Pseudo Static Random Access Memory (PSRAM)#
Few IoT applications may need more RAM than what is available in SiWG917. An option to add external RAM is available in SiWG917.
PSRAM is a pseudo random-access memory whose internal structure is a dynamic memory with refresh control signals generated internally in standby mode so that it can mimic the function of a static memory. It combines the high density of DRAM with the ease of use of true SRAM.
The following are the SiWG917 OPNs with the possible PSRAM options.
Part Number | PSRAM |
|---|---|
SiWG917M110LGTBA | External PSRAM |
SiWG917M100MGTBA | No PSRAM support |
SiWG917M111MGTBA | External PSRAM |
SiWG917M121XGTBA | 2 MB In-package PSRAM |
SiWG917M141XGTBA | 8 MB In-package PSRAM |
SiWG917M111XGTBA | External PSRAM |
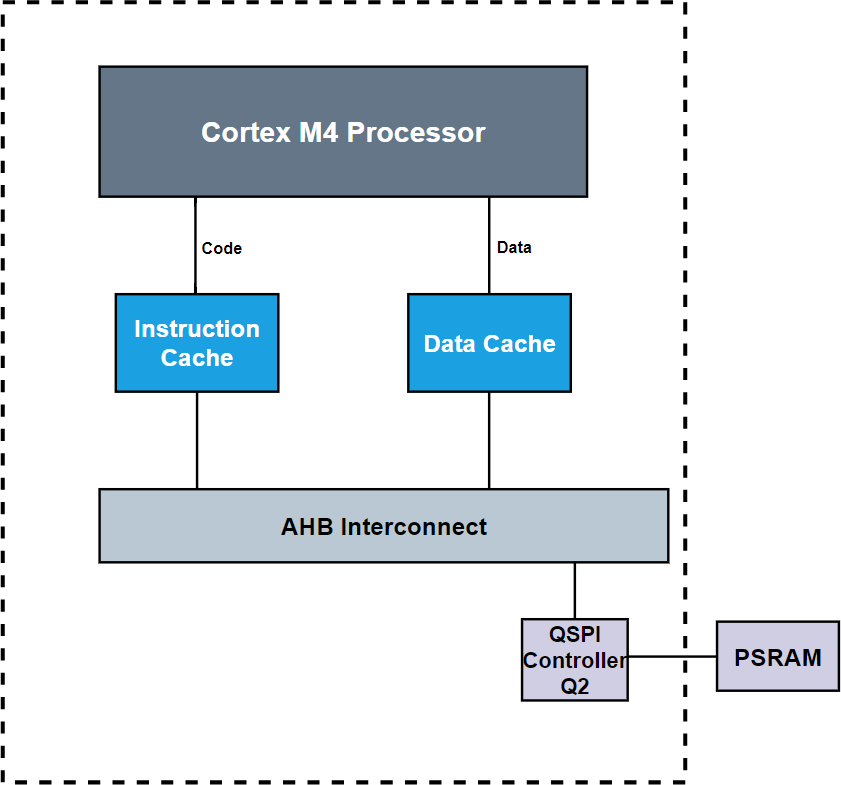
In SiWG917, the M4 communicates with PSRAM through Quad SPI interface (also called QSPI RAM).

Features:
M4 supports external RAM (PSRAM) with Data-cache.
PSRAM can be accessed by M4 through both I-cache and D-cache
QSPI controller (Q2) supports PSRAM with dedicated Single/Dual/Quad SPI SDR mode interface with maximum 80 MHz frequency
QSPI controller (Q2) supports the following mappings at the same time for external Flash and PSRAM:
Instruction memory space can be mapped into flash.
Read-only data memory space can be mapped into flash or PSRAM.
Read-write data memory space can be mapped into PSRAM.
QSPI controller (Q2) supports auto mode write to PSRAM only.
Only in auto mode write data encryption and read data decryption is supported.
QSPI controller (Q2) supports manual read and write access to PSRAM without security.
PSRAM data encryption or decryption is supported only in CTR mode with 128-bit and 256-bit key sizes.
Both Flash and PSRAM controllers use the same keys from the Keyholder for data encryption or decryption.
QSPI Secondary | In-Package PSRAM Size | External PSRAM Max Size |
|---|---|---|
PSRAM | 2 MB or 8 MB | 16 MB |
In-Package PSRAM#
The SiWG917 No In-package flash OPNs mentioned below have In-package PSRAM available.
