Clock Manager Configuration#
Configuration Files Overview#
The Clock Manager uses two primary configuration files to define board-specific clock settings and behavior. These files are typically generated by the Universal Configurator but can be manually edited for advanced customization. The configuration is device-specific and reflects the oscillators and clock tree architecture of each device family, with different parameters and options available depending on the available hardware.
sl_clock_manager_oscillator_config.h#
This file defines oscillator-specific settings and hardware configurations:
Purpose: Controls which oscillators are enabled and their configuration parameters
Generated by: Universal Configurator based on component selections
Location:
config/sl_clock_manager_oscillator_config.hFormat: Uses CMSIS Configuration Wizard Annotations for GUI integration
Device-Specific: Configuration files are specific to each device family
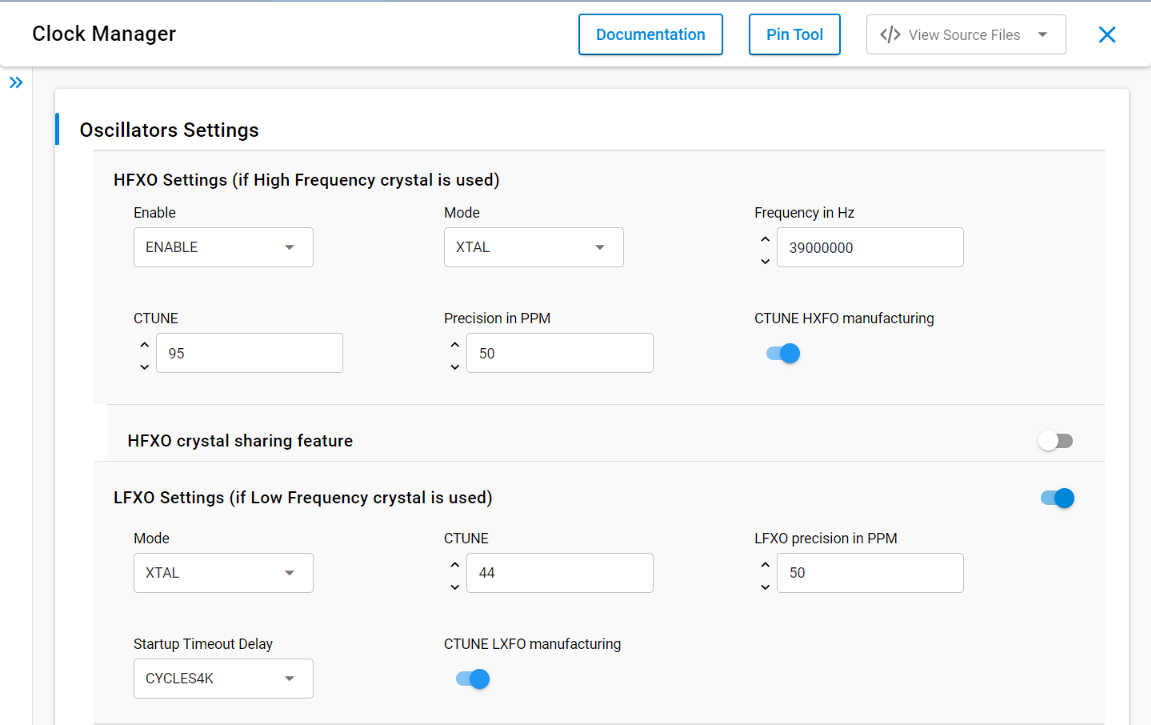

Key Configuration Parameters:
// HFXO oscillator enable/disable with AUTO mode support
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_EN SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_EN_ENABLE // Explicitly enable HFXO
// Options: SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_EN_AUTO (Will select HFXO if RAIL is present), SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_EN_ENABLE, SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_EN_DISABLE.
