Firmware Update Examples and Models#
To perform firmware updates, you need an Initiator, a Distributor, and at least one Target node. This section describes the setup to run the Distributor and Target nodes examples provided in the Bluetooth mesh SDK, and the procedures to create an update image archive. See QSG183: Bluetooth Mesh SDK Quick-Start Guide for Bluetooth Mesh 1.1 for an introduction to configuring and building your own projects, and for a guide to additional resources.
The Initiator and Stand-alone Updater are not discussed in this document. However, these functionalities are demonstrated using the Silicon Labs Bluetooth Mesh mobile app, described in Firmware Update Demonstration and Firmware Update with Stand-alone Updater, respectively.
Firmware storage is an important part of the device firmware update process. The flash memory is managed by and accessed via the bootloader. See Bootloader Configurations for Firmware Updates for the flash configurations. The table in Appendix – Silicon Labs Product Positioning for Bluetooth Mesh DFU is a recommendation of the Silicon Labs parts for running the DFU roles.
Distributor Example Application#
The Distributor example application is provided as a pre-built demo binary image, ready to download and use, and a corresponding example project that you can modify and then build for the target part. The precompiled demo is only available for selected EFR32xG21 and EFR32xG24 parts.
This section describes how to build the example project and run the example application on a Silicon Labs device. The example is only available for a limited set of parts, including selected EFR32xG12, xG21 and xG24 parts.
Open Simplicity Studio 5 with a compatible SoC wireless kit connected to the computer. Select the part in Debug Adapters view to open the Launcher perspective.
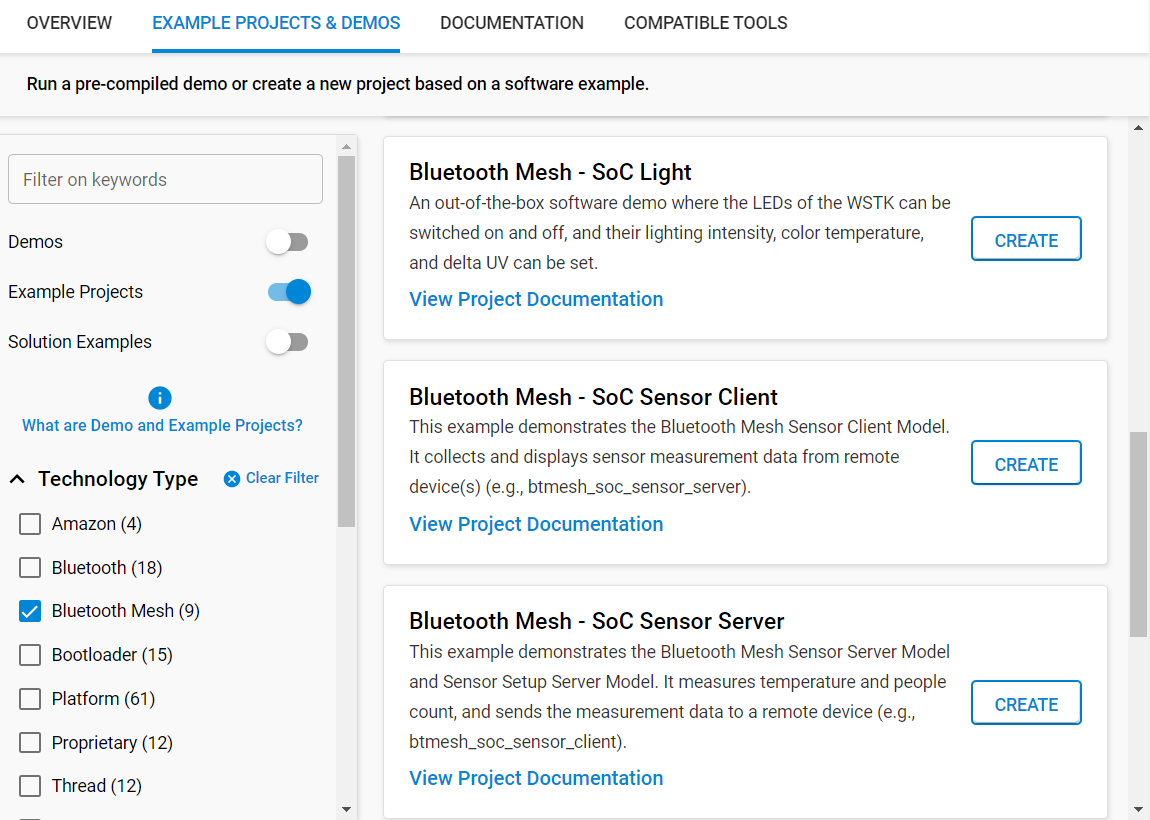
Click the Example Projects & Demos tab.
