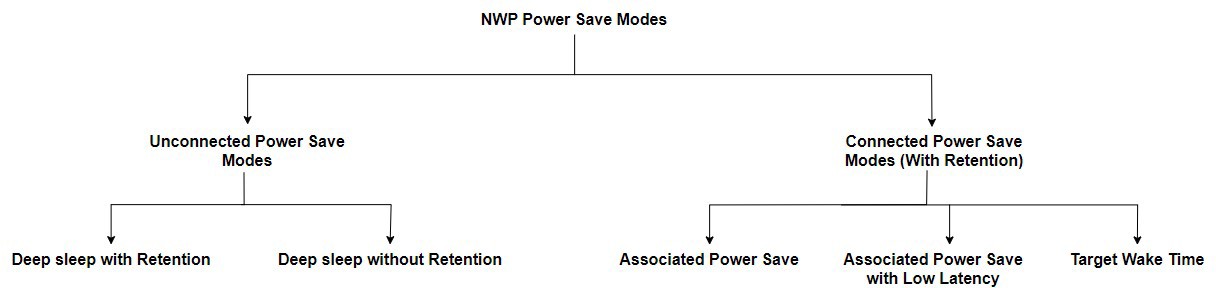
NWP Power Save Modes#
The SiWG917 NWP can be set to Power Save state via any of the Power Save Modes below based on the application use case. The NWP Power Save Modes are broadly classified into the following:

Note: For Connected Power Save, the RAM Retention configuration alone is supported, while for Unconnected Power Save, with and without RAM Retention configurations are supported.
The SiWG917 uses the following four flags as a handshake mechanism between M4 and NWP over the sleep-wakeup cycles:
TA_wakeup_M4: Set when NWP needs M4 to be awake. Cleared to indicate NWP allowing M4 to sleep.
TA_is_Active: Set when NWP is in high-power mode. Cleared when NWP is going to sleep.
M4_wakeup_TA: Set when M4 needs NWP to be awake. Cleared to indicate M4 allowing NWP to sleep.
M4_is_Active: Set when M4 is in high-power mode. Cleared when M4 is going to sleep.
Note: The above flags are modified by the internal driver APIs and should not be modified in the application layer.
Unconnected Power Save Modes#
The NWP can be set into Unconnected Power Save before establishing a wireless connection.
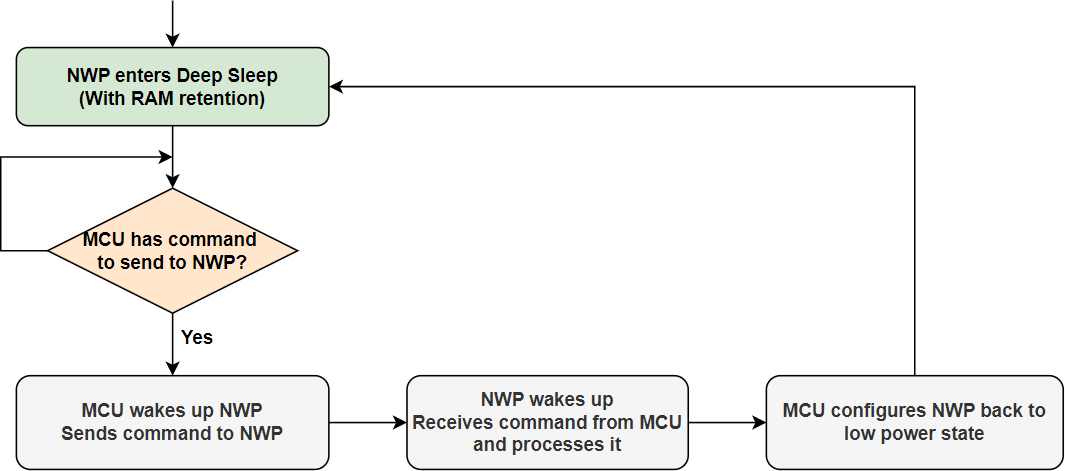
Deep Sleep with RAM Retention#
In Deep Sleep with RAM Retention mode, the NWP SRAM contents are retained. After wake up, the NWP can continue the execution.
Configuration:
After wireless initialization and before establishing a wireless connection, the NWP can be set into Deep Sleep with RAM Retention.
To configure the NWP to Standby Power Save mode, call the
sl_wifi_set_performance_profile()API with the performance profile set to DEEP_SLEEP_WITH_RAM_RETENTION.To switch the NWP back to High Performance mode, call the
sl_wifi_set_performance_profile()API with the performance profile set to HIGH_PERFORMANCE.Once the NWP is shifted back to High Performance mode, there is no need to perform NWP initialization again, as the previous state of the device is retained.

