Start a Project#
On this page:
Project Creation#
New Simplicity Studio® 5 (SSv5) projects are created through a sequence of three dialogs:
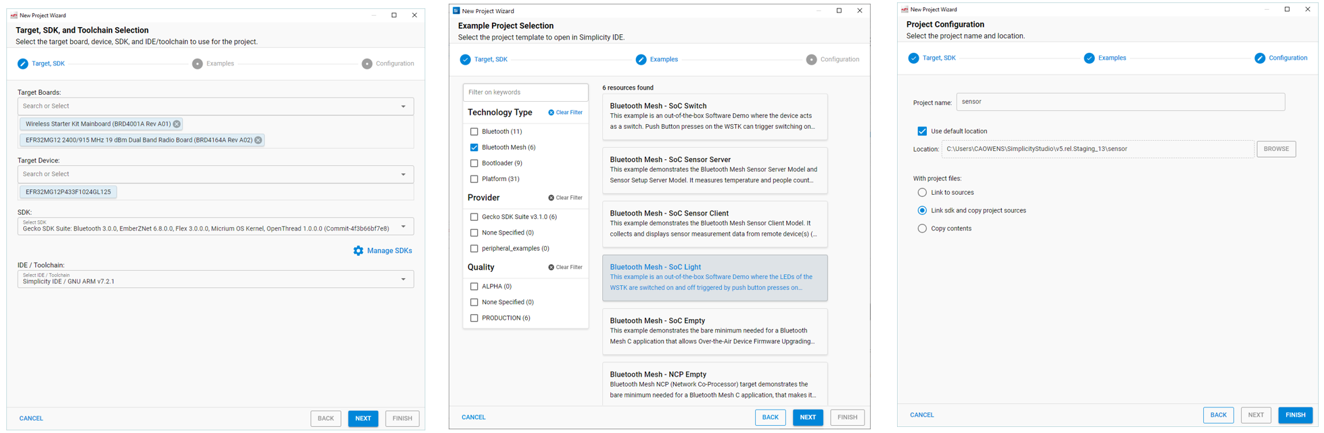

An indicator at the top of the dialog shows you where you are.

You can start a project from three different locations in the Launcher Perspective. Where you start determines which of the three dialogs you will land on. Click BACK to move to an earlier dialog, if you need to make a change.
From the OVERVIEW tab: Click Create New Project. Starts on the Examples dialog.
From the EXAMPLE PROJECTS tab: Use the filters as needed, select a project, and click CREATE. Starts on the Project Configuration dialog.
From the file menu: Select New >> Silicon Labs Project Wizard. Starts on the Target, SDK, and Toolchain Selection dialog. NOTE: SSv5 contains several project wizards. See About the Launcher for more information.
While you are getting started, you can leave the default values in place.
Target, SDK, and Toolchain Selection#
If you have connected or selected a target, all information is pre-populated. Otherwise you can select target parts here. Click NEXT.
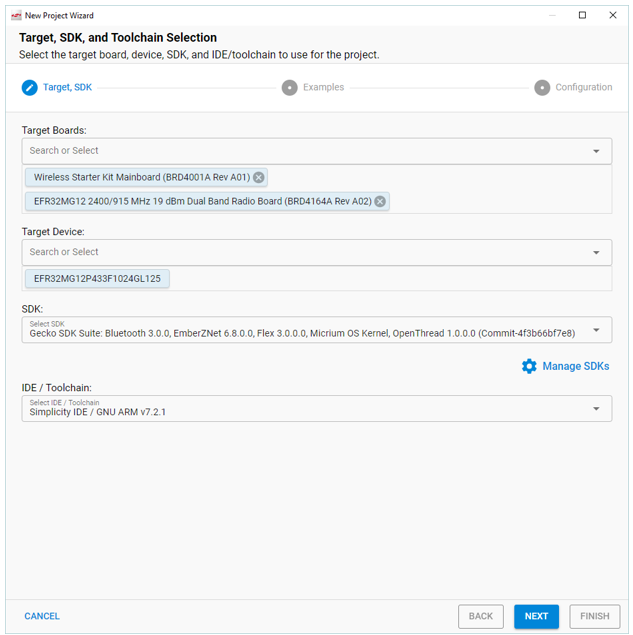

