Secure and Privileged Programming Model#
The implementation of BLS on Series 2 devices, both flash and RAM, use a programmable watermark to delineate Secure, Non-secure Callable, and Non-secure regions. On the other hand, peripherals exist in both a Secure and Non-secure alias of memory.
BLS SMU Programming#
Enabling SMU Clock#
Except for the EFR32xG21 devices, all Series 2 devices enable the SMU clock in CMU before programming the SMU registers.
#if (_SILICON_LABS_32B_SERIES_2_CONFIG > 1)
CMU->CLKEN1_SET = CMU_CLKEN1_SMU;
#endif
Cortex-M33 Lock Control#
The Cortex-M33 security and privileged configurations can be locked by programming the SMU_M33CTRL register.
// Lock Secure MPU configuration
SMU->M33CTRL |= SMU_M33CTRL_LOCKSMPU;
Locking SMU Configuration#
Th entire SMU configuration can be locked down to avoid runaway code. Below is an example of how to lock and unlock the SMU.
uint32_t lock_status;
// Lock Down SMU
SMU->LOCK = ~SMU_LOCK_SMULOCKKEY_UNLOCK;
// Grab Lock Status
lock_status = (SMU->STATUS & _SMU_STATUS_SMULOCK_MASK) >> _SMU_STATUS_SMULOCK_SHIFT;
// Unlock SMU
SMU->LOCK = SMU_LOCK_SMULOCKKEY_UNLOCK;
Interrupt Control#
Each interrupt flag in SMU_IF can generate an interrupt when its corresponding interrupt enable flag in the SMU_IEN register is set. Each interrupt flag can be cleared by writing the clear alias of the SMU_IF register.
// Clear and enable the SMU PPUSEC and BMPUSEC interrupt
NVIC_ClearPendingIRQ(SMU_SECURE_IRQn);
SMU->IF_CLR = SMU_IF_PPUSEC | SMU_IF_BMPUSEC;
NVIC_EnableIRQ(SMU_SECURE_IRQn);
SMU->IEN = SMU_IEN_PPUSEC | SMU_IEN_BMPUSEC;
BLS ESAU Programming#
Region Types#
The SMU_ESAURTYESn registers are used to configure memory regions with a specific security attribute. All configurable memory regions reset to Secure. Below is an example of programming regions 3 and 11 to Non-secure.
// Region 3 (Info flash) is Non-secure
SMU->ESAURTYPES0 = SMU_ESAURTYPES0_ESAUR3NS;
// Region 11 (EPPB) is Non-secure
SMU->ESAURTYPES1 = SMU_ESAURTYPES1_ESAUR11NS;
Region Sizes#
The code and figure below highlight how to program the Movable Region Boundaries (MRBs) of ESAU.
// ESAU region 0/1/2 programming
// Boundary01 at 252kB and Boundary12 at 256kB
SMU->ESAUMRB01 = 0x0003F000U & _SMU_ESAUMRB01_MASK;
SMU->ESAUMRB12 = 0x00040000U & _SMU_ESAUMRB12_MASK;
// ESAU region 4/5/6 programming
// Boundary45 at 44kB and Boundary56 at 44kB (region 5 size = 0)
SMU->ESAUMRB45 = 0x0000B000U & _SMU_ESAUMRB45_MASK;
SMU->ESAUMRB56 = 0x0000B000U & _SMU_ESAUMRB56_MASK;


Notes:
The mrb12 (
ESAUMRB12inSMU_ESAURMBR12) has to be greater than or equal to mrb01 (ESAUMRB12inSMU_ESAURMBR12).The mrb56 (
ESAUMRB56inSMU_ESAURMBR562) has to be greater than or equal to mrb45 (ESAUMRB45inSMU_ESAURMBR45).If one of the rules above is violated, the
SMU_STATUS.SMUPRGERRis asserted.When mrb01 and mrb12 are equal, region 1 (NSC) is a size of 0 and is not seen by the system.
When mrb45 and mrb56 are equal, region 5 (NSC) is a size of 0 and is not seen by the system.
BLS SAU Programming#
All Secure Configuration#
All secure configuration is the default state after reset. It clears the SAU_CTRL.ENABLE and the SAU_CTRL.ALLNS bits in SAU, and the entire memory is in a Secure attribute.
All Non-secure Configuration#
All Non-secure Configuration occurs when the SAU_CTRL.ENABLE bit is cleared, and the SAU_CTRL.ALLNS bit is set. The ESAU controls the security attribute of a Cortex-M33 transaction.
