Generic SPI#
Introduction#
The Generic SPI Primary (GSPI) is available for MCU HP peripherals and provides an I/O interface for a wide range of SPI-compatible peripheral devices. SPI is a synchronous four-wire interface composed of two data pins (MOSI and MISO), a device select pin (CSN), and a gated clock pin (SCLK). With its two data pins, GSPI supports full-duplex operation with other SPI-compatible devices. GSPI can be utilized in various applications within embedded systems where high-speed, synchronous serial communication is essential. Common use cases include:
Test and Measurement Equipment
Sensor Interfacing
Display Interfaces
Memory Devices
Communication Interfaces
Motor Control
Audio Processing
Wireless Communication
The GSPI controller's internal architecture is depicted in the block diagram below. The following diagram provides a visual representation of the key components and their interactions within the GSPI controller.
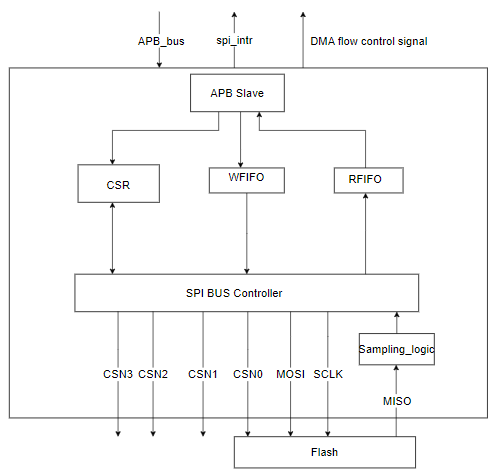

Configuration#
Configuring the GSPI in a microcontroller involves several steps, including setting up the peripheral registers, configuring GPIO pins, and selecting the appropriate operating mode and settings. To configure the GSPI operating mode:
Modify clock_mode_typedef_t (Modes 0 and 3 can be configured)
Set the Bit Rate (Range: 1 - 116,000,000)
Set the Data Width from 1-16 bits
Configure the GSPI secondary select mode by setting slave_select_mode_typedef_t All of these parameters must be configured in the sl_gspi_control_config_t structure and then passed to the API sl_si91x_gspi_set_configuration(). For more details on configuring available parameters, see the respective peripheral example README document.
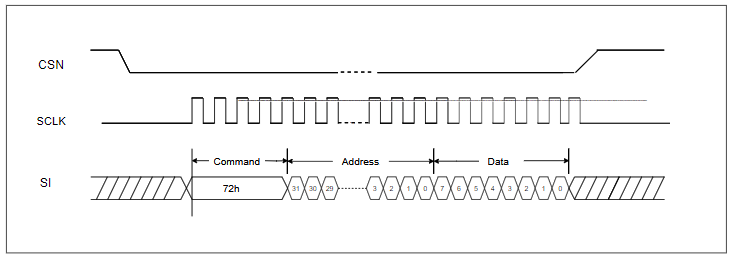
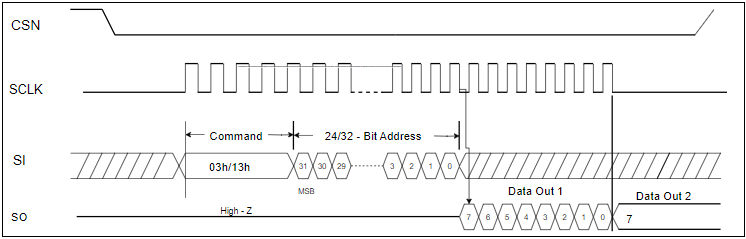
The following images illustrate the GSPI bus operations. The first image shows the waveform for a GSPI write operation, detailing how data is transmitted from the primary to the secondary. The second image depicts the waveform for a GSPI read operation, highlighting how data is received from the secondary to the primary.
GSPI bus write operation waveform: This diagram illustrates the sequence of signals during a write operation, including the timing of the clock, data, and chip select signals.

GSPI bus read operation waveform: This diagram shows the timing and sequence of signals during a read operation, highlighting how data is transferred from the secondary to the primary.

