Range Test Applications' Metrics#
Range Test creates a radio link between the evaluation kits and sends a predefined number of packets from the transmitter to the receiver node. The receiver node continually recalculates and reports PER during the entire measurement. The application displays the current Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) level in dBm units and draws a chart of the RSSI historical data. For long tests the transmitter can be set up to transmit infinitely.
Range Test's Packet Assembly#
Simple PHY Range Test applications' packet structure includes a packet counter, a destination and a source id, as shown in the source code below.
typedef struct range_test_packet_t{
uint16_t packet_counter; ///> Value showing the number of this packet.
uint8_t destination_id; ///> Destination device ID this packet was sent to.
uint8_t source_id; ///> Device ID which shows which device sent this packet.
uint8_t repeat; ///> Unused.
} range_test_packet_t;In 802.15.4 mode the application sets up a similar packet payload, immediately after setting up the MAC header (MHR) field. Both destination address and PAN ID are set to broadcast (0xFFFF), while the source address is 0x0000.
data_frame->payload.source_id = range_test_settings.source_id;
data_frame->payload.destination_id = range_test_settings.destination_id;
data_frame->payload.packet_counter = packet_number;
data_frame->payload.repeat = 0x00;In BLE mode the application sends non-connectable undirected advertisement packets. The packet number and the IDs are configured as shown in the following code snippet:
ble_tx_pdu->manufactSpec.payload.packet_counter = packet_number;
ble_tx_pdu->manufactSpec.payload.destination_id = range_test_settings.destination_id;
ble_tx_pdu->manufactSpec.payload.source_id = range_test_settings.source_id;
ble_tx_pdu->manufactSpec.payload.repeat = 0xFF;In each cases the remaining part of the packet/payload is padded with 0x55 and 0xAA at the odd and even byte indexes, respectively.
Definition of Packet Error Rate#
Packet error rate is calculated according to the following equation:
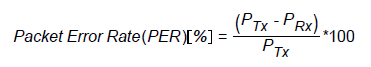
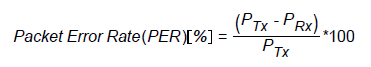
Where PTX is the number of sent packets and PRX is the number of received packets.