// HFXO configuration parameters
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_MODE HFXO_CFG_MODE_XTAL // Crystal mode
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_FREQ 39000000 // Frequency in Hz
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_CTUNE 140 // CTUNE value (0-255)
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_PRECISION 50 // Precision in PPM
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFRCO_BAND cmuHFRCODPLLFreq_80M0Hz // RC oscillator frequency
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFRCO_DPLL_EN 0 // 0=disabled, 1=enabled
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DPLL_FREQ 78000000 // DPLL target frequency
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DPLL_N 3839 // DPLL numerator
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DPLL_M 1919 // DPLL denominator
// SOCPLL configuration (Series 3 devices only)
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_SOCPLL_EN 1 // 0=disabled, 1=enabled
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_SOCPLL_FREQ 150000000 // SOCPLL target frequency (145 MHz or 150 MHz)
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_SOCPLL_REFCLK CMU_SOCPLLREFCLKCTRL_CLKSEL_HFXO // Reference clock: HFXO, HFRCO, or EXTCLK
// Crystal sharing configuration (requires special hardware design)
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_CRYSTAL_SHARING_EN 0 // 0=disabled, 1=enabled
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_CRYSTAL_SHARING_LEADER_EN 0 // Leader mode
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_CRYSTAL_SHARING_FOLLOWER_EN 0 // Follower mode
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_CRYSTAL_SHARING_GPIO_PORT 0 // GPIO port for sharing
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_CRYSTAL_SHARING_GPIO_PIN 10 // GPIO pin for sharing
// LFXO oscillator enable/disable
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_LFXO_EN 0 // 0=disabled, 1=enabled
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_LFXO_MODE LFXO_CFG_MODE_XTAL // Crystal mode
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_LFXO_CTUNE 63 // CTUNE value (0-127)
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_LFXO_PRECISION 50 // Precision in PPM
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_LFXO_TIMEOUT LFXO_CFG_TIMEOUT_CYCLES4K // Startup timeoutLFXO Timeout Configuration and Startup Impact#
Carefully select the SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_LFXO_TIMEOUT configuration based on the crystal characteristics and your application’s requirements. This setting affects the timing of peripheral initialization when low-frequency peripherals, such as the RTC, first request the LFXO during their initialization sequence.
Selection Guidelines:
// Fast startup (high-quality crystals, controlled environment)
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_LFXO_TIMEOUT LFXO_CFG_TIMEOUT_CYCLES1K // ~31 ms
// Standard configuration (recommended for most applications)
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_LFXO_TIMEOUT LFXO_CFG_TIMEOUT_CYCLES4K // ~125 ms
// Conservative (challenging conditions, low-cost crystals)
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_LFXO_TIMEOUT LFXO_CFG_TIMEOUT_CYCLES16K // ~500 mssl_clock_manager_tree_config.h#
This file defines clock tree routing and default clock source selections:
