TrustZone Platform Examples#
The following TrustZone platform examples located in the C:\Users<PC USER NAME>\SimplicityStudio\SDKs\gecko_sdk\app\common\example folder (Windows) demonstrate the TrustZone implementation on Series 2 devices. All TrustZone platform examples do not include Gecko Bootloader.
TrustZone PSA Attestation#


| Example Folder | Description |
|---|---|
tz_psa_attestation | The workspace description file (tz_psa_attestation_ws.slcw) creates the TrustZone PSA Attestation example. The project description file (tz_psa_attestation_s.slcp) configures a Secure application that provides the Secure Library functionality required by the Non-secure application. |
tz_psa_attestation_ns | The project description file (tz_psa_attestation_ns.slcp) configures a Non-secure application for the TrustZone PSA Attestation example. |
Notes:
This example cannot run if the
SECURE_BOOT_ENABLE(root of trust of the attestation) option in SE OTP is disabled.The combined image of Secure and Non-secure applications is signed by the
example_signing_key.pem(private key) in C:\Users<PC USER NAME>\SimplicityStudio\SDKs\gecko_sdk\platform\commonfolder (Windows). Theexample_signing_pubkey.pem(public key) in the same folder is installed to the SE OTP to verify the image signature during Secure Boot.
TrustZone PSA Crypto ECDH#



Example Folder | Description |
|---|---|
tz_psa_crypto_ecdh | The workspace description file (tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ws.slcw) upgrades the existing Platform - PSA Crypto ECDH example to TrustZone-aware. The project description file (tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_s.slcp) configures a Secure application that provides the Secure Library functionality required by the Non-secure application. |
tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ns | The project description file (tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ns.slcp) configures the existing Platform - PSA Crypto ECDH example as a Non-secure application. The source code can be reused without changes. |
The following sections use Simplicity Studio v5.6.3.0 and GSDK v4.2.2. The procedures and pictures may be different if using higher versions of Simplicity Studio 5 and GSDK.
Project Description File#
The project description file (.slcp) contains references to the GSDK used and a list of components to use from these. The TrustZone-aware application requires separate slcp files for the Secure and Non-secure applications.
Users should not directly edit the slcp files, but rather use the Memory Editor and Post Build Editor in Simplicity Studio to update the memory configuration and post-build actions.
Secure Application#
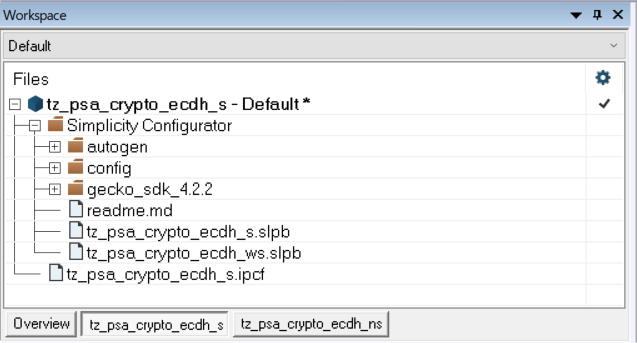
The following figure describes which TrustZone software components are installed for the TrustZone Secure library of the TrustZone PSA Crypto ECDH example.


Notes:
The services provided by the Secure library are standardized.
The source files for the Secure library will be automatically added to the application when generating the Secure project from the
slcpfile. For the current TrustZone implementation, modifications of the source files of the Secure library are not recommended.
Non-secure Application#
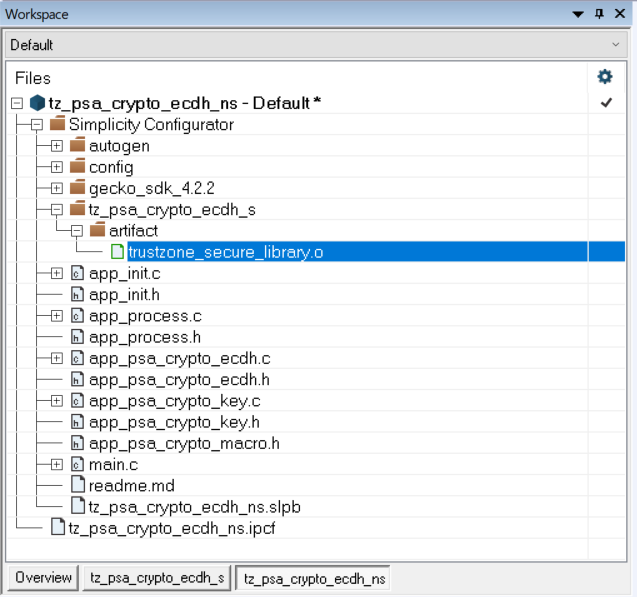
The following figure describes which TrustZone software components are installed for the Non-secure application of the TrustZone PSA Crypto ECDH example.


