Example#
BTMesh SOC Empty CBP#
This section covers the use of the “Bluetooth Mesh – SoC Empty with Certificate-Based Provisioning Support” sample application found in the Gecko SDK.
Creating Device Certificate on Device#
Follow the steps for creating a device certificate, which are detailed in section Creating Example Certificate Authority and Device Certificate.
Create an instance of the “Bluetooth Mesh – SoC Empty with Certificate-Based Provisioning Support” sample application for your chosen device.
Build the application and flash the output file to your device.
Provisioning with the Bluetooth Mesh mobile app#
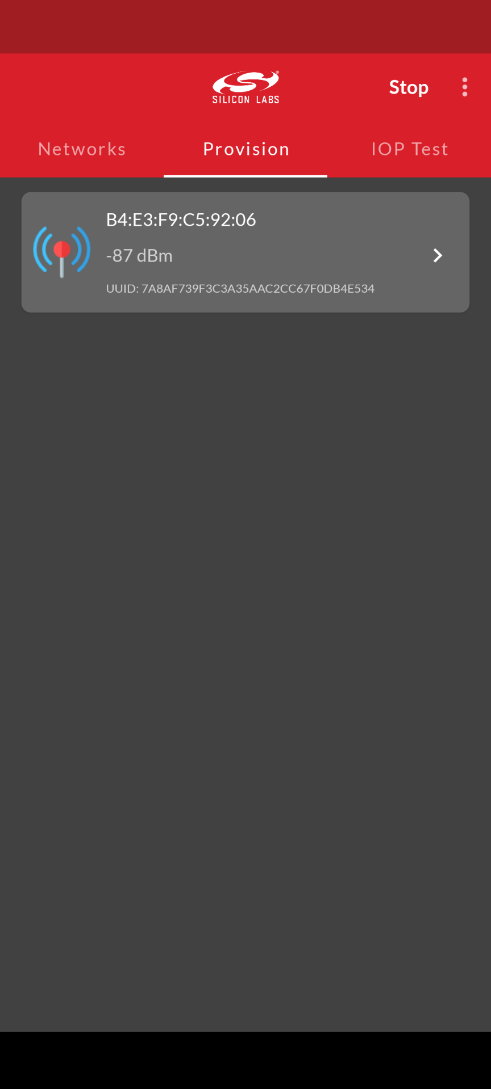
Silicon Labs Bluetooth Mesh mobile app supports Certificate-Based Provisioning starting in version 4.1.0. To being provisioning a node with CBP, open the Bluetooth Mesh mobile app, select the Provision tab, and tap the scan icon as shown below.


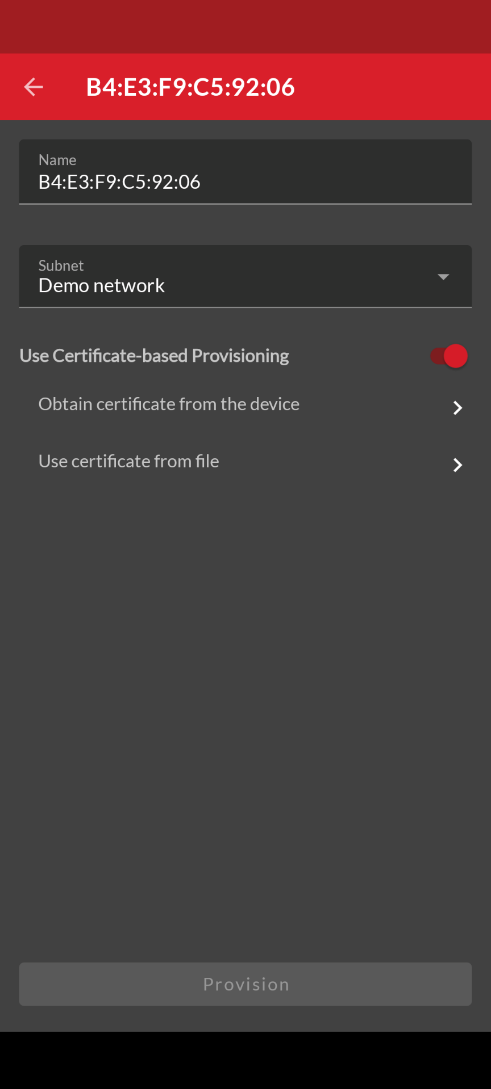
In the dialog for the unprovisioned node, ensure that the Use Certificate-based Provisioning option is enabled then tap the Obtain certificate from the device icon as shown below.