Note that if you want to use IAR in SSv5, select it here. If you are developing in the Project Configurator environment, it is difficult to change compilers once the project is created.
Examples#
Use the checkboxes or keywords to find the example of interest, then select it and click NEXT.
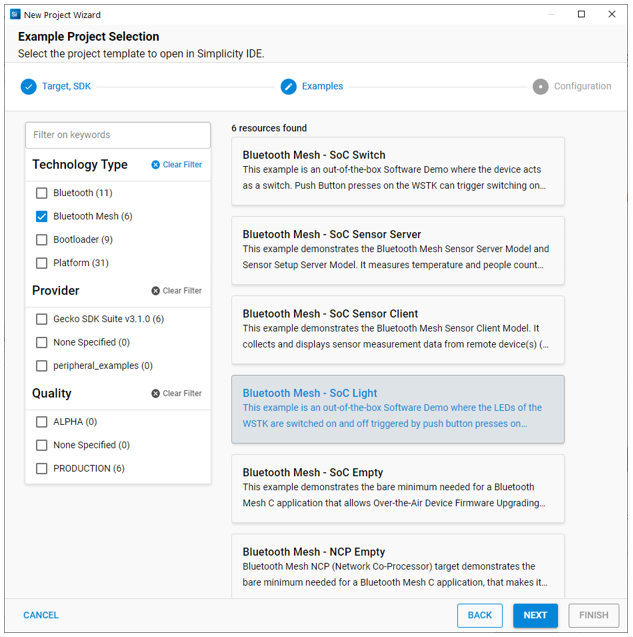

Configuration#
Rename your project if you want, and click FINISH. The three selections under "With project files" control which resources are copied and which are linked. If you modify a linked source, your changes will apply to any other project linking to that source.
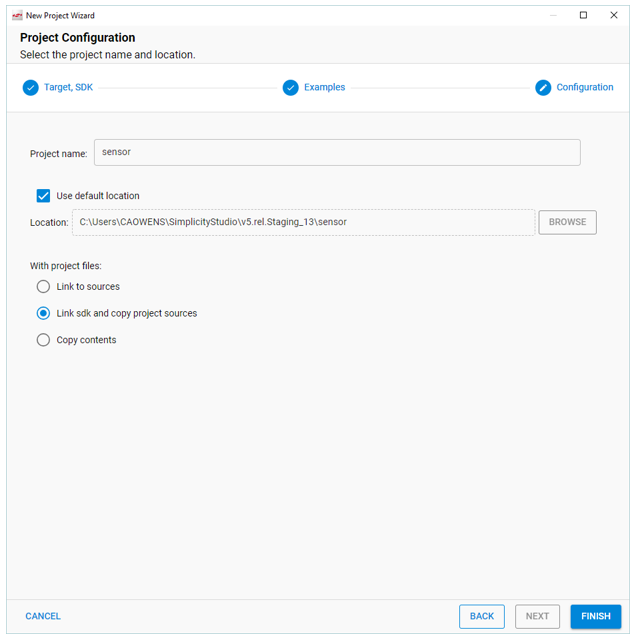

Once you finish project creation, the Simplicity IDE perspective opens. For details on all the features and functions available in this perspective, see About the Simplicity IDE.
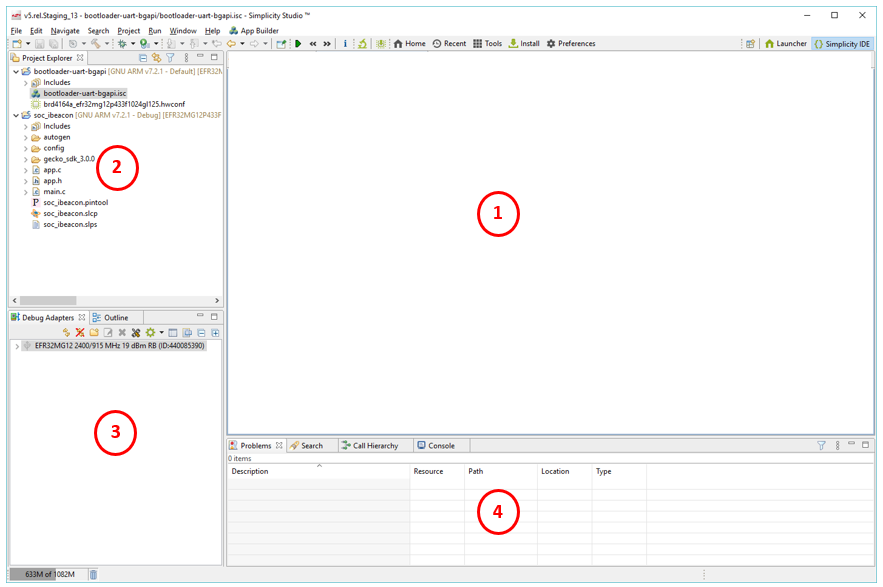