Notes:
The following software components are automatically installed when PSA Crypto and ITS services are used on the Non-secure application.
MSC Service for TrustZone Secure Key Library
NVM3 Service for TrustZone Secure Key Library
PSA Crypto Service for TrustZone Secure Key Library
PSA ITS Service for TrustZone Secure Key Library
SYSCFG Service for TrustZone Secure Key Library
The following software components can be installed to the Non-secure application when those services are required.
Workspace#
A workspace is a structure that can contain multiple projects. 'Workspace' is a generic term for this construct. In the context of Simplicity Studio, where workspace has a different, Eclipse-based, meaning, workspaces are referred to as Solutions.
The workspace description file (.slcw) contains references to projects (.slcp) that make up the workspace. Users should not directly edit the slcw file, but rather use the Post Build Editor in Simplicity Studio to update the post-build actions.
Memory Configuration#
The memory configurations in the TrustZone platform examples are based on the Series 2 radio board with minimum flash (512 kB) and RAM (32 kB), so these configurations can run on all Series 2 radio boards. Users can customize the settings when more flash and RAM are available on the selected device.
Memory flash size (total) =
memory_flash_size(S) +memory_flash_size(NS) = 512 kBMemory RAM size (total) =
memory_ram_size(S) +memory_ram_size(NS) = 32 kB
Secure Application#
The project description file of the Secure application (*_s.slcp) uses the default memory setting below to generate the Secure linker file (linkerfile.ld for GCC and linkerfile.icf for IAR in the project autogen folder).
The actual memory usage during software development is unknown, so it needs to reserve enough flash (memory_flash_size: 176 kB) and RAM (memory_ram_size: 12 kB) for the Secure part of all TrustZone platform examples. The bigger RAM size (including stack and heap) is mainly for the software fallback on cryptographic operations in PSA Crypto.
| Default Memory Setting (Secure) | xG21 and xG22 Devices | Other Series 2 Devices |
|---|---|---|
memory_flash_start | 0x00000000 | 0x08000000 |
memory_flash_size | 0x0002C000 (176 kB) | 0x0002C000 (176 kB) |
memory_ram_start | 0x20000000 | 0x20000000 |
memory_ram_size | 0x00003000 (12 kB) | 0x00003000 (12 kB) |
MEMORY
{
FLASH (rx) : ORIGIN = 0x0, LENGTH = 0x2c000
RAM (rwx) : ORIGIN = 0x20000000, LENGTH = 0x3000
}
Non-secure Application#
The project description files of the Non-secure application (*_ns.slcp) use the default memory setting below to generate the Non-secure linker file (linkerfile.ld for GCC and linkerfile.icf for IAR in the project autogen folder).
The actual memory usage during software development is unknown, so the remaining flash (memory_flash_size: 336 kB) and RAM (memory_ram_size: 20 kB) should be big enough for the Non-secure part of all TrustZone platform examples.
| Default Memory Setting (Non-secure) | xG21 and xG22 Devices | Other Series 2 Devices |
|---|---|---|
memory_flash_start | 0x0002C000 (176 kB) | 0x0802C000 (176 kB) |
memory_flash_size | 0x00054000 (336 kB) | 0x00054000 (336 kB) |
memory_ram_start | 0x20003000 (12 kB) | 0x20003000 (12 kB) |
memory_ram_size | 0x00005000 (20 kB) | 0x00005000 (20 kB) |
MEMORY
{
FLASH (rx) : ORIGIN = 0x2c000, LENGTH = 0x54000
RAM (rwx) : ORIGIN = 0x20003000, LENGTH = 0x5000
}
Note: The usable flash for Non-secure code should be equal to
memory_flash_size-NVM size(default is 40 kB) if NVM3 storage is required.
Memory Editor#
The default memory setting of Secure and Non-secure applications are good enough for software development and debugging. The final memory layouts of Secure and Non-secure projects are deduced by inspecting the flash and RAM usage in the Secure application memory map file (.map).
The Memory Editor in Simplicity Studio 5 is a graphical tool for editing the memory layout (flash and RAM) of the applications in the workspace. The Memory Editor will update the linker file in the project autogen folder with the custom settings. Rebuild the projects to use the new memory configurations in the linker files.
The Memory Editor is located at the Quick Links and CONFIGURATION TOOLS of Secure or Non-secure slcp file.


The following items will be determined by the flash usage in the Secure application memory map file:
memory_flash_size (S)
memory_flash_start (NS)
memory_flash_szie (NS)
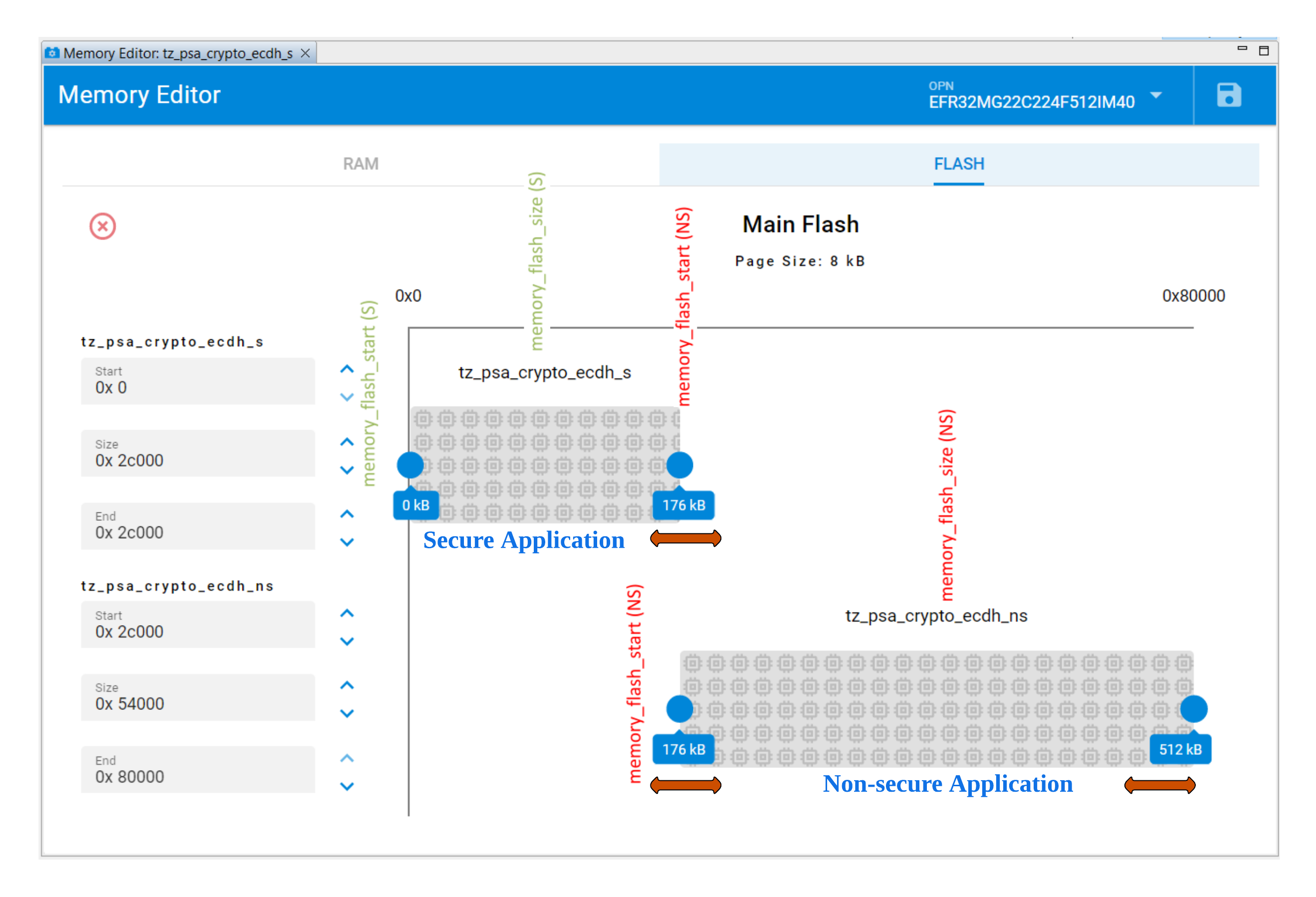