Usage#
After specifying the GSPI configuration through the sl_gspi_control_config_t structure, you can use the following common GSPI functions to initiate and configure GSPI:
sl_si91x_gspi_configure_clock - Configures the GSPI clock.
sl_si91x_gspi_init - Initializes the GSPI module.
sl_si91x_gspi_set_configuration - Sets the GSPI configuration.
sl_si91x_gspi_register_event_callback - Registers a callback for GSPI events.
sl_si91x_gspi_send_data - Sends data using the GSPI.
sl_si91x_gspi_receive_data - Receives data using the GSPI.
sl_si91x_gspi_transfer_data - Transfers data using the GSPI.
sl_si91x_gspi_deinit - De-initializes the GSPI module.
Modules#
Enumerations#
Enumeration for different GSPI callback events.
Enumeration for GSPI power states.
Enumeration for GSPI clock modes.
Enumeration for GSPI primary modes.
Enumeration for GSPI secondary select modes.
Enumeration for GSPI Primary instance.
Enumeration for GSPI slave numbers.
Typedefs#
Renamed signal event structure.
Renamed status structure.
Renamed GSPI driver structure.
Created GSPI handle type.
Functions#
To configure the clock for the GSPI module.
To initialize the GSPI module.
To uninitialize the GSPI module.
To configure the GSPI module.
To receive data from the secondary device.
To send data to the secondary device.
To send and receive data to and from the secondary device simultaneously.
To set the primary state as active or inactive.
To register the user callback function for GSPI events.
To unregister the user callback function for GSPI events.
To fetch the GSPI version.
To get the transfer status of GSPI.
To fetch the data receive count of the GSPI.
To get the transmit data count of GSPI.
To fetch the clock division factor.
To fetch the frame length, i.e., bit width.
To set the secondary number in multi-secondary operation.
Enumeration Documentation#
gspi_event_typedef_t#
gspi_event_typedef_t
Enumeration for different GSPI callback events.
This enumeration defines the possible events that can trigger a GSPI callback. Each event corresponds to a specific condition or state in the GSPI operation.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| SL_GSPI_TRANSFER_COMPLETE | Transfer complete event. |
| SL_GSPI_DATA_LOST | Data lost event. |
| SL_GSPI_MODE_FAULT | Mode fault event. |
sl_gspi_power_state_t#
sl_gspi_power_state_t
Enumeration for GSPI power states.
This enumeration defines the possible power states for the GSPI peripheral. Each state corresponds to a specific power mode that the GSPI can operate in.
Enumeration for GSPI power states.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| SL_GSPI_POWER_OFF | Power mode OFF. |
| SL_GSPI_LOW_POWER | Low power mode. |
| SL_GSPI_FULL_POWER | Full power mode. |
| SL_GSPI_POWER_MODE_LAST | Last member of enum for validation. |
clock_mode_typedef_t#
clock_mode_typedef_t
Enumeration for GSPI clock modes.
This enumeration defines the possible clock modes for the GSPI peripheral. Each mode corresponds to a specific combination of clock polarity (CPOL) and clock phase (CPHA).
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| SL_GSPI_MODE_0 | Mode 0: CPOL0, CPHA0. |
| SL_GSPI_MODE_3 | Mode 3: CPOL1, CPHA1. |
master_mode_typedef_t#
master_mode_typedef_t
Enumeration for GSPI primary modes.
This enumeration defines the possible primary modes for the GSPI peripheral. Each mode indicates whether the GSPI is active or inactive in primary mode.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| SL_GSPI_MASTER_INACTIVE | Primary mode inactive. |
| SL_GSPI_MASTER_ACTIVE | Primary mode active. |
| SL_GSPI_MASTER_MODE_LAST | Last member of enum for validation. |
slave_select_mode_typedef_t#
slave_select_mode_typedef_t
Enumeration for GSPI secondary select modes.