Deep Sleep without RAM Retention#
In Deep Sleep without RAM Retention mode, the NWP SRAM content and current state are not retained. Upon wake up, the NWP needs to be re-initialized again.
Configuration:
After the wireless initialization and before establishing wireless connection, the NWP can be set to Standby Power Save (Without RAM Retention).
To configure the NWP to Standby Power Save, call the sl_wifi_set_performance_profile API with the performance profile set to
DEEP_SLEEP_WITHOUT_RAM_RETENTION.
To switch the NWP back to High Performance mode, the NWP needs to be initialized again, as the previous state of the NWP is not retained. Call the sl_net_init() API to initialize the NWP and bring it back to Active mode.
Wi-Fi Associated Power Save Modes#
NWP can be set into Associated/Connected Power Save after wireless connection during the NWP idle times, which can be switched back to Active state for transmitting/receiving data to/from Access Point.
Before going through the types of Associated Power Save Modes, it is important to understand the sleep/active state switching mechanism and wake interval concepts of NWP during Associated Power Save Mode.
Sleep/Active State Switching#
The SiWG917 NWP connects to an Access Point and goes to sleep state.
When the NWP is in Associated Power Save Mode, it can be configured to wake up every Delivery Traffic Indication Message (DTIM) Interval or Beacon Interval (BI) or Listen Interval (LI) or Target Wake Time (TWT) Wake Interval during its Connected Power Save Mode.
Beacon Interval-based wakeup: Beacon Interval is the period between two subsequent beacon frames transmitted by AP. The station wakes every beacon interval.
DTIM Interval-based wakeup: DTIM period specifies how often an AP beacon includes Buffered Traffic Indication to its connected clients via TIM element in the beacon frame. When the AP includes TIM information in a beacon frame, the beacon is called DTIM beacon. DTIM interval is the time between two subsequent DTIM beacons transmitted by AP. DTIM Interval = Beacon Interval * DTIM Period.
Listen Interval-based wakeup: Based on the Listen Interval configured, the station wakes up at the nearest integral multiples of DTIM beacon/beacon interval broadcasted by the connected AP which is just less than or equal the Listen Interval.
Note: In case of Listen Interval based wakeup, configuring larger listen intervals greater than 1000 milliseconds might lead to AP disconnecting the NWP. It is highly recommended to use 1000 ms as Listen Interval for low power consumption.
When the station wakes up to receive the beacon, it checks if there are data packets to send or receive to/from the remote peer and performs data transfer according to the Power Save Mode configuration.
After performing the data transfer/receive, the station goes back to sleep state.
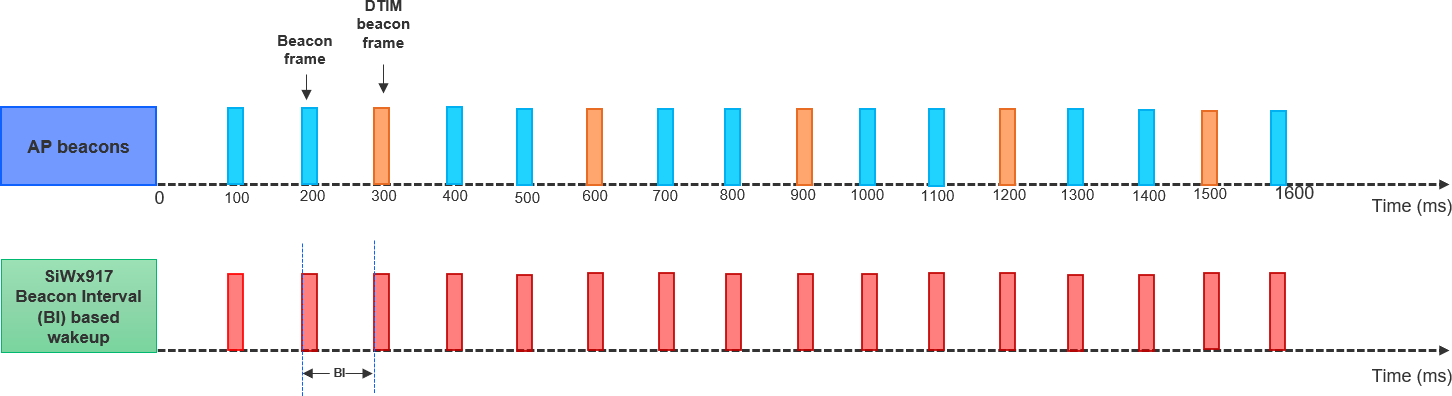
Beacon Interval#
The SiWG917 NWP wakes every Beacon Interval configured in the AP. Longer Beacon Interval implies reduced current consumption.
