Bluetooth Mesh Firmware Update Process#
Multiple Target nodes can be updated either simultaneously using a multicast address or individually using unicast addresses. For efficiency, a multicast address should be used when multiple Target nodes indicate that they can accept the same firmware image. The Initiator does this by adding all Target nodes that support the same firmware image to the Target nodes list that is transferred to the Distributor. The Initiator transfers the firmware image to the Distributor and the Distributor distributes the firmware image to the nodes in the Target nodes list. Finally, the Target nodes apply the firmware image when the Distributor instructs them to do so. The Initiator can order the Distributor to either trigger applying the update immediately after the transfer is complete, or to wait for another message from the Initiator before applying the new firmware.
The Initiator optionally can transfer multiple firmware images to the Distributor, but the Distributor can distribute only one firmware image to Target nodes in a firmware update. This means that some nodes may not participate in the firmware update. The Initiator manages firmware images that are identified by the Firmware ID and determines what nodes are to be included in the Target nodes list.
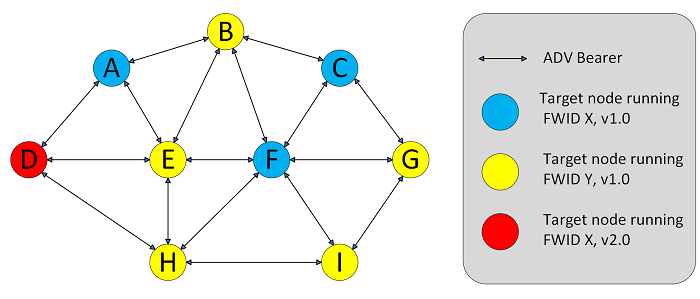
The following figure illustrates an example of the case that only the nodes running the same firmware accept the firmware update. The mesh network has two sets of Target nodes running different firmware, one running Firmware X v1.0 (blue nodes: A, F, and C) and another running Firmware Y v1.0 (yellow nodes: B, E, H, I, and G). Both belong to the same network. The Distributor Node D is distributing Firmware X v2.0.
The blue nodes accepted the Firmware X v2.0. They therefore have subscribed to a multicast address and are simultaneously updating their firmware to version X v2.0. The yellow nodes are not participating in the firmware update because they did not accept the Firmware X v2.0 during the compatibility check and were not added to the Target nodes list by the Initiator.

The following subsections briefly review the firmware update process.
Setting Up an Update#
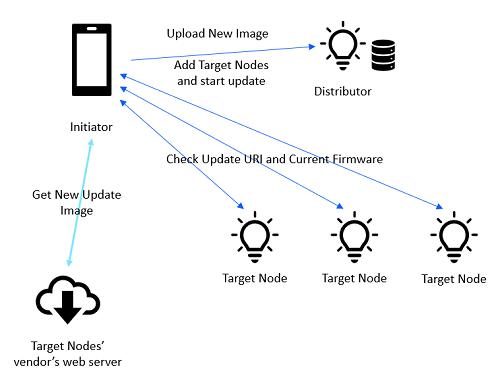
The first step is to set up an update. The Initiator polls the Target nodes for their update URIs and current firmware. The Initiator uses the information to get a newer firmware image and its metadata. The Initiator transfers a Target nodes list and an update image to the Distributor. The Initiator then starts the firmware distribution process. When the distribution is started, the Initiator specifies to the Distributor whether the update should be applied immediately after the transfer completes, or whether the update should be applied only after the Initiator sends a message to the Distributor to trigger applying the update. This mechanism can be used to defer rebooting the devices to a suitable time.
The Initiator receives a list of Target nodes from the higher-layer application.
When a new firmware image is available, the Initiator optionally may check whether nodes in the Target nodes list can accept the new firmware image. The nodes also inform the Initiator whether they will become unprovisioned or will have some changes to their composition data. The same information will be provided to the Distributor later on in the process.
The Initiator optionally may check the information of the firmware images stored on a Distributor and can remove a firmware image from the Distributor at any time.
The Initiator is not necessarily present on the mesh network after the distribution has started.
The Initiator may check the status of the firmware image distribution via the Distributor at any time.