This enumeration defines the possible secondary select modes for the GSPI peripheral. Each mode indicates how the secondary select (SS) signal is managed in primary mode.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| SL_GSPI_MASTER_UNUSED | Primary unused mode. |
| SL_GSPI_MASTER_SW | Primary software mode. |
| SL_GSPI_MASTER_HW_OUTPUT | Primary hardware output mode. |
| SL_GSPI_SLAVE_SELECT_MODE_LAST | Last member of enum for validation. |
sl_gspi_instance_t#
sl_gspi_instance_t
Enumeration for GSPI Primary instance.
This enumeration defines the GSPI Primary instance. It currently has one member, with a provision for future expansion.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| SL_GSPI_MASTER | GSPI Primary instance. |
| SL_GSPI_INSTANCE_LAST_ENUM | Last member of the enum for validation. |
sl_gspi_slave_number_t#
sl_gspi_slave_number_t
Enumeration for GSPI slave numbers.
This enumeration defines the possible slave numbers for the GSPI peripheral. Each value represents a specific slave device connected to the GSPI.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| GSPI_SLAVE_0 | Secondary No. 0. |
| GSPI_SLAVE_1 | Secondary No. 1. |
| GSPI_SLAVE_2 | Secondary No. 2. |
| GSPI_SLAVE_LAST_ENUM | Last member of enum for validation. |
Typedef Documentation#
sl_gspi_signal_event_t#
typedef ARM_SPI_SignalEvent_t sl_gspi_signal_event_t
Renamed signal event structure.
Function Documentation#
sl_si91x_gspi_configure_clock#
sl_status_t sl_si91x_gspi_configure_clock (sl_gspi_clock_config_t * clock_configuration)
To configure the clock for the GSPI module.
| Type | Direction | Argument Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| sl_gspi_clock_config_t * | [in] | clock_configuration | Pointer to the clock configuration structure sl_gspi_clock_config_t. |
This API sets the clock for the GSPI peripheral. It configures the PLL clock and SOC clock according to the values set by the user in the clock configuration structure.
Returns
Status code indicating the result:
SL_STATUS_OK (0x0000) - Success.
SL_STATUS_FAIL (0x0001) - Function failed.
SL_STATUS_NOT_INITIALIZED (0x0011) - Clock is not initialized.
SL_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER (0x0021) - Parameters are invalid.
SL_STATUS_NULL_POINTER (0x0022) - The parameter is a null pointer.
For more information on status codes, see SL STATUS DOCUMENTATION.
sl_si91x_gspi_init#
sl_status_t sl_si91x_gspi_init (sl_gspi_instance_t instance, sl_gspi_handle_t * gspi_handle)
To initialize the GSPI module.
| Type | Direction | Argument Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| sl_gspi_instance_t | [in] | instance | GSPI instance sl_gspi_instance_t. |
| sl_gspi_handle_t * | [in] | gspi_handle | Double pointer to the GSPI driver handle sl_gspi_handle_t. |
This API initializes the GSPI module. If DMA is enabled, it also initializes the DMA module. The API takes the address of a pointer to store the GSPI primary handle, which can be used for subsequent function calls.
Pre-condition:
sl_si91x_gspi_configure_clock must be called before this function.
Returns
Status code indicating the result:
SL_STATUS_OK (0x0000) - Success.
SL_STATUS_BUSY (0x0004) - Driver is busy.
SL_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER (0x0021) - Parameters are invalid.
For more information on status codes, see SL STATUS DOCUMENTATION.
sl_si91x_gspi_deinit#
sl_status_t sl_si91x_gspi_deinit (sl_gspi_handle_t gspi_handle)
To uninitialize the GSPI module.
| Type | Direction | Argument Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| sl_gspi_handle_t | [in] | gspi_handle | Pointer to the GSPI driver handle sl_gspi_handle_t. |
This API uninitializes the GSPI module. If DMA is enabled, it also uninitializes the DMA module.
Pre-condition:
sl_si91x_gspi_init must be called before this function.
Returns
Status code indicating the result:
SL_STATUS_OK (0x0000) - Success.
SL_STATUS_NULL_POINTER (0x0022) - The parameter is a null pointer.
