Using Co-Processor Communication Daemon with wsbrd#
Overview#
Co-Processor Communication (CPC) enables one host system to communicate with a Network co-processor device (NCP), by physical transport (UART, SPI, and so on). In CPC, data transfers between processors are segmented in sequential packets. Transfers are guaranteed to be error-free and sent in order. Multiple applications can send or receive on the same endpoint without worrying about collisions. A CPC daemon (CPCd) is provided to allow applications on Linux to interact with a secondary running CPC.
For the purpose of having Silicon Labs Wi-SUN stack running in harmony with other services such as Bluetooth, ZigBee, or others on the same Co-Processor, Silicon Labs added support of CPCd to wsbrd.
The next sections explain how to install and configure CPCd and wsbrd, and also how to set up an RCP with the CPC Secondary Service component in Simplicity Studio v5. This chapter only covers UART communication between a WSTK and Raspberry Pi.
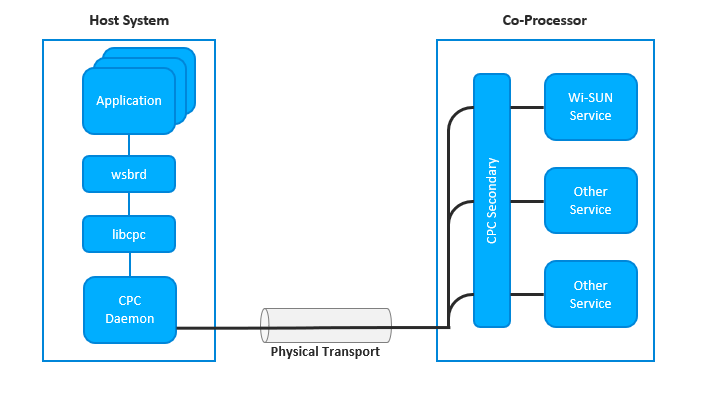

Setting Up the RCP with CPC Secondary Service#
This part is the RCP project creation and configuration in Simplicity Studio.
To use the Wi-SUN – RCP sample application as CPC secondary device, users should enable the Co-Processor Communication components in the Wi-SUN – RCP project in Simplicity Studio v5.
Components Installation#
After creating a Wi-SUN – RCP project, open the slcp file and select the Software Component tab. In the search box, enter secondary to filter the components and install the following components:
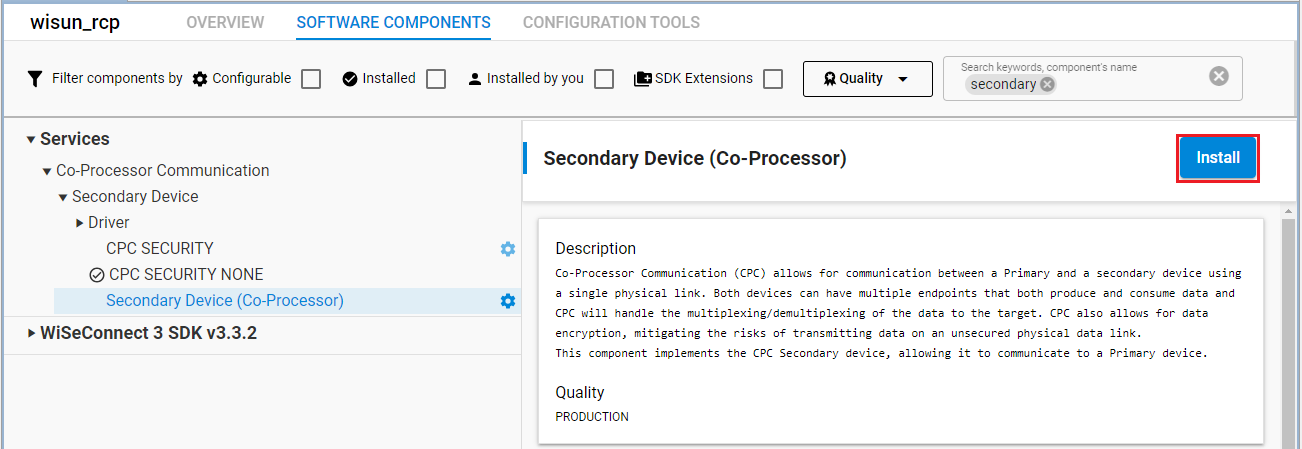

Install Services/Co-Processor Communication/Secondary Device (Co-Processor).
