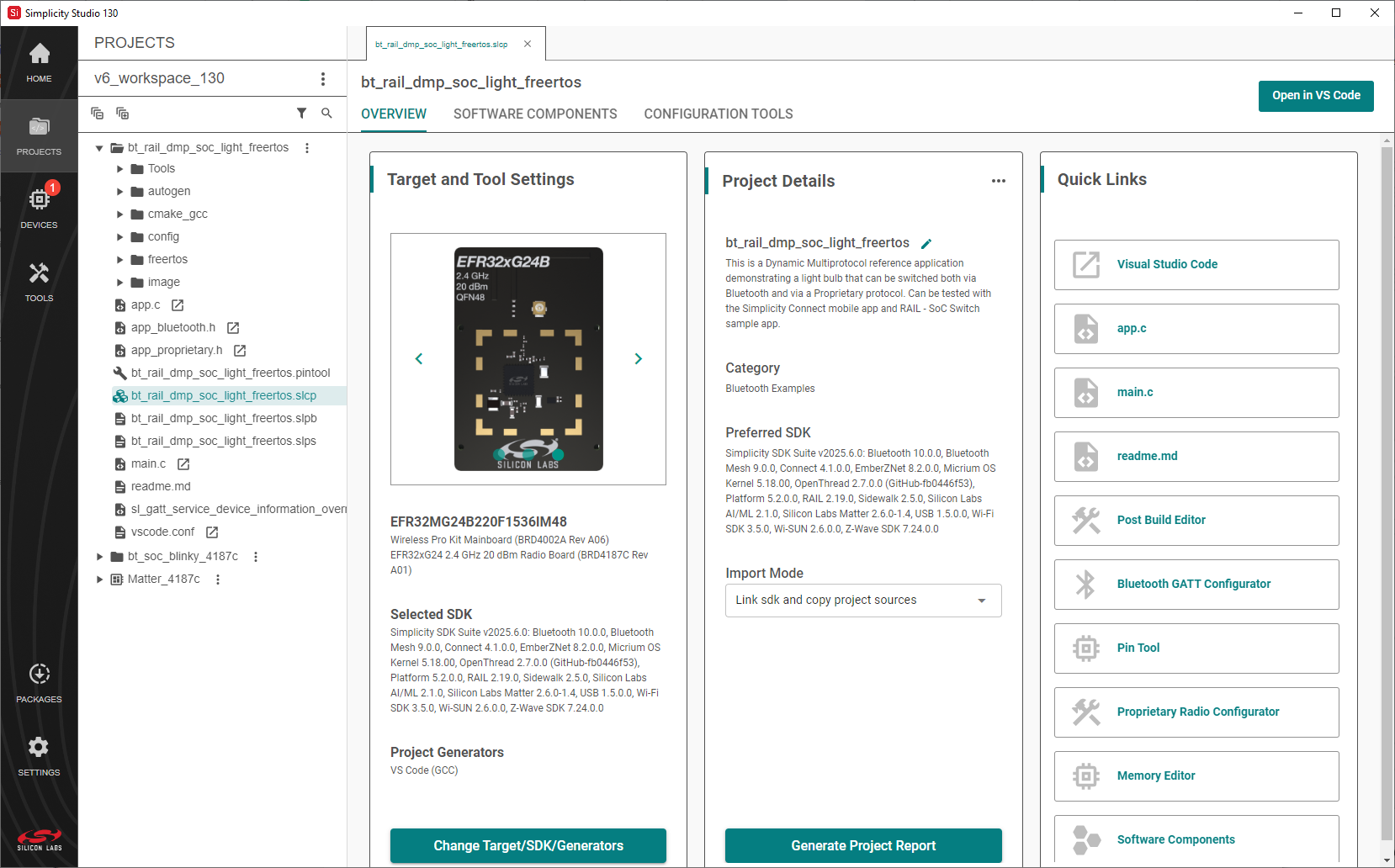
Project Configuration#
From the new project wizard (Project Configuration) window, you can set the