For more information on status codes, see SL STATUS DOCUMENTATION.
Note
When the GSPI module is used in combination with other peripherals, see the notes below while deinitializing in the application:
Whenever sl_si91x_gspi_deinit() is called, it will disable the clock for the peripheral. To power off the peripheral, you must power down the power domain (PERI_EFUSE), which contains different peripherals mentioned below: USART, UART, I2C, SSI Primary, SSI Secondary, Generic-SPI Primary, I2S Primary, I2S Secondary, Micro-DMA Controller, Config Timer, Random-Number Generator, CRC Accelerator, SIO, QEI, MCPWM, and EFUSE. Use the following API to power down the particular power domain if other peripherals are not being used: sl_si91x_peri_efuse_power_down(power_down);
A few peripherals (ULP Peripherals, UULP Peripherals, GPDMA, and SDIO-SPI) have separate domains; those can be powered down independently. For additional details, see the Power architecture section in the Hardware Reference Manual. For example, ULP_UART has a separate power domain ULPSS_PWRGATE_ULP_UART, which can be powered down independently. Refer to the rsi_power_save.h file for all power gate definitions.
sl_si91x_gspi_set_configuration#
sl_status_t sl_si91x_gspi_set_configuration (sl_gspi_handle_t gspi_handle, sl_gspi_control_config_t * control_configuration)
To configure the GSPI module.
| Type | Direction | Argument Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| sl_gspi_handle_t | [in] | gspi_handle | Pointer to the GSPI driver handle sl_gspi_handle_t. |
| sl_gspi_control_config_t * | [in] | control_configuration | Pointer to the configuration structure sl_gspi_control_config_t. |
The GSPI control and configuration options are listed below:
swap_read (enable/disable)
swap_write (enable/disable)
bit_width (1-16 bits)
clock_mode (mode0/mode3)
slave_select_mode (hw_output/sw)
bitrate
Note
Swap Read and Swap Write can be used only if the bit_width is configured as 16.
Pre-conditions:
Returns
Status code indicating the result:
SL_STATUS_OK (0x0000) - Success.
SL_STATUS_FAIL (0x0001) - Function failed.
SL_STATUS_BUSY (0x0004) - Driver is busy.
SL_STATUS_NOT_SUPPORTED (0x000F) - Parameter is not supported.
SL_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER (0x0021) - Parameters are invalid.
SL_STATUS_NULL_POINTER (0x0022) - The parameter is a null pointer.
SL_STATUS_INVALID_MODE (0x0024) - Secondary select mode is invalid.
SL_STATUS_INVALID_TYPE (0x0026) - SPI frame format is not valid.
SL_STATUS_INVALID_RANGE (0x0028) - Data bits (frame length) are not in range.
For more information on status codes, see SL STATUS DOCUMENTATION.
sl_si91x_gspi_receive_data#
sl_status_t sl_si91x_gspi_receive_data (sl_gspi_handle_t gspi_handle, void * data, uint32_t data_length)
To receive data from the secondary device.
| Type | Direction | Argument Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| sl_gspi_handle_t | [in] | gspi_handle | Pointer to the GSPI driver handle sl_gspi_handle_t. |
| void * | [in] | data | Pointer to the variable that will store the received data. |
| uint32_t | [in] | data_length | (uint32_t) Number of data items to receive. |
If DMA is enabled, it configures the DMA channel and required parameters. When the received data is equal to the data_length passed in this function, a callback event is generated which can be registered using sl_si91x_gspi_register_event_callback.
Pre-conditions:
Returns
Status code indicating the result:
SL_STATUS_OK (0x0000) - Success.
SL_STATUS_FAIL (0x0001) - Function failed.
SL_STATUS_BUSY (0x0004) - Driver is busy.
SL_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER (0x0021) - Parameters are invalid.
SL_STATUS_NULL_POINTER (0x0022) - The parameter is a null pointer.
