Clock API Architecture#
The SiWG917 Clock Manager application programming interface (API) defines how clock sources are generated, distributed, and configured across the core processor and peripheral subsystems on the SiWG917.
This section provides an overview of the architecture, core components, and software dependencies that support efficient clock management and synchronization on the SiWG917 platform.
High-Level Architecture#
The SiWG917 clock subsystem supports multiple clock sources and dynamic routing to balance performance and power. Clock signals drive the M4 processor, high-performance peripherals, and ultra-low-power (ULP) domains.
Understanding this structure helps you configure frequencies correctly when switching power modes or enabling wireless subsystems.
Clock Domain Organization#
The SiWG917 SoC architecture is organized into three primary clock domains. Each domain operates across different power states to balance performance and power consumption:
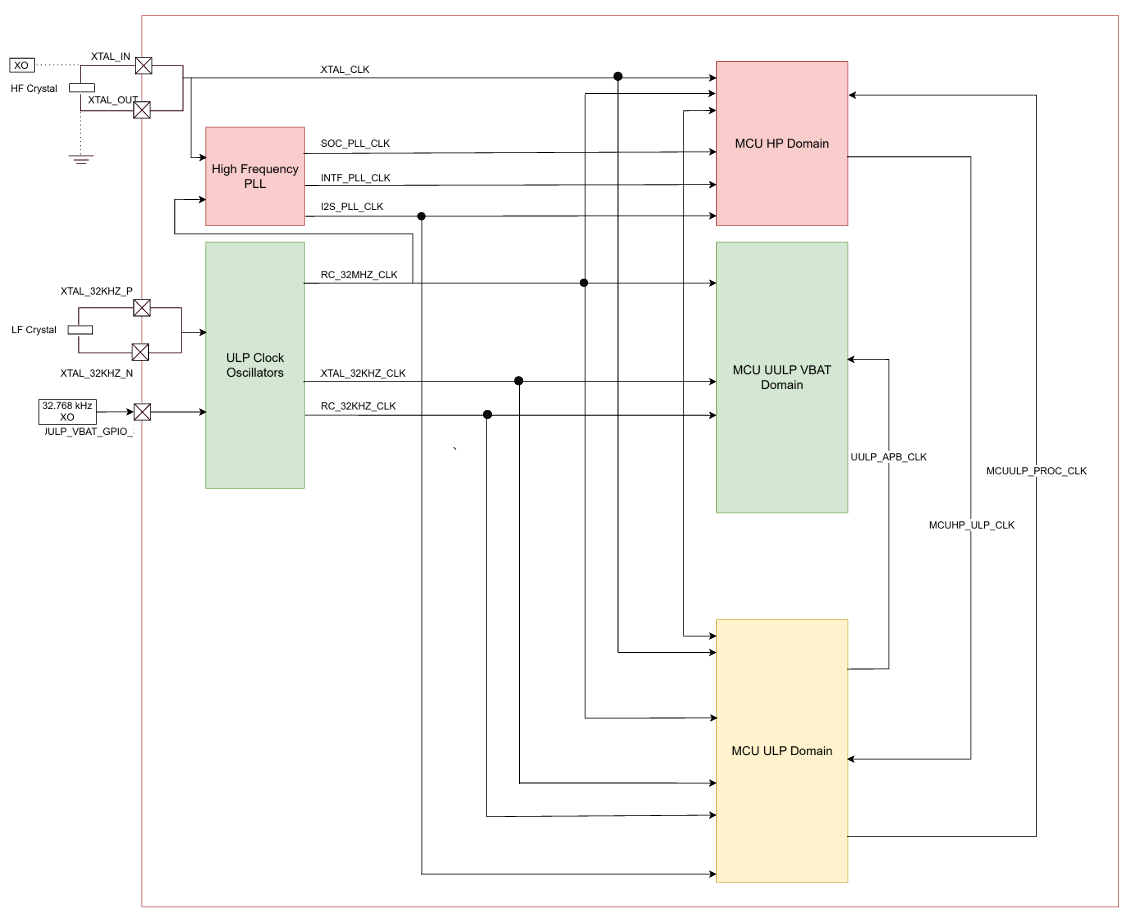

MCU high-performance (HP) domain
This domain runs the processor core, debug block, FPU, high-speed peripherals, and HP DMA. It operates in PS4 and PS3 power states and supports performance-oriented tasks such as wireless processing or compute-heavy workloads. Use this domain when your application requires high throughput or frequent interactions with HP peripherals.
