Firmware Update Examples#
Examples for Firmware Update via Bootloader#
The SiWx917’s Bootloader and host interact with each other to perform firmware update over SPI/UART/SDIO interface. The host can be Tera Term or a host MCU application.
Using Simplicity Commander as Host#
In this method, the SiWx917’s Bootloader and Simplicity Commander host interact with each other via UART Interface. Simplicity Commander transfers the firmware file present in your local drive to SiWx917’s Bootloader via UART. To update the Firmware using Simplicity Commander, follow the steps mentioned in Getting Started with EFR32 in NCP mode.
Using a Host MCU Application#
In the method, the host MCU application and SiWx917 NCP interact with each other through SPI/SDIO/UART. The reference example is Firmware Flashing from Host UART. Please check SiWx917 NCP release notes to know the working status of the example.
Examples for OTA Firmware Update#
This section details on the OTA Firmware Update examples available in the WiSeConnect SDK. Listed below are the examples:
OTA-based Firmware Update from the host
OTA-based Firmware Update
OTA-Based Firmware Update from the Host#
In this method, the SiWx917 downloads the Firmware file in chunks and forwards the chunks to host application. The host application then forwards the chunks to SiWx917 firmware, which in turn writes them to Firmware Image backup location. The reference example in the WiSeConnect SDK is Firmware Update via a TCP server. In this example application, the SiWx917, as a TCP client receives the Firmware file in chunks from a remote TCP server application. Each chunk is 1024 bytes long. When a Firmware file of 1.6 MB is considered, the Firmware file would be transferred in about 1638 chunks.
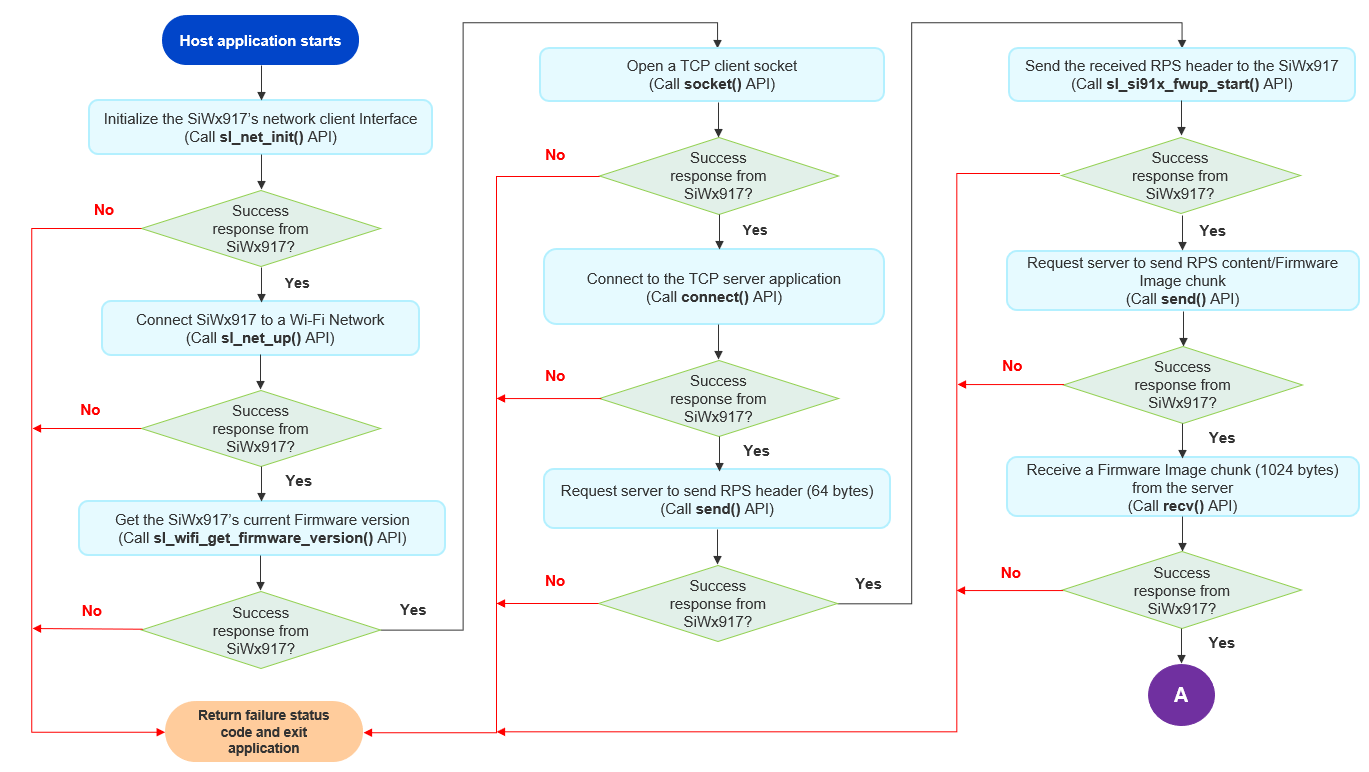
The detailed application flow is as follows:
The host application initializes the SiWx917’s Network client Interface by calling sl_net_init() API.
