Introducing Low Power Sensor Networks#
A typical low power network includes a single "always-on" device that serves as the coordinator for the network and one or more end nodes operating as sleepy end devices. Such devices spend most of their time in deep sleep mode, waking only briefly to transmit data to the central coordinator. An example of a low power network is a simple sensor network where the sensors are all sleepy end devices and the central hub serves as the always-on coordinator, or sink, for the network.
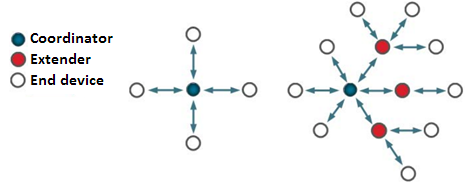
The Silicon Labs Flex SDK includes example sensor and sink applications, based on the Connect stack, for exactly this scenario. Supported network structures are star and extended star topologies:

The example applications are:
Connect (SoC): Sensor
Connect (SoC): Sink
Together the applications demonstrate a star topology. Bi-directional communication is possible between the sensor(s) and the sink nodes. This document reviews using Simplicity Studio to build a sensor-sink network, and then to modify it for the lowest power consumption.
If you are not familiar with building the example applications in Simplicity Studio, review the Proprietary Flex SDK v3.x Quick Start Guide. If you are not familiar with the features and functions of the Silicon Labs Connect stack, see Silicon Labs Connect Fundamentals.