By default, the CPC SECURITY NONE component will be installed automatically after installing the Secondary Device (Co-Processor) component. If you wish to enable security on the CPC link, install CPC SECURITY.
The Wi-SUN/Application/Wi-SUN RCP/Wi-SUN Border Router RCP - CPC Interface will be automatically added to your project.
Secondary Device Configuration#
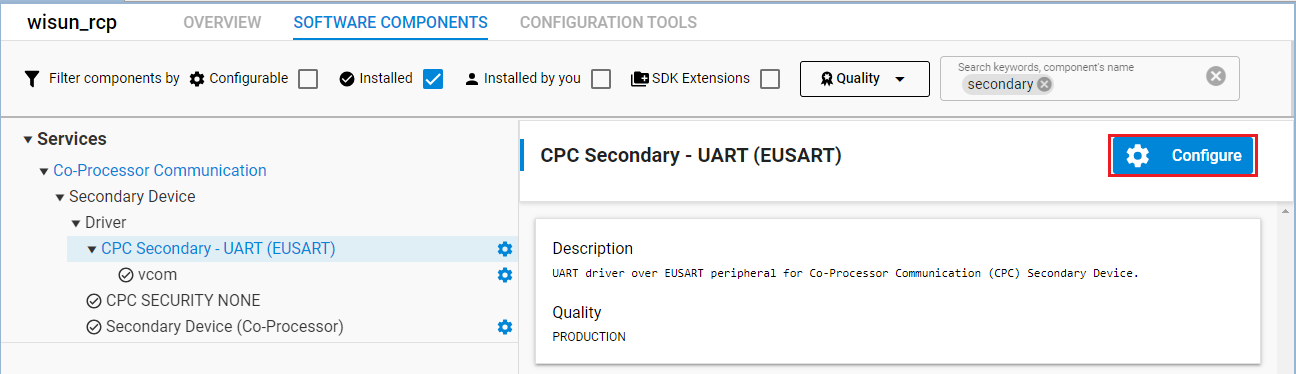
CPC Secondary - UART (EUSART) Component#
After installing all the components, configure the created instance with the desired Flow control and Baud rate. Select your created instance in the slcp perspective, and then click Configure.

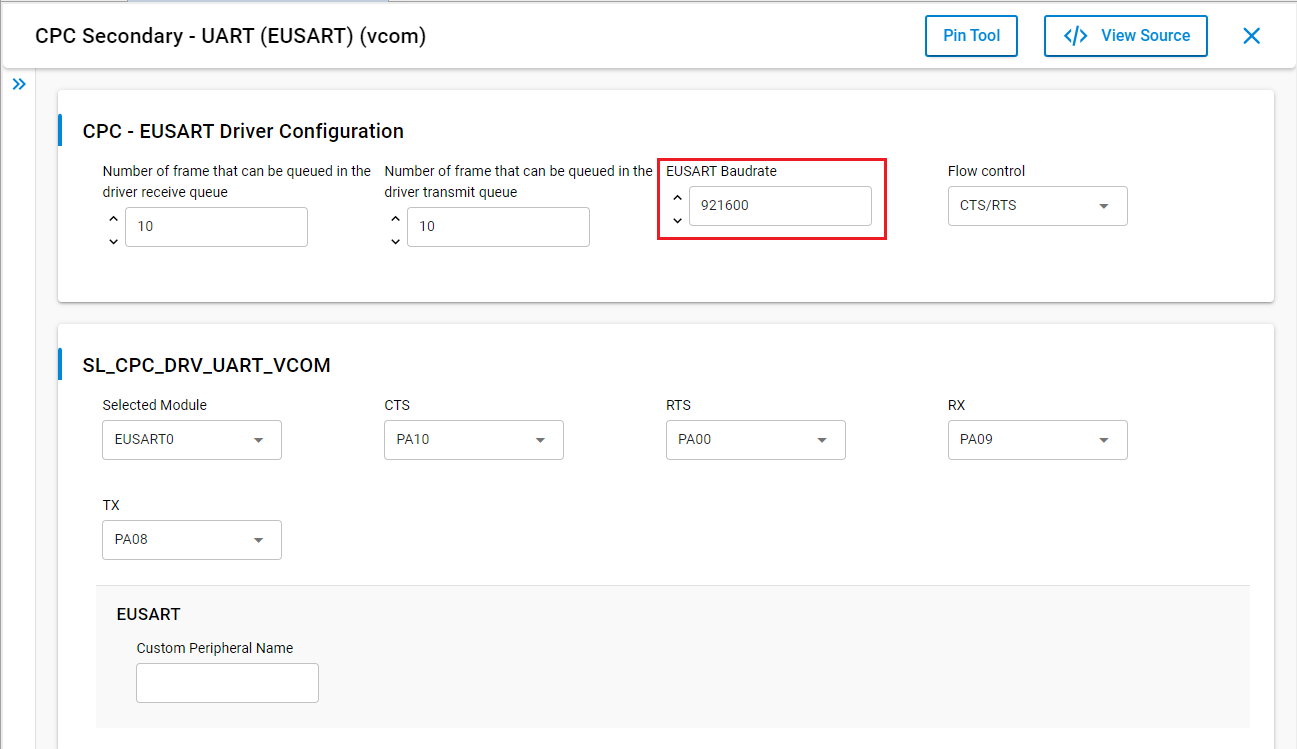
In the configuration perspective, the recommended EUSART Baudrate value is 921600. Concerning the Flow Control, it is set by default to CTS/RTS. Silicon Labs recommends this default; do not set it to None.

WSTK Configuration#