Call
sl_si91x_set_join_configuration()API with join_feature_bitmap set as NULL, before calling Wi-Fi connection APIs.Set the DTIM alignment type in sl_wifi_set_performance_profile() API to
SL_SI91X_ALIGN_WITH_BEACON.
The following figure illustrates the BI-based wakeup of NWP when AP BI = 100 ms and DTIM period = 3. In this case, the SiWx917’s wake interval = 100 ms.

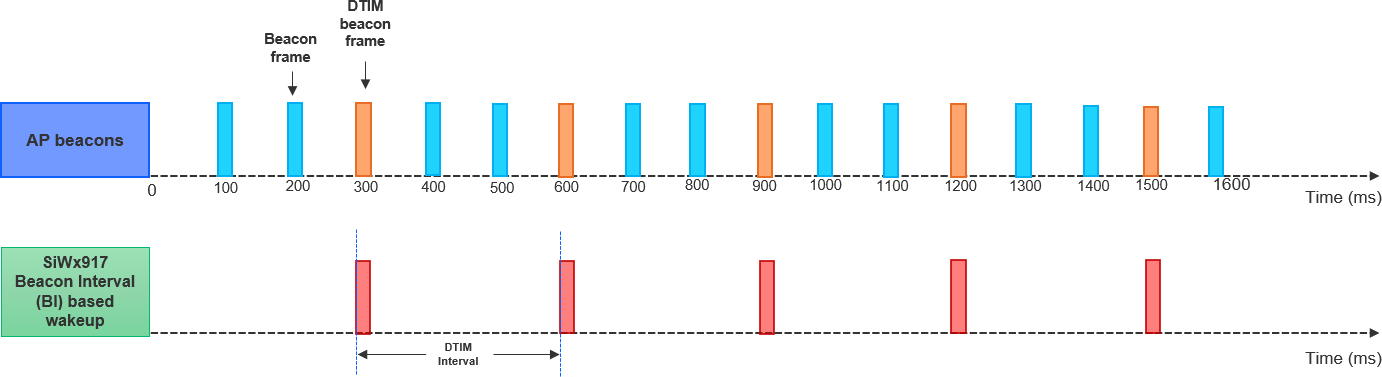
DTIM Interval#
The SiWG917 NWP wakes every DTIM Interval, as per DTIM period configured in the AP. Shorter the DTIM interval, implies reduced RX latency to retrieve data from the remote peer.
Configuration:
Call
sl_si91x_set_join_configuration()API with join_feature_bitmap set as NULL, before calling Wi-Fi connection APIs.Set the DTIM alignment type in
sl_wifi_set_performance_profile()API toSL_SI91X_ALIGN_WITH_DTIM_BEACON.
The following figure illustrates the DTIM Interval-based wakeup of NWP when AP Beacon Interval = 100 ms and DTIM period =3, then the NWP wake interval would be 300 ms.

Listen Interval#
The Listen Interval indicates how often the SiWG917 NWP in Connected Power Save Mode wakes to listen to AP beacons.
The Wake Interval of NWP can be aligned with the DTIM interval or Beacon Interval of the AP.
For example, If Listen Interval = 1000 ms, the DTIM period = 3 and Beacon Interval = 100 ms at AP (It means every third beacon contains DTIM information.).
If DTIM alignment type is
SL_SI91X_ALIGN_WITH_DTIM_BEACON, NWP wakes every 900 ms (<= Listen Interval).If DTIM alignment type is
SL_SI91X_ALIGN_WITH_BEACON, NWP wakes every 1000 ms (<= Listen Interval). In this case, the NWP does not take DTIM period of AP into consideration.
Configuration:
The Listen Interval can be configured in two methods:
To configure Listen Interval before association with an AP:
Set
SI91X_JOIN_FEAT_LISTEN_INTERVAL_VALIDinjoin_feature_bitmapand callsl_si91x_set_join_configuration()before calling Wi-Fi connection APIs.Call
sl_si91x_set_listen_interval()API to set the listen interval.Call
sl_net_up()API to establish Wi-Fi connection with the AP.
