Inter-IC Sound (I²S) Architecture#
This topic describes the Inter-IC Sound (I²S) architecture for the SiWx917 platform and how to use it effectively in your audio applications. It introduces the relevant hardware blocks, software layers, power domains, and development tools required to implement reliable digital audio communication.
Peripheral Overview#
The SiWx917 platform includes multiple I²S controllers designed to support a wide range of digital audio applications:
High-performance I²S (I2S0)
Operates in the high-performance (HP) domain
Supports sample rates up to 192 kHz
Supports 16, 24, and 32-bit audio word lengths
Ideal for:
Music and media playback
High-quality voice processing
Low-latency, full-duplex audio streaming
Ultra-low-power I²S (ULP_I2S)
Operates in the ultra-low-power (ULP) domain
Remains active in low-power states (for example, PS2)
Optimized for:
Always-on audio capture
Voice-trigger and low-power sensing
Battery-powered audio nodes
All I²S instances support:
Programmable audio formats and word widths
First-in, first-out (FIFO) buffers on transmit (TX) and receive (RX) paths
Interrupt-driven or direct memory access (DMA)–assisted operation
Primary (controller) or secondary (target) clocking roles
I²S Frame Format#
I²S communication is organized into frames. Each frame carries one audio sample for the left channel and one sample for the right channel.
Key signals:
Word Select (WS / LRCLK):
Indicates the active audio channel (left or right).Serial Clock (SCK / BCLK):
Clocks each data bit within a frame.Serial Data (SD / DIN / DOUT):
Serial audio data transmitted most-significant bit (MSB) first.Primary Clock (MCLK):
High-frequency reference clock (typically 256× or 512× the sample rate), required by some codecs and digital-to-analog converters (DACs).
A typical stereo frame contains:
One left-channel word
One right-channel word
Frames repeat at the configured sample rate to maintain continuous audio streaming.
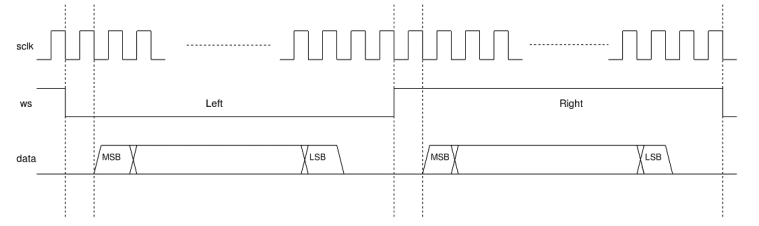

Figure: Typical I²S transfer showing WS (Word Select), SCK (Clock), and SD (Data) signals with left/right channel timing.
Key Features#
High-Quality Audio Performance
Supports a wide range of audio sampling rates: 8 kHz, 11.025 kHz, 16 kHz, 22.05 kHz, 24 kHz, 32 kHz, 44.1 kHz, 48 kHz, 88.2 kHz, 96 kHz, and 192 kHz
Configurable word lengths of 16, 24, and 32 bits to meet various precision and fidelity requirements
Supports stereo and multi-channel audio streaming, ideal for playback and recording systems
Primary or Secondary Operation
Can function as a primary (controller) to generate all I²S clocks
Can function as a secondary (target) synchronized with an external clock source
Full-duplex data transfer capability with independent transmit (TX) and receive (RX) paths
Efficient Data Handling
Integrated FIFO buffers (depth of 8) for both transmit and receive to reduce CPU load
Direct Memory Access (DMA) support enables continuous audio streaming with minimal software overhead.
Programmable FIFO thresholds allow tuning for latency or throughput optimization
Flexible Audio Operation Modes
Supports both standard I²S and time-division multiplexing (TDM) modes for multi-channel applications
Configurable left-justified and right-justified data alignment options
Optional Primary Clock (MCLK) output for driving external audio codecs
Robust and Reliable Streaming
Generates interrupts for
transmit completion
receive readiness
error conditions (underrun or overrun).
Independent clock and frame synchronization circuits ensure stable operation in noisy or high-speed environments
Uses an AMBA Advanced Peripheral Bus (APB) interface for register access and peripheral integration
Low-Power Optimization
ULP_I²S supports DMA-based transfers in PS2 and PS1 low-power states, allowing the MCU to enter sleep while audio transfers continue
Extends battery life in always-on and portable audio use cases by offloading data movement to UDMA
Architecture Notes
The I²S block is integrated through an APB interface.
