Reduce Power Consumption#
This section describes techniques for reducing power consumption, including:
Disable Network LED
Disable UART reception to enable sleep mode
Change Report Periodicity
Initialize the SPI Flash Chip
Finally, the reduced power consumption results are described.
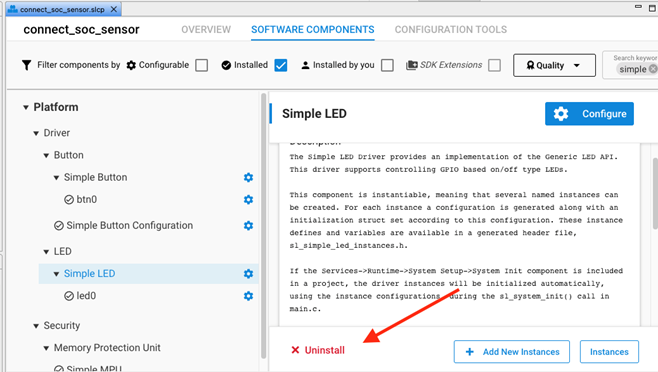
Disable Network LED#
The sensor example sets an LED when the device is joined to a network, which draws a constant current, depending on the hardware (e.g., about 500uA on BRD4001). The easiest way to disable it is to remove the simple LED component.

Disable UART Reception during Sleep#
Next, the step that reduces the consumption the most is disabling UART reception during sleep. This enables entering EM2 mode when it is possible. This option can be enabled in the Component Editor under IO Stream USART (vcom) settings.
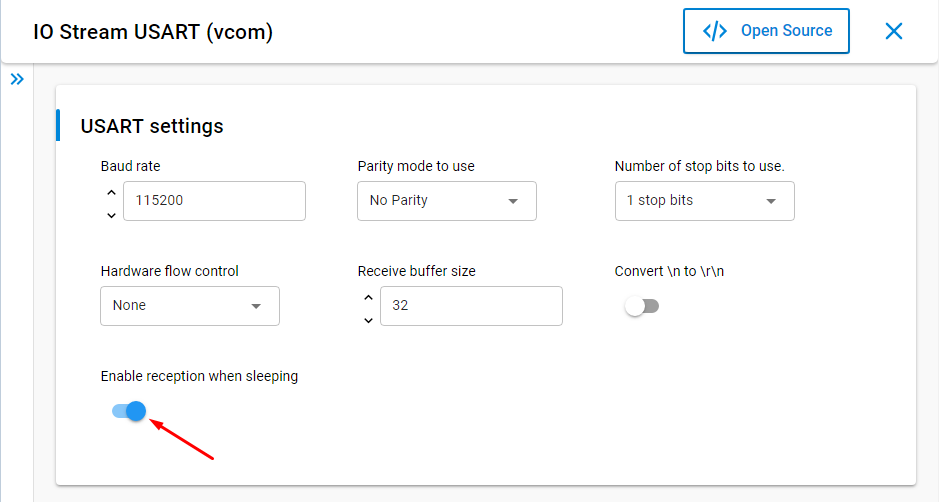

Note: If reception is disabled during sleep, issuing commands through the CLI (UART) is not possible. The sensor example has a feature where PB0 toggles between enabled and disabled reception mode.
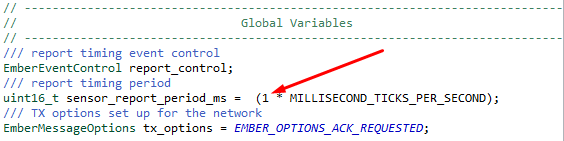
Change Report Periodicity#
Changing the report period can significantly reduce the average consumption if the sleep consumption is significantly lower than consumption in active periods. To change the report period, open app_process.c and modify the sensor_report_period_ms value.

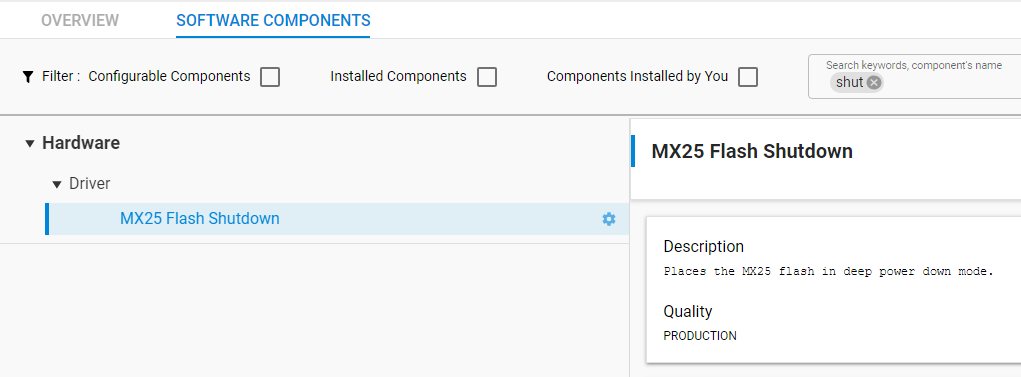
Initialize the SPI Flash Chip#
This step shouldn’t be necessary, as it is always implemented if you create the project for a Silicon Labs radio board. However, if your design includes an external flash, or if you decided to create the project for the given MCU part, not the Silicon Labs radio board, it might be necessary. All the radio boards designed by Silicon Labs contain an SPI flash chip that consumes ~8-10 μA if left uninitialized. To reduce the SPI Flash current consumption, the MX25 Flash Shutdown component must be installed. In the sensor application, it is installed by default.

