Bluetooth Mesh DFU and BLOB Transfer#
Bluetooth Mesh Device Firmware Update is designed as a two-layer architecture to run different protocols. The DFU layer runs the DFU protocol for higher-level decision making that manages and coordinates firmware updates among different types of nodes. The BLOB Transfer layer runs the underlying data transport protocol handling generic large binary object transfer. In principle, the BLOB Transfer component could be used standalone for transferring any data objects that are much larger than the maximum Access Layer PDU size between the network devices.
BLOB Transfer#
The Bluetooth Mesh BLOB Transfer (MBT) is a component on a node transferring or receiving binary large objects (BLOBs) over a Bluetooth Mesh network. The MBT client sends a BLOB to one or multiple nodes and the MBT server receives the BLOB. Bluetooth Mesh Device Firmware Update uses the MBT component to transfer update images.
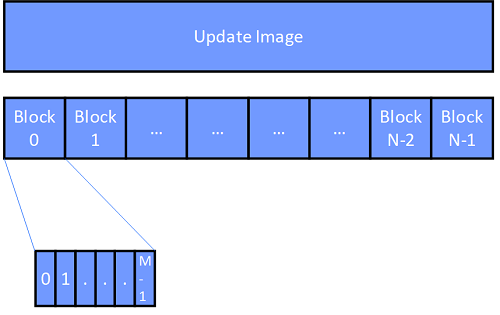
The following figure illustrates the concept of how the MBT component transfers an update image. The MBT client breaks an update image into suitably-sized blocks based on the capabilities of the MBT servers and transfers these blocks to the servers. Each block is composed of identically sized chunks of data, except for the last chunk which may be smaller than the other chunks if the block’s size is not an integer multiple of the chunk’s size. A single message carries only a single chunk.

The transfer may be performed in two modes: Push BLOB Transfer mode and Pull BLOB Transfer mode. The MBT client selects the transfer mode based on the capabilities supported by the servers. The MBT server may support both or only one of these modes.
In the Push BLOB Transfer mode, the client controls the flow of chunks to the servers, sending all the chunks from a block, then queries the servers to determine which chunks were received. All missing chunks are retransmitted.
In the Pull BLOB Transfer mode, the client transfers a BLOB typically to a single server at a time, although multiple simultaneous receivers can be supported as well. The server requests chunks from the client as it can process them, and the flow of chunks is controlled by the server.
A Low Power Node (LPN) typically only supports the Pull BLOB Transfer mode and therefore the Pull BLOB Transfer mode is typically used only if some of the MBT servers are Low Power Nodes. This mode makes it possible for the MBT server to throttle the transfer speed. This is necessary to ensure that no more chunks than the Friend node can store in its Friend Queue are transmitted at once.
The MBT client or server model is normally used as a transport in a higher-layer model such as the Firmware Update models.
Firmware Update Roles#
Two to three roles participate in a firmware update over a Bluetooth mesh network: Initiator, Distributor, and Target Node, or Stand-alone Updater and Target Node. The Stand-alone Updater and Distributor as well as the Initiator can also be Target nodes. A firmware update is distributed simultaneously to the devices that have the same firmware. Sets of homogenous nodes are updated sequentially.

Initiator role: checks for available updates for the firmware running on Target nodes that are included in a list provided by a higher-layer application and then sends the new firmware images to a Distributor. The procedures performed by an Initiator are controlled by a higher-layer application. An Initiator might be a smartphone or gateway device that periodically checks product websites for the availability of new firmware images.
Distributor role: delivers new firmware images to the Target nodes and monitors the progress of the firmware update. The Distributor acts as an intermediary on behalf of the Initiator so that the Initiator does not always need to be present on the mesh network. The Distributor reports progress back to the Initiator when requested. The Distributor continues to have the configured functionality when distributing updates.
Stand-alone Updater role: checks for available updates for the firmware running on Target nodes and delivers the new firmware images directly to the Target nodes. A Stand-alone Updater might be a smartphone or mesh gateway device that has access to the Internet while present on the mesh network to check for the availability of new firmware images for the Target nodes. When a new firmware image is available, it manages the delivery of the firmware image to the Target nodes without an intermediary Distributor.
Target Node role: receives firmware updates and updates itself. The Target node stays in normal operation until a reboot with the new firmware.
Firmware Update Models#
The Bluetooth Mesh Model specification v1.1 adds new models to support the Bluetooth Mesh Device Firmware Update feature. There are no changes in the Bluetooth Mesh Profile specification. The table below summarizes the models required by each role that participates in firmware updates. A node may support multiple roles. For example, a Distributor may support the Target node role.
Role | Firmware Distribution Client | Firmware Distribution Server | Firmware Update Client | Firmware Update Server | BLOB Transfer Client | BLOB Transfer Server |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Target node | – | – | – | M | – | M |
Initiator | M | – | M | – | M | – |
Distributor | – | M | M | – | M | M |
Stand-alone Updater | C.1 | C.2 | M | – | M | C.2 |
M: Mandatory
C.1: Mandatory if Initiator role is supported, otherwise optional
C.2: Mandatory if Distributor role is supported, otherwise optional
Firmware Distribution Client is the model used by the Initiator to send the firmware image and the firmware distribution parameters to the Distributor, and to start the firmware image transfer.
Firmware Distribution Server is the model used by the Distributor to receive from the Initiator the firmware update parameters, the set of Target nodes to update, and the firmware image to transfer. This model can transfer one firmware image at a time.
Firmware Update Client is the model used by the Distributor and Initiator to manage firmware updates. The Initiator uses this model to retrieve the information about the firmware subsystems installed on the Target node, and to get the download URIs of the new firmware images. The Distributor uses this model to start a firmware image transfer to the Target nodes.
Firmware Update Server is the model used by the Target node to report the firmware images installed on the node and the download URI of new firmware images, and to initiate a firmware update to receive a new firmware image.
BLOB Transfer Client is the model used to transfer BLOBs over a Bluetooth Mesh network. An MBT client can transfer a BLOB to one or more MBT servers, either unicasting or multicasting depending on the situation.
BLOB Transfer Server is the model used to receive BLOBs over a Bluetooth mesh network from an MBT client.