Once the device certificate has been sent, the Device certificate status changes to Available as shown below.
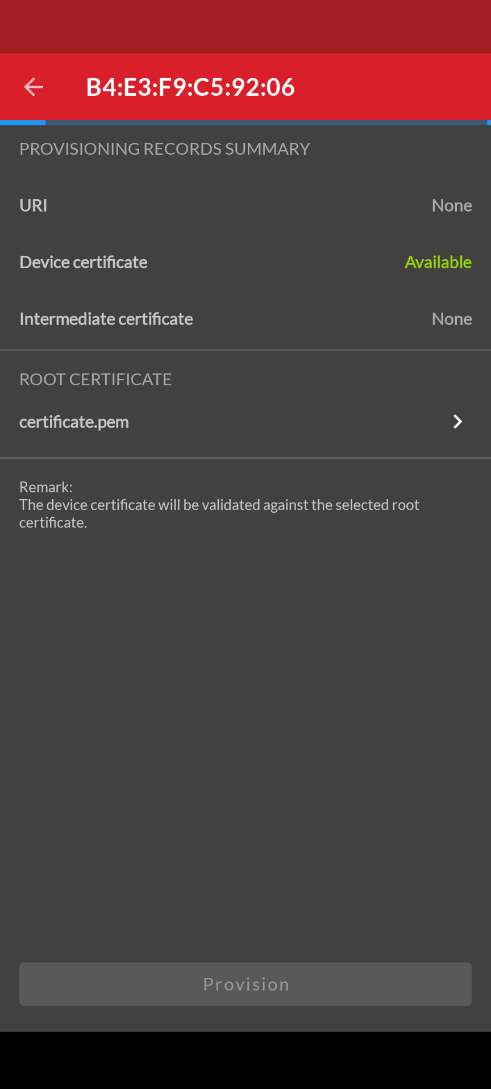