Reduced Power Consumption Results#
Finally, if these modifications are applied, the sleep mode current consumption should be reduced significantly.
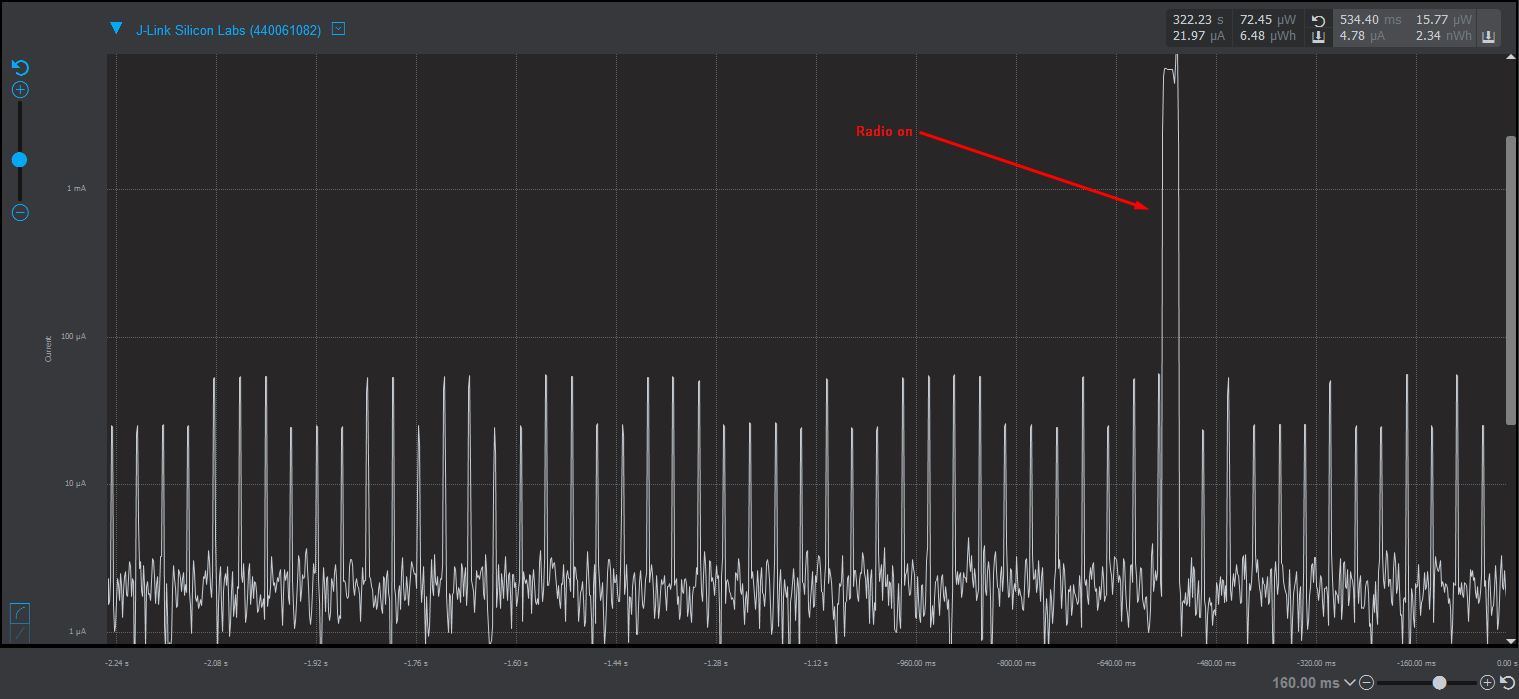

Note: The built-in current measurement of the WSTK board is not really accurate in the μA range and below. The sleep mode current consumption of the sensor node, once all modifications have been applied, should be in the 2-5 μA range.