To see only the example projects, turn off Demos.
Under Technology Type, filter on Bluetooth Mesh.
Next to the Bluetooth Mesh – SoC DFU Distributor, click CREATE, modify project settings, click FINISH.
Build and flash the project to the device.
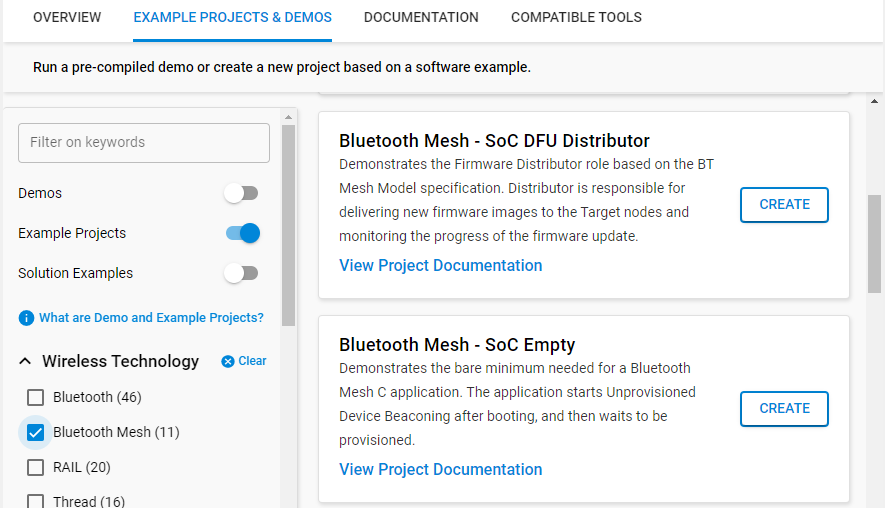

The example has the components that are required for the Distributor functionality installed by default. To enable the Distributor functionality in other Bluetooth mesh projects, install the DFU distributor component that automatically brings the necessary model components:
Open the project .slcp file in Project Explorer view of the Simplicity IDE perspective.
Click the Software Components tab.
Select the DFU distributor component under Bluetooth Mesh > DFU Roles and click Install.
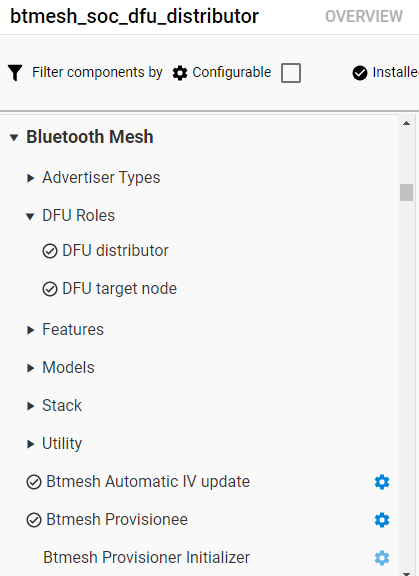

This component automatically installs the following model components:
Bluetooth Mesh > Models > Firmware Update > Firmware Distribution Server
Bluetooth Mesh > Models > Firmware Update > Firmware Update Client
Bluetooth Mesh > Models > Transport > BLOB Transfer Client
Bluetooth Mesh > Models > Transport > BLOB Transfer Server
See DFU Model Configurations for the configurations of these Firmware Update and BLOB Transfer models.