The host application drives the SiWx917 to connect to a Wi-Fi network. The SiWx917 connects to a Wi-Fi network and gets an IP address.
The host application gets the current firmware version of SiWx917 by calling sl_wifi_get_firmware_version() API.
The SiWx917 establishes a TCP connection with the remote TCP server application that hosts the SiWx917’s firmware File.
The host application makes a request to the server to send the RPS header of the Firmware file (referred to as SL_FWUP_RPS_HEADER in the application), which is usually 64 bytes long.
The TCP server application sends the RPS header of the firmware file.
Upon receiving the RPS header, the host application sends it to the SiWx917’s firmware by calling sl_si91x_fwup_start() API.
The host application now makes a request to the TCP server to send the RPS content (SL_FWUP_RPS_CONTENT) or Firmware Image in chunks.
The TCP server application sends Firmware chunk, which is 1024 bytes long.
For receiving a Firmware Image chunk, the host application makes a request to the TCP server to send a Firmware Image chunk.
As soon as the host application receives a Firmware Image chunk, it sends it to SiWx917’s firmware by calling sl_si91x_fwup_load() API. The SiWx917 then writes it to the Firmware Image backup location.
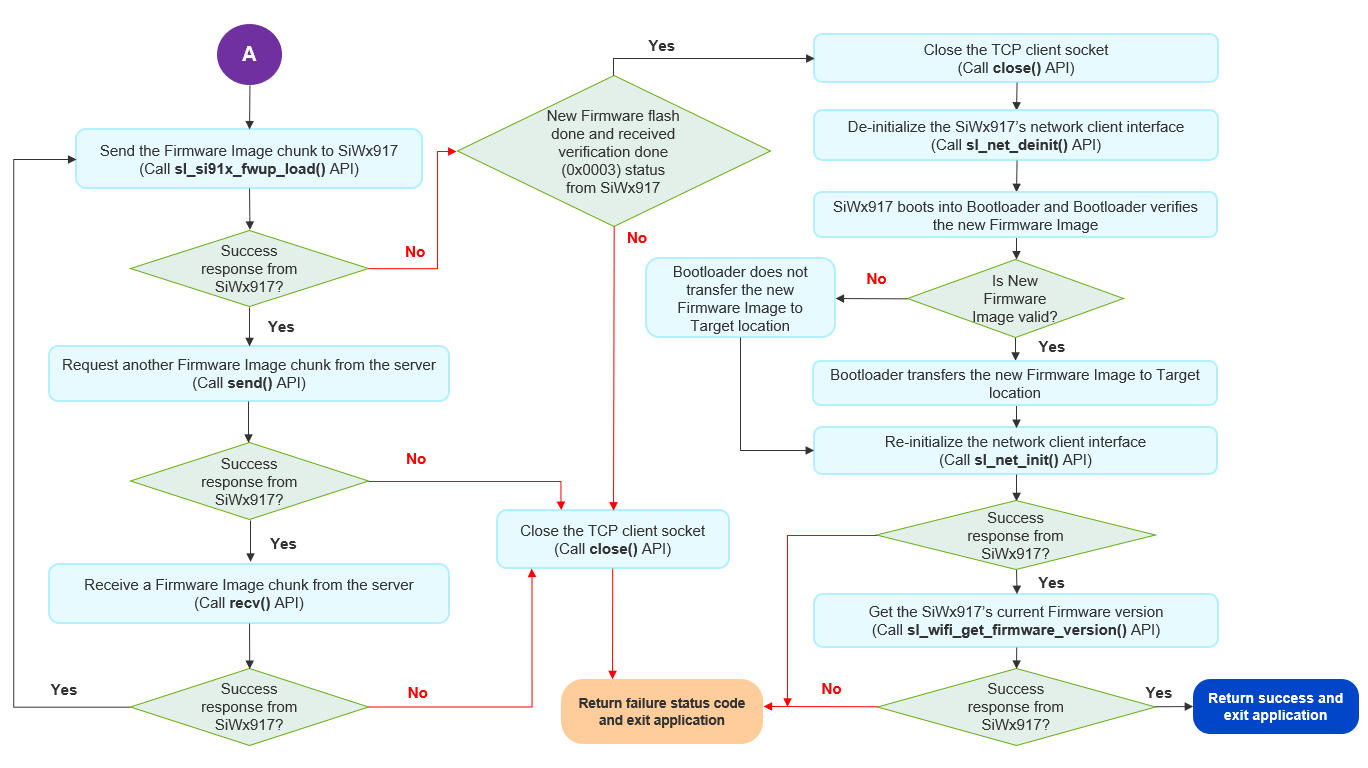
The process continues until the host application receives all the firmware chunks.