MCU ultra-low-power (ULP) domain
This domain includes ULP peripherals and an AHB interconnect to the processor. It remains active in PS4, PS3, PS2, and PS1 power states, enabling low-power operation while maintaining essential functionality. Use this domain for sensor interfaces, background timers, or low-duty-cycle workflows that must remain active in sleep modes.
MCU ultra-ultra-low-power (UULP) VBAT domain
This always-on domain powers the most critical timing and control peripherals that must remain functional across all power states, including PS4, PS3, PS2, PS1, and PS0. The UULP VBAT domain operates from a battery-backed supply (VBAT) and is clocked by low-frequency sources to minimize power consumption during deep sleep modes.
Low-frequency (LF) clock operation: The UULP VBAT domain is clocked exclusively by low-frequency clock sources operating at 32 kHz (such as
RC_32KHZ_CLKorXTAL_32KHZ_CLK). These sources are optimized for power consumption while maintaining accurate timekeeping functionality. The reduced operating frequency substantially lowers dynamic power consumption compared to high-frequency clocks operating, enabling continuous operation of battery-backed peripherals, including the watchdog timer, sleep timer, and system real-time clock (SYSRTC), during deep sleep modes and system power cycling events.
Additional Resources: For information about configuring the system real-time clock, see the System Real-Time Clock (SYSRTC) Developer Guide.
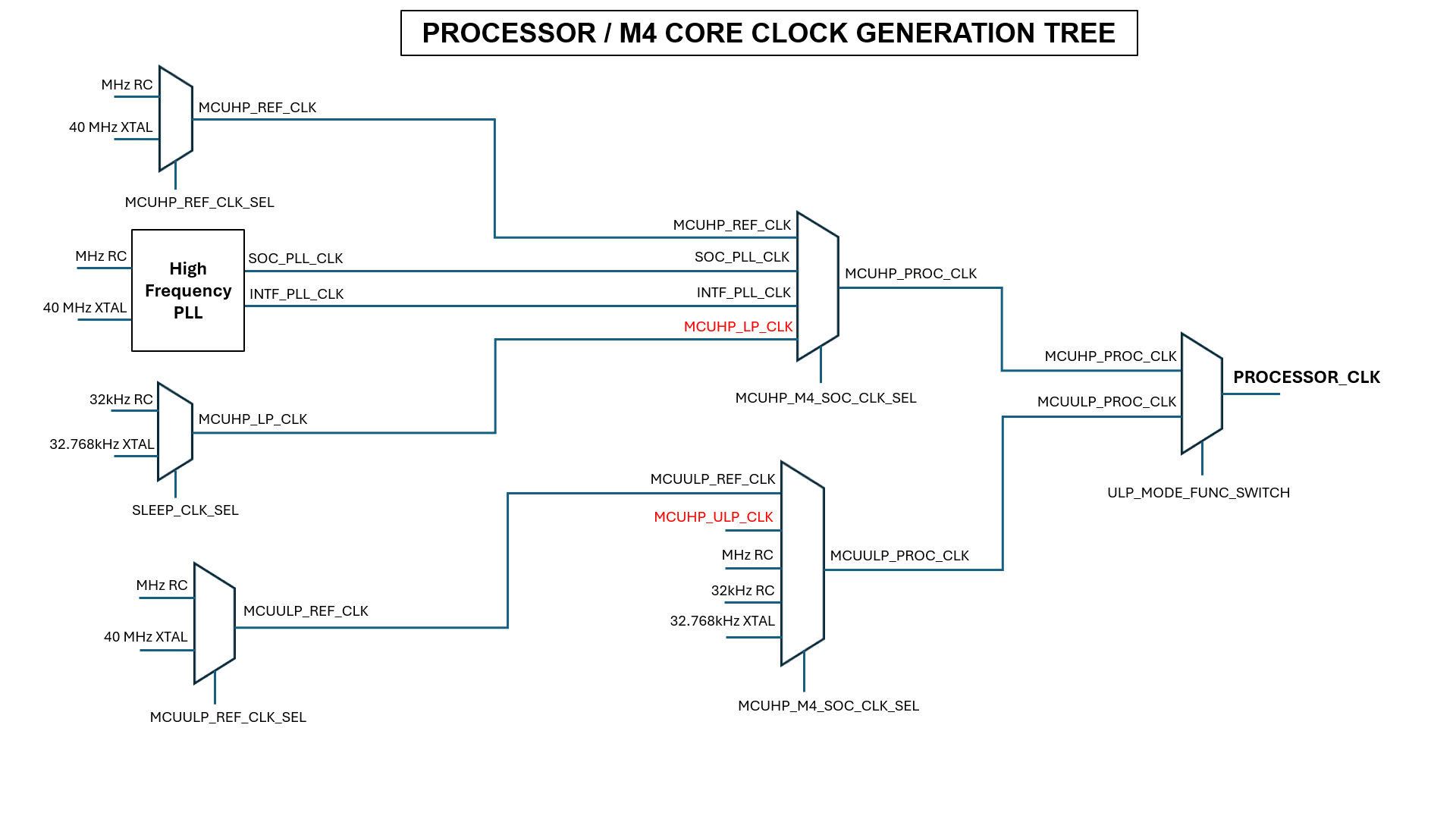
M4 Core (Processor) Clock Generation#
The M4 core clock subsystem supports multiple selectable sources, allowing you to tailor performance and power usage dynamically:
High-frequency internal oscillator (RC). On-chip oscillator for fast startup and basic timing operations.