// Disable SAU (ALLNS = 1) and clear data and instruction pipe
SAU->CTRL = SAU_CTRL_ALLNS_Msk;
__DSB();
__ISB();
Configurable Configuration#
Configurable configuration occurs when the SAU_CTRL.ENABLE bit is set (SAU_CTRL.ALLNS is irrelevant). Both SAU and ESAU determine the security attribute of a Cortex-M33 transaction. The code and figure below highlight how to program the SAU regions.
// Define all Non-secure (NS) and Non-secure Callable (NSC) Regions
#define REGION0_BASE 0x0001E000UL
#define REGION1_BASE 0x00020000UL
#define REGION2_BASE 0x20004000UL
#define REGION0_LIMIT 0x0001FFFFUL
#define REGION1_LIMIT 0x000FFFFFUL
#define REGION2_LIMIT 0x20017FFFUL
// CMSIS calls to enable SAU Regions
// SAU region 0 - Flash NSC at 120 kB to 128 kB (0x0001E000 - 0x0001FFFF)
SAU->RNR = (0UL & SAU_RNR_REGION_Msk);
SAU->RBAR = (REGION0_BASE & SAU_RBAR_BADDR_Msk);
SAU->RLAR = (REGION0_LIMIT & SAU_RLAR_LADDR_Msk) | SAU_RLAR_NSC_Msk | SAU_RLAR_ENABLE_Msk;
// SAU region 1 - Flash NS at 128 KB to 1024 kB (0x00020000 - 0x000FFFFF)
SAU->RNR = (1UL & SAU_RNR_REGION_Msk);
SAU->RBAR = (REGION1_BASE & SAU_RBAR_BADDR_Msk);
SAU->RLAR = (REGION1_LIMIT & SAU_RLAR_LADDR_Msk) | SAU_RLAR_ENABLE_Msk;
// SAU region 2 - RAM NS at 16 kB to 96 kB (0x20004000 - 0x20017FFF)
SAU->RNR = (2UL & SAU_RNR_REGION_Msk);
SAU->RBAR = (REGION2_BASE & SAU_RBAR_BADDR_Msk);
SAU->RLAR = (REGION2_LIMIT & SAU_RLAR_LADDR_Msk) | SAU_RLAR_ENABLE_Msk;
// CMSIS functions to enable SAU and clear data and instruction pipe
TZ_SAU_Enable();
__DSB();
__ISB();


BLS BMPU Programming#
Bus Master Privileged Attribute#
A Bus Master can be configured as either privileged (default) or unprivileged by programming the corresponding index in the SMU_BMPUPATDn register.
// Configure all odd Bus Masters unprivileged
for (i = 0; i < SMU_NUM_BMPUS; i++) {
if (i & 0x01) {
SMU->BMPUPATD0 &= ~(1 << i);
}
}
Bus Master Security Attribute#
A Bus Master can be configured as either Secure (default) or Non-secure by programming the corresponding index in the SMU_BMPUPATDn register. Configure a Bus Master as Non-secure results in the Bus Master only being able to access Non-secure addresses.
// Configure all odd Bus Masters Non-secure
for (i = 0; i < SMU_NUM_BMPUS; i++) {
if (i & 0x01) {
SMU->BMPUSATD0 &= ~(1 << i);
}
}
Bus Master Fault Status#
The Bus Master ID and the address that triggered the fault can be read from the SMU_BMPUFS and SMU_BMPUFSADDR registers.
uint32_t fs_bmpu_id;
uint32_t fs_bmpu_addr;
uint32_t fs_bmpu_secfault;
// Read Bus Master fault status
fs_bmpu_id = SMU->BMPUFS;
fs_bmpu_addr = SMU->BMPUFSADDR;
fs_bmpu_secfault = (SMU->IF & _SMU_IF_BMPUSEC_MASK) >> _SMU_IF_BMPUSEC_SHIFT;
// Clear the IF to capture a new fault
SMU->IF_CLR = SMU_IF_BMPUSEC;
BLS PPU Programming#
Peripheral Privileged Attributes#
A peripheral can be configured as either privileged (default) or unprivileged by programming the corresponding index in the SMU_PPUPATDn register.
