Network Layer#
The Connect network layer is only available in Extended Star mode and Direct mode. It is responsible for routing (Extended Star mpode only) and endpoint handling. Endpoints implement channel sharing between protocols, similar to TCP/IP's port concept. For example, the Mailbox component uses endpoint 15, OTA uses endpoint 14, and other endpoints are sent to the application with the help of the application framework.
Network Layer Header#
The Network layer header is illustrated in the following figure.
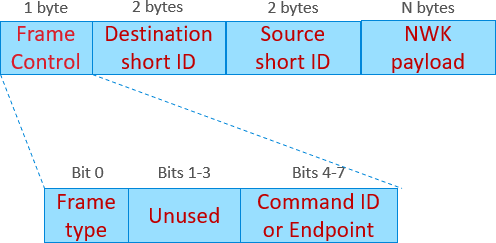

The Network layer header is included in all MAC data frames.
If the frame type bit is set, the frame is a network command message and handled by the network layer. If the frame type is cleared, the message is a data frame. A data frame is either routed towards its destination, or if it has been received by the destination, it is forwarded to the application layer with the emberIncomingMessageHandler() callback (which includes the NWK payload, the source short ID, and the endpoint as arguments).
Routing (Extended Star Mode only)#
Routing Tables#
The routing protocol is centralized and the coordinator knows a route to all devices in the network. This is achieved with the following routing data stored on the devices:
End device stores the address of its parent.
Range extender stores the address of all children connected to it (child table).
Coordinator stores the address of all children connected to it (child table) and keeps a table for each range extender with their children's addresses (coordinator routing tables, RAM only).
Aging#
The child tables also store the timestamp of the last received message. If the child table is full and a new child wants to join, the coordinator can remove a child which has not communicated for "Child timeout" amount of time (configurable in the Parent support component, 1 hour by default).
Child Table Limitations#
The child table has the following limitations:
The maximum number of children for coordinators is 64 (limited by the maximum child table size).
The maximum number of children for range extender is 32 (limited by the format of the range extender update command).
Forwarding Rules#
The routing protocol can be expressed in these forwarding rules:
End Device: always forward to the parent (coordinator or range extender).
Range Extender: if the final destination is in the child table, forward the packet to the final destination. Otherwise, forward to the coordinator.
Coordinator: if the final destination is in the child table, forward the packet to the final destination. Otherwise, look up the final destination in the routing table and forward it to the corresponding range extender.
Leaving the Network (Extended Star Mode only)#
A child (end device, sleepy end device, or range extender) can leave the network (without notifying its parent) by calling emberResetNetworkState(). This action will burden the network with failed message routing attempts until the device times out from the routing and child tables. To avoid this problem, a device can notify its parent before leaving the network by calling emberNetworkLeave() (instead of emberResetNetworkState()). This will trigger a Leave notification message to be sent. Upon receiving the message, the parent will remove the child from its child table. If the parent does not acknowledge the Leave notification, the child will try to send it 7 more times (with 200ms delay between the messages) before leaving the network.
A parent can also request that a child be removed from the network by calling emberRemoveChild(). This will immediately mark the child ID in the child table to be reusable. (Hence, if the child table is full, it may be reassigned to any new child that is allowed to join.) The function will also cause a Leave request message to be sent. For a non-sleepy device, this will happen immediately. For a sleepy device, it will be sent as a response to data polls. The child will be removed from the child table if it acknowledges the Leave request message, or if it does not respond to 8 Leave request messages. Leave request messages will be sent when the child tries to communicate with the parent.
Network Layer Commands#
The network layer supports the following commands:
0x01: Short address request
0x02: Short address response
0x03: Range extender update request
0x04: Range extender update
0x05: Leave request
0x06: Leave notification
All of these commands use secure communication if both sides support it.
Short address request and Short address response are used to get a short address from the coordinator if a device joins a range extender. (For more information, see section Device Joins Range Extender.)
Range extender updates are used to maintain the routing tables on the coordinator. Their payload is an array of short addresses. Each range extender periodically sends this command to the coordinator, every 60 seconds by default or can be configured with the compile time define EMBER_NWK_RANGE_EXTENDER_UPDATE_PERIOD_SEC. This command is also the response to range extender update requests.
Range extender update requests are used if the coordinator needs to update its routing tables. Currently this is only used when a coordinator reboots.
Network Layer Payload#
The only requirement on the payload is that it must exist: 0 length messages are not supported. Messages with no payload are usually used for beaconing. Silicon Labs recommends using data poll messages for beaconing.
