Supported Protocols#
SiWG917 supports the following protocols:
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
Transport Layer Security (TLS)
The following subsections explains these protocols in detail.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)#
UDP is a Transport Layer Protocol. It is a lightweight protocol with no support for handshaking, ordering, error recovery etc., UDP takes a datagram from Network Layer, attaches its header, and sends it to the user. So, it works fast.
Unlike TCP, UDP is an unreliable and connectionless protocol. So, there is no need to establish a connection prior to data transfer. The UDP helps to establish low-latency and loss-tolerating connections establish over the network.
For real-time services like computer gaming, voice or video communication, or live conferences, we need UDP. Since high performance is needed, UDP permits packets to be dropped instead of processing delayed packets. There is no error checking in UDP, so it also saves bandwidth. User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is more efficient in terms of both latency and bandwidth.
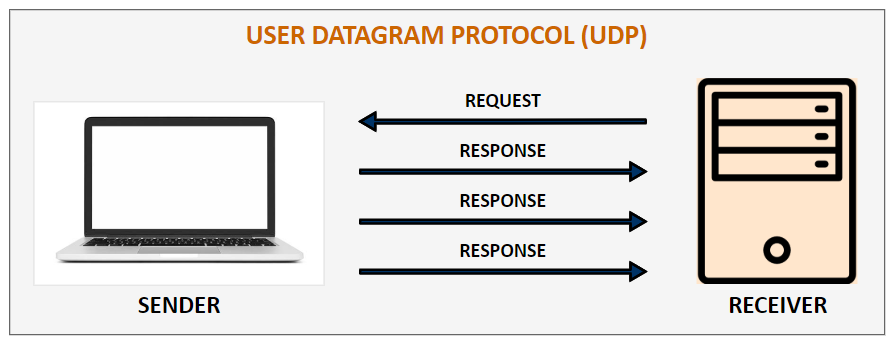

UDP Tx:
To measure UDP Tx throughput, configure the SiWG917 as a UDP client and open UDP server at the remote peer using the following command:
C:\> iperf.exe -s -u -p <SERVER_PORT> -i 1
Example: C:\> iperf.exe -s -u -p 5000 -i 1UDP Rx:
To measure UDP Rx throughput, configure the SiWG917 as a UDP server and open UDP client at the remote peer using the following command.
C:\> iperf.exe -c <Module_IP> -u -p <Module_Port> -i 1 -b <Bandwidth> -t <time interval in seconds>
Example: C:\> iperf.exe -c 192.168.50.91 -u -p 5005 -i 1 -b 40M -t 30Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)#
TCP is one of the main protocols of the Internet protocol suite. TCP is connection-oriented, meaning once a connection has been established, data can be transmitted in two directions. TCP has built-in systems to check for errors and to guarantee data will be delivered in the order it was sent, making it the perfect protocol for transferring information like still images, data files, and web pages.
TCP protocol integrates a mechanism that checks that all packets are correctly delivered. This mechanism is called acknowledgment, and it consists of having the receiver transmit a specific packet or flag to the sender to confirm the proper reception of a packet.
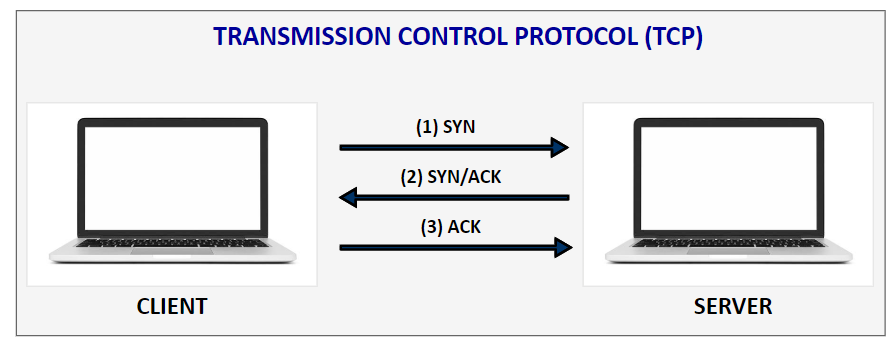