project name, location, how SDK files are included, and the target IDE.
Steps to Configure Your Project#
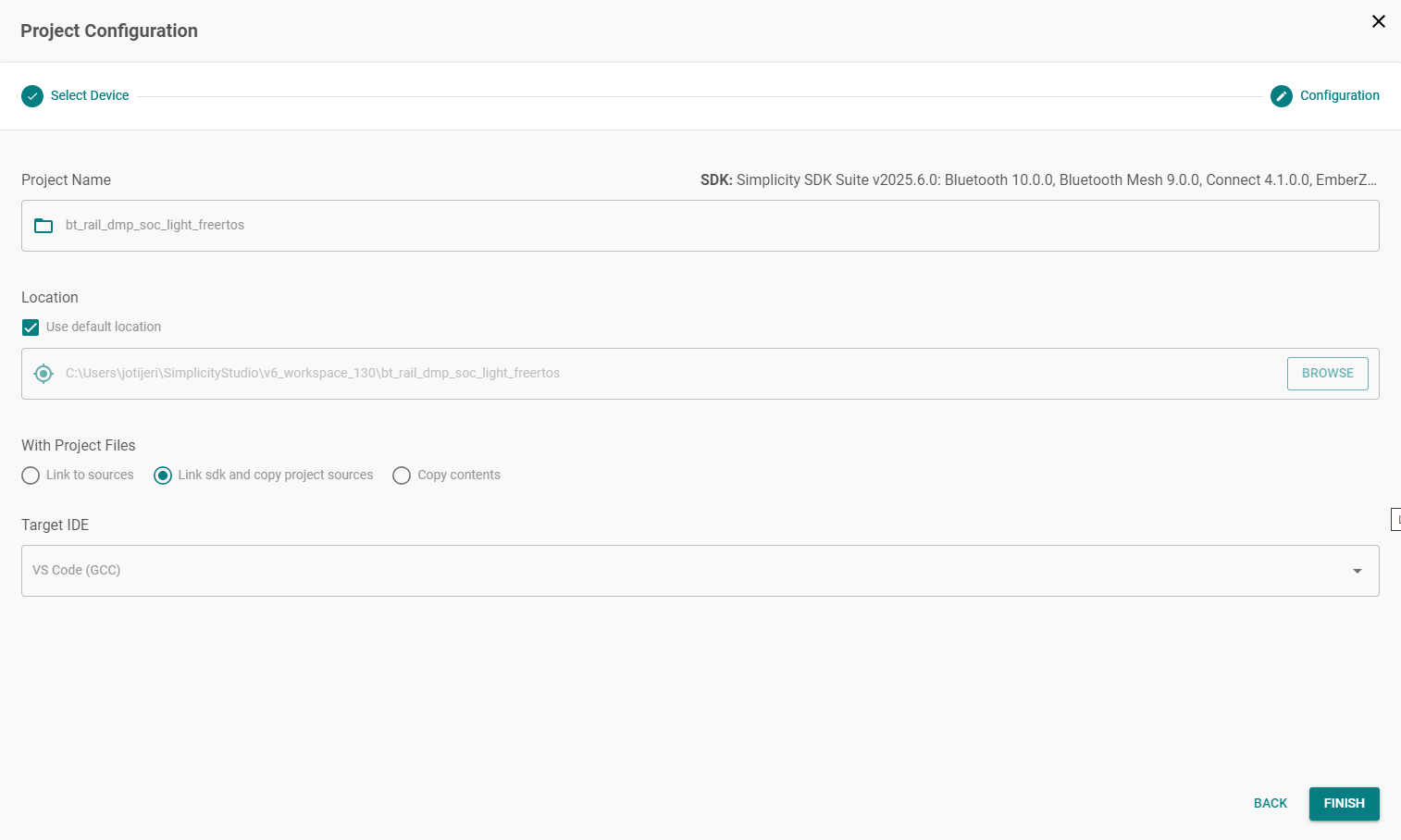