Note: The Memory Editor in Simplicity Studio v5.6.3.0 can only adjust the flash size in 8 kB (page size) alignment, which may not fit the 4kB alignment between the Secure and Non-secure flash boundary.
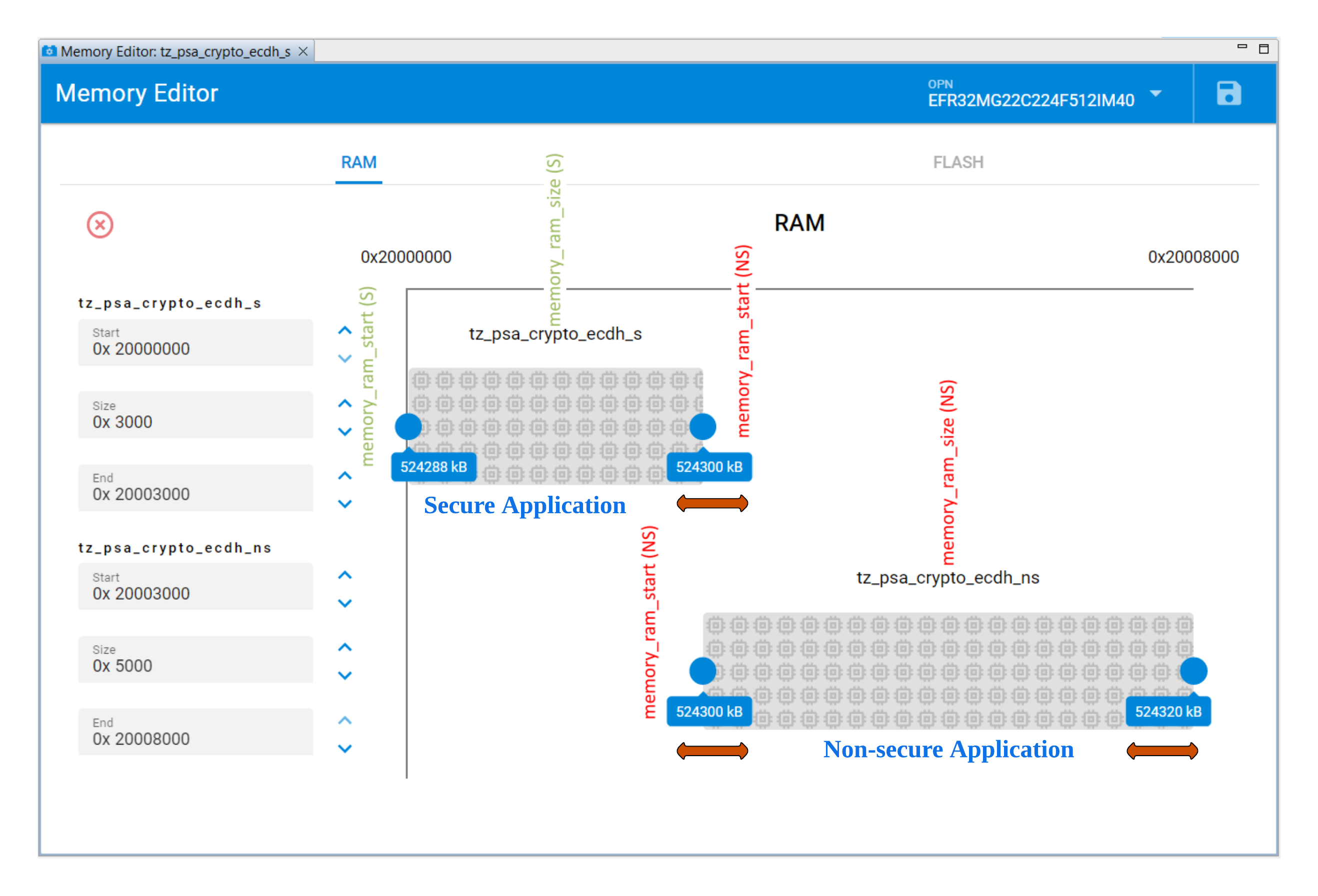
The following items will be determined by the RAM usage in the Secure application memory map file:
memory_ram_size (S)
memory_ram_start (NS)
memory_ram_szie (NS)

