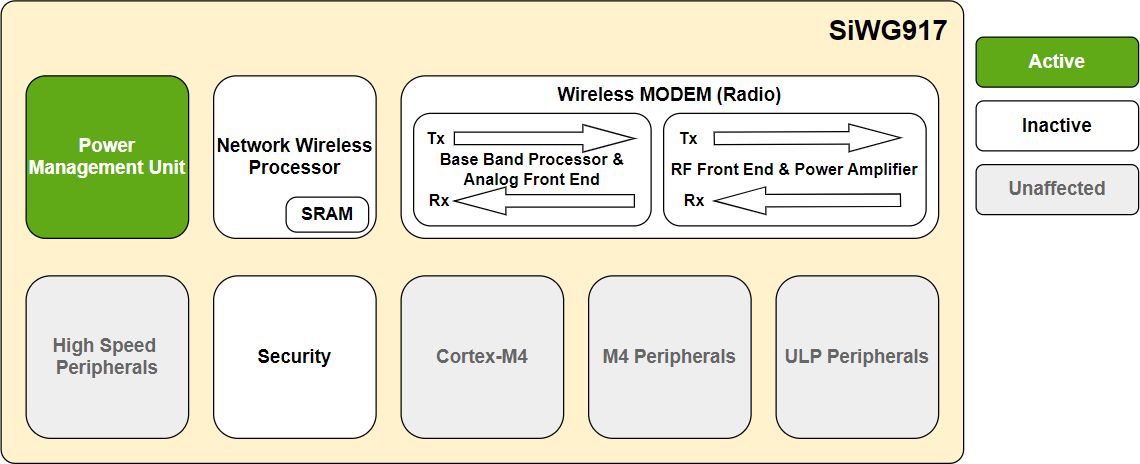
NWP Power States#
The SiWG917 SoC NWP can be in any of the following power states:
Active or High-Performance State: All the power domains are powered ON and are active.
Sleep State: Based on the power save mode used, certain power domains are active, certain domains are powered OFF, and certain domains are in sleep (consume low power).
Active or High-Performance State#
The NWP can be in three operational modes in Active State as described below:
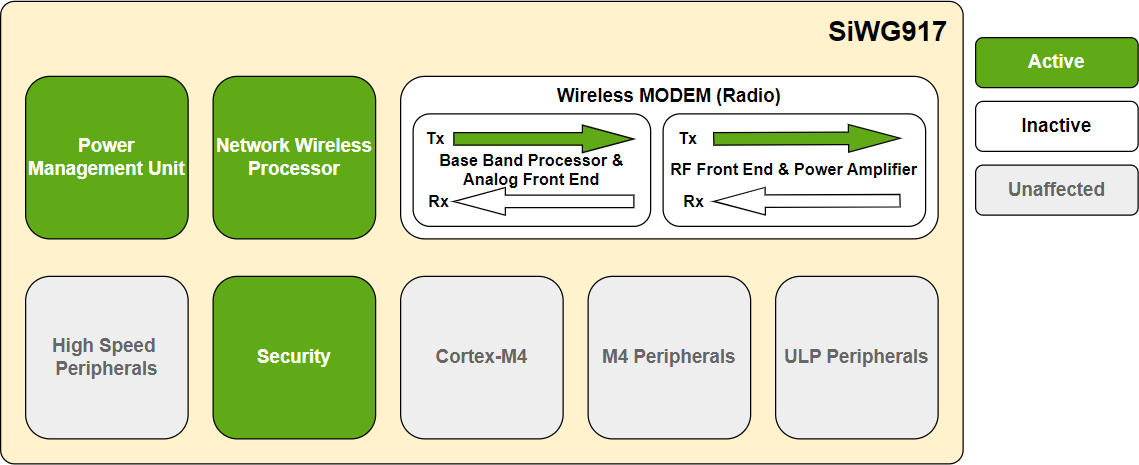
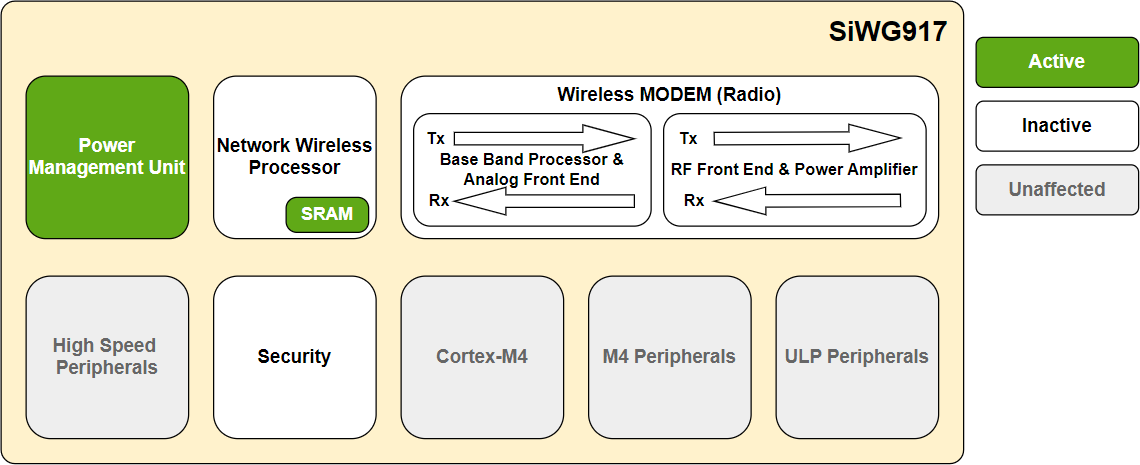
Transmit Mode#
In the transmit mode, all the power domains of the NWP are active/operational except the receiver section of the Base Band Processor (BBP), Analog Front End (AFE), and RF Front End (RFFE). This is the highest power-consuming mode of NWP.