1 - Editor area (depends on the project).
2 - Project Explorer view: Lists the projects available in your workspace.
3 - Debug Adapters view: Lists the kits or SEGGER J-Links connected to your computer via USB or detected on a local network.
4 - Developer views: A set of views of use during the development process.
The editor in the Simplicity IDE perspective depends on the project:
AppBuilder: Used for Zigbee EmberZNet and Gecko Bootloader; Project files end in .isc.
Project Configurator: Used for Proprietary Flex, Bluetooth, Bluetooth Mesh, 32-bit MCU, and OpenThread; Project files end in .slcp.
8-bit Hardware Configurator: Used for 8-bit device applications.
AppBuilder Projects#
AppBuilder Projects are configured by modifying parameters in various tabs, especially the PLUGINS tab. See Developing with AppBuilder for details.
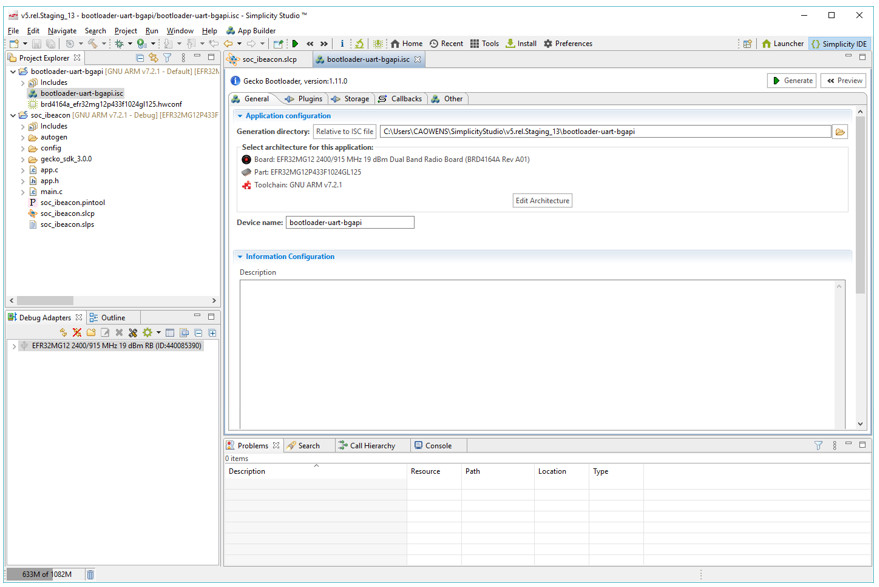

When you have configured the project, click Generate to create project files. Build the application image and flash it to your target device as in Building and Flashing.
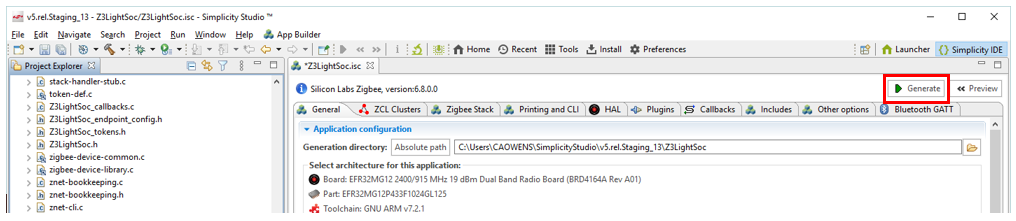

To modify the target device's pin use and parameters, use the Hardware Configurator available on the HAL tab. Note that, although the interface is similar to the 8-bit Hardware Configurator, this is a different tool.
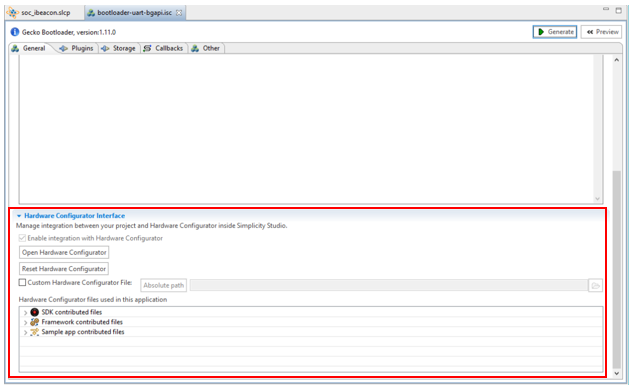