Build#
The Secure project must be built first to create the Secure object library (trustzone_secure_library.o) with function entries for the Non-secure project. Both projects need to be rebuilt if any changes in the Secure project. Users can use Simplicity IDE in Simplicity Studio 5 or IAR EWARM v9.20.4 to build the TrustZone platform examples.
Simplicity IDE#
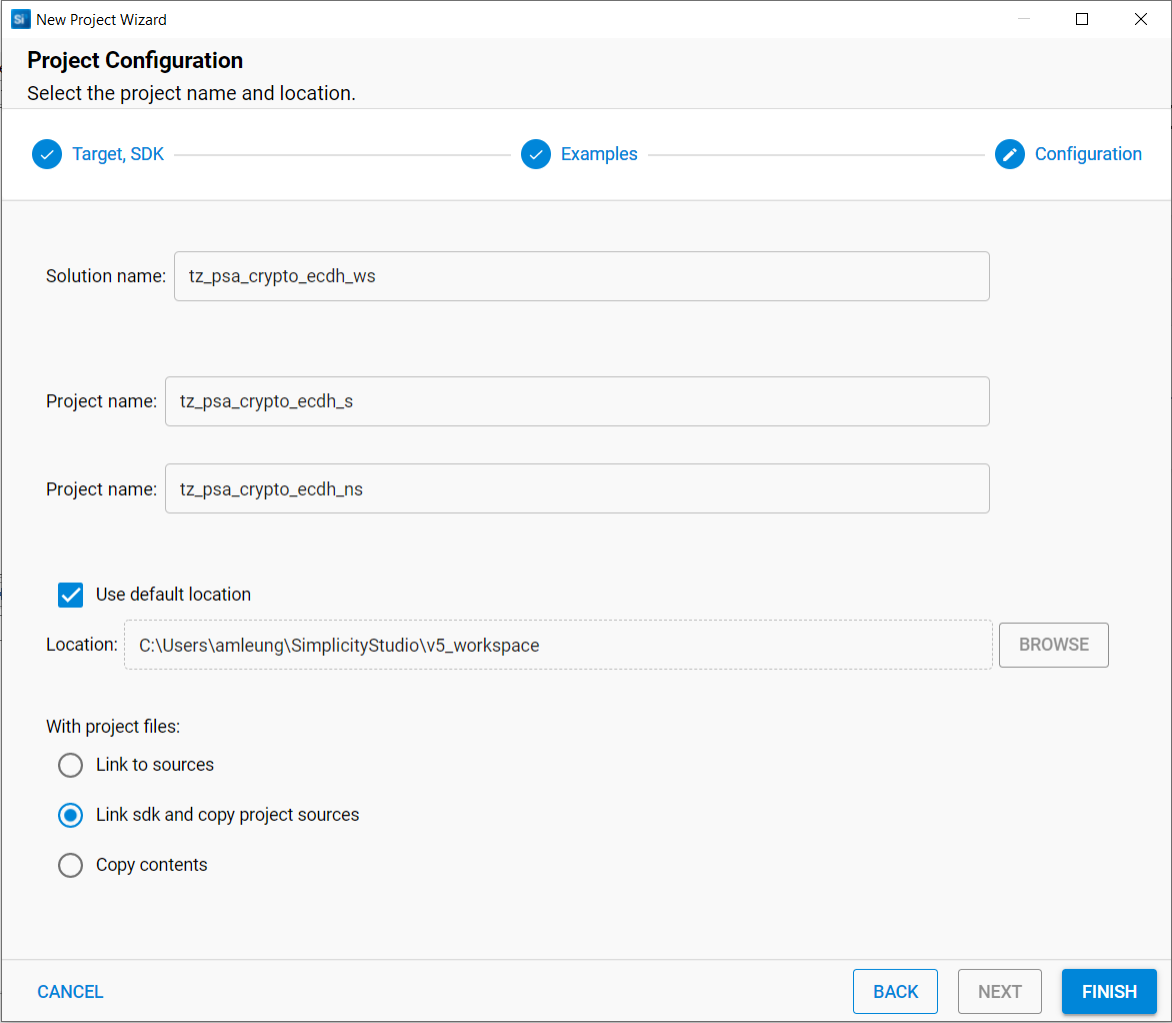
The following procedures are based on the TrustZone PSA Crypto ECDH example on BRD4182A Radio Board (EFR32MG22C224F512IM40).
Use the
tz_psa_cryptokeyword to search in EXAMPLE PROJECTS & DEMOS tab. Select thetz_psa_crypto_ecdh_wsexample.