Target Node Applications#
A Target node is a node whose firmware is to be updated. The Bluetooth mesh examples provided in the Bluetooth mesh SDK except Bluetooth Mesh – NCP Empty and Bluetooth Mesh – SoC Empty have the firmware update functionality enabled by default, i.e., are Target nodes.
These example applications are provided both as prebuilt demo binary images, ready to download and use, and corresponding example projects that you can modify and then build for the target part. The precompiled demos are only available for a limited set of parts, including selected EFR32xG13, xG21 and xG24 parts and BGM13 and MGM21 modules. The examples can be built for any part supported by the Bluetooth Mesh SDK.
Note: EFR32xG22 parts have limited support for Bluetooth Mesh.
To build an example project for the device firmware update target, refer to the procedure described in Distributor Example Application.

The examples have the components that are required for the Target node functionality installed by default. To enable the Target node functionality in other Bluetooth mesh projects, install the DFU target node component that automatically brings the necessary model components:
Open the project .slcp file in Project Explorer view of the Simplicity IDE perspective.
Click the Software Components tab.
Select the DFU target node component under Bluetooth Mesh > DFU Roles in the left panel and click Install.
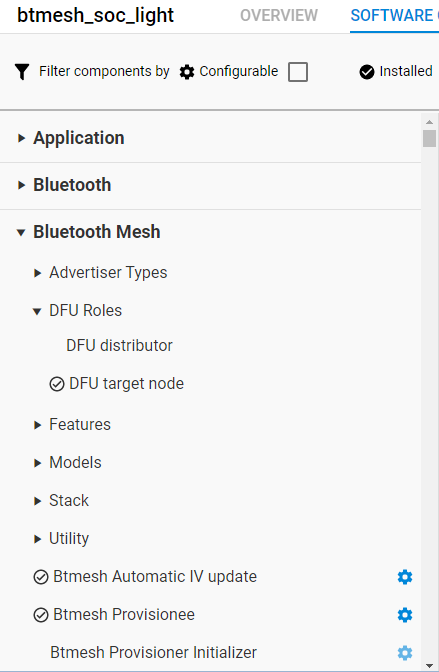

This component automatically installs the following model components:
Bluetooth Mesh > Models > Firmware Update > Firmware Update Server
Bluetooth Mesh > Models > Transport > BLOB Transfer Server
See the section below for the configurations of these Firmware Update and BLOB Transfer models.
DFU Model Configurations#
This section describes the main settings of the Firmware Update and BLOB Transfer models. Open the project .slcp file in Project Explorer view of the Simplicity IDE perspective.
Click the Software Components tab.
Select Bluetooth Mesh > Models > Firmware Update or Bluetooth Mesh > Models > Transport in the left panel.
Click the gear icon next to the model to be configured.