FIFO logic ensures register access remains synchronized with on-wire data transmission, maintaining consistent audio flow across power modes.
I²S Software Architecture#
The SiWx917 I²S software architecture uses a layered abstraction model to simplify development, improve modularity, and support scalable audio designs. High-level audio control logic is separated from low-level hardware access, enabling reuse across both high-performance and low-power I²S instances.
The following diagram illustrates the structure and flow of the I²S software stack.
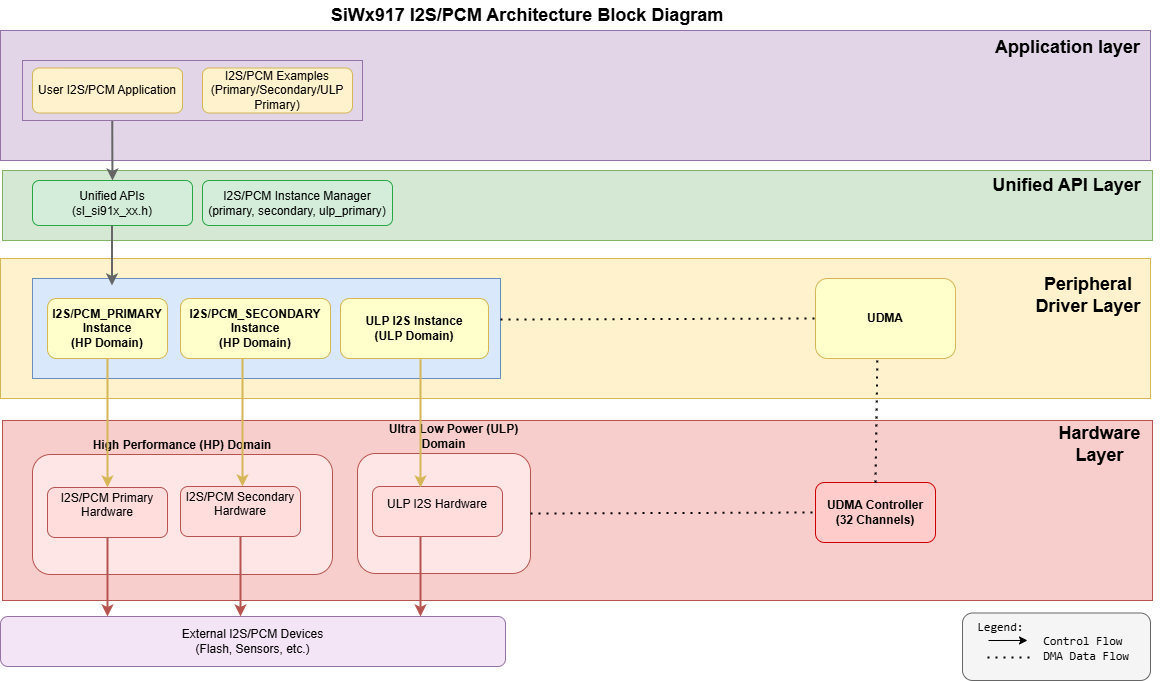

Figure: I²S software architecture.
Core Components#
Application Layer
User application code or example projects that call I²S APIs for streaming, recording, or codec communication.Unified API Layer
High-level driver APIs for I²S initialization, configuration, and data transfer. These APIs abstract hardware differences to make the application code portable across HP and ULP domains.Peripheral Driver Layer
Low-level drivers that interact directly with the I²S hardware instances (I2S0 in the HP domain and ULP_I2S in the ULP domain). They manage register-level operations, interrupts, and DMA control for TX and RX streams.Hardware Layer
The physical I²S peripheral within the SiWx917 system-on-chip (SoC) that performs the actual digital audio data transfer to and from external devices.
Note on CMSIS Layer:
A generic Cortex Microcontroller Software Interface Standard (CMSIS) driver abstraction exists on this platform for some peripherals. It does not apply directly to I²S and is shown in the diagram for completeness only.
How the Layers Work Together#
Control path: Application → Unified API → Peripheral Driver → I²S instance (I2S0/ULP_I2S).
Data path: For audio streaming, the driver programs UDMA to move audio samples between memory and the I²S TX/RX FIFOs, minimizing CPU involvement and latency.
Design Benefits at a Glance#
Unified API abstracts hardware details, making it easy to migrate between HP and ULP I²S instances.