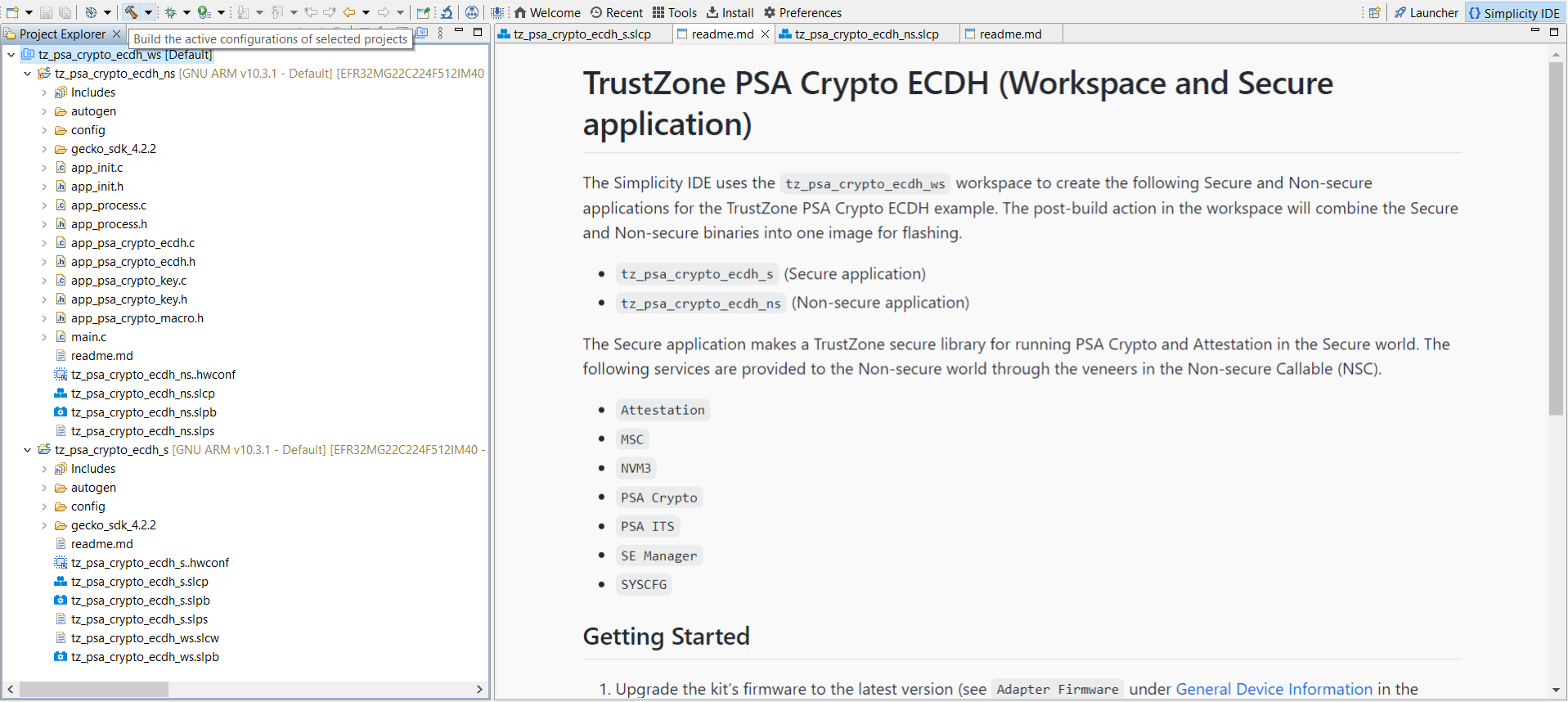

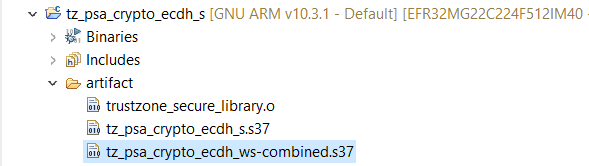
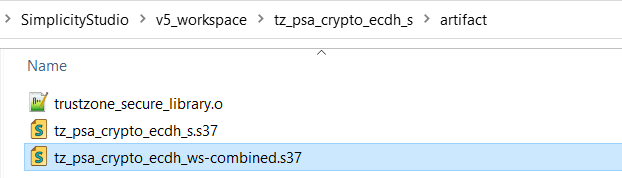
.slpb files) of the Secure project, Non-secure project, and workspace will be processed in sequence if the solution is successfully built. The combined image (tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ws-combined.s37) in the Secure project artifact folder can be used for programming the device or debugging.

Note: The Simplicity IDE can only apply the post-build action to a particular project if multiple Secure or Non-secure projects exist in the solution.
IAR EWARM#
The following procedures are based on the TrustZone PSA Crypto ECDH example on BRD4181A Radio Board (EFR32MG21A010F1024IM32).
Follow steps 1 to 3 in TrustZone PSA Crypto ECDH to generate the solution for the
tz_psa_crypto_ws. Select thetz_psa_crypto_ecdh_s.slcpfile.The Overview tab shows the Target and Tool Settings card on the left side. Scroll down if necessary and click [ChangeTarget/SDK/Generators].

