Security Features#
The following sections provide information on enabling SiWG917 security features using the manufacturing utility, (Simplicity Commander CLI).
Secure Boot#
Secure Boot is a feature designed to ensure that only authenticated code can run on the chip. If a device fails its security check, it is not permitted to run, and program control will typically stall in the validating module. SiWG917 possess two bootloaders: the Security Bootloader, and the Application Bootloader.
The Security Bootloader runs on the NWP, while the Application Bootloader runs on the Cortex M4 processor. Secure Boot is implemented within the Security Bootloader.
The Secure Boot process is as follows:
The Security Bootloader authenticates the MBR in the flash.
The Security Bootloader validates the integrity and authenticity of the firmware (NWP and M4) in the flash and subsequently invokes the Application Bootloader.
For enabling only Secure Boot or Secure Boot along with other security features, refer to the Security Levels section.
Secure Key Management and Protection#
Inject custom public and private keys and other custom secret keys on the chips during manufacturing—safeguard your keys right from the beginning of their lifecycle.
Physically Unclonable Function (PUF) derived intrinsic keys are shown in the following table. These keys are unique per device and are generated randomly when the PUF is initialized.
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| Master Key | This key is used for MIC calculation and wrapping/unwrapping of TA keys. Keys encrypted using Master Key is done using AES ECB Mode. MIC is calculated using AES CBC mode. |
| Unwrap Key | This key is used for MIC calculation and wrapping/unwrapping of M4 keys. Keys encrypted using Unwrap Key is done using AES ECB Mode. MIC is calculated using AES CBC mode. |
| TA FW key 1, TA FW key 2 |
These two keys are being used for encryption and inline decryption of TA firmware in CTR or XTS mode based on configuration from security configs of eFuse. |
| M4 FW key 1, M4 FW key 2 |
These two keys are being used for encryption and inline decryption of M4 firmware in CTR or XTS mode based on configuration from security configs of eFuse. |
Keys generated by Simplicity Commander and stored on the device are as follows.
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| OTP Symmetric Key | Used for flash content MIC verification. AES CBC is used for MIC calculation. |
| OTP Public Key | Used for flash content digital signature verification (ECDSA-P256). This key is used to verify the signature of the MBR. |
| TA Public Key | Used for TA firmware signature verification (ECDSA-P256) by the security bootloader. This key is wrapped with PUF-derived intrinsic keys. |
| TA OTA Key | Used for TA firmware image encryption and MIC calculation of TA firmware. This key is wrapped with PUF-derived intrinsic keys. |
| M4 OTA Key | Used for M4 firmware image encryption and MIC calculation of M4 firmware. This key is wrapped with PUF-derived intrinsic keys. |
| M4 Public Key | Used for M4 firmware signature verification (ECDSA-P256) by the security bootloader. This key is wrapped with PUF-derived intrinsic keys. |
| Attestation Private Key | Used for signing secure attestation tokens (ECDSA-P256). This key is wrapped with PUF-derived intrinsic keys. |
Note: In this document, TA Public Key, TA OTA Key, M4 OTA Key, and M4 Public Key are referred to as static keys.
For information on how to generate the keys at Commander, refer to Generate Static Keys from Simplicity Commander.
For PUF activation, refer to Activation Code Generation for PUF, and to generate intrinsic keys and load the keys, refer to Provisioning Static Keys.
| S.No | Key | Key Storage Requirements | Algorithm | Operation | Modes | Storage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NWP eFuse | NWP Flash | ||||||
| 1 | OTP Symmetric Key | 16 bytes | AES | MIC Calculation | AES-CMAC | ✓ | – |
| 2 | OTP Public Key | 91 bytes - NIST Curve P-256 | ECDSA | Sign verification | – | ✓ | – |
| 3 | TA Public Key | 96 bytes* - NIST Curve P-256 | ECDSA | Sign verification | – | – | ✓ |
| 4 | TA OTA Key | 32 bytes | AES | Encryption, MIC Calculation |
Encryption: AES-ECB MIC Calculation: AES-CMAC |
– | ✓ |
| 5 | M4 OTA Key | 32 bytes | AES | Encryption, MIC Calculation |
Encryption: AES-ECB MIC Calculation: AES-CMAC |
– | ✓ |
| 6 | M4 Public key | 96 bytes* - NIST Curve P-256 | ECDSA | Sign verification | – | – | ✓ |
| 7 | Attestation Private Key | 240 Bytes* - NIST Curve P-256 | ECDSA | Sign | – | – | ✓ |
| 8 | Master Key | 52 bytes key code used to initialize key in Key Holder | AES | Encryption, MIC Calculation |
Encryption: AES-ECB MIC Calculation: AES-CMAC |
– | ✓ |
| 9 | Unwrap Key | 52 bytes key code used to initialize key in Key Holder | AES | Encryption |
Encryption: AES-ECB MIC Calculation: AES-CMAC |
– | ✓ |
| 10 | TA FW Key (2 keys) | 52 bytes key code used to initialize key in Key Holder | AES | Encryption | AES CTR, AES XTS | – | ✓ |
| 11 | M4 FW Key (2 keys) | 52 bytes key code used to initialize key in Key Holder | AES | Encryption | AES CTR, AES XTS | – | ✓ |
Notes: In the preceding table * signifies:
For TA and M4 public keys, the actual key size is 91 bytes. The remaining 5 padding bytes are added to make the key size a multiple of 16 for AES encryption.