To configure Listen Interval after association with the AP (Recommended for Dynamic Listen Interval modification):
Set
SI91X_JOIN_FEAT_PS_CMD_LISTEN_INTERVAL_VALIDinjoin_feature_bitmap, and callsl_si91x_set_join_configuration()before calling Wi-Fi connection APIs.Call the
sl_net_up()for associating with an AP.To change the listen interval dynamically after associating with the AP, call the
sl_wifi_set_performance_profile()API with the updated Listen Interval.
Note: The Listen Interval configured in the
sl_wifi_set_performance_profile()API must not be greater than the Listen Interval set usingsl_si91x_set_listen_interval()API. The default Listen Interval configured in the WiSeConnect SDK is 1000 ms. During association with an AP.
The following figure illustrates the Listen Interval based wakeup of NWP when
AP Beacon Interval = 100 ms
DTIM period = 3
Listen Interval = 800 ms
In this case, the NWP’s wake interval = 600 ms with DTIM-aligned configuration, or 800 ms with Beacon-aligned configuration.
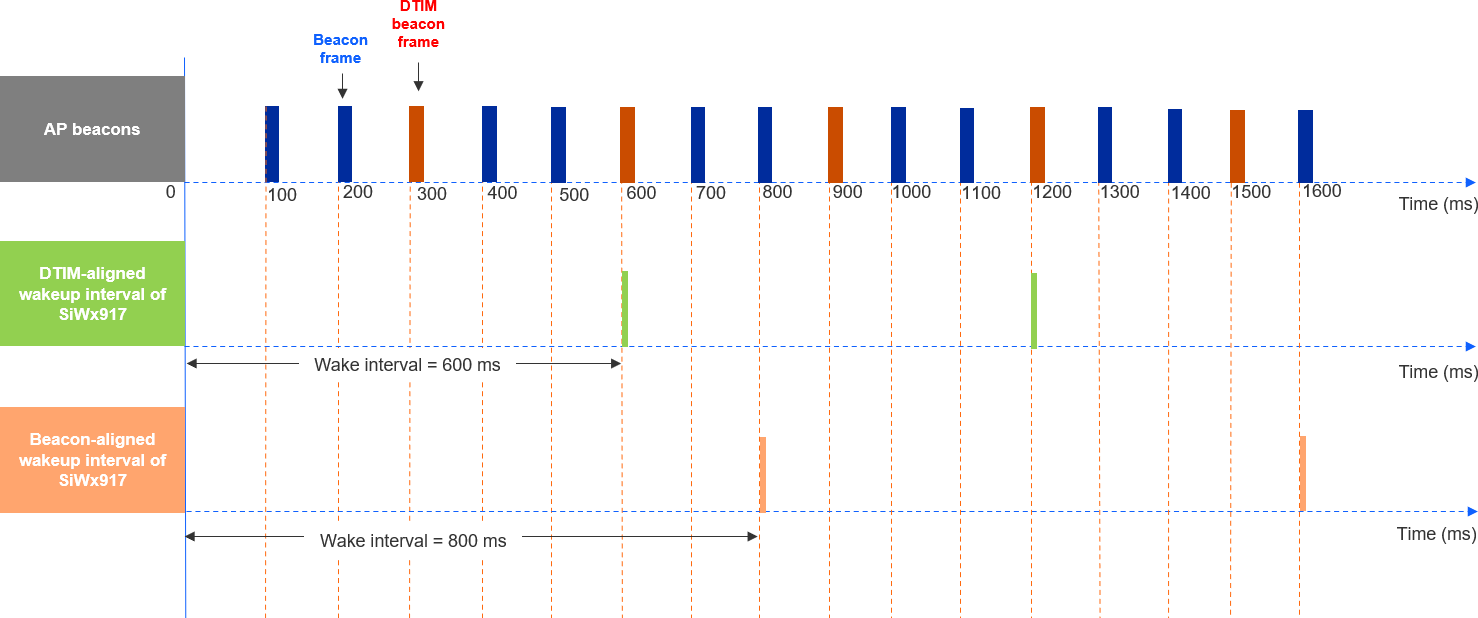

Note: For Listen Interval-based wakeup, the broadcast and multicast frames transmitted by the AP when the device is asleep may be lost.
Associated Power Save#
The Associated Power Save Mode follows Max PSP.
Communication between AP and SiWG917 NWP#
When in the Associated Power Save Mode, the NWP can send data to AP at any instance. For retrieving unicast data buffered at the AP, the following mechanism is used:
Maximum Power Save Profile (Max PSP)#
Whenever the AP receives packets that are destined for a station (NWP), it buffers the frames.
NWP wakes up for every DTIM or Listen Interval as configured in the application, reads the beacon and checks the TIM bit.