Firmware Distribution Server#
Configuration of Bluetooth Mesh > Models > Firmware Update > Firmware Distribution Server:
| Configuration Option | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| Max node list size | Maximum number of firmware update server nodes which can participate in the distribution. Range: 1 to 65535. | 8 |
| Default Multicast Threshold | If the number of servers for any step exceeds or is equal to this number then the group address will be used, otherwise servers will be looped through one by one. Range: 1 to 65535. The value of 0 disables the feature. | 1 |
| Retry time of message transmissions | Retry time of firmware update message transmissions. Range: 0 to 65535. | 3000 |
| NVM key of the firmware list | NVM key of the firmware list. Range: 0 to 65535. | 16393 |
| Enable Logging | Enable / disable logging of Firmware Distribution Server model specific messages. | On |
|
Enable Logging: Enable BT Mesh Stack Platform Callback Logging |
Enable / disable logging of BT Mesh Stack Firmware Distribution Server model platform callbacks. The FW Distribution Server model in BT Mesh stack calls platform callback functions to query the remaining space, firmware count and firmware information. | Off |
|
Enable Logging: Text prepended to every log message |
Every log message in the component is started with this text. | FwDistributor |
Firmware Update Server#
Configuration of Bluetooth Mesh > Models > Firmware Update > Firmware Update Server:
| Configuration Option | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| General | ||
| Number of firmware on device | Number of firmware on device. Range: 1 to 255. | 1 |
| Maximum length of metadata | Maximum length of metadata. Range: 0 to 255. | 255 / LPN:31 |
| Firmware Information | ||
| Firmware identifier | Firmware identifier | fwid or <specific_node_id> |
| Update URI | Update URI | https://example.com/upd_uri |
| Company Identifier: CID MSB | Most Significant Byte of the Company ID. Hexadecimal string literal. | \x02 |
| Company Identifier: CID LSB | Least Significant Byte of the Company ID. Hexadecimal string literal. | \xFF |
The weak functions for the Firmware Update Server model are mostly implementation-dependent and can be overwritten in the application:
Function | Description |
|---|---|
sl_btmesh_fw_update_server_metadata_check_start() | User callback indicating start of metadata check |
sl_btmesh_firmware_update_server_metadata_check_step() | User callback executing one step of metadata check |
sl_btmesh_fw_update_server_verify_start() | User callback for determining the maximum chunk size of verification |
sl_btmesh_fw_update_server_verify_step() | User callback to execute one step of the verification |
sl_btmesh_fw_update_server_apply() | User callback indicating firmware apply request |
See <sdk>/app/bluetooth/common/btmesh_firmware_update_server/sl_btmesh_firmware_update_server_api.h for further information.
A Target node will become unprovisioned by default after a firmware update. You can overwrite the following functions in sl_btmesh_firmware_update_server_api.c and modify the code described below to change the behavior:
sl_btmesh_fw_update_server_apply()– removesl_btmesh_node_reset()andsl_bt_nvm_erase_all().if (BOOTLOADER_OK == bootloader_setImageToBootload(idx)) { // Reset node sl_btmesh_node_reset(); // Erase NVM data sl_bt_nvm_erase_all(); // Delay install sl_simple_timer_start(&timer, 1000, apply_step, NULL, true); apply_cntdwn = APPLY_DELAY; }sl_btmesh_fw_update_server_metadata_check_start()– set another value to*additional_information. The additional information is provided to the Bluetooth mesh stack and will appear in the Firmware Update Status and Firmware Update Firmware Metadata Status messages.*additional_information = BTMESH_FW_UPDATE_SERVER_ADDITIONAL_INFORMATION_UNPROVISION;sl_btmesh_firmware_update_server_metadata_check_step()– set another value to*additional_information. The additional information is provided to the Bluetooth mesh stack and will appear in the Firmware Update Status and Firmware Update Firmware Metadata Status messages.*additional_information = BTMESH_FW_UPDATE_SERVER_ADDITIONAL_INFORMATION_UNPROVISION;
BLOB Transfer Client#
Configuration of Bluetooth Mesh > Models > Transport > BLOB Transfer Client:
| Configuration Option | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| Enable Logging | Enable / disable logging of BLOB Transfer Client model specific messages. | On |
|
Enable Logging: Text prepended to every log message |
Every log message in the component is started with this text. | BlobTfClient |