For more information on status codes, see SL STATUS DOCUMENTATION.
sl_si91x_gspi_send_data#
sl_status_t sl_si91x_gspi_send_data (sl_gspi_handle_t gspi_handle, const void * data, uint32_t data_length)
To send data to the secondary device.
| Type | Direction | Argument Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| sl_gspi_handle_t | [in] | gspi_handle | Pointer to the GSPI driver handle sl_gspi_handle_t. |
| const void * | [in] | data | Const pointer to the variable that contains the data to be sent. |
| uint32_t | [in] | data_length | (uint32_t) Number of data items to send. |
If DMA is enabled, it configures the DMA channel and required parameters. When the sent data is equal to the data_length passed in this function, a callback event is generated which can be registered using sl_si91x_gspi_register_event_callback.
Pre-conditions:
Returns
Status code indicating the result:
SL_STATUS_OK (0x0000) - Success.
SL_STATUS_FAIL (0x0001) - Function failed.
SL_STATUS_BUSY (0x0004) - Driver is busy.
SL_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER (0x0021) - Parameters are invalid.
SL_STATUS_NULL_POINTER (0x0022) - The parameter is a null pointer.
For more information on status codes, see SL STATUS DOCUMENTATION.
sl_si91x_gspi_transfer_data#
sl_status_t sl_si91x_gspi_transfer_data (sl_gspi_handle_t gspi_handle, const void * data_out, void * data_in, uint32_t data_length)
To send and receive data to and from the secondary device simultaneously.
| Type | Direction | Argument Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| sl_gspi_handle_t | [in] | gspi_handle | Pointer to the GSPI driver handle sl_gspi_handle_t. |
| const void * | [in] | data_out | Const pointer to the variable that has data which needs to be sent. |
| void * | [in] | data_in | Pointer to the variable that will store the received data. |
| uint32_t | [in] | data_length | (uint32_t) Number of data items to receive. |
If DMA is enabled, it configures the DMA channel and required parameters. When the received data and sent data are equal to the data_length passed in this function, a callback event is generated which can be registered using sl_si91x_gspi_register_event_callback.
Pre-conditions:
Returns
Status code indicating the result:
SL_STATUS_OK (0x0000) - Success.
SL_STATUS_FAIL (0x0001) - Function failed.
SL_STATUS_BUSY (0x0004) - Driver is busy.
SL_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER (0x0021) - Parameters are invalid.
SL_STATUS_NULL_POINTER (0x0022) - The parameter is a null pointer.
For more information on status codes, see SL STATUS DOCUMENTATION.
sl_si91x_gspi_set_master_state#
sl_status_t sl_si91x_gspi_set_master_state (sl_gspi_handle_t gspi_handle, boolean_t value)
To set the primary state as active or inactive.
| Type | Direction | Argument Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| sl_gspi_handle_t | [in] | gspi_handle | Pointer to the GSPI driver handle sl_gspi_handle_t. |
| boolean_t | [in] | value | (boolean_t) Enable or Disable. |
Sets the primary state (i.e., activate/deactivate). If the primary is not required in the application for a specific time, it can be turned on/off at runtime by using this API.
Pre-conditions:
Returns
Status code indicating the result:
SL_STATUS_OK (0x0000) - Success.
SL_STATUS_BUSY (0x0004) - Driver is busy.
SL_STATUS_NULL_POINTER (0x0022) - The parameter is a null pointer.
SL_STATUS_INVALID_MODE (0x0024) - Mode is invalid (fails to activate primary).
For more information on status codes, see SL STATUS DOCUMENTATION.
sl_si91x_gspi_register_event_callback#
sl_status_t sl_si91x_gspi_register_event_callback (sl_gspi_handle_t gspi_handle, sl_gspi_signal_event_t callback_event)
To register the user callback function for GSPI events.
| Type | Direction | Argument Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| sl_gspi_handle_t | [in] | gspi_handle | Pointer to the GSPI driver handle ( sl_gspi_handle_t). |
| sl_gspi_signal_event_t | [in] | callback_event | Pointer to the function that needs to be called at the time of interrupt ( sl_gspi_signal_event_t). |
At the time of the event, the function passed in the parameter is called with the respective event as the parameter. Before calling this function again, it is mandatory to call the sl_si91x_gspi_unregister_event_callback function to unregister the callback; otherwise, it returns SL_STATUS_BUSY error code.
