Introduction and Background#
Silicon Labs provides performance testing results from embedded mesh networks as part of developer conferences and industry white papers. The basic performance data of throughput, latency, and impact of security can be used by system designers to define expected behavior. Testing was done across our different mesh network technologies – Zigbee, Thread, and Bluetooth - and each are presented separately over various Application Notes. This application note presents the Zigbee network performance.
Underlying Physical Layer and Packet Structure#
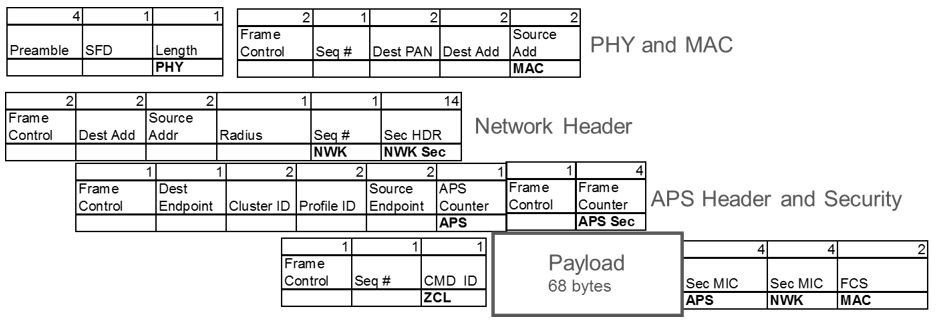
Network performance is based on payload sizing since the application usage does not account for the packet overhead.
Zigbee uses IEEE 802.15.4 with 127-byte packets and an underlying data rate of 250 kbps. The Zigbee packet format is shown below and results in a 68-byte payload. For payloads above 68 bytes, the Zigbee protocol fragments into multiple packets. Our data on performance is based on payload size as this is the design parameter of concern when building an application.

Network Routing Differences#
Zigbee was designed for home and building automation. Zigbee supports several routing techniques including flooding of the mesh for route discovery or multicast messages, next hop routing for controlled messages in the mesh, and many-to-one routing to a gateway or concentrator which then may use source routing out to devices. It is normal for a Zigbee network to use these methods at the same time.
Networks fragment larger messages into smaller ones. For Zigbee, fragmentation is done at the application layer and is end-to-end from the source to the destination.
For unicast forwarding within these networks, the message is forwarded as soon as the device is ready to send. For multicast forwarding, there are generally networking requirements for how messages are forwarded. For Zigbee devices, a multicast message is forward- ed by a device only after a jitter of up to 64 milliseconds. Unless a repeat of a multicast message has been heard from all known neighbors, each node will transmit two repeats of the multicast message spaced by 500ms. This 500ms gap is observed in the performance data results presented in this AN.