|
Enable Logging: Log BLOB Status messages |
Log the content of BT Mesh BLOB status messages. | 1 |
|
BLOB Transfer Limits: Max number of servers |
Maximum number of BLOB transfer servers that can be serviced in a transfer (affects BT Mesh stack memory usage). Range: 1 to 1008. | 8 |
|
BLOB Transfer Limits: Max number of blocks |
Maximum number of blocks supported in a BLOB Transfer (affects BT Mesh stack memory usage). Range: 1 to 1888. | 1850 |
|
BLOB Transfer Limits: Max number of chunks per block |
Maximum number of chunks per block supported in a BLOB Transfer (affects BT Mesh stack memory usage). Range: 1 to 2000. | 128 |
|
BLOB Transfer Limits: Max chunk size |
Maximum chunk size that can be selected during BLOB Transfer. Range: 1 to 241. | 241 |
|
Retry and Separation parameters: Default separation time between chunks |
Default minimum separation time between two chunks in the same block. Range: 0 to 65535. | 0 |
|
Retry and Separation parameters: Default max retry of message transmissions |
Default max retries of message transmissions (query info, transfer start, block start, block query). Range: 0 to 1000. | 50 |
|
Retry and Separation parameters: Default retry time of message transmissions |
Default retry time of message transmissions (query info, transfer start, block start, block query). Range: 0 to 65535. | 2000 |
The weak functions for the BLOB Transfer Client model are mostly implementation-dependent and can be overwritten in the application:
Function | Description |
|---|---|
sl_btmesh_blob_transfer_client_calculate_block_size_log() | Calculates the binary logarithm of the block size for the current BLOB transfer from the provided parameters, which are the result of the Retrieve Capabilities procedure of the BLOB Transfer. The parameters passed represent the aggregated capabilities of the BLOB transfer client and every BLOB transfer server which participates in the current transfer. The default implementation calculates the greatest possible block size from the parameters. |
sl_btmesh_blob_transfer_client_calculate_chunk_size() | Calculates the chunk size for the next block in the current BLOB transfer from the previously selected binary logarithm of the block size and from the result of the Retrieve Capabilities procedure of the BLOB Transfer. The default implementation calculates the greatest possible chunk size. |
See <sdk>/app/bluetooth/common/btmesh_blob_transfer_client/sl_btmesh_blob_transfer_client.h for further information.
BLOB Transfer Server#
Configuration of Bluetooth Mesh > Models > Transport > BLOB Transfer Server:
| Configuration Option | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| General | ||
| Min Block Size Log | Block states need to be monitored. The smaller the blocks, the bigger the state storage. Range: 6 to 32. Note that decreasing the minimum block size will result in increased heap usage. Change this value with care. | 9 |
| Max Block Size Log | Blocks are cached on heap before being written into NVM. Range: 6 to 32. Note that increasing the maximum block size will result in increased heap usage. Change this value with care. | 9 |
| Maximum of number of chunks per block | Maximum of number of chunks per block. Range: 8 to 64. Step: 8. | 16 / LPN:64 |
| Maximum chunk size |
If the max chunk size is 8, the chunk data fits into a single BT Mesh advertisement message. If the chunk data is segmented, N segments can transfer (N*12)-7 bytes of data. Range: 8 to 241. The advantage of a higher chunk size is higher throughput in a low noise environment. The advantage of a lower chunk size is fewer messages are retransmitted in a high noise environment due to lost chunk messages. LPN only: the number of chunk messages (segments) multiplied by requested chunk count in Partial Block Report should fit into the friend queue. |
241 / LPN:8 |
| Logging | Enable / disable logging of BLOB Transfer Server model-specific messages. | On |
| Transfer Start user callback | Enable / disable callback function when BLOB transfer starts. | On |
| Transfer Progress user callback | Enable / disable callback function when block transfer is finished. | On |
| Transfer Done user callback | Enable / disable callback function when BLOB transfer is finished. | On |
| Supported Transfer Modes | ||
| Push Mode | Push BLOB Transfer Mode. | On / LPN: Off |
| Pull Mode | Pull BLOB Transfer Mode. | On |
|
Pull Mode: Number of chunks requested in Block Status or Partial Block Report |
Number of chunks requested in Block Status or Partial Block Report. Range: 1 to 32. | 4 |
|