If the data pending (TIM) bit is set in the beacon, NWP sends a Power Save Polling (PS-Poll) frame to the AP, to retrieve the data frame.
The AP acknowledges the PS-Poll frame and transmits a data frame with the "More Data" field set to 1 in case there are more data frames buffered for the station.
NWP receives and processes the data frame.
NWP repeats the cycle by sending a PS-Poll frame to retrieve each data frame from the AP.
While sending the last data frame to the station, the AP shall set the "More Data" field to 0.
After receiving the last data frame, the NWP goes into sleep state.
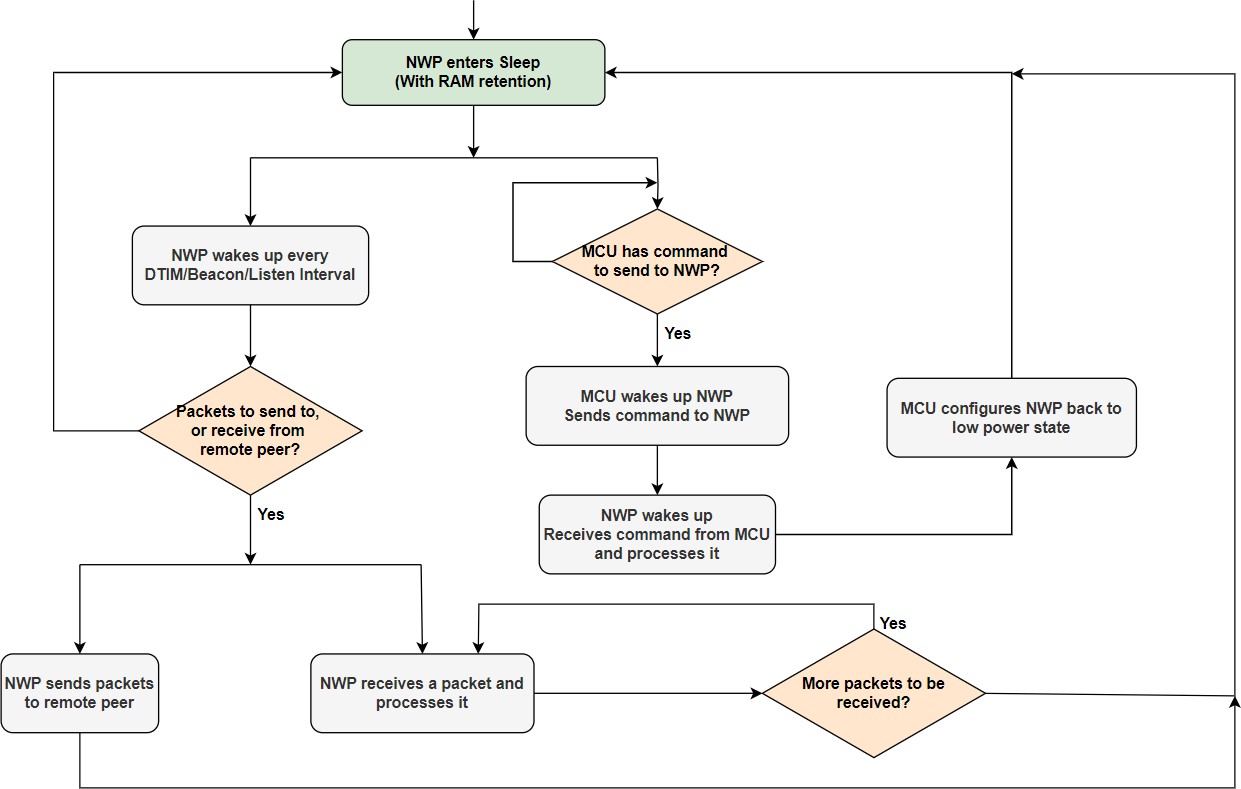

The Max PSP saves more power but produces lower throughputs. Sending a PS-Poll frame to retrieve each packet affects the through-put as it induces a considerable amount of delay when bulk data is to be retrieved.
Configuration#
After a wireless connection, the NWP can be set into Associated Power Save.
To configure NWP in Max PSP mode, call sl_wifi_set_performance_profile() with power save profile set to ASSOCIATED_POWER_SAVE.
The listen interval can be configured as described in the Sleep/Active State Switching subsection at the beginning of the Associated Power Save section.
Associated Power Save with Low Latency#
The Associated Power Save with Low Latency Mode follows Fast PSP.
Communication between AP and NWP#
When in the Associated Power Save Mode, the station can send data to AP at any instance. For retrieving unicast data buffered at the AP, the following mechanism is used.