// Configure all odd peripherals unprivileged
for (i = 0; i < SMU_NUM_PPU_PERIPHS; i++) {
if (i & 0x01) {
if (i >= 32){
SMU->PPUPATD1 &= ~(1 << (i-32));
} else {
SMU->PPUPATD0 &= ~(1 << i);
}
}
}
Notes:
The peripherals in
SMU_PPUPATD0andSMU_PPUPATD0are device-dependent.The privileged attribute of the radio subsystem (
AHBRADIOindex) is configured as a unit.
Peripheral Security Attributes#
A peripheral can be configured as either Secure (default) or Non-secure by programming the corresponding index in the SMU_PPUSATDn register. The figure below shows the memory map when the ADC, I2C0, USART1, and RADIO are configured as Non-secure and other peripherals (e.g., SMU, RTCC, TIMER1, TIMER0, USART0...) as Secure.
// Configure all the Non-secure peripherals
SMU->PPUSATD0 &= ~SMU_PPUSATD0_USART1;
SMU->PPUSATD1 &= ~(SMU_PPUSATD1_I2C0 | SMU_PPUSATD1_IADC0 | SMU_PPUSATD1_AHBRADIO);
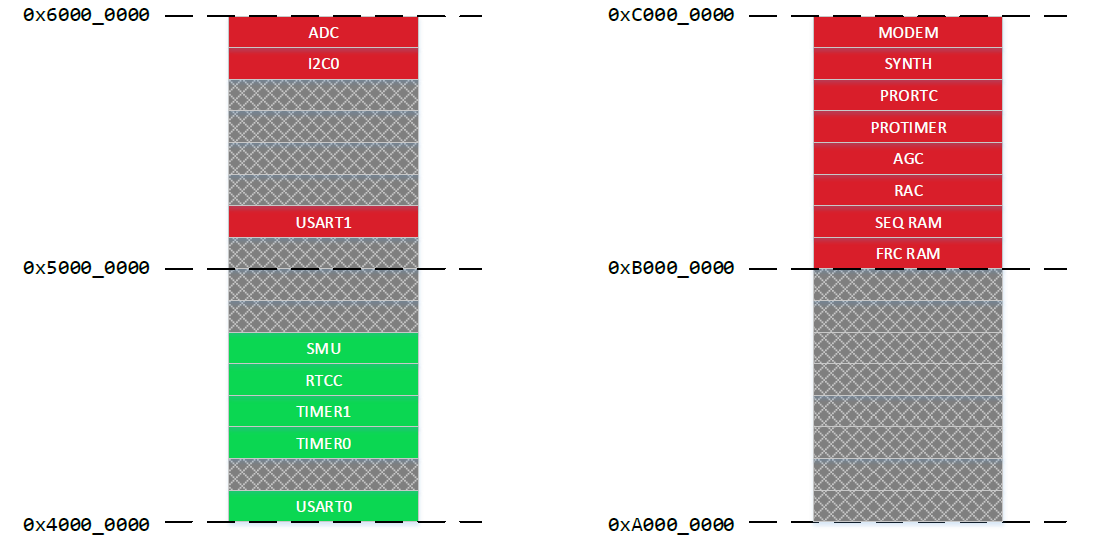

Notes:
The peripherals in
SMU_PPUSATD0andSMU->PPUSATD1are device-dependent.The security attribute of the radio subsystem (
AHBRADIOindex) is configured as a unit.
Peripheral Fault Status#
The peripheral ID that triggered the fault can be read from the SMU_PPUFS register.
uint32_t fs_ppu_periph_id;
uint32_t fs_sec_fault;
uint32_t fs_priv_fault;
uint32_t fs_inst_fault;
// Read peripheral fault status
fs_ppu_periph_id = SMU->PPUFS;
fs_sec_fault = (SMU->IF & _SMU_IF_PPUSEC_MASK) >> _SMU_IF_PPUSEC_SHIFT;
fs_priv_fault = (SMU->IF & _SMU_IF_PPUPRIV_MASK) >> _SMU_IF_PPUPRIV_SHIFT;
fs_inst_fault = (SMU->IF & _SMU_IF_PPUINST_MASK) >> _SMU_IF_PPUINST_SHIFT;
// Clear the IF to capture a new fault
SMU->IF_CLR = SMU_IF_PPUSEC | SMU_IF_PPUPRIV | SMU_IF_PPUINST;
Floating Point Unit (FPU) Programming#
If the Non-secure application enables the FPU at initialization, the Secure software needs to set up the NSACR register in SCB to grant the FPU access for Non-secure software.
// Enable Non-secure access to the FPU
SCB->NSACR |= SCB_NSACR_CP10_Msk + SCB_NSACR_CP11_Msk;