External crystal oscillator (XTAL). Provides accurate and stable clocking for precision timing.
Phase-locked loop (PLL). Generates high-frequency signals derived from a reference clock for higher performance modes.
Each clock source passes through programmable dividers before reaching the M4 core.
This flexible design allows real-time frequency adjustments to meet application needs, while balancing throughput and energy consumption.

Low-Level Design#
The SiWG917 clock system provides configurable clock routing for high-performance (HP) and ultra-low-power (ULP) peripherals. Each subsystem can select from multiple clock sources, as summarized in the following table.
| S.No | Peripherals | Current Clock Source (Software) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |
Instruction Cache (ICACHE), Data Cache (DCACHE), Matrix Vector Processor (MVP), MCU High-Performance (HP) DMA, Micro-DMA, Motor-Control PWM, Quadrature Encoder, I2C, SSI Slave, RNG, CRC, SIO, GPIO, eFUSE |
Processor Clock |
| 2 |
Inter-Integrated Sound (I2S) HP peripheral sources: REF_CLK, SoC PLL, INTF PLL |
I2S_PLL_CLK |
| 3 |
M4 Core |
SoC PLL, REF_CLK (during sleep) |
| 4 |
UART1, UART2 |
REF_CLK |
| 5 |
SPI and SPI Master, Configuration Timers, GSPI Master, QSPI1/2 ULP peripheral sources: REF_CLK, RC_32KHZ_CLK, XTAL_32KHZ_CLK, RC_32MHZ_CLK, SOC_CLK, DOUBLER_CLK |
INTF PLL |
| 6 |
ULP Aux-ADC and DAC, ULP UART, ULP SSI, ULP Timer, ULP I2S LF-FSM sources: RC_32KHZ_CLK, RO_32KHZ_CLK, XTAL_32KHZ_CLK |
REF_CLK |
| 7 |
LF-FSM HF-FSM sources: FSM_MHZ_RC, 20 MHz RO |
XTAL_32KHZ_CLK, RC_32KHZ_CLK (if an external oscillator is used) |
| 8 |
HF-FSM |
FSM_MHZ_RC |
Note: Peripheral clock sources and routing options vary by subsystem and application mode. See the SiWx917 family Reference Manual – Clock Management Unit for a complete signal map.
Core Components#
The Clock Manager architecture includes modular components that handle initialization, configuration, and runtime management of all clock domains.
Clock manager module – Provides APIs for clock source selection, divider configuration, PLL control, and runtime clock adjustments.
emlib – Silicon Labs’ embedded library that enables low-level access to device hardware registers.
Device initialization layer – Configures default system clocks and applies startup settings automatically.
Hardware register interface – Allows direct manipulation of SiWG917 clock control registers for advanced custom configurations.
Tip: Use Clock Manager APIs for standard configurations. Direct register access should be reserved for expert-level debugging or timing-critical applications.
Dependencies#
The SiWG917 clock system integrates with multiple hardware and software layers to ensure reliable timing operation.
Operating system (OS) – Supports bare-metal and RTOS-based implementations.
Middleware – Includes
emlibanddevice_initmodules from the Gecko Software Development Kit (GSDK).Drivers – Provide low-level control for oscillators, PLLs, and clock gating mechanisms.
Hardware interfaces – Implements the SiWG917 hardware blocks for clock generation and distribution. See the SiWx917 family Reference Manual – Clock Management Unit.