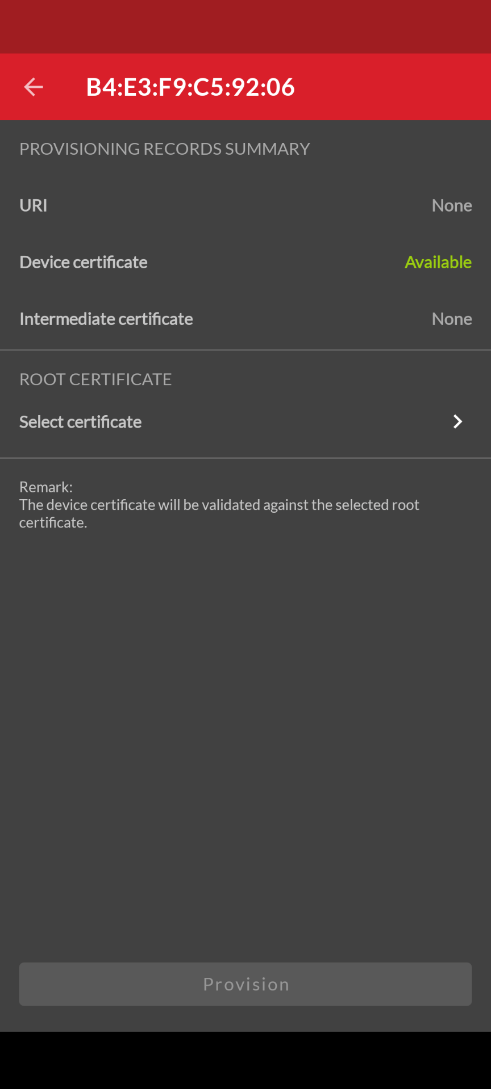

Tap the Select certificate icon to browse for the root certificate. Note: The root certificate must be accessible to the mobile device either through its filesystem or in a cloud storage service such as Dropbox. Once the root certificate file has been selected, it is shown on the Provisioning Records Summary dialog.
Tap the Provisioning button at the bottom of the screen to complete the provisioning process.
Provisioning with the BT Mesh Host Provisioner Sample Application#
The btmesh-host_provisioner sample application runs on a posix-type platform such as RaspberryPi. For instructions on getting started building the Host Provisioner sample app, see AN1371 - Bluetooth Mesh NCP Host Provisioner Example Walkthrough. Note that when exporting the Bluetooth Mesh Host Provisioner code it is necessary to include the CBP flag as follows:
make export CBP=1To enable Certificate-Based Provisioning, rebuild the sample with the following command:
make CBP=1Installing Root Certificates#
For the BT Mesh provisioner to validate device certificate chains, it must have the root certificate for those chains. The root certificates must be stored in PEM format in the file CA/ca-certificate.crt under the BT Mesh host provisioner source folder.
Example
The root certificate generated by the script mentioned in section will be C:\Users\<user>\SimplicityStudio\SDKs\gecko_sdk\app\bluetooth\script\certificate_authorities\central_authority\certificate.pem.
Copy this file to the provisioner host:
\<path to exported files\>/app/btmesh/example_host/btmesh_host_provisioner/CA/ca-certificate.crtSpecifying a Base URI for Certificate Retrieval#
This section describes how to customize the sample application to include a base URI for certificate retrieval in the provisioning records.
Add the following code to the top level of the project’s app.c file.
struct mesh_const_provisioning_record { const uint8_t *ptr; //< Provisioning record data uint16_t len; //< Length of provisioning record data }; /** Number of spec-defined intermediate certificates */ #define MESH_INTERMEDIATE_CERTIFICATE_COUNT 15 struct mesh_const_provisioning_records { /** Certificate-based provisioning base URI */ struct mesh_const_provisioning_record base_uri; /** Complete local name */ struct mesh_const_provisioning_record complete_local_name; /** Appearance */ struct mesh_const_provisioning_record appearance; /** Intermediate certificate 1 to 15 */ struct mesh_const_provisioning_record intermediate_certificate[MESH_INTERMEDIATE_CERTIFICATE_COUNT]; }; extern const struct mesh_const_provisioning_records *mesh_const_provisioning_records; static const struct mesh_const_provisioning_records records = { .base_uri = { (const uint8_t *)"\x17//www.example.com/", 19, }, .complete_local_name = { NULL, 0, }, .appearance = { NULL, 0, }, .intermediate_certificate = { { NULL, 0 }, { NULL, 0 }, { NULL, 0 }, { NULL, 0 }, { NULL, 0 }, { NULL, 0 }, { NULL, 0 }, { NULL, 0 }, { NULL, 0 }, { NULL, 0 }, { NULL, 0 }, { NULL, 0 }, { NULL, 0 }, { NULL, 0 }, { NULL, 0 }, }, };Edit the ‘base_uri’ member to point to the desired URI.
Add the following line to
app_init():mesh_const_provisioning_records = &records;Build the project and download the binary to the target board.
Scan for the node as described above. Now the BTMESH mobile app will show that the URI is available as shown below:
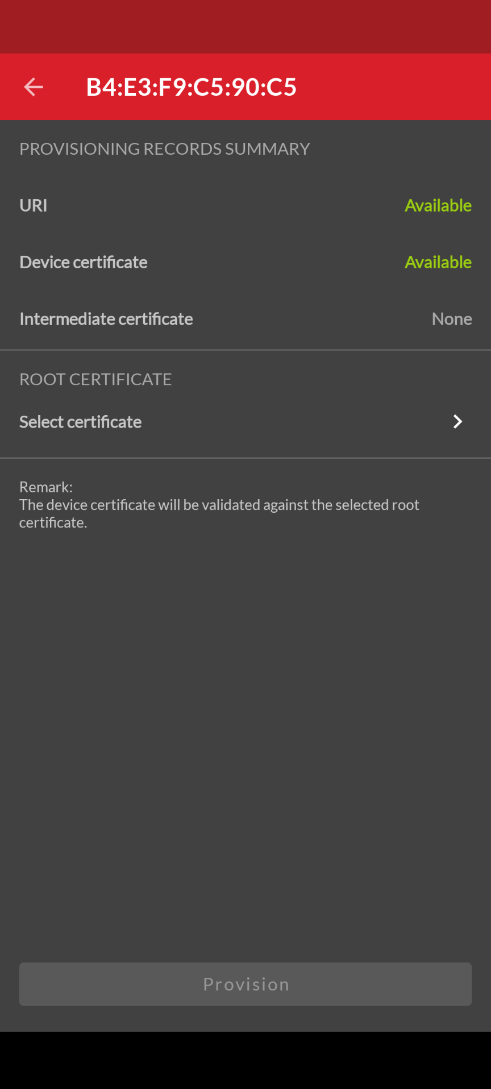

Running the BT Mesh Host Provisioner#
The BT Mesh host provisioner can provision nodes to a network with the node’s 128-bit UUID which is obtained by scanning as shown below:
./exe/btmesh_host_provisioner -u \<serial port\> --scan --c
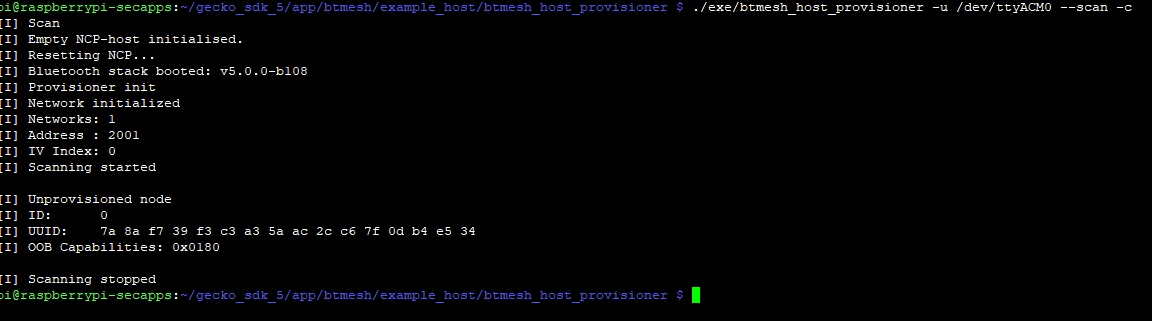