SiWG917M121XGTBA – 2 MB In-package PSRAM
SiWG917M141XGTBA – 8 MB In-package PSRAM
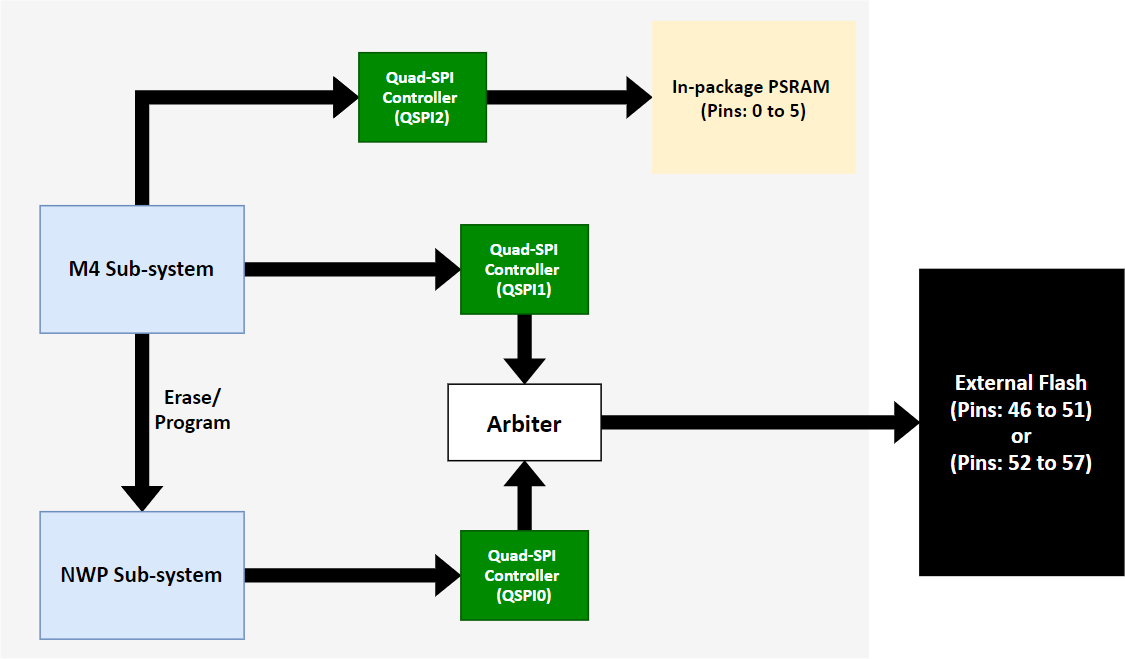
In-package PSRAM (Common Flash Mode)#

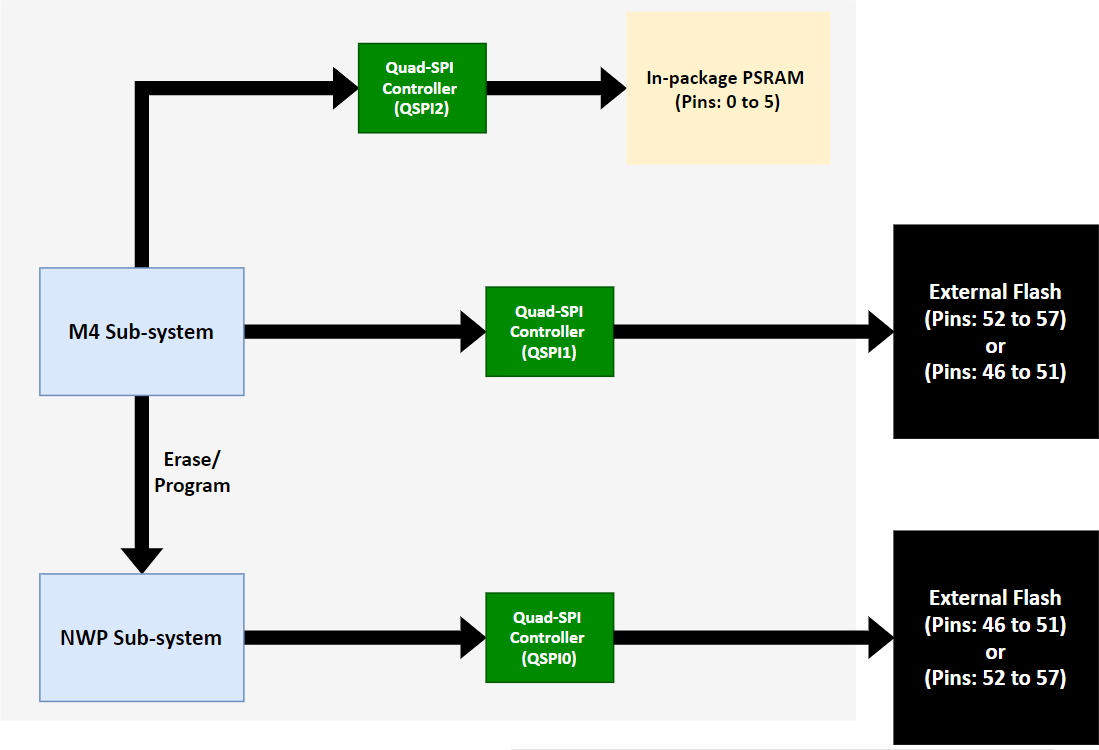
In-package PSRAM (Dual Flash Mode)#

Access Diagram#
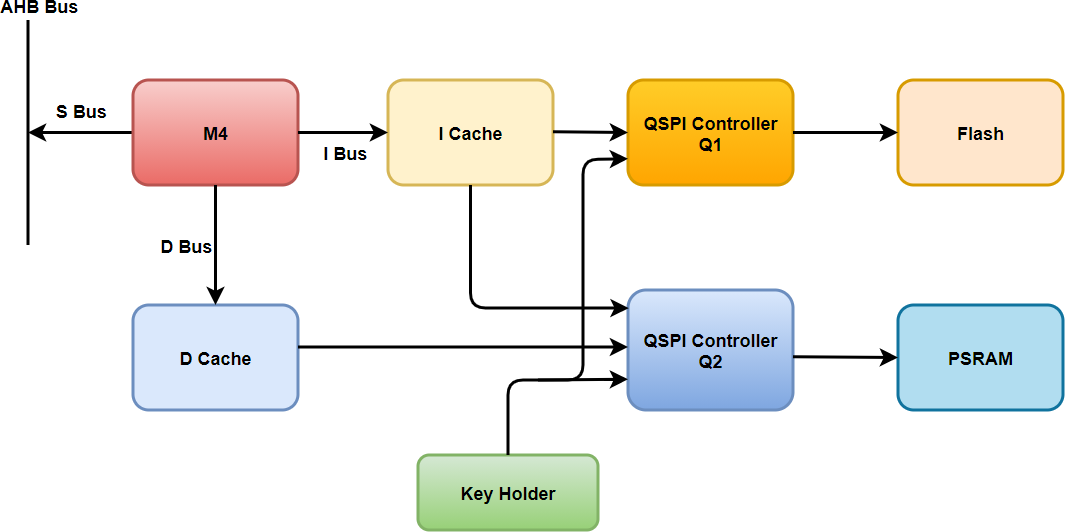

The PSRAM memory is connected to the AHB interconnect via the QSPI controller (Q2), and memory read-write operations for PSRAM are taken care by Q2 Controller.
Controller | Auto AHB Address (Direct Access Mode) | Manual AHB Address (Indirect Access Mode) |
|---|---|---|
Q2 | 0x0A00_0000 – 0x0BFF_FFFF | 0x1204_0000 – 0x1207_FFFF |
PSRAM is accessed through an additional memory called cache memory which improves the memory performance significantly by caching the data.
The M4 core accesses instructions and data through separate caches namely, "Data cache" and "Instruction cache", and then later both access PSRAM. The cache immediately provides data to the core when the requested data is available in the cache, which is called "Cache Hit". If the requested data isn't available, the cache brings in the block of data (a cache line) into the cache and provides the requested data to the core which is called "Cache Miss".
The PSRAM data path is provided with a 16 KB, 4-way set associative, 32-byte cache line. The instruction path uses existing cache i.e., i-cache, which is shared between flash and the PSRAM.
Note:
Only Row-boundary crossing or Linear bursting PSRAMs are supported.
The PSRAM ORIGIN address and LENGTH are defined in the linkerfile_SoC.ld.