Changes made through the Hardware Configurator are stored in a board-specific .hwconf file.
Project Configurator Projects#
As well as introducing Project Configurator projects, this page introduces the Pin Tool, the Bluetooth and Bluetooth Mesh SDK's GATT Configurator, the Bluetooth Mesh SDK's Bluetooth Mesh Configurator and the Proprietary SDK's Radio Configurator.
Project Configurator projects are defined in .slcp files. Users can modify the project by adding, removing, and configuring components on the Software Components tab. See Developing with Project Configurator for details.
The project opens on an OVERVIEW tab.
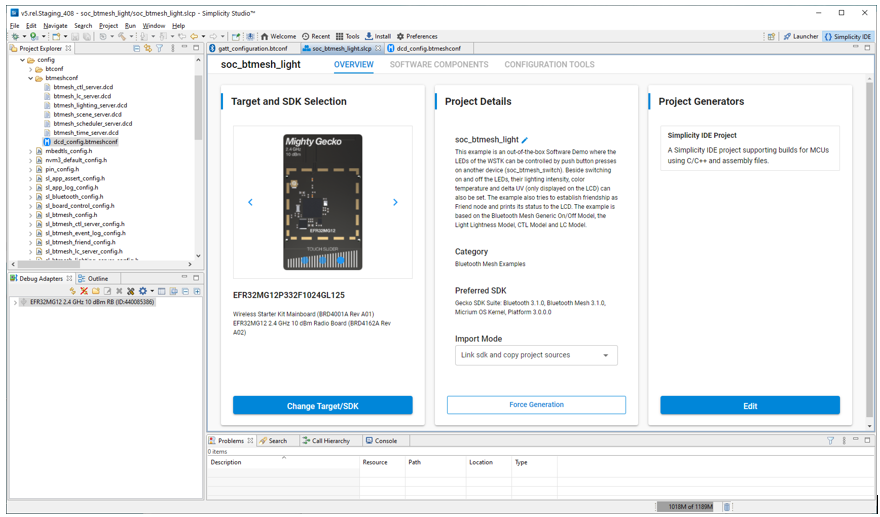

The OVERVIEW tab has three cards with information, some with settings that may be changed:
Target and SDK selection, where you can change your development target and SDK.
Project Details, where you can rename the project, change the project source import mode and, if necessary, force the generation of project and source files (in the autogen folder).
Import mode controls which resources are copied and which are linked. If you modify a linked source, your changes apply to any other project linking to that source.
Force Generation can be used in rare cases when auto-generation is not triggered, usually because of some change made outside of SSv5 such as editing the .slcp file.
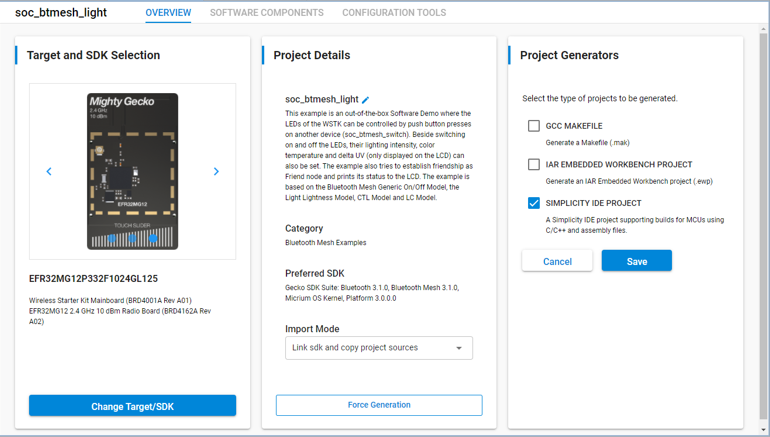
Project Generators allows you to change the IDE or build system project files that SSv5 will automatically generate (and update) as you configure your project. (Note: The compiler / toolchain used by Simplicity IDE is configurable in Project > Build Configurations. The default IDE is configurable in Preferences > Simplicity Studio > Preferred IDE.)