Modular software layering (App → API → Driver → Hardware) streamlines integration and long‑term maintenance.
HP and ULP domains allow applications to switch between performance and power efficiency without changing application logic.
UDMA integration enables continuous audio streaming with minimal CPU overhead.
Separation of concerns improves readability, scalability, and debugging efficiency
Instance Capabilities at a Glance#
Instance | Domain | Max Sample Rate | DMA | Low-Power Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|---|
I2S0 | HP | Up to 192 kHz | TX/RX | Available in PS4/PS3 Active |
ULP_I2S | ULP | Up to 96 kHz | TX/RX | Active in PS2/PS1; ideal for always-on audio |
Why This Matters to Your Application#
You call a single I²S API, and the driver automatically handles instance selection, FIFO configuration, DMA setup, and interrupt management.
Use UDMA for continuous audio transfers to reduce CPU load during playback or recording.
Choose ULP_I2S for low-power, always-on voice or sound detection scenarios while keeping the MCU in sleep (PS1/PS2).
Take advantage of FIFO and interrupt-driven designs to achieve balanced latency and performance for real-time audio streaming.
Directory Structure in WiSeConnect SDK#
Use the following directory layout to locate headers, sources, and examples in the WiSeConnect software development kit (SDK).
wiseconnect/
├── components/
│ └── device/
│ └── silabs/
│ └── si91x/
│ └── mcu/
│ └── drivers/
│ └── unified_api/
│ ├── inc/
│ │ └── sl_si91x_I2S.h
│ └── src/
│ └── sl_si91x_I2S.c
└── examples/
└── si91x_soc/
└── peripheral/
├── sl_si91x_I2S_loopback
├── sl_si91x_I2S_primary
├── sl_si91x_I2S_secondary
└── sl_si91x_ulp_I2SClock and Power Management#
On the SiWx917, I²S clocks and power domains are managed automatically by the WiSeConnect SDK and Simplicity Studio. Peripherals are clock‑gated by default, and the SDK enables the required clocks and domains when you add and configure an I²S component in Simplicity Studio.
High-Performance I²S (I2S0)
Available in PS4/PS3 Active states. Use these instances for high-fidelity or low-latency audio applications that require sample rates up to 192 kHz and 32-bit resolution.Ultra-Low-Power I²S (ULP_I²S)
Available in PS4/PS3/PS2 Active states. Ideal for battery-powered, always-on, or voice-triggered designs that require low-power, continuous audio streaming or capture.
You typically do not need to adjust register-level clock or power configurations manually. These are handled by the SDK during component setup.
For advanced customization or debugging, refer to the SiWx917 Hardware Reference Manual, WiSeConnect SDK documentation, and the I²S Low-Power Instance Guide.
Power Domain Overview#
The SiWx917 SoC provides multiple I²S controllers distributed across HP and ULP domains to balance audio quality and energy efficiency.
High-Performance I²S Interface#
I2S0 (base address: 0x4705_0000)
This interface operates in the MCU HP domain. They are available in PS4 and PS3 Active states and are suited for high-bandwidth or frequent audio streaming applications such as voice, music, or media playback.
Support up to 192 kHz sample rate and 32 bit data width.
Enable fast and stable data transfer through DMA and FIFO buffering.
Ultra-Low-Power I²S Interface#
ULP_I²S (base address: 0x2404_0400)
This controller belongs to the ULP domain and remains active in PS4, PS3, and PS2 power states.
It supports sample rates up to 96 kHz and is optimized for low-power, always-on, or voice-detection applications.
Dependencies (Setup Checklist)#
Before using I²S on SiWx917, make sure the following setup and configuration steps are complete:
WiSeConnect SDK installed and configured in Simplicity Studio.
The project’s
.slcpconfiguration includes the I²S components.Set sample rate, bit depth, and thresholds using the Universal Configurator (UC).
Ensure clock source and divider settings are managed by the SDK.
Configure power domains; I²S availability depends on PS2, PS3, and PS4.
Initialize GPIO pins (WS, SCK, SD, and MCLK) using
sl_si91x_i2s_pin_init().Place DMA buffers in ULP memory for optimal low-power performance.
For a step-by-step walkthrough of installation, configuration, and initialization—including Simplicity Studio setup, component selection, UC configuration, and code generation—see the I²S Initialization and Configuration Guide.