Fast Power Save Profile (Fast PSP)#
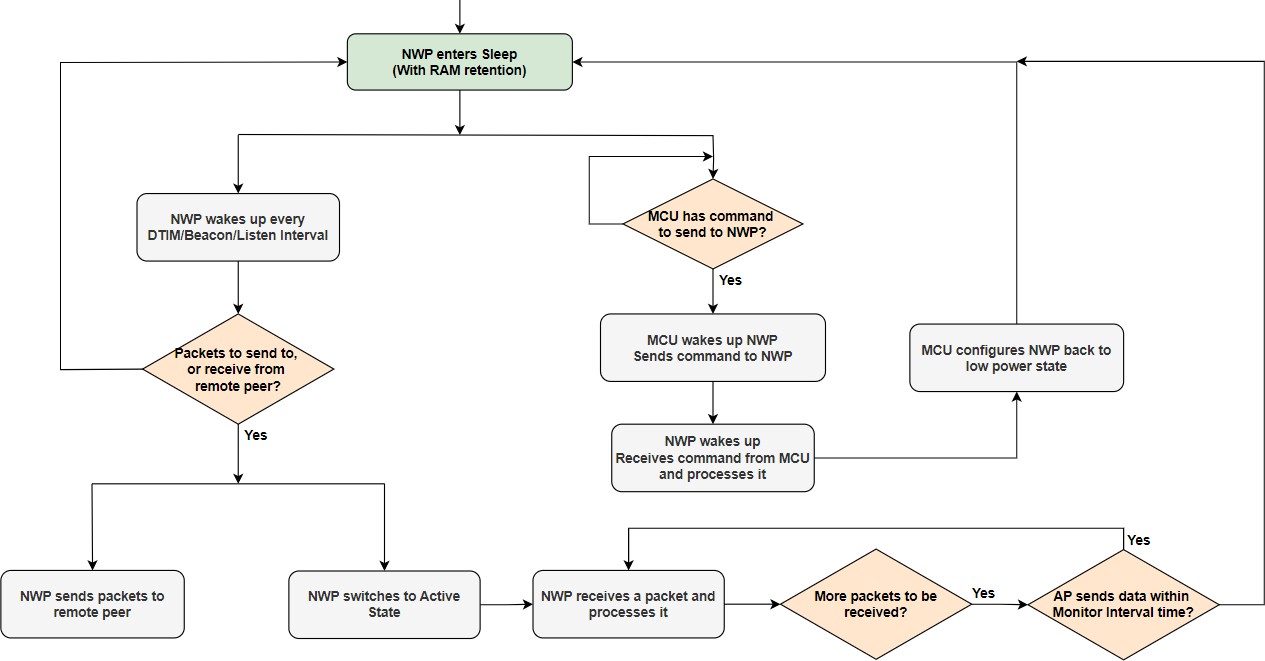
Whenever the AP receives data frames that are destined for a Station (NWP), it buffers the packets.
NWP wakes up for every DTIM or Listen Interval as configured in the application, reads the beacon and checks the TIM bit.
If the data pending (TIM) bit is set in the beacon, NWP switches to active state, and indicates the AP using a NULL data frame with PWR MGT bit set to ‘0’, to retrieve all the data frames.
The AP transmits a data frame with the "More Data" field set to ‘1’ in case there are more data frames buffered for the station.
NWP receives and processes the data frame.
If the AP sends the next data packet within Monitor Interval time, NWP receives the packet. Else, NWP goes back to Sleep state by sending a NULL data frame with the PWR MGT bit set to 1 to the AP.
While sending the last data frame to the station, the AP shall set the "More Data" field to 0.
After receiving the last data frame, the NWP goes into the sleep state.

Configuration:
After a wireless connection, the NWP can be set into Associated Power Save with low latency.
To configure NWP in Fast PSP, call
sl_wifi_set_performance_profile()with performance profile set toASSOCIATED_POWER_SAVE_LOW_LATENCYThe Monitor Interval can be configured by defining the structure parameter’s member
sl_wifi_performance_profile_t.monitor_interval.The listen interval can be configured as described in the Sleep/Active State Switching subsection at the beginning of the Associated Power Save Modes section.
Enhanced Max PSP Feature#
In Associated Power Save Mode, during unicast data retrieval, some Access Points do not acknowledge the PS-Poll frames and do not deliver buffered data destined for the Station. This interoperability issue can be avoided with the Enhanced Max PSP feature.
