Waking the NCP from Sleep#
Waking up the NCP involves a simple handshaking routine as illustrated in the following figure. This handshaking ensures that the Host will wait until the NCP is fully awake and ready to accept commands from the Host. If the NCP is already awake when the handshake is performed (such as when the Host resets and the NCP is already operating), the handshake will proceed as described below with no ill effects.
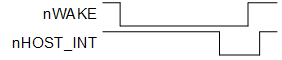

Note: A wake handshake cannot be performed if nHOST_INT is already asserted.
nWAKE should not be asserted after the NCP has been reset until the NCP has fully booted, as indicated by the NCP asserting nHOST_INT. If nWAKE is asserted during this boot time, the NCP may enter bootloader mode. Refer to section Bootloading the NCP.
Waking the NCP should be a straightforward implementation that only requires you to choose between a polling or an interrupt mechanism for knowing when the NCP is ready (much like the rest of the EZSP-SPI Protocol). After asserting the nWAKE signal, the host should either poll for a falling edge of nHOST_INT or set up for an interrupt on the falling edge. As soon as the edge is seen, the host should deassert nWAKE and continue operating the EZSP as desired.
The only major caveat, is to make sure the proper piece of code gets triggered in response and to not perform further EZSP operations inside of interrupt context.
Waking the NCP involves the following steps:
Host asserts nWAKE.
NCP interrupts on nWAKE and exits sleep.
NCP performs all operations it needs to and will not respond until it is ready to accept commands.
NCP asserts nHOST_INT within 300 ms of nWAKE asserting.
If the NCP does not assert nHOST_INT within 300 ms of nWAKE, it is valid for the Host to consider the NCP unresponsive and to reset the NCP.
Host detects nHOST_INT assertion. Because the assertion of nHOST_INT indicates the NCP can accept SPI transactions, the Host does not need to hold Slave Select high for the normally required minimum 1 ms of inter-command spacing.
Host deasserts nWAKE after detecting nHOST_INT assertion.
NCP will deassert nHOST_INT within 25 μs of nWAKE deasserting.
After 25 μs, any change on nHOST_INT will be an indication of a normal asynchronous (callback) event.