The WSTK boards are factory programmed to support 115200bps with no flow control. To align the WSTK configuration with the chosen CPC EUSART Baudrate configuration, follow the next steps:
In Debug Adapters, right-click your device and click Launch Console….
On the console, select the Admin tab, and enter the following commands:
serial vcom config speed 921600
serial vcom config handshake rtsctsThe following figure shows the resulting console output.
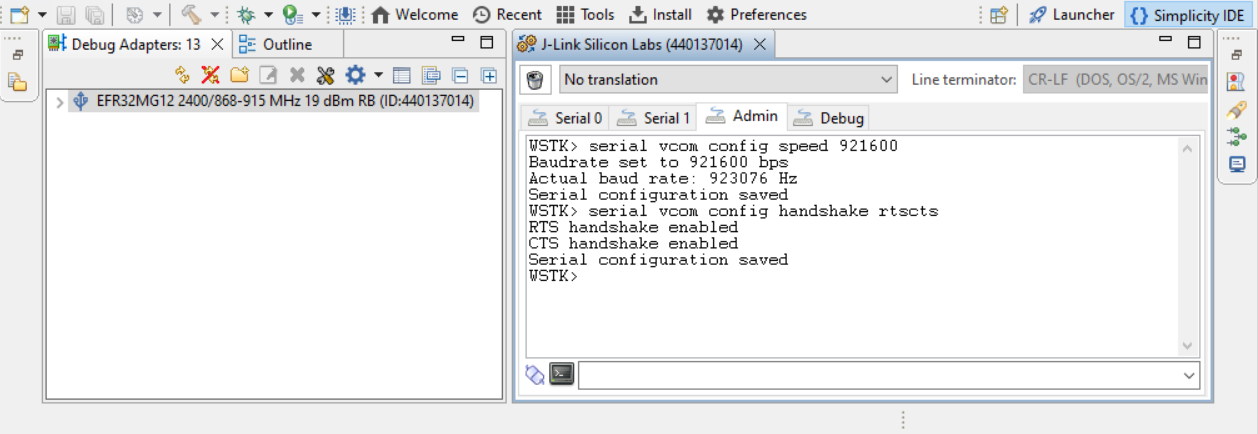

After finishing these steps, you can Build your project and flash it to the device.
CPCd Installation and Configuration#
This part is to be executed on the linux host.
CPCd Installation#
CPCd is delivered as a CMake project. The minimum version of CMake required to generate the project is 3.10. CPCd requires MbedTLS to encrypt the endpoints. The minimal version required for Mbed-TLS is 2.7.0. libmbedtls-dev must be installed to compile from sources.