To configure the project through the component library, click the SOFTWARE COMPONENTS tab. A number of filters as well as a keyword search are available to help you explore the various component categories. Note that components for all installed SDKs are presented.
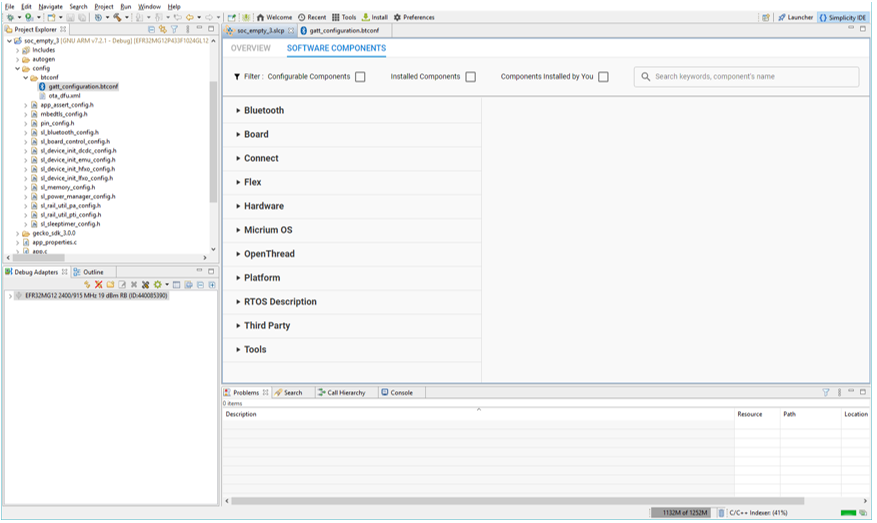

Expand a component category\subcategory to see individual components. Components installed in the project are checked (1), and can be uninstalled. Configurable components are indicated by a gear symbol (2).
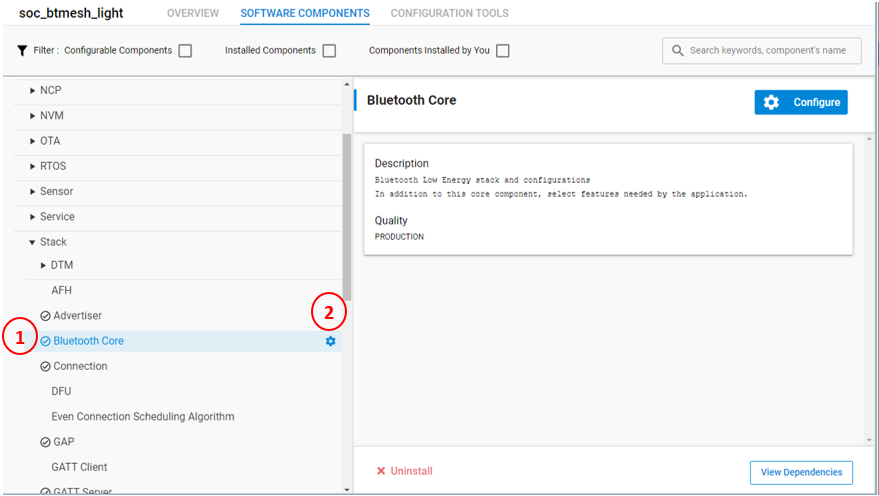

Click the gear symbol next to the component name or Configure in the configurable component description to open the Component Editor. Here you can change parameters or edit the component source directly.

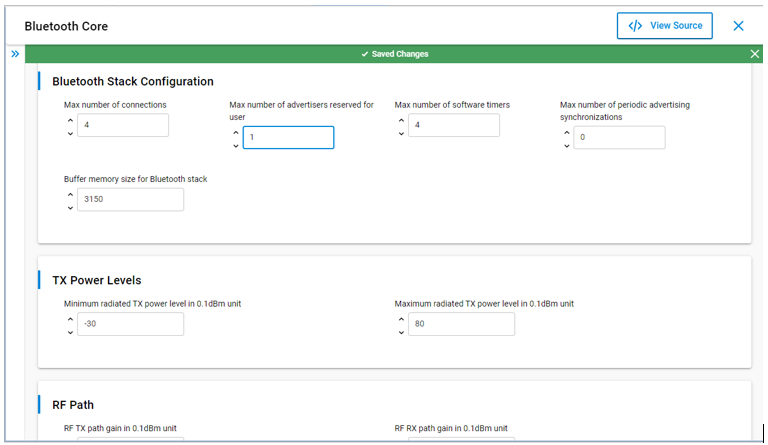
Changes are autosaved in the Component Editor.