After receiving the new Firmware Image, the existing Firmware verifies the Integrity and Authenticity of new Firmware Image based on the RPS header. If the firmware is valid, the sl_si91x_fwup_load() returns SL_STATUS_FW_UPDATE_DONE (0x10003) for the last chunk, else the sl_si91x_fwup_load() returns an error code (0x10004).
Upon receipt of SL_STATUS_FW_UPDATE_DONE from SiWx917, the host application closes the TCP socket connection and calls sl_net_deinit() API to de-initialize the Network Interface and enable the SiWx917 to boot into the Bootloader.
The Bootloader finds a new Firmware Image in the Firmware Image backup and does Integrity and Authenticity verification of new Firmware Image based on the RPS header and Master Boot Record (MBR) configuration. If the Firmware Image is valid, the Bootloader transfers it to the target Firmware location, else it doesn’t.
The host application then calls sl_net_init() API to enable the Bootloader to execute the new Firmware Image, if it is valid or executes the previous firmware, if the new Firmware Image is invalid.
The host application gets the current firmware version of SiWx917 by calling sl_wifi_get_firmware_version() API. This shall give the new Firmware Image’s version number if its valid or else gives the previous Firmware Image’s version number.
For more details on the example application, refer to Firmware Update example in the WiSeConnect SDK.
The following flow chart illustrates the Firmware Update via TCP Server application flow:


OTA-Based Firmware Update#
In this method, the host application initiates a Firmware download and SiWx917 downloads the Firmware file in chunks and directly writes them to Firmware Image backup location without forwarding to the host. The reference example in the WiSeConnect SDK is Firmware Update via HTTP/HTTPS server. In this example application, the SiWx917, as an HTTP client initiates a Firmware file download from a remote HTTP or HTTPS (secures HTTP Request and Responses via TLS) server that hosts the Firmware Image file with which the SiWx917 is to be updated. This application uses Apache server as an HTTP or HTTPS server or AWS cloud storage services such as AWS S3 bucket or Azure Blob Storage as an HTTPS server.
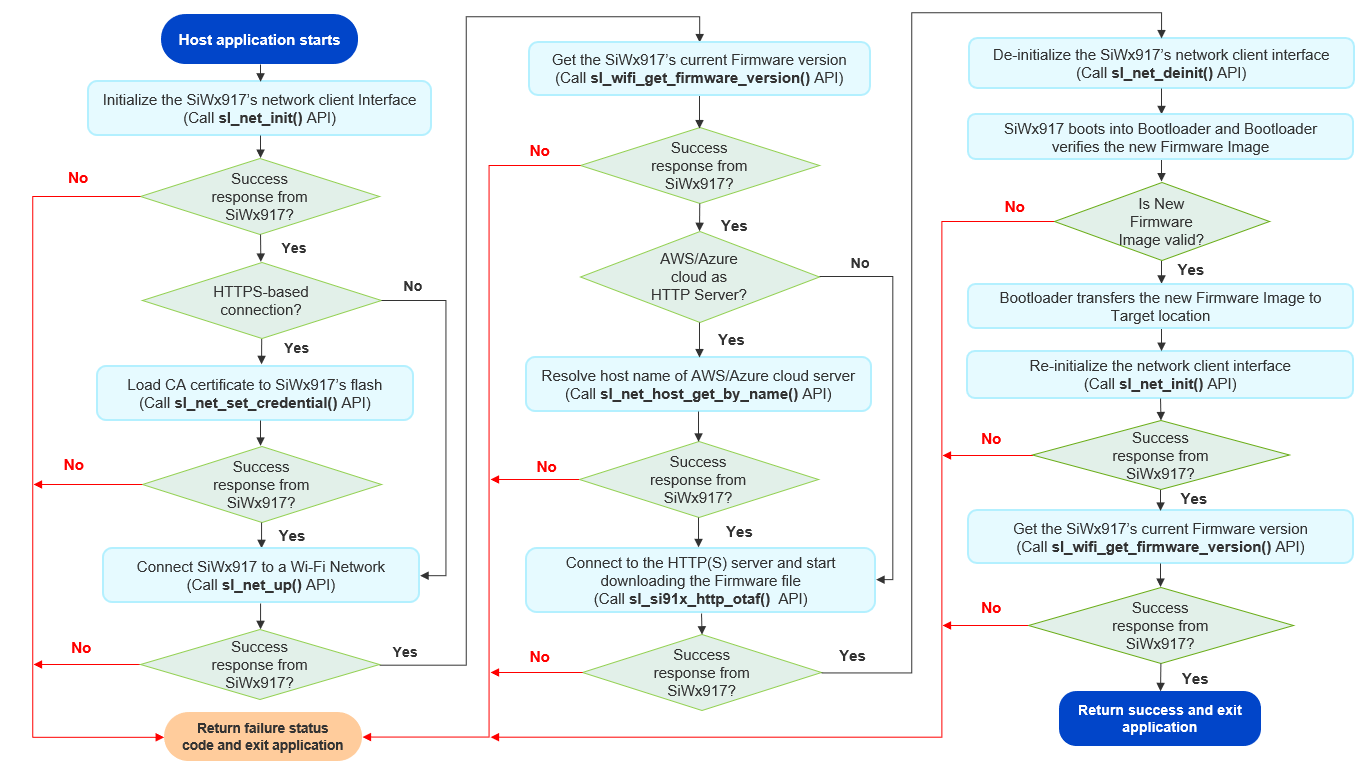
The detailed application flow is as follows:
The host application initializes the SiWx917’s Network client Interface by calling sl_net_init() API.