Refer to cpc-deamon readme , sections Compiling CPCd and Installing CPCd and CPC library to install CPCd.
Checking cpcd / libcpc Installs#
$ ls -al /usr/local/bin | grep cpc
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 748024 May 29 11:01 cpcd$ ls -al /usr/local/lib/arm-linux-gnueabihf/ | grep libcpc
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 11 May 29 11:01 libcpc.so -> libcpc.so.3
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 17 May 29 11:01 libcpc.so.3 -> libcpc.so.4.4.2.0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 87776 May 29 11:01 libcpc.so.4.4.2.0$ cpcd --version
4.4.2.0
GIT commit: 37bc19f2dfffa8cd954162bb42b8f80755e31e99
GIT branch: refs/heads/main
Sources hash: bbf8593d1941a71988883e18e2bfeb85ec27aaffbb84aadbf12a50a7e0c2a226CPCd Configuration#
After installing CPCd, a configuration file can be found under “/usr/local/etc/cpcd.conf”. This file can be accessed using the following command:
sudo nano /usr/local/etc/cpcd.confThe modifications that need to be applied to this file to configure CPCd for a secured UART communication between a WSTK and Raspberry Pi are:
instance_name: cpcd_0
bus_type: UART
uart_device_file: /dev/ttyACM0
uart_device_baud: 921600
disable_encryption: trueNote that the uart_device_file and uart_device_baud values above are examples and can be changed to suit your use case. The uart_device_file must match what is visible in dmesg after plugging the WSTK/WPK on the host.
If security was enabled on the secondary device (the RCP) by installing the CPC SECURITY component, the value of disable_encryption must be set to false.
wsbrd Configuration#
CPC is supported by wsbrd version 1.4 and above. Make sure to update and re-build wsbrd if you are running an older version. In case of reinstalling wsbrd, make sure to delete the /wisun-br-linux/CMakeCache.txt file.
In the /etc/wsbrd.conf file (copied from wisun-br-linux/examples/wsbrd.conf), comment-out cpc_instance and give it the same value as instance_name in /usr/local/etc/cpcd.conf and comment the uart_device option.
cpc_instance = cpcd_0
#uart_device = /dev/ttyACM0Setup Cross-check#
$ cat /etc/wsbrd.conf | grep cpc_instance
cpc_instance = cpcd_0
$ cat /usr/local/etc/cpcd.conf | grep instance_name
instance_name: cpcd_0
$ cat /usr/local/etc/cpcd.conf | grep uart_device_baud
uart_device_baud: 921600The uart_device_baud value must match the WSTK Stored port speed when calling serial vcom in the 'Admin' console tab.
Launching CPDC and wsbrd#
Starting cpcd before starting wsbrd#
If cpcd is not running when wsbrd is launched, the following error will occur:
$ sudo wsbrd -F /etc/wsbrd.conf
Silicon Labs Wi-SUN border router...
cpc_init: Connection refusedManually starting cpcd#
Before starting CPCd and wsbrd, connect the RCP to your Raspberry Pi. Then you can manually start the CPCd using the following command:
$sudo cpcd --conf /usr/local/etc/cpcd.conf
..
..
Info : Daemon startup was successful. Waiting for client connectionsManually Starting wsbrd#
After the line indicating that the CPC deamon startup was successful appears in the logs, use a separate terminal to manually launch wsbrd using the command:
sudo wsbrd -F /etc/wsbrd.confStarting cpcd as a Service#
Starting cpcd as a service is a better option once the system has been tested using a manual start. With the Restart=on-failure, cpcd will be restarted automatically in case of failure.