Configuration:
Enable the
SL_SI91X_ENABLE_ENHANCED_MAX_PSPin config_feature_bit_map of the structuresl_wifi_device_configura-tion_t.boot_config.Call
sl_wifi_set_performance_profile()with performance profile set toASSOCIATED_POWER_SAVE_LOW_LATENCY.
Internal Functionality:
Initially, the NWP Power Save Mode will be set to
ASSOCIATED_POWER_SAVE.After sending a PS-Poll frame to AP, if the AP delivers the buffered data within 20 ms, the NWP remains to be in
ASSOCIATED_POWER_SAVE.When the AP does acknowledge PS-Poll and does not deliver the buffered data within 20 ms, the Power Save Mode is switched to
ASSOCIATED_POWER_SAVE_LOW_LATENCY, where the NWP switches to Active mode by sending Null data frame to AP and waits for Monitor Interval time to retrieve the buffered data from AP.
Note: To switch the NWP from connected power save to active mode, call the sl_wifi_set_performance_profile API with the profile parameter
sl_wifi_performance_profile_t.sl_performance_profile_tset toHIGH_PERFORMANCE.
Target Wake Time (TWT)#
In the Legacy Power Save Modes, the Wi-Fi stations go to sleep and wakeup at random times to perform data transfer independent to the wakeup timings of other stations. With TWT, the AP schedules wake timings for its connected stations, ensuring no two Wi-Fi stations wake up at the same time. This method helps avoid packet collisions, thus reducing retransmissions and in turn reducing the station’s current consumption.
Along with this, TWT allows the Wi-Fi stations to be in sleep for longer durations. TWT is a beneficial Wi-Fi6 feature which allows connected stations to manage power efficiency with the reduced network contention.
The SiWG917 NWP supports two ways of configuration for Individual TWT as follows:
Using Manual TWT configuration: The TWT parameters such as sleep duration, wakeup duration, and the wake interval will be calculated based on the TWT specification parameters configured in the application. User needs to have knowledge of individual TWT setup negotiation.
Using Automatic (Auto) TWT: Auto TWT is a Silicon Labs implementation that configures TWT parameters automatically based on the user application requirements. The user can provide the application requirements in terms of average Throughput and RX la-tency. Based on these inputs, the SiWG917 NWP automatically configures the TWT parameters and negotiates them with the AP.
Note: It is recommended to use Auto TWT over standard TWT for better throughput and interoperability. The configuration structure parameters and example usage are explained at TWT TCP Client example documentation.
TWT-based Power Save Mechanism#
This section explains the TWT Power Saving Mechanism of SiWG917 NWP with the following TWT parameters set:
Individual TWT: The connected station (NWP) indicates a negotiation with the Access Point using its individual TWT Wake Interval and Wake duration.
Broadcast TWT: The AP broadcasts predefined TWT parameters (TWT Wake Interval and Wake duration) in its beacon and schedules wake times for different connected stations (not supported by SiWG917).
Implicit TWT: The TWT requesting station (NWP) calculates the next TWT by adding a fixed value to the current TWT value.
Explicit TWT: The start time of the next TWT period is calculated and intimated to the station by the AP (not supported by SiWG917).
Unannounced TWT: The TWT requesting STA does not announce its wake up to AP through PS-POLLs or UAPSD Trigger frames.
Announced TWT: The TWT requesting station transmits a PS-POLL or a UAPSD trigger frame to the AP to indicate it’s ready to receive data.
Non-triggered TWT: The TWT SP does not contain any triggered frames.
Triggered TWT: AP sends a trigger frame to solicit data from the station.