As you make changes in the Project Configurator, for example installing or uninstalling a component, project output files are autogenerated. Progress is shown in the lower right of the Perspective.

Speed varies depending on your system. Be sure that generation is complete before building the application image.
Build the application image and flash it to your target device as described in Building and Flashing.
A CONFIGURATION TOOLS tab provides an easy way to open a tool when the tool's tab is not already open. It shows configuration tools relevant to the project type. For example, a Bluetooth Mesh project shows a number of tools, while an OpenThread project might only show the Pin Tool. Click Open on the tool's card to open it in a separate tab.
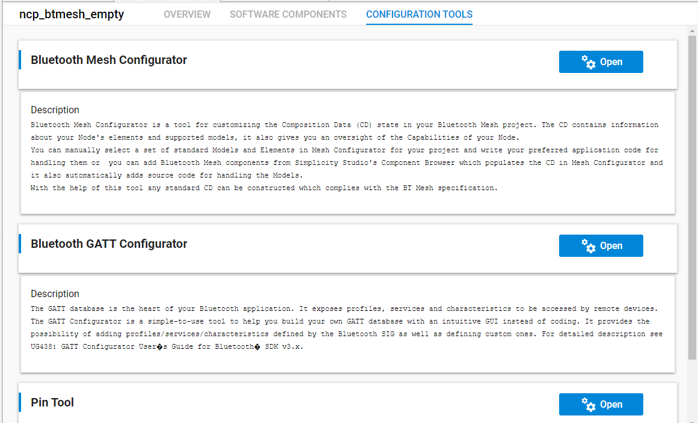

Pin Tool#
The Pin Tool lets you modify the target device's pin use and parameters. As well as opening the Pin Tool through the CONFIGURATION TOOLS tab, you can also double-click the <project>.pintool file in the Project Explorer view.

Double-click a Software Component to open the Component Editor and configure that function. Pin Tool does not autosave.
Bluetooth GATT Configurator#
Bluetooth and Bluetooth Mesh projects are also configured with the Bluetooth GATT Configurator.
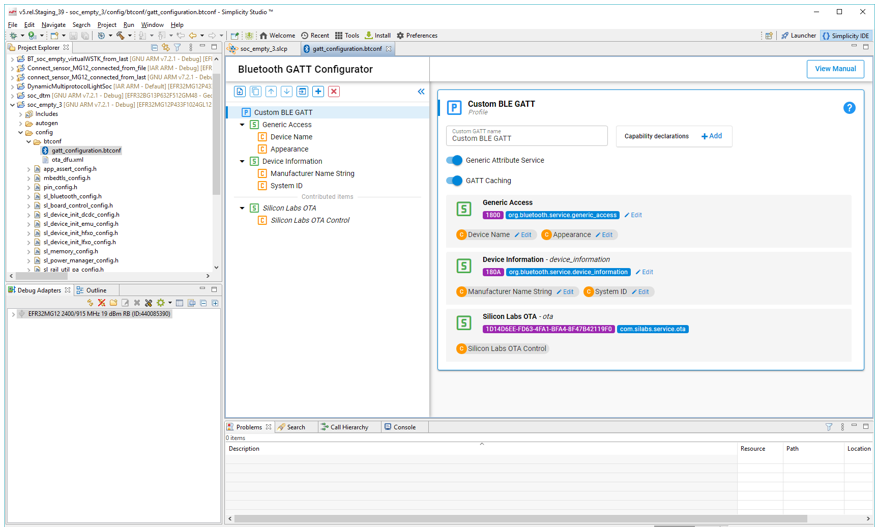

The Bluetooth GATT configurator menu allows you to add and remove services and characteristics.


