Z-Wave Development Basics#
NOTE: This section replaces APL13475: Z-Wave Development Basics. Further updates to this application note will be provided here.
Easy-reading introduction to Z-Wave development.
This application note introduces the Z-Wave Specifications and how they are to be used. Refer to the other application nodes in the "Basics" series for more networking and application specific topics.
Z-Wave Documentation#
There are several specification documents defining how nodes must be implemented in a Z-Wave network. The documents’ constellation is depicted in the figure below. The blue color indicates Z-Wave Plus specific documents.
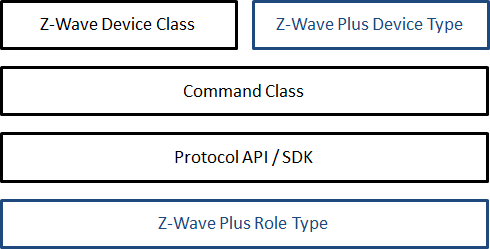

Command Class Specification#
Commands Classes are used for example to switch devices on or off, to monitor the battery status or convey sensor measurements. They cover a broad range of applications.
The Command Class Specification can be found in latest documentation package from the Z-Wave Alliance located at https://z-wavealliance.org/development-resources-overview/specification-for-developers/.
The specification handles the four overall types of Command Classes:
Z-Wave Application Command Classes: Commands classes providing application level functionalities, which can typically be supported by any node, regardless of its Device or Role Type.
Z-Wave Management Command Classes: Commands classes providing functionalities to support nodes’administration and management. Those Command Classes are often mandated by the Z-Wave Plus Role Type and/or Device Type and provide functionalities like battery support, firmware update or associations.
Z-Wave Transport-Encapsulation Command Classes: Command classes used for encapsulating other command classes.
Z-Wave Network-Protocol Command Classes: Command classes providing functionalities related to RF or Z-Wave/IP networks.
A device typically implements a small subset of Command Classes depending on the application and Device Type requirements. It is therefore not recommended to read the Command Class specification in whole. It should only be referred to when implementing a Command Class.
Z-Wave Plus Device Type and Role Type Specifications#
The Device Type and Role Type specifications can be found in the latest documentation package from the Z-Wave Alliance located at https://z-wavealliance.org/development-resources-overview/specification-for-developers/. These documents specify Z-Wave Plus framework requirements that a Z-Wave Plus node must comply with.
When creating a Z-Wave Plus product, the developer must choose a Z-Wave Plus Device Type depending on the intended application. The chosen Device Type must reflect Z-Wave functionalities and not the physical product appearance. For example, if the intended product is a gateway built into a TV, the Device Type must be Gateway and not TV. If several Device Types seem to match the product needs, the Device Type must be selected based on the best match. Additional Command Classes may be added to meet the application needs.
The developer must also choose a Z-Wave Plus Role Type that matches the nature of the product. The Role Types Specification defines the networking and battery requirements for a device. Based on the Role Type, nodes can be either Controllers or End devices.
Controllers must be capable of setting up and performing maintenance operations in a Z-Wave network.
End devices do not offer any network management functions. End devices can only be added or removed from a network by a controller. End devices can nevertheless send commands to other nodes and “control” others at the application level.
Protocol API/SDK#
The protocol API and the Software Developer’s Kit (SDK) is a software implementation running on Silicon Labs chips. It enables developers to use the Z-Wave protocol with API functions and therefore build applications in a fast and cost-effective manner.
The SDK contains among others:
Z-Wave API libraries (both for controllers and End devices)
Z-Wave Plus sample applications
PC sample applications
Tools
Programming boards and chips are provided with the SDK.
The SDK implementation is compliant with RF and protocol requirements mandated by the Z-Wave Plus specifications. The implementation and sample application intends to show development best practices.
Application Notes: Basics Documents#
The intended use and best practices for certain Command Classes may not be obvious when reading the Command Class Specifications. The Basic series documents provide examples of how to use and implement Command Classes in specific applications. It is recommended to consult the Basic series before getting started with an implementation. See References.
Application Framework#
The Z-Wave Application Framework relieves end product developers from the burden of implementing Command Classes. The framework implements a generic Command Class parser structure and a range of Command Classes.
Product sample applications in the SDK are built using the application framework. For more details, refer to [1].
Z-Wave over IP (Z/IP)#
The Z/IP architecture allows Z-Wave nodes to be represented as IP hosts, which can be discovered via mDNS, the standard LAN Service Discovery mechanism, and can exchange Z-Wave application commands via the standard Z-Wave UDP port assigned by the IANA.
The Z/IP Gateway may operate as a native IPv6 router, presenting the Z-Wave network as an IPv6 subnet, or it may operate in compatibility mode in existing IPv4 infrastructures, requesting an IPv4 LAN address for each Z-Wave node.
Thus, a Z/IP client sends IP packets to the IP address of a Z-Wave light dimmer just as IP packets are sent to a network printer. In the same way, a Z/IP Client discovers a Z-Wave light dimmer just as it discovers a network printer.
For more information regarding the Z-Wave over IP, refer to www.silabs.com/developers/z-wave-controller.
Certification#
When a product is getting ready, the Certification portal located at z-wavecertification.z-wavealliance.org/ is used to fill a list of functionalities that the device implements. This list is then used to ensure that the product complies with all requirements from the Device Class/Device Type, Role Type and additional Command Classes.
A Compliance Test Tool (CTT) can be found on Z-Wave Alliance home page. The CTT allows developers to perform automated test on their product before submitting for certification.
References#
Silicon Labs, SDS12804, Z-Wave Plus Application Framework v6.51.0x
Silicon Labs, APL13031, Z-Wave Networking Basics
Silicon Labs, APL12955, Z-Wave Multi-Channel Basics
Silicon Labs, APL13298, Z-Wave Device Configuration Basics
Silicon Labs, APL12956, Z-Wave Association Basics
Silicon Labs, APL12957, Z-Wave Battery Support Basics
Silicon Labs, APL13128, Z-Wave Time and Date Basics
Silicon Labs, APL13084, Z-Wave Control Application Basics