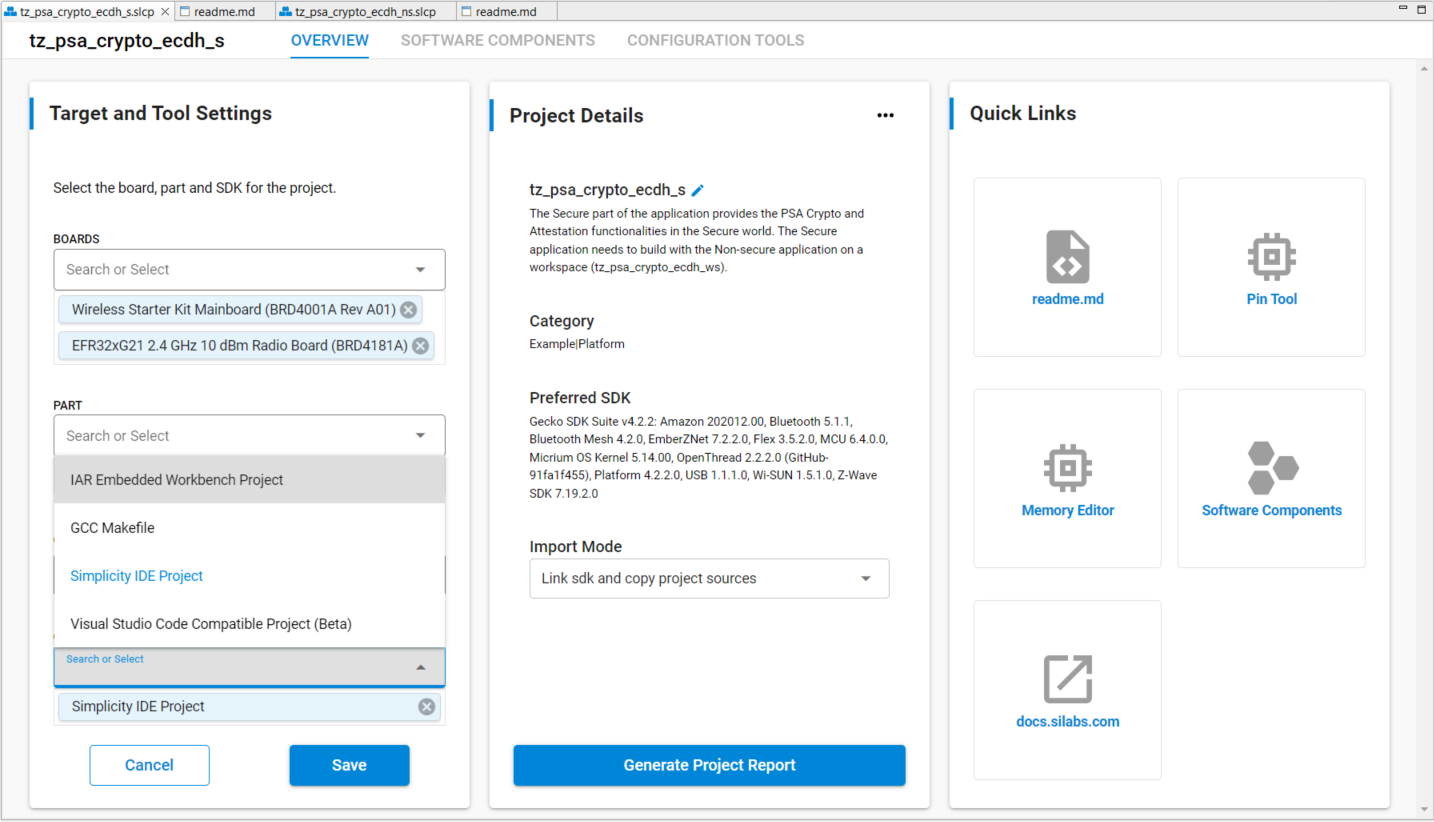

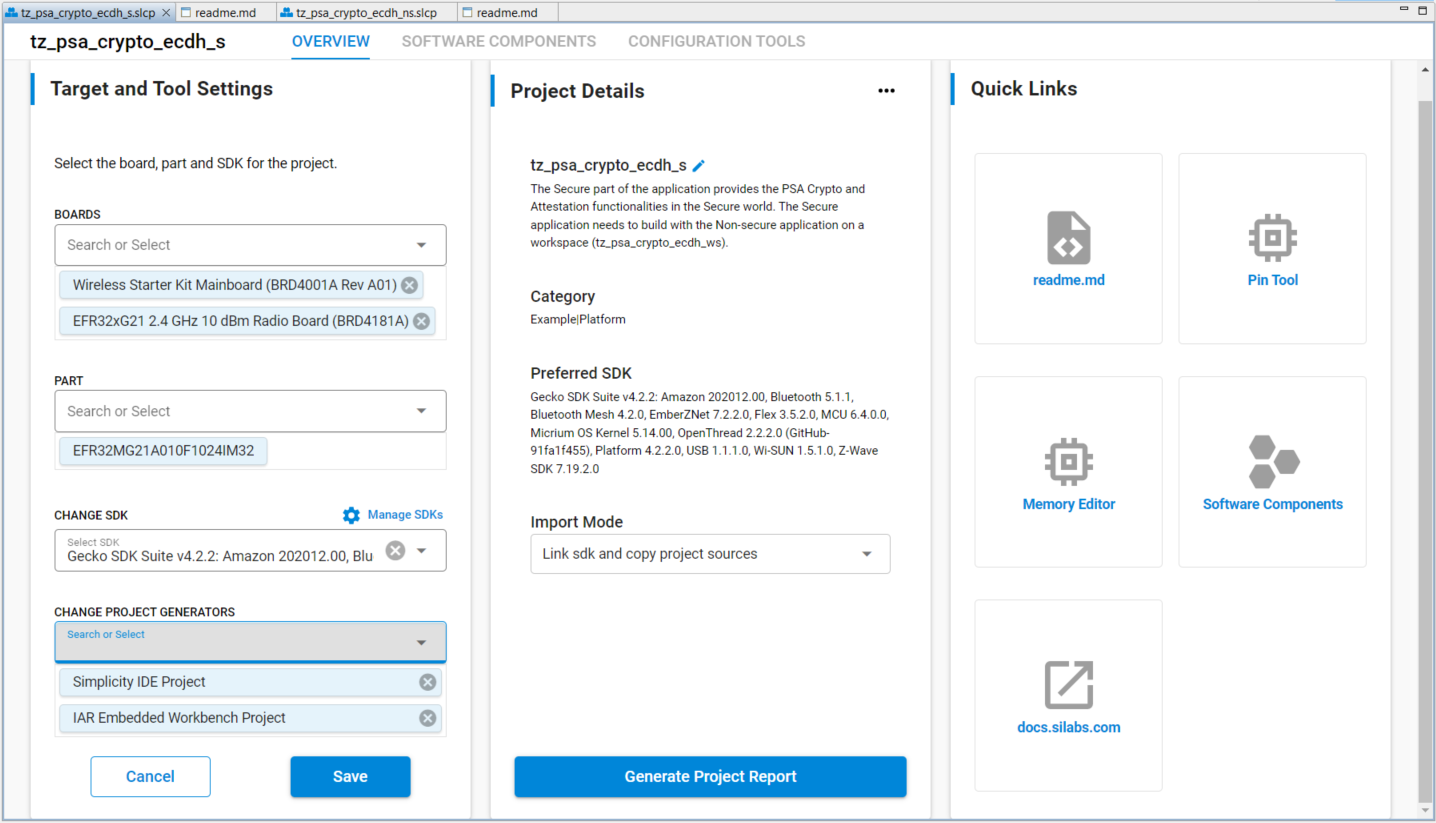

tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ns.slcp file. Repeat steps 2 to 4 to generate an IAR Non-secure* project (tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ns.ewp).
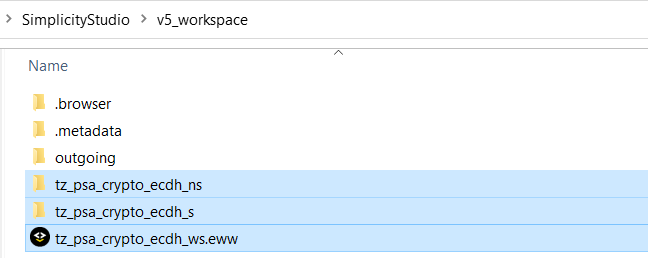
6. Use a text editor to create an IAR tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ws.ewwfile (shown below) to house the projects (tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_s.ewpand tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ns.ewp) generated in steps 4 and 5. The location of the tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ws.eww is the directory for
<?xml version ="1.0" encoding="iso-8859-1"?>
<workspace>
<project>
<path>$WS_DIR$\tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_s\tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_s.ewp</path>
</project>
<project>
<path>$WS_DIR$\tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ns\tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ns.ewp</path>
</project>
<batchBuild/>
</workspace>






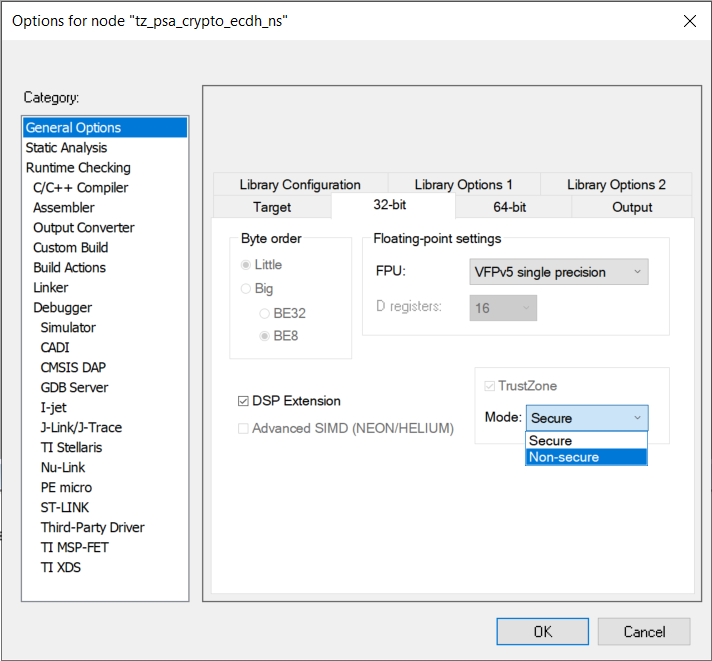
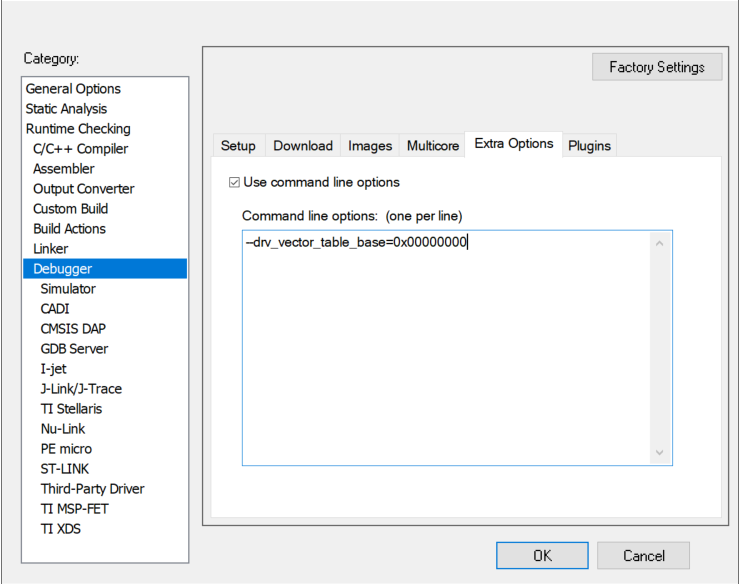
SL_TRUSTZONE_NONSECURE defined in the Non-secure project disables the CMSE compiler option (--cmse) regardless of whether the Project → Options... → General Options → 32-bit → TrustZone → Mode: setting is Secure or Non-secure. So changing this configuration from Secure to Non-secure is optional. Click [OK] to exit.



tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_s for programming the device.

Note: The IAR EWARM can only apply the workspace post-build action to a particular project if multiple Secure or Non-secure projects exist in the workspace.
Debugging#
Users can use Simplicity IDE in Simplicity Studio 5 or IAR EWARM v9.20.4 to debug the TrustZone platform examples. Building the projects with Optimization Level None (-O0) is recommended for debugging.
Simplicity IDE#
The TrustZone debugging process on Simplicity IDE is similar to the existing sample projects in Simplicity Studio.
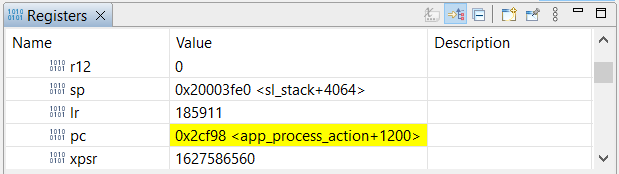
GNU Debugger (GDB) is recommended to debug TrustZone applications.
Flash the combined image (tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ws-combined.s37) generated in Simplicity IDE to the device.
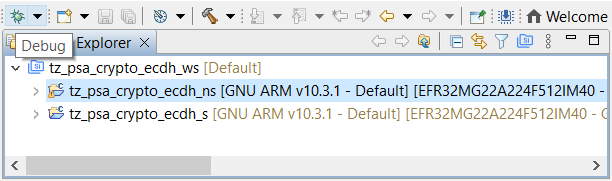
Select the Secure or Non-secure project and use the Debug icon to launch a debug session.


IAR EWARM#
Use the tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ws.eww workspace created in IAR EWARM for the debugger settings. Except for a minor difference in step 3, the following steps are the same as those to set up the Secure (tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_s) and Non-secure (tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ns) projects for debugging.
Select Options... in the



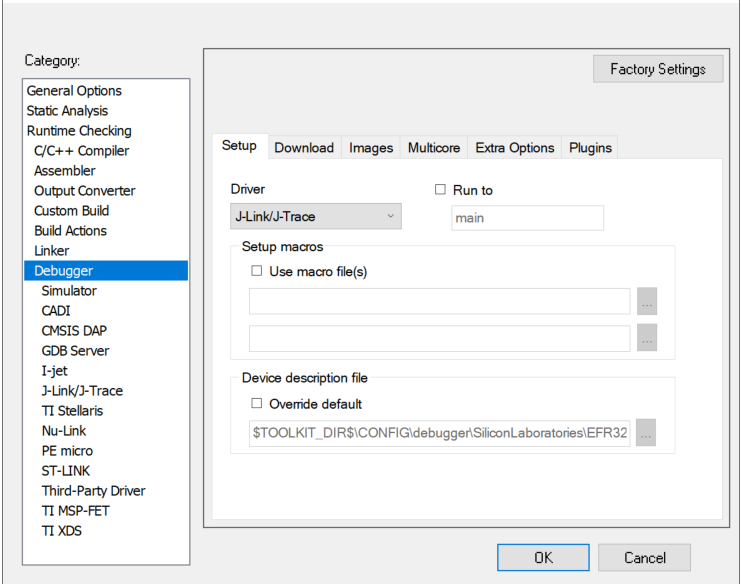

Location of Non-secure .out file for Secure project: tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ns\ewarm-iar\exe\tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ns.out
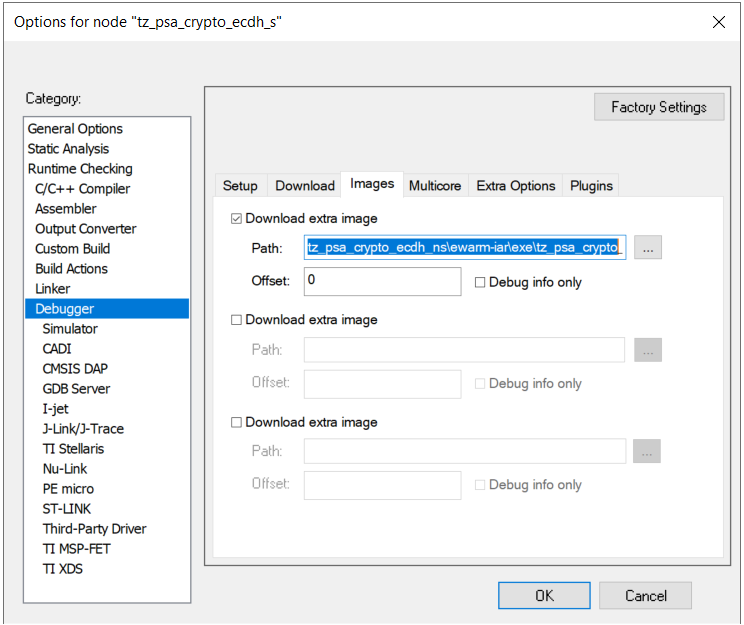