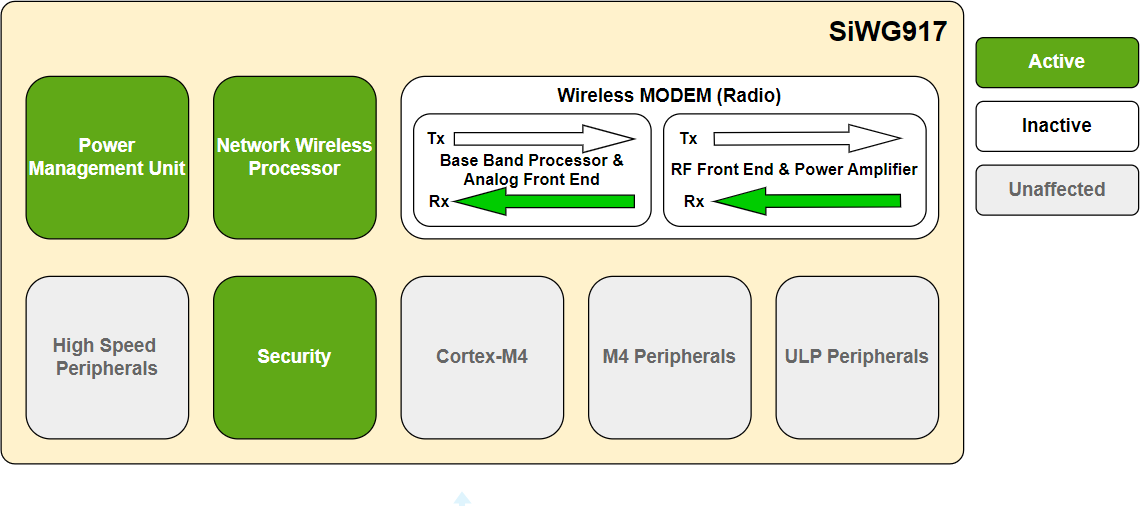
Receive Mode#
In the receive mode, the transmit sections of the BBP, AFE, and RFFE are inactive.

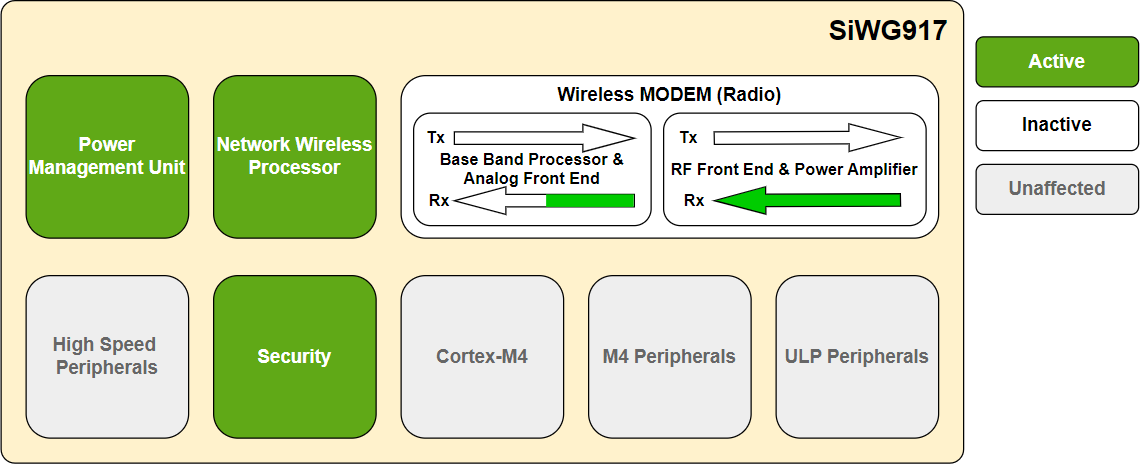
Listen Mode#
This mode is a subset of the receive mode where certain receive portions of the BBP and AFE are inactive as no packet reception is in progress.

Sleep State (Ultra-low-power Mode)#
The Wireless Modem, NWP, and Security sections are inactive in the ultra-low-power mode. The Power Management Unit (PMU) has control over the other sections of the chip.
The ULP mode can be categorized into the following modes:
With RAM Retention, the SiWG917 NWP SRAM is retained.

Without RAM Retention, the NWP SRAM is not retained.