Add an item.
Duplicate the selected item.
Move the selected item up.
Move the selected item down.
Import a Bluetooth GATT database.
Add Predefined.
Delete the selected item.
To add a custom service, click Profile (Custom BLE GATT), and then click Add (1). To add a custom characteristic, select a service and then click Add (1). To add a predefined service/characteristic click Add Predefined (6).
Bluetooth Mesh Configurator#
Bluetooth Mesh project Device Composition Data is configured through the Bluetooth Mesh Configurator. The Device Composition Data is presented in three areas: device information, elements, and models.
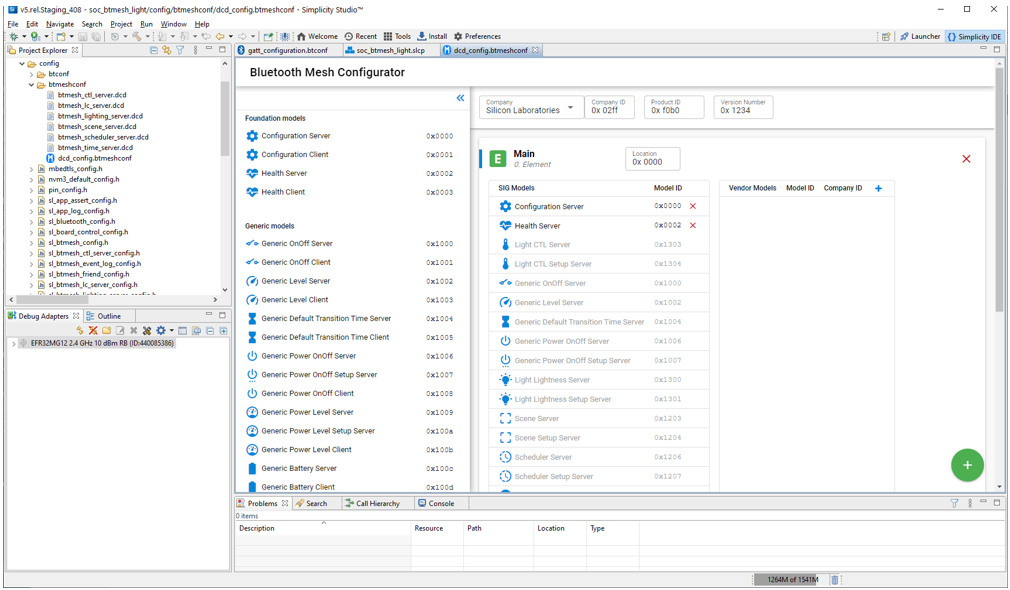

Device information is determined by the company selected in the first field.
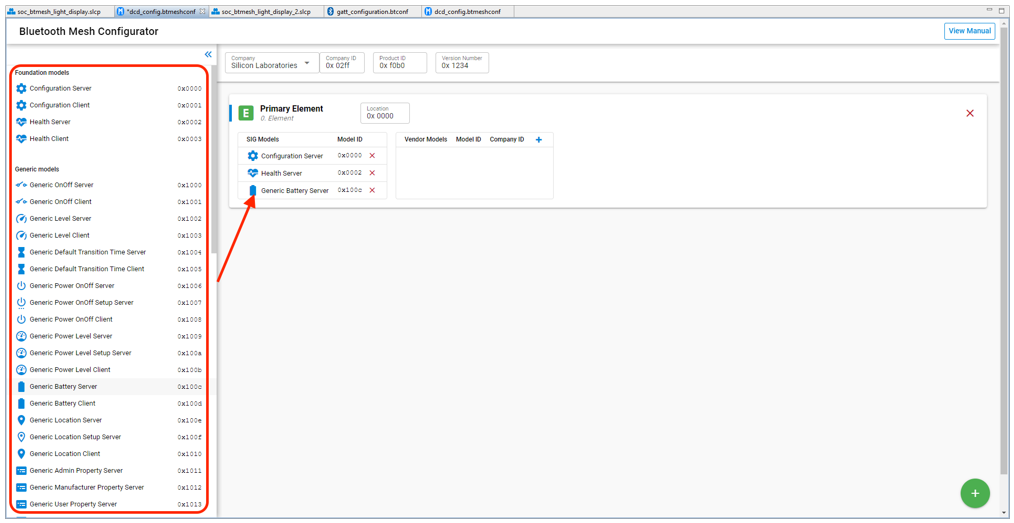
Each node has at minimum a primary element. To add more elements click the green + symbol in the bottom right.
The Bluetooth Mesh Configurator has editors for both SIG-adopted models and vendor models. SIG-adopted model components are provided but cannot be edited. You can, however, delete those models, and then add models to meet your needs. To delete a model, select it and click the red X symbol. To add a SIG-adopted model, drag the model from the left model pool to the SIG Models table in the correct element. A list of all the SIG-adopted models is displayed, and you can choose the one you want.