This requires:
Creating a service file for cpcd
nano $ sudo nano /usr/local/lib/systemd/system/cpcd.service# SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0 or APACHE-2.0
[Unit]
Description=Silicon Labs CPC Service
Documentation=file:////usr/local/etc/cpcd.conf
After=network.target
After=freeradius.service
# If you rely on an external DHCP server, don't forget to add a dependency here
[Service]
ExecStart=cpcd --conf /usr/local/etc/cpcd.conf
#Restart=on-failure
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetreloading the system services
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadChecking cpcd Service Status#
$ sudo systemctl status cpcd.service
● cpcd.service - Silicon Labs CPC Service
Loaded: loaded (/usr/local/lib/systemd/system/cpcd.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2023-11-06 15:45:08 CET; 2min 48s ago
Docs: file:////usr/local/etc/cpcd.conf
Main PID: 7608 (cpcd)
Tasks: 5 (limit: 1595)
CPU: 62ms
CGroup: /system.slice/cpcd.service
└─7608 cpcd --conf /usr/local/etc/cpcd.conf
Nov 06 15:47:56 rns-md-wisun-br cpcd[7608]: [2023-11-06T14:47:56.882099Z] Core : Endpoint #10: rxd data frame queued
Nov 06 15:47:56 rns-md-wisun-br cpcd[7608]: [2023-11-06T14:47:56.882121Z] Core : Endpoint #10 sent ACK: 6
Nov 06 15:47:56 rns-md-wisun-br cpcd[7608]: [2023-11-06T14:47:56.882147Z] Core : Pushed frame to driver : 14:0A:00:00:86:B9:14
. . .Starting wsbrd as a Service#
Starting wsbrd as a service is a good option once the system has been tested using a manual start. With the Restart=on-failure, wsbrd will be restarted automatically in case of failure.
This requires:
Creating a service file for wsbrd
nano $ sudo nano /usr/local/lib/systemd/system/wisun-borderrouter.service# SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0 or Apache-2.0
[Unit]
Description=Wi-SUN Border Router Service
Documentation=file:///usr/local/share/doc/wsbrd/examples/wsbrd.conf
After=network.target
After=freeradius.service
# If you rely on an external DHCP server, don't forget to add a dependency here
[Service]
BusName=com.silabs.Wisun.BorderRouter
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/wsbrd -F /etc/wsbrd.conf
Restart=on-failure
# Files created by wsbrd contain secrets, so remove read permissions
UMask=0066
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetreloading the system services
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadCPC/wsbrd Communication#
A log of CPC/wsbrd communication can be obtained adding cpc trace to /etc/wsbrd.conf
Once CPC is working, removing the cpc trace is recommended.
If the Connected to RCP "x.y.z" (x.y.z), API t.u.v message is present, everything is working as expected (the RCP version string comes from the RCP binary, not from wsbrd, so it validates proper communication between the host and the RCP over CPC).
Error Messages and Corrections#
As a general rule, always check the traces from
cpcdandwsbrdin case of issues. These can be obtained directly from the command line is the applications are manually started from a command line, and usingjournalctlif started as services:
tail -f sudo journalctl -u cpcd.service -f
tail -f sudo journalctl -u wisun-borderrouter.service.service -f'support for CPC is disabled'
cpcdhas been installed afterwsbrdhad already been compiled.You need to rebuild
wsbrdfollowingcpcdinstallation.Make sure to delete the
/wisun-br-linux/CMakeCache.txtfile and the/wisun-br-linux/CMakeFilesfolder before rebuildingwsbrd.
'cpc_init: Connection refused'#
cpcdis not running yet when startingwsbrd.Make sure
cpcdis started first and thecpcdtraces containInfo : Daemon startup was successful. Waiting for client connectionsYou may need to disconnect/reconnect the RCP is some cases.
'cpc_init: No such file or directory'#
Failed to connect, secondary seems unresponsive#
RCP Not Communicating#
When communication issues appear with the RCP, check cpc status to know more:
sudo systemctl status cpcd.servicePossible causes are:
There is no WSTK/WPK plugged in, if the setup has been running before. Unplug/Replug the WSTK/WPK. Check
dmesgfor theUSB ACM devicename.There is a mismatch between the
uart_device_filein/usr/local/etc/cpcd.conf. Startdmesg -wthen unplug/plug the WSTK/WPK to check theUSB ACM devicename and update theuart_device_fileto match.There is an invalid binary running on the RCP. Make sure you flash it with a RCP project with CPC enabled and the correct UART baudrate.
The serial vcom speed on the WSTK/WPK is incorrect. Refer to WSTK Configuration.