Returns
Status code indicating the result:
SL_STATUS_OK (0x0000) - Success.
SL_STATUS_BUSY (0x0004) - Driver is busy.
SL_STATUS_NULL_POINTER (0x0022) - The parameter is a null pointer.
For more information on status codes, see SL STATUS DOCUMENTATION.
sl_si91x_gspi_unregister_event_callback#
void sl_si91x_gspi_unregister_event_callback (void )
To unregister the user callback function for GSPI events.
| Type | Direction | Argument Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| void | N/A |
This API unregisters the user callback function that was previously registered using sl_si91x_gspi_register_event_callback. It is mandatory to call this function before registering the callback again to avoid conflicts.
Pre-condition:
sl_si91x_gspi_get_version#
sl_gspi_version_t sl_si91x_gspi_get_version (void )
To fetch the GSPI version.
| Type | Direction | Argument Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| void | N/A |
This API reads and returns the current API version of GSPI.
Returns
sl_gspi_version_t type structure containing the version information.
sl_si91x_gspi_get_status#
sl_gspi_status_t sl_si91x_gspi_get_status (sl_gspi_handle_t gspi_handle)
To get the transfer status of GSPI.
| Type | Direction | Argument Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| sl_gspi_handle_t | [in] | gspi_handle | Pointer to the GSPI driver handle ( sl_gspi_handle_t). |
This API returns the sl_gspi_status_t type structure. The members are:
Busy
Data Lost
Mode Fault It is used to poll the busy status of the GSPI Primary.
Returns
sl_gspi_status_t type structure.
sl_si91x_gspi_get_rx_data_count#
uint32_t sl_si91x_gspi_get_rx_data_count (sl_gspi_handle_t gspi_handle)
To fetch the data receive count of the GSPI.
| Type | Direction | Argument Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| sl_gspi_handle_t | [in] | gspi_handle | Pointer to the GSPI driver handle ( sl_gspi_handle_t). |
If a receive operation is started, this function can be used to get the number of data bytes received.
Returns
uint32_t value of the RX data count.
sl_si91x_gspi_get_tx_data_count#
uint32_t sl_si91x_gspi_get_tx_data_count (void )
To get the transmit data count of GSPI.
| Type | Direction | Argument Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| void | N/A |
If a send operation is started, this function can be used to get the number of data bytes sent.
Returns
uint32_t Value of the TX data count.
sl_si91x_gspi_get_clock_division_factor#
int32_t sl_si91x_gspi_get_clock_division_factor (sl_gspi_handle_t gspi_handle)
To fetch the clock division factor.
| Type | Direction | Argument Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| sl_gspi_handle_t | [in] | gspi_handle | Pointer to the GSPI driver handle ( sl_gspi_handle_t). |
The clock division factor is calculated based on the configured peripheral clock. It determines the baud rate of GSPI.
Returns
factor (int32_t) The value of the clock division factor.
sl_si91x_gspi_get_frame_length#
uint32_t sl_si91x_gspi_get_frame_length (void )
To fetch the frame length, i.e., bit width.
| Type | Direction | Argument Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| void | N/A |
This API fetches the frame length. The frame length ranges between 1 and 15.
Returns
frame_length (uint32_t) The value of the frame length.
sl_si91x_gspi_set_slave_number#
__STATIC_INLINE sl_status_t sl_si91x_gspi_set_slave_number (uint8_t number)
To set the secondary number in multi-secondary operation.
| Type | Direction | Argument Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| uint8_t | [in] | number | Secondary number ( sl_gspi_slave_number_t). |
For a single secondary, this API needs to be called before transferring the data.
Returns
Status code indicating the result:
SL_STATUS_OK (0x0000) - Success
SL_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER (0x0021) - Invalid parameter
For more information on status codes, see SL STATUS DOCUMENTATION.