Starting an Update#
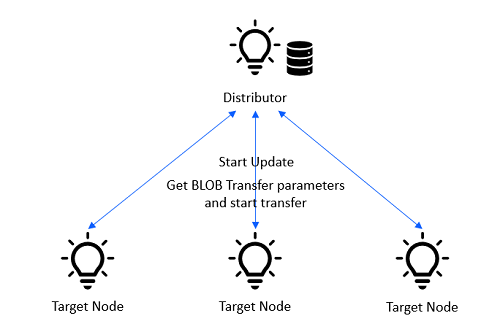
The Distributor has received an update image, a Target nodes list, and the Distribution Start command from the Initiator. The Distributor notifies the Target nodes to prepare for an update and sends the metadata of the update image to the Target nodes. The Distributor then negotiates suitable BLOB Transfer parameters with the Target nodes and starts the BLOB Transfer.
The Target nodes check the metadata and may reject the update.
The Target nodes inform the Distributor whether they will become unprovisioned after the update or not, and whether they will have changes to their composition data, based on the metadata.
Upon a request from the Initiator to retrieve the progress of the firmware update for each Target node, the Distributor provides a list of Target nodes and the progress of the firmware image transfer, the update phase of the transfer, and any potential errors.

Sending the Update Image#
The MBT client sends the update image to the MBT servers. The section, BLOB Transfer, explains how an update image is transferred.
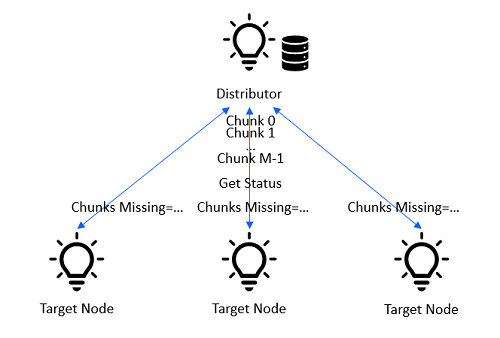
In the Push BLOB Transfer Mode, the Distributor transfers the chunks from a block to the Target nodes. After the Distributor has sent all chunks of a block, the Distributor queries the Target nodes to report missing chunks and transfers each missing chunk to the Target nodes, until no missing chunks are reported. The Distributor then moves on to next block, until all blocks are sent.
In the Pull BLOB Transfer Mode, the Distributor receives an initial list of chunks from the Target nodes and transfers the chunks from the initial list to the Target nodes. The Distributor then waits for the BLOB Partial Block Report from the Target nodes before transferring the next set of chunks. The Distributor repeats the step transferring the requested chunks to the Target nodes until all blocks are sent.
The higher-layer application can cancel the BLOB Transfer at any time.

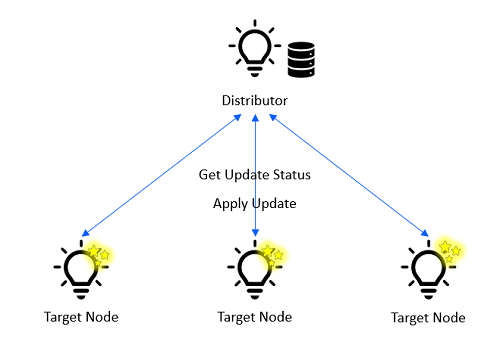
Applying an Update#
The firmware image distribution is complete when the Target nodes have received the update image. The Target nodes check the integrity of the update image, and the Distributor polls them until all Target nodes complete. Then, if the Initiator had instructed the Distributor to start applying the update immediately in the Distribution Start message, the Distributor instructs the Target nodes to apply the update image. Otherwise, the Distributor waits for the applying signal from the Initiator before triggering applying the new firmware. The Target nodes reboot with the new firmware.
The higher-layer application can cancel the verify firmware procedure at any time.
The Target nodes can remain provisioned or become unprovisioned after an update image is applied. The states of the Target nodes are reported to the Distributor and Initiator.