Once the node’s UUID has been found, it can be used to provision the device as shown below:
./exe/btmesh_host_provisioner -u \<serial port. –c –provision \<UUID\>Example:
./exe/btmesh_host_provisioner -u /dev/ttyACM0 --c -b 115200 --provision 9c93e21b4ea4a65d871031d7f67bb702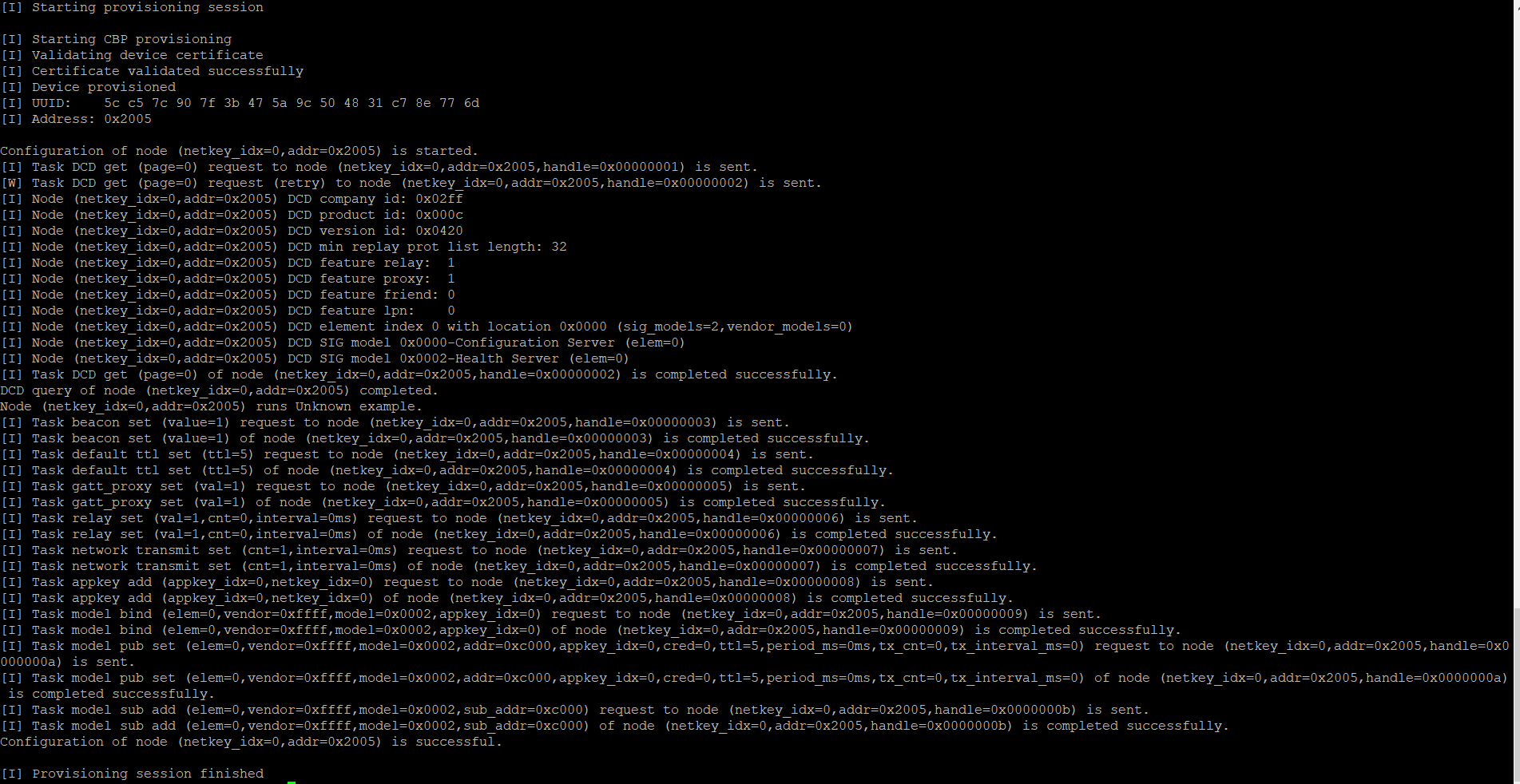

Now the node is provisioned on the network and can be configured for groups and functionality. For specifics, refer to AN1371, Bluetooth Mesh NCP Host Provisioner Example Walkthrough.