Location of Secure .out file for Non-secure project: tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_s\ewarm-iar\exe\tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_s.out






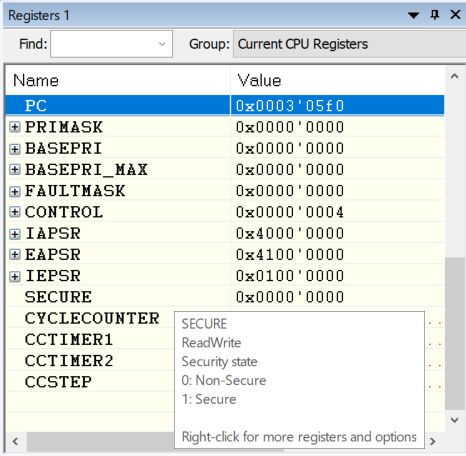



Benchmark#
The TrustZone implementation will affect the memory footprint and performance of cryptographic operations. The following comparisons are based on the TrustZone PSA Crypto ECDH example on BRD4182A Radio Board (EFR32MG22C224F512IM40) with SE firmware v1.2.14.
Memory Footprint#
The memory footprint of a TrustZone project depends on which services (software components in the figure below) provided by the Secure Library are used in the Non-secure application (tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ns project).


The following tables compare the memory footprint of the TrustZone-unaware (Platform - PSA Crypto ECDH) and TrustZone-aware projects (tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ws) based on the following conditions.
The
tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_nsreuses the source code from thePlatform - PSA Crypto ECDHexample without any changes.The total size in
tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_nsdoes not consider the 4 kB alignment on the Secure and Non-secure flash and RAM. The 4 kB alignment requirement will increase the actual usage of flash and RAM.All source code is compiled with Optimize for size (-Os) in Simplicity IDE (GNU ARM v10.3.1) of Simplicity Studio 5.
Table: Flash Size Comparison
| Platform Example | Secure | NSC | Non-secure | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Platform - PSA Crypto ECDH | 64688 B | - | - | 64688 B |
tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ws | 79172 B | 288 B | 29264 B | 108724 B |
Note: The NSC is part of the Secure code, and the total size does not include the flash for NVM3 storage.
Table: RAM Size Comparison
| Platform Example | Secure | NSC | Non-secure | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Platform - PSA Crypto ECDH | 3784 B | - | - | 3764 B |
tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ws | 2156 B | - | 1200 B | 3356 B |
Note: The total size does not include the RAM for the stack and heap. The Secure and Non-secure applications have their independent stack and heap.
PSA Crypto Performance#
The following sections compare the PSA Crypto performance of the TrustZone-unaware (Platform - PSA Crypto ECDH) and TrustZone-aware projects (tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ws) based on the following conditions.
The
tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_nsreuses the source code from thePlatform - PSA Crypto ECDHexample without any changes.All source code is compiled with Optimize most (-O3) in Simplicity IDE (GNU ARM v10.3.1) of Simplicity Studio 5.
Use ECC curve
SECP256R1on volatile and persistent keys.The EFR32MG22C224 runs at 38 MHz HFRCODPLL.
Volatile key ECDH operation on Platform - PSA Crypto ECDH#
. ECDH Client
+ Creating a SECP256R1 (256-bit) VOLATILE PLAIN client key... PSA_SUCCESS (cycles: 2928 time: 77 us)
+ Creating a SECP256R1 (256-bit) VOLATILE PLAIN server key... PSA_SUCCESS (cycles: 2960 time: 77 us)
+ Exporting a public key of a SECP256R1 (256-bit) VOLATILE PLAIN server key... PSA_SUCCESS (cycles: 332134 time: 8740 us)
+ Computing client shared secret with a SECP256R1 (256-bit) server public key... PSA_SUCCESS (cycles: 336860 time: 8864 us)
Volatile key ECDH operation on tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ws#
. ECDH Client
+ Creating a SECP256R1 (256-bit) VOLATILE PLAIN client key... PSA_SUCCESS (cycles: 5047 time: 132 us)
+ Creating a SECP256R1 (256-bit) VOLATILE PLAIN server key... PSA_SUCCESS (cycles: 5067 time: 133 us)
+ Exporting a public key of a SECP256R1 (256-bit) VOLATILE PLAIN server key... PSA_SUCCESS (cycles: 333956 time: 8788 us)
+ Computing client shared secret with a SECP256R1 (256-bit) server public key... PSA_SUCCESS (cycles: 338470 time: 8907 us)
Persistent key ECDH operation on Platform - PSA Crypto ECDH#
. ECDH Client
+ Creating a SECP256R1 (256-bit) PERSISTENT PLAIN client key... PSA_SUCCESS (cycles: 27489 time: 723 us)
+ Creating a SECP256R1 (256-bit) PERSISTENT PLAIN server key... PSA_SUCCESS (cycles: 27587 time: 725 us)
+ Exporting a public key of a SECP256R1 (256-bit) PERSISTENT PLAIN server key... PSA_SUCCESS (cycles: 332949 time: 8761 us)
+ Computing client shared secret with a SECP256R1 (256-bit) server public key... PSA_SUCCESS (cycles: 337803 time: 8889 us)
Persistent key ECDH operation on tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ws#
. ECDH Client
+ Creating a SECP256R1 (256-bit) PERSISTENT PLAIN client key... PSA_SUCCESS (cycles: 46998 time: 1236 us)
+ Creating a SECP256R1 (256-bit) PERSISTENT PLAIN server key... PSA_SUCCESS (cycles: 45962 time: 1209 us)
+ Exporting a public key of a SECP256R1 (256-bit) PERSISTENT PLAIN server key... PSA_SUCCESS (cycles: 334127 time: 8792 us)
+ Computing client shared secret with a SECP256R1 (256-bit) server public key... PSA_SUCCESS (cycles: 338321 time: 8903 us)
The overheads on the TrustZone-aware project (tz_psa_crypto_ecdh_ws) are due to the following operations of Secure Library implementation.
Packages the list of input arguments in the appropriate format before calling into the NSC function.
Switches from a Non-secure to a Secure state.
Validates all input arguments before calling into the function in SPE.
Encrypts PSA ITS if using a persistent key.
Returns to a Non-secure state.