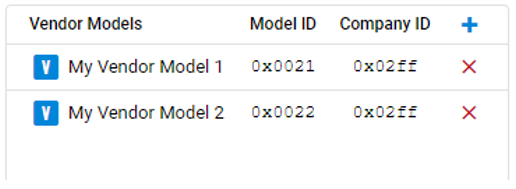
Vendor models give you more flexibility when developing products not covered by the SIG-adopted models. Vendors can define their own specification in these vendor models, including states, messages, and the associated behaviors. The vendor model editor is shown in the following figure.

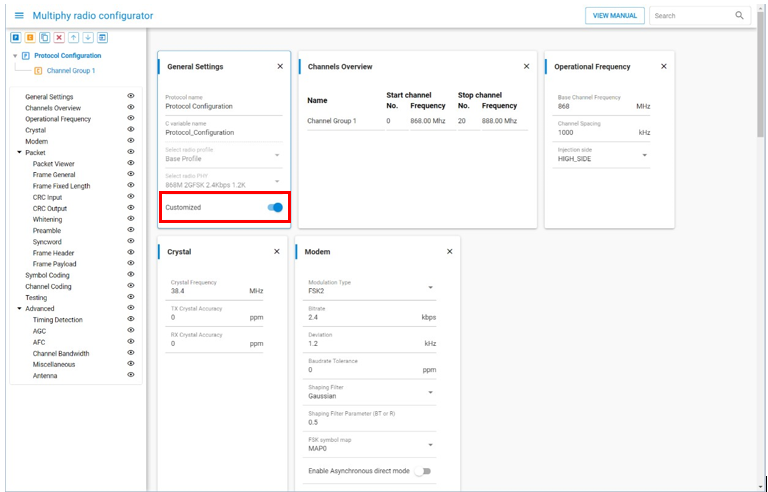
Proprietary Radio Configurator#
The Radio Configurator is provided as part of the Proprietary SDK. Use the Radio Configurator to create standard or custom radio configurations for your RAIL-based radio applications.
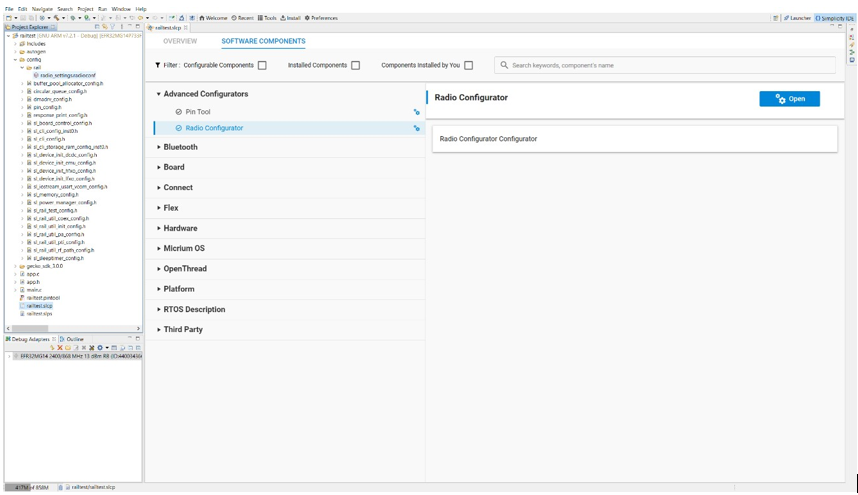

The parameters in the Radio Configurator are arranged in cards, some of which are grouped together. Different radio profiles offer different views and parameter sets.

In the General Settings card, select a radio profile in the Select radio profile drop-down menu. A radio profile may be any supported radio link technology. These technologies can be bound by standards (for example the Sigfox or WMBus protocols) or can be fully customized. The fully customizable profile is called the "Base Profile".
Select a radio PHY (radio configuration) in the Select a radio PHY dropdown list. Each profile has "built-in" configurations ready to use.
Review and update the profile options. By default, no changes are allowed; fields are grayed out. To enable customization, use the Customized switch on the General Settings card. This allows access to all the parameters defined by the profile.