Purpose: Configures which oscillators supply different parts of the clock tree
Generated by: Universal Configurator based on performance and power requirements
Location:
config/sl_clock_manager_tree_config.h
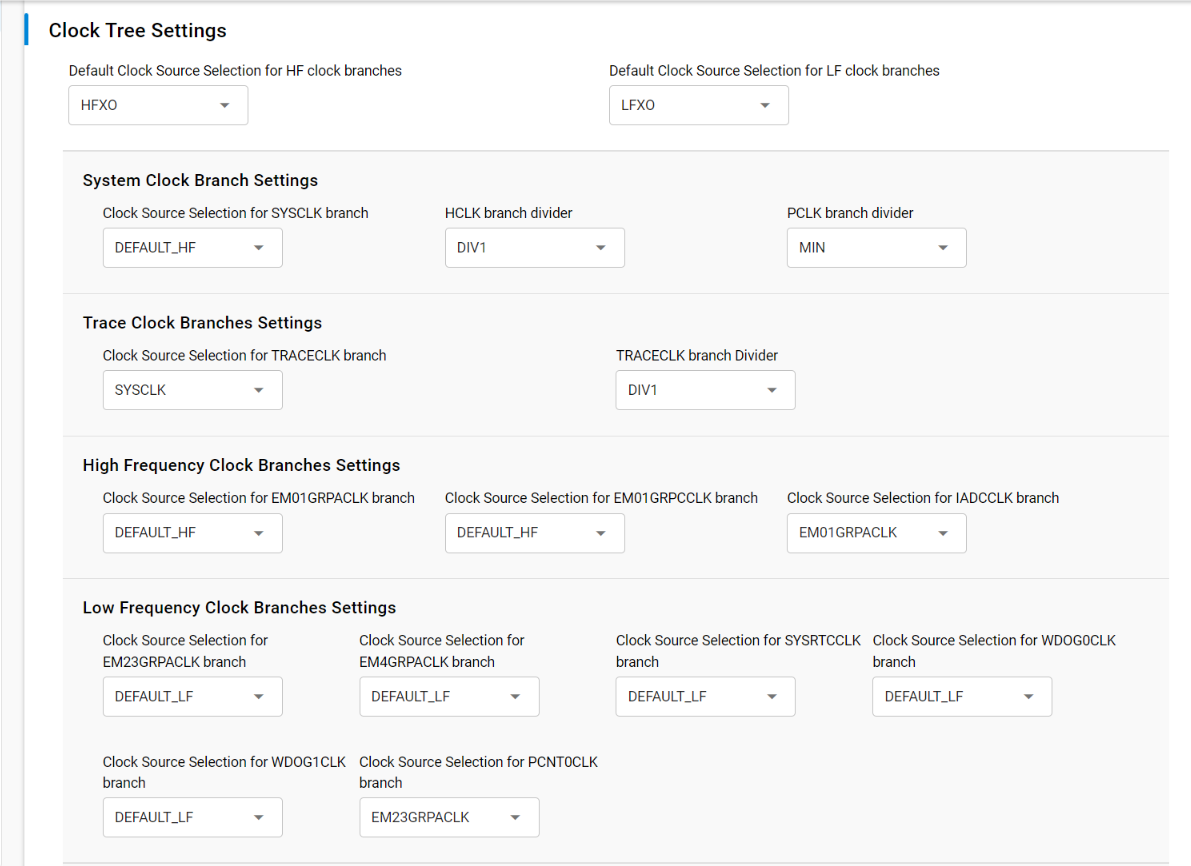

Key Configuration Parameters:
// Default clock source selections (support AUTO mode)
// The default HF and LF clock sources provide system-wide fallback oscillator selections
// that are used by multiple clock branches when not explicitly configured.
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_HF_CLOCK_SOURCE SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_HF_CLOCK_SOURCE_AUTO // AUTO selects HFXO if RAIL present
// Options: AUTO, HFRCODPLL, HFXO, FSRCO
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_LF_CLOCK_SOURCE SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_LF_CLOCK_SOURCE_LFRCO // Default LF oscillator for low-power peripherals
// Options: LFRCO, LFXO, ULFRCO
// System clock branch configuration
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_SYSCLK_SOURCE SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_HF_CLOCK_SOURCE // System clock source
// Note: May be overridden by Power Manager Execution Modes feature if SL_POWER_MANAGER_EXECUTION_MODES_FEATURE_EN is enabled.
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HCLK_DIVIDER CMU_SYSCLKCTRL_HCLKPRESC_DIV1 // AHB bus divider
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_PCLK_DIVIDER CMU_SYSCLKCTRL_PCLKPRESC_DIV1 // APB bus divider
// Individual clock branch configurations (examples)
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_EM01GRPACLK_SOURCE SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_HF_CLOCK_SOURCE // Timer peripherals
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_EM23GRPACLK_SOURCE SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_LF_CLOCK_SOURCE // Low-power peripherals
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_EUSART0CLK_SOURCE CMU_EUSART0CLKCTRL_CLKSEL_EM01GRPCCLK // UART clock sourceUniversal Configurator Integration#
The Universal Configurator provides a GUI interface for configuring Clock Manager settings without manual file editing:
Access Path: Component → Services → System → Clock Manager
Key Configuration Sections:
Oscillator Configuration: Enable/disable oscillators, set tuning parameters
Clock Tree Configuration: Select default clock sources for different branches
Advanced Features: HFXO crystal sharing, clock export, calibration settings
Configuration Workflow:
Open project in Simplicity Studio.
Navigate to Universal Configurator.
Find Clock Manager service component.
Configure oscillator presence and parameters.
Set clock tree routing preferences.
Generate configuration files.
Build project with updated settings.
Clock Tree Configuration Limitations:
Compile-time Only: Clock tree configuration is available at compile-time only.
No Runtime APIs: Clock Manager does not offer API functions to manipulate the clock tree at runtime.
Peripheral Internal Dividers: Some peripherals have internal clock dividers that are not handled by the Clock Manager configuration. These dividers are typically exposed by the peripheral driver configuration when present.
Boundary Responsibility: Clock Manager handles the clock tree up to the peripheral boundary, while internal peripheral dividers are managed by individual peripheral drivers.