For the Attestation key, the actual key size is 227 bytes.
All keys stored in flash are appended with MIC and other metadata that are not reflected in the table.
Secure Firmware Upgrade#
The secure firmware update feature of the bootloader checks the authenticity of the new firmware image along with its integrity. The bootloader updates the image only after successfully validating the authenticity and integrity of the image. It prevents downgrade to a lower version of firmware using the anti-rollback feature if it is enabled.
The bootloader also supports transparent migration to a wirelessly updated image and protection against failures by providing recovery mechanisms.
The security bootloader uses a proprietary format for its upgrade images, called RPS. These files have extension “. rps”.
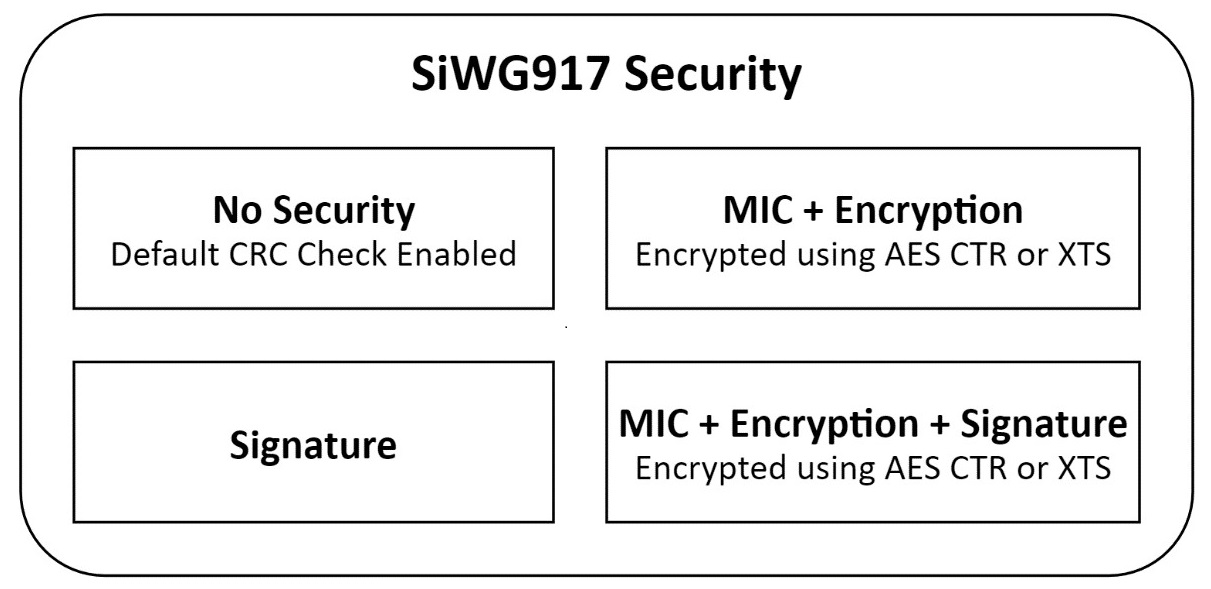

The firmware image for both NWP and M4 supports the following parameters:
No Security: Default CRC of the image within the RPS header.
Message Integrity Check (MIC) + Encryption: The MIC is calculated for the whole plain image and saved within the RPS header. The image is encrypted and appended to the RPS header. The image can be encrypted using AES CTR or XTS mode.
Signature: The whole RPS file's (RPS Header+ image) signature is calculated and appended to the end of the file.
MIC + Encryption + Signature: The MIC is calculated for the whole plain image and saved within the RPS header. The image is encrypted and appended to the RPS header. The image can be encrypted using AES CTR or XTS mode. Finally, the whole RPS file's (RPS Header+ image) signature is calculated and appended to the end of the file.
To understand how to select the security level of your choice refer to Security Levels section.
To enable security for NWP and M4 images refer to Enable Security Configurations in NWP and M4 Firmware Images.
Debug Lock#
Configure the debug port securely before the chips leave the factory with the Debug Lock Feature (which can be unlocked with a token)
The SiWG917 has a hardware debug solution. This provides high system visibility of the processor and memory through either a traditional JTAG port or a 2-pin Serial Wire Debug (SWD) port that is ideal for microcontrollers and other small package devices. The Secure Lock Feature locks the Debug Port. Any unauthorized access will be restricted.
This will be a one-time update of the MBR, however. This update should happen when the user has completed the development phase and entered the manufacturing phase for their products. Locking the NWP and M4 debug ports is a necessary step in production to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information. Refer to the AN1428: SiWx917 Debug Lock for more information on enabling debug lock.