Communication between AP and NWP
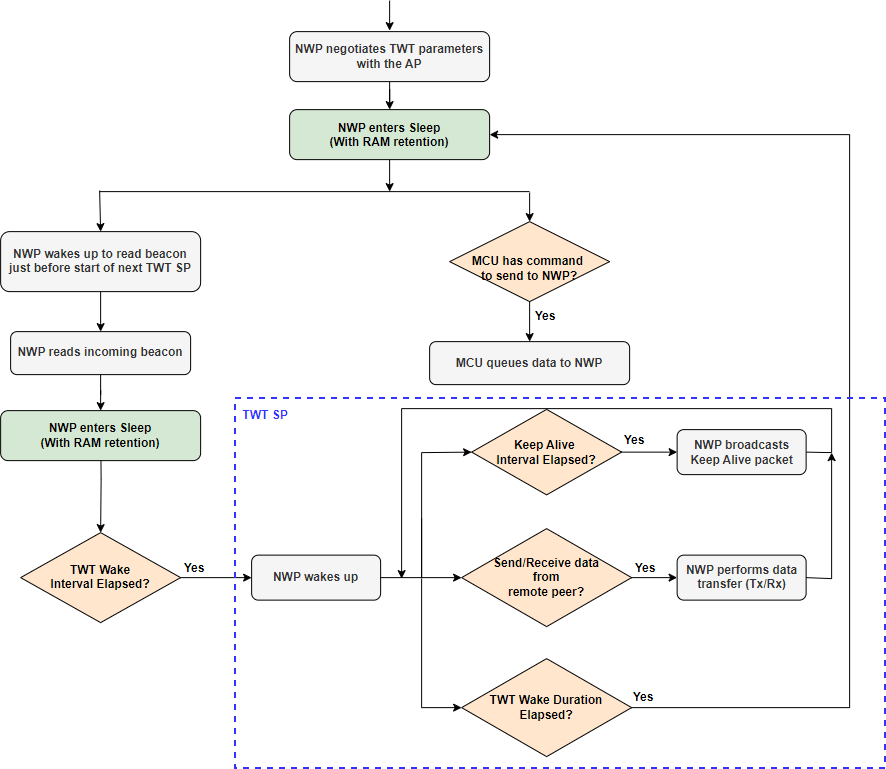
When in the Associated Power Save Mode with TWT, the station can send or receive data to/from AP only during the twt_wake_duration.
The SiWG917 NWP sends an Association frame with TWT Requester Support bit set in the High Efficiency (HE) MAC capabilities field.
After connecting to an Access Point, the NWP transmits a TWT Setup frame with the TWT parameters depending on the request type (Request TWT/Suggest TWT/Demand TWT).
If the AP agrees on the TWT parameters, it transmits a TWT Accept frame.
The NWP sends a Null data frame and goes to sleep.
Whenever the AP receives destined packets for a station (NWP), it buffers them.
The AP sets the corresponding AID in the TIM element of the upcoming beacons to indicate that the data is available for the station. The TIM bit will remain set until the station wakes up to receive the data.
The NWP wakes just before its TWT SP (as per the programmed TWT wake interval) to read the incoming beacon from the AP for Time Synchronization.
As soon as it reads the beacon, the NWP goes back to sleep and wakes at start of TWT SP.
In standard TWT, irrespective of TIM element being set or not, the NWP wakes up at the scheduled TWT SP and receives the buffered data within the TWT SP if there is any.
The AP transmits a data frame with the "More Data" field set to 1 in case there are more data packets buffered for the Station.
After receiving a data packet, the NWP sends it to the host.
In case there are no data frames to be received, the station will be active for the rest of wake duration and goes back to Sleep state.
Immediately following the TWT SP, the device enters sleep mode, even if there are additional data frames pending transmission or reception. These data transfers will be conducted during the subsequent TWT SP.
TWT Mechanism can be used when your M4 application has predictable and deterministic data traffic. The M4 application should be aware of the times at which data traffic is expected.
Configuration
Ensure that the
SLI_SI91X_ENABLE_TWT_FEATUREandSLI_SI91X_CONFIG_WIFI6_PARAMSpre-processor macros are enabled in the project settings.After calling
sl_net_up()API, register a callback function for TWT negotiation response events using thesl_wifi_set_twt_config_callback ()API.Trigger the TWT parameters negotiation by calling the API
sl_wifi_enable_target_wake_time ()with the structure parametersl_wifi_performance_profile_t.sl_wifi_twt_request_tset with TWT setup configuration.Once the AP sends a TWT response frame, the registered callback function gets triggered. The callback function gives the negotiat-ed TWT parameters that are agreed with the AP.
Next, set the SiWx917 into Associated Power Save by calling the
sl_wifi_set_performance_profile()API with the performance profile set to ASSOCIATED_POWER_SAVE
Auto TWT#
TWT parameters (wake duration and wake interval) are computed based on the latency and throughput parameters as configured by the user in the application.
The Auto TWT algorithm also checks if TWT is useful for a specific combination of the latency and throughput parameters. If found inefficient, TWT is not enabled, instead legacy listen Interval-based power save is enabled.
It uses a combination of LP and HP chains to reduce current consumption. It also infers internally based on traffic patterns when to wake up next.
It does not wake up unnecessarily and sleep for an extended time when there is no data. But if there is data to receive and transmit, it wakes up on TWT to meet the latency requirements and ensures timely data transfer.
Benefits of Automatic TWT over TWT#
Power optimization when compared to standard TWT
Handles TX and RX activities based on latency that the application can withhold, which is not possible with standard TWT.
