Y | Y | Y | — |
secp384r1 | Y | Y | Y | Hardware acceleration only on HSE-SVH devices. |
secp521r1 | Y | Y | Y | Hardware acceleration only on HSE-SVH devices. |
Curve25519 | Y | Y | Y | Hardware acceleration only on HSE devices. |
Curve448 | — | — | Y | Only on HSE-SVH devices with hardware acceleration. |
Note:
This example does not include secp224r1 and secp256k1. The secp256k1 ECDH on HSE devices is not yet implemented.
The PSA Crypto does not yet support software fallback on the Curve448.
The HSE-SVM devices require SE firmware v1.2.11 or higher (EFR32xG21) and v2.1.7 or higher (other HSE devices) to support hardware acceleration on Curve25519. This feature also requires GSDK v4.0.1 or higher.
X.509 Certificate#
An X.509 certificate is a digital certificate that uses the widely accepted international X.509 public key infrastructure (PKI) standard to verify that a public key belongs to the user, computer, or service identity contained within the certificate.
An X.509 certificate contains a public key and an identity (a hostname, an organization, an individual). It is either signed by a certificate authority or self-signed. When a certificate is signed by a trusted certificate authority or validated by other means, someone holding that certificate can rely on the public key it contains to establish secure communications with another party or validate documents digitally signed by the corresponding private key.
Algorithms
| Algorithm | Mbed TLS | PSA Crypto |
|---|---|---|
ECDSA (SHA-2) |
— |
PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_224) |
Key Attributes in PSA Crypto
Algorithm | Key Type | Key Size in Bits | Key Usage Flag |
|---|---|---|---|
• PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_224) | PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1 | • secp192r1 : 192 | • PSA_KEY_USAGE_SIGN_HASH |
• PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_256) | • secp256r1 : 256 | • PSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_HASH | |
• PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_384) | • secp384r1 : 384 | ||
• PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_512) | • secp521r1 : 521 |
Note: The key usage flag must use PSA_KEY_USAGE_SIGN_HASH and PSA_KEY_USAGE_VERIFY_HASH.
Security Software Components
Algorithm | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_224) | ECDSA and SHA-224 |
PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_256) | ECDSA amd SHA-256 |
PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_384) | ECDSA and SHA-384 |
PSA_ALG_ECDSA(PSA_ALG_SHA_512) | ECDSA and SHA-512 |
PSA_ECC_FAMILY_SECP_R1 | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
secp192r1 | secp192r1 |
secp256r1 | secp256r1 |
secp384r1 | secp384r1 |
secp521r1 | secp521r1 |
Built-in Key | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
secp256r1 keys in SE OTP | Built-In Keys |
Item | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
SHA-1 for X.509 certificate | SHA-1 |
Item | Security Software Components |
|---|---|
X.509 certificate support | X.509 |
Using Opaque ECDSA Key to Generate Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
Declare (and allocate) an object of type
mbedtls_pk_context(PK context) and an object of typepsa_key_id_t(key identifier).Use the key identifier to generate an ECDSA key or load the built-in ECDSA key. Refer to the Asymmetric Key for details.
Set up the PK context to wrap that PSA key by calling
mbedtls_pk_setup_opaque(mbedtls_pk_context \*ctx, const psa_key_id_t key).Configure the pending CSR object to use that key by calling
mbedtls_x509write_csr_set_key(mbedtls_x509write_csr \*ctx, mbedtls_pk_context \*key)on that PK context.Call any other function that needs to configure and generate the CSR.
After generating the CSR, free the PK context using
mbedtls_pk_free(mbedtls_pk_context \*ctx). It only frees the PK context itself and leaves the key identifier untouched.Either keep using the key identifier or call
psa_destroy_key()on it, depending on the application flow.
PSA Crypto Platform Example
Click the View Project Documentation link to open the readme file.

The following table describes the implementation status of the PSA Crypto X.509 platform example.
ECDSA Key | Series 1 | Series 2 - VSE | Series 2 - HSE | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
secp192r1 | Y | Y | Y | — |
secp256r1 | Y | Y | Y | — |
secp384r1 | Y | Y | Y | Hardware acceleration only on HSE-SVH devices. |
secp521r1 | Y | Y | Y | Hardware acceleration only on HSE-SVH devices. |
Private Device Key | — | — | Y | Only on HSE-SVH devices. |
Note: This example can select the Private Device Key (secp256r1) to generate the root certificate CSR.