1. Name the Project#
In the Project Name field, the default name of the sample project displays. You can use the default project name or type a unique name for the project in this field.
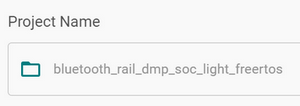

2. Set the Project Location#
In the Location field, the default path for your workspace is listed.

If you work for a company that has source control, it is recommended that you change this location to the appropriate source-controlled folder. Workspaces contain metadata that is not appropriate for source control.
To change the location, uncheck the Use default location box and enter the path in the field below, or click the BROWSE button to navigate to your preferred location.
3. Choose How to Include Project Files#
The With Project Files area has three options that describe how the project is created related to the files coming from the SDK:
Link to sources: For SDK developers only. This option creates links to every source file.
Link SDK and copy project sources: The recommended option, which is selected by default. This option copies links to the non-project-specific SDK files and copies the project-specific source files into the project group folder. Linking the SDK files tends to save disk space because duplicate files are not stored in multiple locations.
Copy contents: Copies all project-specific and non-project files into your project. This option is recommended if you are building the project in a CI/CD environment where you do not want to have Simplicity Studio installed, or if you want to create a standalone project.


Click the radio button at the left of the option name to select it.
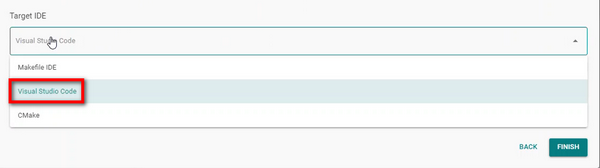
4. Select a Target IDE#
In the Target IDE section, select one of these options:
Makefile IDE: This option generates a Makefile-based project that can be built from the command line using GNU Make and the GCC toolchain.
The project includes:
A Simplicity Studio configuration file (
.slcp) for managing software componentsPROJECTNAME.MakefileandPROJECTNAME.project.makbuild scriptsSupport for peripheral and stack configuration using Simplicity Studio’s Project Configurator and Advanced Configurators (for example, Pintool and GATT Configurator)
Use this format if you prefer a terminal-based build process while still leveraging Studio’s powerful configuration and code generation tools.
Visual Studio Code: This option sets up the project for development in Visual Studio Code, while still using Simplicity Studio for initial configuration and code generation.
The project includes:
A Simplicity Studio .slcp file for managing software components and peripheral settings
Configuration files for building and debugging in VS Code (
tasks.json,launch.json, etc.)Full support for Advanced Configurators (such as, Pintool, GATT Configurator, and ZCL AP)
Use this format if you want to do all source code editing, building, and debugging inside VS Code and keep using Simplicity Studio for software component updates and configuration. Refer to the Simplicity Studio VS Code User Guide for setup and usage details.
CMake: This option creates a CMake-based project along with a Simplicity Studio configuration file (
.slcp). It is designed for developers who prefer using the CMake build system with GCC in command-line or external IDE environments.The project includes:
CMake build files (CMakeLists.txt) compatible with standard CMake tools
A
.slcpfile for configuring software components and peripheral settings in Simplicity StudioSupport for Advanced Configurators (such as, Pintool, GATT Configurator, and ZCL AP)
Use this format if you want to build the project using CMake and external build tools or CI.
IAR EWARM (IAR): During project creation, you cannot select the IAR EWARM IDE project generator. However, some projects (generally Bluetooth, Bluetooth Mesh, Connect, RAIL and Zigbee projects) support it after creation.
For those projects, to enable it:
Create the project using another generator.
In Project Configurator, open the Overview tab.
Select Change Target/SDK/Generators.
From the Change Project Generators dropdown, enable IAR Embedded Workbench Project.
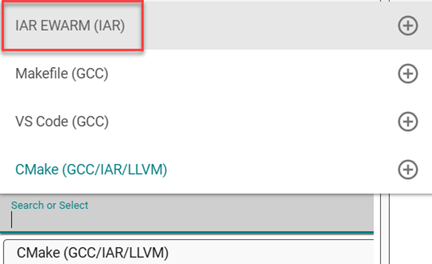

The IAR EW project files are created. If the
PROJECTNAME.ewwextension is associated with IAR Embedded Workbench, double-clicking the file opens the project in IAR EW. On launch, IAR EW may display a notice that the project file is in an old format (for IAR EW 8.30.1).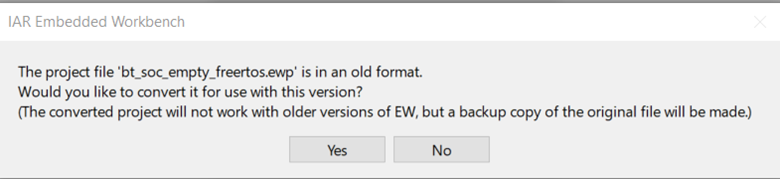

5. Finish Project Creation#
Review your settings.
Click Finish.

The Running Initial Project Configuration Tools generation message displays while your project is created.


When complete, the project appears in the PROJECTS pane. The project .slcp opens in a tab displaying information about the project and details on how to use and configure it.