Pull Mode: Interval, in milliseconds, between Partial Block Reports, if nothing is received |
Interval, in milliseconds, between Partial Block Reports, if nothing is received. Range: 1000 to 30000. Step: 100. | 1000 |
|
Pull Mode: Number of retries sending the same Partial Block Report, before giving up |
Number of retries sending the same Partial Block Report, before giving up. Range: 1 to 10. | 8 |
|
Pull Mode: LPN Mode |
Used on LPN nodes. | Off / LPN:On |
|
Pull Mode - LPN Mode: LPN high throughput mode |
In high throughput mode the LPN node polls the friend node more frequently to increase the throughput at the expense of power consumption. | On |
|
Pull Mode - LPN Mode - LPN high throughput mode: LPN poll delay in milliseconds |
The delay of first LPN poll when the BLOB Transfer Server expects messages from the client after an event. The major part of BLOB transfer to LPN is waiting for the poll timeout to elapse in order to poll the friend node for BLOB Transfer messages. The maximum number of messages that can be transferred per polling is equal to the friend queue size during BLOB transfer to LPN. This poll delay parameter makes the polling more frequent when BLOB Transfer messages are expected to increase the throughput. Range: 100 to 30000. Step: 100. The LPN poll delay should be less than SL_BTMESH_LPN_POLL_TIMEOUT_CFG_VAL in sl_btmesh_lpn_config.h file. | 500 |
Creating the Update Image Archive#
An update image archive is a gzip archive file that consists of:
Manifest: a file named manifest.json, which is in the format of JavaScript Object Notation (JSON). It contains a description of the firmware package, including the name of the firmware image file and an optional metadata file for the update.
Firmware Image: the firmware image file in GBL format, as identified in the manifest file.
Metadata: an optional file provided by the vendor and identified in the manifest file, that may provide metadata for the firmware image.
This section describes the procedure to generate a firmware image, manifest file, and update image archive.
Step 1: generating a firmware image#
Building a C-based Bluetooth mesh application in Simplicity Studio does not automatically generate the OTA DFU update images (GBL files). The GBL files need to be created separately by running a script located in the project's root folder. Two scripts are provided in the SDK examples:
create_bl_files.bat (for Windows)
create_bl_files.sh (for Linux / Mac)
Define two environmental variables, PATH_SCMD and PATH_GCCARM shown in the following table, before running the script.
Variable Name | Variable Value |
|---|---|
PATH_SCMD | C:\SiliconLabs\SimplicityStudio\v5\developer\adapter_packs\commander |
PATH_GCCARM | C:\SiliconLabs\SimplicityStudio\v5\developer\toolchains\gnu_arm\7.2_2017q4 |
Running the create_bl_files script creates six GBL files in a subfolder named output_gbl. The file named application.gbl is the firmware update image.
If you use a bootloader that supports LZMA compression of the firmware update image, as described in Compressed Update Image, you must compress the GBL file with the –compress option of the commander utility. The create_bl_files script does not support compressed GBL update image generation. Therefore, run the following commands instead of the create_bl_files script and then the file named application-lzma.gbl is the firmware update image. Change soc_btmesh_empty.axf to the name of your project firmware image in the command line below.
arm-none-eabi-objcopy -O srec -R .text_apploader* -R .text_signature* soc_btmesh_empty.axf application.srec
commander gbl create application-lzma.gbl --app application.srec --compress lzmaFor more information about the GBL file format, see Silicon Labs Gecko Bootloader User’s Guide for GSDK 4.0 and Higher (series 1 and 2 devices). For more information on using the Simplicity Commander commands, see Simplicity Commander Reference Guide.
Step 2: creating a manifest file#
Create a file named manifest.json that is a text file in JSON format containing the name of the firmware update image, the firmware ID and optionally the name of the metadata file. The format of the manifest/firmware/firmware_id member is Base16. The manifest/firmware/metadata_file member contains the metadata file name if present. The following is an example of the content of the manifest.json file.
{
"manifest": {
"firmware": {
"firmware_file": "application.gbl",
"firmware_id": "4181C01592"
}
}
}Step 3 – making an update image archive#
Run the following command to generate a zipped tar archive:
tar czf firmware.gz application.gbl manifest.json