Configuration Examples#
Example 1: High-Performance Wireless Application#
// sl_clock_manager_oscillator_config.h for wireless applications
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_EN SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_EN_ENABLE // Required for wireless precision
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_FREQ 39000000 // 39 MHz crystal frequency
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_CTUNE 140 // Board-specific tuning
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_LFXO_EN 1 // For sleep timing precision
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFRCO_DPLL_EN 1 // Enable DPLL for alternative configuration
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DPLL_FREQ 78000000 // 2x HFXO frequency
// sl_clock_manager_tree_config.h for wireless applications
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_HF_CLOCK_SOURCE SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_HF_CLOCK_SOURCE_HFXO
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_LF_CLOCK_SOURCE SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_LF_CLOCK_SOURCE_LFXO
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_SYSCLK_SOURCE CMU_SYSCLKCTRL_CLKSEL_HFRCODPLL // Alternative: HFRCO+DPLL at 2x HFXO frequency.
// Alternative high-performance configuration:
// - SYSCLK uses HFRCO+DPLL at 2x HFXO frequency (78 MHz)
// - Radio clock branch derives HFXO frequency via its internal divider
// - Provides performance boost while maintaining wireless precision
// - Higher power consumption due to both oscillators being activeExample 2: Low-Power Sensor Application#
// sl_clock_manager_oscillator_config.h for low-power applications
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_EN SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_EN_DISABLE // Disable for power savings
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_LFXO_EN 1 // Keep for RTC precision
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFRCO_DPLL_EN 0 // Disable DPLL for power savings
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFRCO_BAND cmuHFRCODPLLFreq_19M0Hz // Lower frequency for power
// sl_clock_manager_tree_config.h for low-power applications
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_HF_CLOCK_SOURCE SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_HF_CLOCK_SOURCE_HFRCODPLL
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_LF_CLOCK_SOURCE SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_LF_CLOCK_SOURCE_LFXO
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_SYSCLK_SOURCE CMU_SYSCLKCTRL_CLKSEL_HFRCODPLL // Explicitly use HFRCO for system clock.Example 3: Battery-Optimized Application#
// sl_clock_manager_oscillator_config.h for battery applications
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_EN SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_EN_DISABLE // No crystal for ultra-low power
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_LFXO_EN 0 // Use LFRCO for power savings
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFRCO_DPLL_EN 0 // Disable for minimal power
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFRCO_BAND cmuHFRCODPLLFreq_19M0Hz // Moderate frequency for low power and moderate performance
// sl_clock_manager_tree_config.h for battery applications
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_HF_CLOCK_SOURCE SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_HF_CLOCK_SOURCE_HFRCODPLL
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_LF_CLOCK_SOURCE SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_LF_CLOCK_SOURCE_LFRCO
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_SYSCLK_SOURCE CMU_SYSCLKCTRL_CLKSEL_HFRCODPLL // Explicitly use HFRCO for system clock
// Note: For battery applications, running at moderate frequency can often provide better
// overall power efficiency than low frequencies, as tasks complete faster
// and allow the system to return to sleep mode sooner.Example 4: Series 3 High-Performance with SOCPLL#
// sl_clock_manager_oscillator_config.h for Series 3 high-performance applications
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_EN SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_EN_ENABLE // Required as SOCPLL reference
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_FREQ 39000000 // 39 MHz crystal frequency
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_HFXO_CTUNE 140 // Board-specific tuning
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_LFXO_EN 1 // For sleep timing precision
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_SOCPLL_EN 1 // Enable SOCPLL for high performance
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_SOCPLL_FREQ 150000000 // 150 MHz for maximum performance
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_SOCPLL_REFCLK CMU_SOCPLLREFCLKCTRL_CLKSEL_HFXO // Use HFXO as reference
// sl_clock_manager_tree_config.h for Series 3 high-performance applications
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_HF_CLOCK_SOURCE SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_HF_CLOCK_SOURCE_HFXO
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_LF_CLOCK_SOURCE SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_DEFAULT_LF_CLOCK_SOURCE_LFXO
#define SL_CLOCK_MANAGER_SYSCLK_SOURCE CMU_SYSCLKCTRL_CLKSEL_SOCPLL0 // Use SOCPLL for system clock
// Benefits of SOCPLL configuration:
// - Maximum performance with 150 MHz system clock
// - High precision clock derived from crystal reference
// - Optimized for compute-intensive applications
// - Power Manager can automatically select SOCPLL for performance modes