TCP Tx:
To measure TCP Tx throughput, configure the SiWG917 as a TCP client and open TCP server at the remote peer using the following command.
C:\> iperf.exe -s -p <SERVER_PORT> -i 1
Example: C:\> iperf.exe -s -p 5000 -i 1TCP Rx:
To measure TCP Rx throughput, configure the SiWG917 as a TCP server and open TCP client at the remote peer using the following command.
C:\> iperf.exe -c <Module_IP> -p <module_PORT> -i 1 -t <time interval in sec>
Example: C:\> iperf.exe -c 192.168.50.91 -p 5005 -i 1 -t 30Transport Layer Security (TLS)#
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and its successor, Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a widely adopted security protocol designed to facilitate privacy and data security for communication over the Internet. The primary use case of TLS is encrypting the communication between web applications and servers.
The three main components to what the TLS protocol accomplishes are encryption, authentication, and integrity.
To provide a high degree of privacy, TLS encrypts data that is transmitted across the web. This means that anyone who tries to intercept this data will only see a garbled mix of characters that is nearly impossible to decrypt. TLS then initiates an authentication process called a handshake between two communicating devices to ensure that both devices are really who they claim to be, and then it digitally signs data to provide data integrity, verifying that the data is not tampered with before reaching its intended recipient.
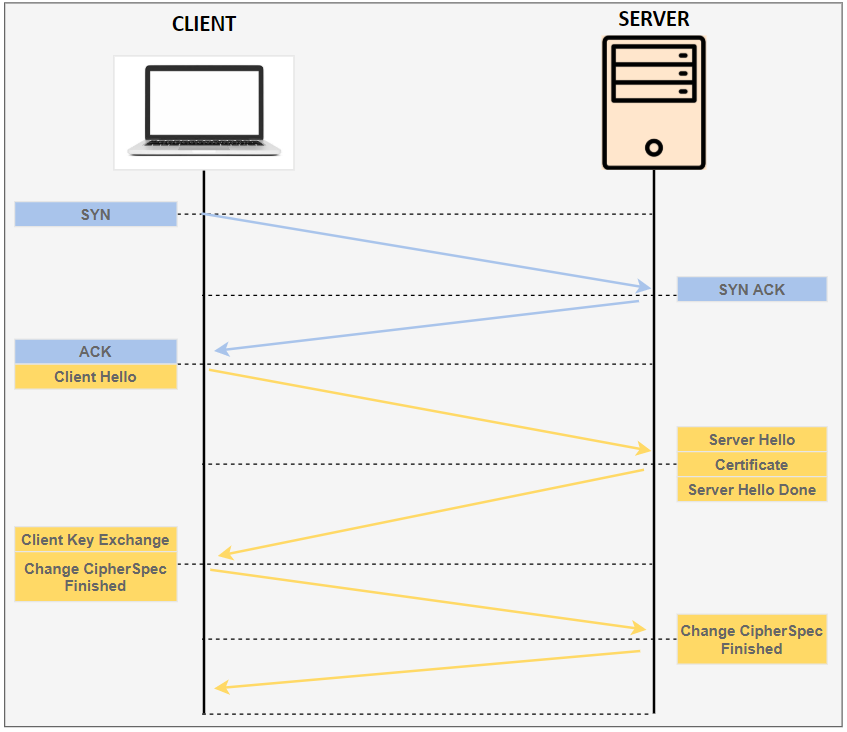

TLS Tx:
To measure TLS Tx throughput, configure the SiWG917 as a TLS client and open TLS server at the remote peer using the below command.
IPv4:
C:\SiWG917_Release\resources\scripts>python SSL_Server_throughput_d.py
IPv6:
C:\SiWG017_Release\resources\scripts>python SSL_Server_throughput_v6.pyTLS Rx:
To measure TLS Rx throughput, configure the SiWG917 as a TLS server and open TLS client at the remote peer using the below command.
IPv4:
C:\SiWG917_Release\resources\scripts>python SSL_tx_throughput_d.py
IPv6:
C:\SiWG917_Release\resources\scripts>python SSL_tx_throughput_v6.py