In case of HTTPS-based connection, the host application loads the certificates required for establishing a secure connection with the HTTP server by calling sl_net_set_credential() API.
The host application drives the SiWx917 to connect to a Wi-Fi network. The SiWx917 connects to a Wi-Fi network and gets an IP address.
The host application gets the current firmware version of SiWx917 by calling sl_wifi_get_firmware_version() API.
It then registers a callback function for SL_WIFI_HTTP_OTA_FW_UPDATE_EVENTS by calling sl_wifi_set_callback() API. Whenever the SiWx917’s current firmware completes the verification of new Firmware Image, it triggers this callback function to notify Firmware Update success or failure status.
In case of AWS S3 bucket or Azure Blob Storage, it is required to resolve the AWS Server/Azure Server’s host names to get the Server IP address. The host application resolves the host names by calling sl_net_host_get_by_name() API.
Next, the host application initiates a Firmware file download by calling sl_si91x_http_otaf() API.
The SiWx917 starts downloading the Firmware File in chunks. As soon as the SiWx917 receives a Firmware Image chunk, it writes it to the Firmware Image backup location. This process continues until the entire Firmware file is downloaded to the backup location.
Once the download is complete, the current Firmware verifies the Integrity and Authenticity verification of new Firmware Image. The SiWx917 notifies the Firmware Image validity as a response to sl_si91x_http_otaf() API.
The host application then calls sl_net_deinit() API to de-initialize the Network Interface and enable the SiWx917 boot into the Bootloader.
The Bootloader finds a new Firmware Image in the Firmware Image backup and verifies Integrity and Authenticity verification of new Firmware Image. If the Firmware Image is valid, the Bootloader transfers it to the target Firmware location, else it does not.
The host application then calls sl_net_init() API to enable the Bootloader to execute the new Firmware Image, if it is valid or executes the previous firmware, if the new Firmware Image is invalid.
The host application gets the current firmware version of SiWx917 by calling sl_wifi_get_firmware_version() API. This shall give the new Firmware Image’s version number if its valid or else gives the previous Firmware Image’s version number.
The following flow chart illustrates the Firmware Update via HTTP/HTTPS Server application flow:

Note:
When downloading the Firmware file via HTTP over TLS/SSL, the server (in this case AWS cloud/Azure cloud) might send 16K TLS records. Hence, it is highly recommended to enable SL_SI91X_EXT_TCP_IP_SSL_16K_RECORD feature in sl_wifi_device_configuration_t. sl_si91x_boot_configuration_t. ext_tcp_ip_feature_bit_map while calling sl_net_init() API.
For firmware update via HTTPS, the SL_SI91X_EXT_TCP_IP_FEAT_SSL_HIGH_PERFORMANCE feature should be enabled in sl_wifi_device_configuration_t.sl_si91x_boot_configuration_t.ext_tcp_ip_feature_bit_map while calling sl_net_init() API.
If you encounter SL_STATUS_SI91X_SSL_TLS_HANDSHAKE_FAIL (0x100D2) error while connecting to the Cloud Servers, even though certificates and credentials required to connect to the server securely are correctly provided, enable SL_SI91X_EXT_TCP_IP_FEAT_SSL_MEMORY_CLOUD feature in sl_wifi_device_configuration_t. sl_si91x_boot_configuration_t. ext_tcp_ip_feature_bit_map while calling sl_net_init() API.
